髓内钉联合重建钢板治疗伴外侧壁损伤的股骨粗隆间骨折的临床研究
2021-03-24王雷赵锁柱吴旭岳勇
王雷 赵锁柱 吴旭 岳勇
【摘要】 目的:比較髓内钉联合重建钢板与单纯髓内钉固定治疗伴外侧壁损伤的股骨粗隆间骨折的临床效果。方法:回顾性分析2018年1月-2020年1月35例在本院行手术治疗的伴外侧壁损伤的股骨粗隆间骨折患者的临床资料。根据手术方式的不同,分为研究组(n=16)和对照组(n=19)。研究组采用髓内钉结合重建钢板,对照组采用单纯髓内钉固定。比较两组一般指标、手术相关指标、骨形成状态指标、功能结局指标。结果:研究组手术时间长于对照组,术中出血量多于对照组,骨折愈合时间短于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。研究组并发症发生率为6.25%,低于对照组的31.58%,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术前,两组BALP比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);术后30 d,两组BALP均高于术前,且研究组高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。术前,两组HHS、PPMS比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);术后6、12个月,研究组HHS、PPMS均高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:髓内钉联合重建钢板固定虽然手术时间较长,术中出血量较多,但在骨折愈合时间、并发症发生率、骨形成状态指标改善、术后功能恢复等方面优于单纯髓内钉固定。
【关键词】 髓内钉 重建钢板 股骨粗隆间骨折 外侧壁损伤
[Abstract] Objective: To compare the clinical effect of intramedullary nail combined with reconstruction plate and simple intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of intertrochanteric fracture with lateral wall injury. Method: Clinical data of 35 patients with intertrochanteric fracture with lateral wall injury who underwent surgical treatment in our hospital from January 2018 to January 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. According to different surgical methods, they were divided into study group (n=16) and control group (n=19). The study group was treated with intramedullary nail combined with reconstruction plate, and the control group was treated with simple intramedullary nail fixation. General indexes, operation-related indexes, bone formation status indexes and functional outcome indexes were compared between two groups. Result: The surgical time of the study group was longer than that of the control group, the amount of intraoperative blood loss was more than that of the control group, and the time of fracture healing was shorter than that of the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The complication rate of the study group was 6.25%, which was lower than 31.58% of the control group, the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05). Before surgery, there was no significant difference in BALP between two groups (P>0.05); at 30 d after surgery, BALP of both groups were higher than those before surgery, and that of the study group was higher than that of the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Before surgery, there were no significant differences in HHS and PPMS between two groups (P>0.05); at 6 and 12 months after surgery, HHS and PPMS of the study group were higher than those of the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: Although the surgical time is longer and the intraoperative blood loss is more, intramedullary nail combined with reconstruction plate is superior than simple intramedullary nail fixation in fracture healing time, complication rate, improvement of bone formation status indicators, and postoperative functional recovery.
[Key words] Intramedullary nail Reconstruction plate Intertrochanteric fracture Lateral wall injury
First-author’s address: 967th Hospital of PLA Joint Logistic Support Force, Dalian 116000, China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2021.25.003
股骨粗隆间骨折是老年人群中最常见的骨科损伤之一,其与骨质疏松有关,通常是由低能量创伤引起的,具有相当高的发病率和死亡率,适合早期手术干预[1-2]。股骨粗隆间骨折的内固定可分为髓外固定和髓内固定,前者以股骨近端锁定加压钢板、动力髋螺钉(DHS)为代表,后者以股骨近端髓内钉(PFN)等头髓钉为代表[3-4]。髓外固定的患者常因生物力学稳定性不足而出现内固定失败。据报道,股骨近端锁定钢板治疗股骨粗隆间骨折有41.4%的患者出现内固定失败[5]。因髓内固定在生物力学方面具有更强的稳定性,近年来在临床应用日趋广泛。与髓外固定相比,髓内固定可防止近端骨折侧向移位,在手术时间、术后负重时间、术后功能恢复、内固定失败率等方面具有显著优势。但在应用髓内钉治疗伴外侧壁损伤的粗隆间骨折中,其内固定失败率可达20.5%~24.2%[6]。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 回顾性分析2018年1月-2020年1月35例在本院行手术治疗的伴外侧壁损伤的粗隆间骨折患者的临床资料。纳入标准:(1)急性单侧闭合性骨折;(2)AO/OTA分型:31-A3型;(3)拟行髓内钉联合重建钢板或单纯髓内钉治疗。排除标准:(1)病理性骨折;(2)既往手术翻修;(3)骨折合并神经血管损伤;(4)处于妊娠期;(5)临床资料不完整。根据手术方式的不同,分为研究组(n=16)和对照组(n=19)。本研究经医院伦理委员会批准。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 研究组 患者在腰麻或全身麻醉下仰卧在牵引床上。在C型臂引导下,采用牵引和轻微内旋等方法进行闭合复位。在距股骨大转子2 cm处做一个5 cm长的皮肤切口。再次透视后确定髓内钉模型。置入引导套,然后以大粗隆顶点或稍偏内侧插入导针于股骨髓腔内,近端扩髓后在透视下沿导针旋入髓内钉,调整角度与深度,植入并锁定远、近端螺钉。股骨近端后外侧成形后,用小型重建钢板固定。股骨远端和近端分别拧入两枚或三枚锁定螺钉。C臂透视下钢板位置良好,螺钉长度合适。最后,冲洗后逐层缝合切口。
1.2.2 对照组 单纯采用髓内钉固定。患者仰卧位,膝关节屈曲约20°,在C型臂引导下使用点复位钳进行经皮复位固定。如果骨折的冠状面成角且难以复位,则放置阻断螺钉以便骨折复位,或使用复位钢板进行临时固定。通过套管针将克氏针引入入口點(入口点在冠状面位于髁间外侧结节的正内侧,在矢状面位于关节面的腹缘),并在透视引导下放置克氏针。带锁髓内钉边插入边渐进扩髓,同时使用C型臂透视确认髓内钉放置于胫骨近端髓腔的中心,骨折排列良好。行膝关节活动度检查以确认髓内钉没有进入膝关节,然后放置远端和近端锁定螺钉,冲洗并缝合切口。
1.2.3 术后处理 术后5~7 d,患者在有限负重的情况下活动,通常在助行器的帮助下活动。术后1、2、3、6个月及术后1年分别拍摄X线片,评价患者的复位固定位置。
1.3 观察指标与判定标准 (1)比较两组手术相关指标。包括手术时间、术中出血量、骨折愈合时间。(2)比较两组手术相关并发症发生情况,包括骨不连、复位丢失[7-8]。(3)比较两组术前和术后30 d的骨形成状态指标。清晨空腹抽取静脉血10 mL,使用ISP-M型半自动生化分析仪测定骨碱性磷酸酶(BALP)表达水平,按照试剂盒中的检测步骤来进行测定。(4)比较两组术前及术后6、12个月的功能结局。包括Harris髋关节评分(HHS)和Parker-Palmer活动度评分(PPMS)。HHS总计100分,包括畸形、关节活动度、关节功能、疼痛4个方面,评分越高,患者髋关节功能越好[9]。PPMS分为3个维度,即可在室内活动、可在室外活动、日常生活自理。每个维度从低到高为1~3分,评分总计9分,评分越高,则活动度越好[10]。
1.4 统计学处理 采用SPSS 22.0软件对所得数据进行统计分析,计量资料用(x±s)表示,组间比较采用独立样本t检验,组内比较采用配对t检验;计数资料以率(%)表示,比较采用字2检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
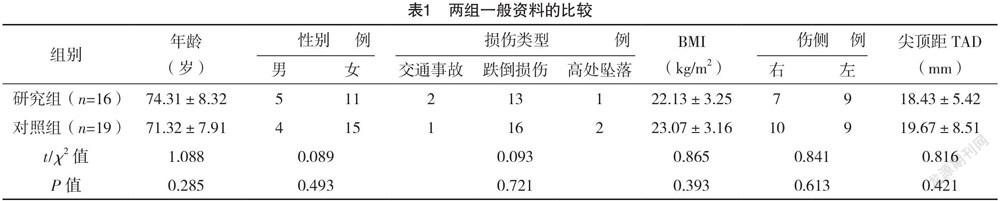
2.1 两组一般资料比较 两组一般资料比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性,见表1。
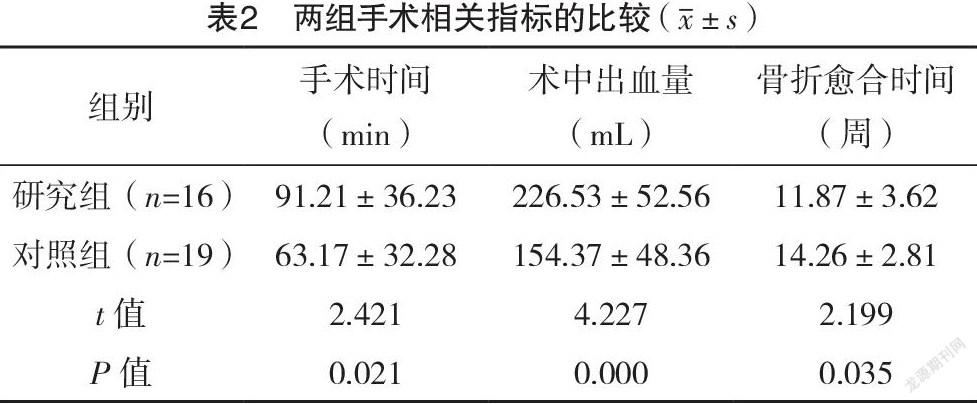
2.2 两组手术相关指标及并发症发生情况比较 研究组手术时间长于对照组,术中出血量为多于照组,骨折愈合时间短于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。研究组发生1例骨不连;对照组发生4例复位丢失,2例骨不连。研究组并发症发生率为6.25%(1/16),低于对照组31.58%(6/19),差异无统计学意义(字2=1.029,P>0.05)。见表2。
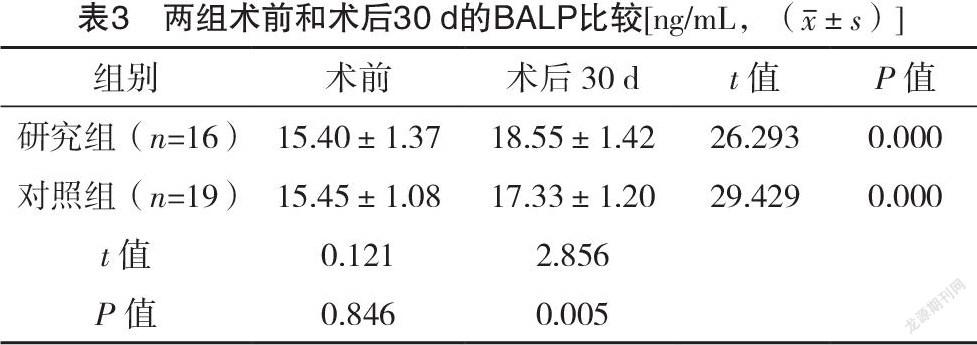
2.3 两组术前和术后30 d的BALP比较 术前,两组BALP比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);术后30 d,两组BALP均高于术前,且研究组高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表3。
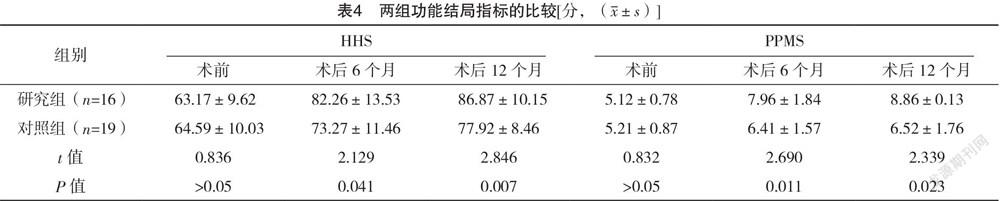
2.4 两组功能结局指标的比较 术前,两组HHS、PPMS比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);术后6、12个月,研究组HHS、PPMS均高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表4。
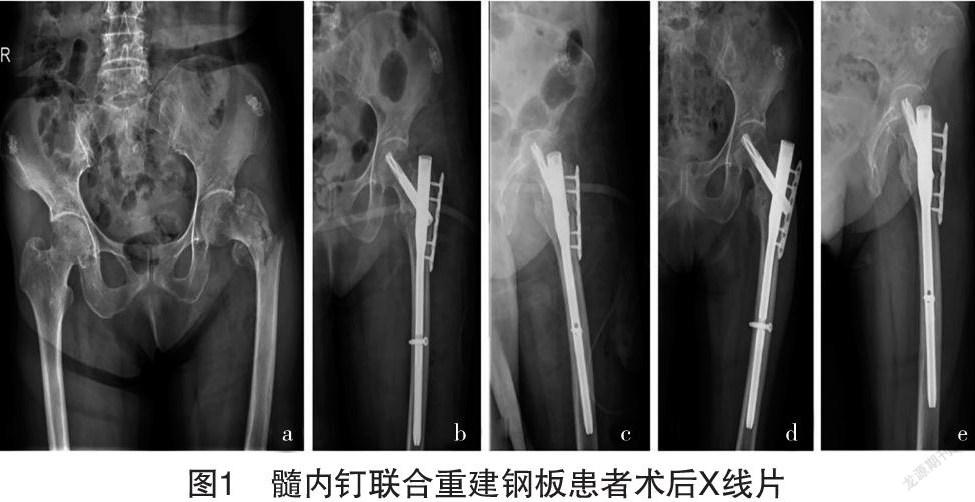
2.5 典型病例 1例行髓内钉联合重建钢板患者术后X线片,见图1。
3 讨论
股骨外侧壁重建是治疗不稳定型粗隆间骨折的重要环节,是降低术后内固定失败的关键[11-12]。本研究中对于伴外侧壁损伤的粗隆间骨折实行髓内钉联合重建钢板固定,以达到5点固定,实现更强的稳定性。采用髓内钉结合重建钢板固定(研究组)和单纯髓内钉固定(对照组)治疗伴有侧壁损伤的不稳定股骨粗隆间骨折,比较两组患者的手术时间、术中出血量、骨折愈合时间、手术相关并发症及术后功能状况。结果表明,两种内固定方法对不稳定股骨粗隆间骨折合并侧壁损伤均有效。但在骨折愈合时间、并发症发生率和术后功能恢复方面,髓内钉联合重建钢板组总体上优于单纯髓内钉组。研究组手术时间长于对照组,术中出血量为多于照组,骨折愈合时间短于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。研究组并发症发生率为6.25%,低于对照组31.58%,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。其他研究显示,滑动式髋螺钉联合侧向支撑板治疗的患者中有9%出现固定失败并发症,单独使用滑动髋螺钉治疗的患者中也有34%出现固定失败并发症[13-14]。在功能结果方面,髓内钉结合重建钢板也优于单纯髓内钉。有研究指出,在再手术率和术后放射学及功能结果方面,滑动加侧支撑板髋螺钉也优于单独加压螺钉。在手术过程中安装了额外的侧板,因此可能导致手术时间延长,增加术中失血量[15]。
与单纯髓内钉相比,髓内钉结合重建钢板保留了传统的微创和优良的生物力学优点。用近端小钢板重建股骨外侧壁的完整性,增强了骨折的稳定性,防止了远端骨块向外移动,改善了近端与远端骨折块之间的抗扭力[16-17]。因此,促进骨折的愈合,减少了骨折复位的丢失,避免了髋部畸形和内固定失败,缩短了患者的负重时间,使患者在医生的指导下可以早期活动。临床上,一些经X线诊断为A2.2或A2.3型的股骨粗隆间骨折,术中置入头髓钉时,发现其外侧壁有纵向(冠状)骨折线[18]。如果采用以前的手术方案(仅使用髓内钉),手术固定失败率会增加。因此,对于存在股骨外侧壁损伤高危因素的粗隆间骨折行术前CT扫描。
BALP主要由成骨细胞合成并分泌到血液中,是反映骨形成状态的重要参数[19-20]。本研究比较两组患者手术前后BALP的表达水平。结果显示,术前,两组BALP比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);术后30 d,两组BALP均高于术前,且研究组高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。在骨重建中,首先破骨细胞开始骨吸收,最后成骨细胞启动骨形成。骨矿化是骨形成的重要环节。碱性磷酸酶以焦磷酸盐为底物,生成矿物质沉积所需的磷酸,从而促进矿化。人体系统分泌高水平的BALP来刺激骨形成活动,恢复这种平衡。以上结果表明,两组患者手术后骨代谢均有改善,但研究组改善效果更好,BALP表达水平高于对照组。
综上所述,髓内钉联合重建钢板固定虽然手术时间较长,术中出血量较多,但在骨折愈合時间、并发症发生率、骨形成状态指标改善、术后功能恢复等方面可能优于单纯髓内钉固定。
参考文献
[1] Pradeep A R,KiranKumar A,Dheenadhayalan J,et al.Intraoperative lateral wall fractures during Dynamic Hip Screw fixation for intertrochanteric fractures-Incidence,causative factors and clinical outcome[J].Injury,2018,49(2):334-338.
[2] Yu X,Wang H,Duan X,et al.Intramedullary versus extramedullary internal fixation for unstable intertrochanteric fracture,a meta-analysis[J].Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc,2018,52(4):299-307.
[3]陈宇翔,唐佩福.股骨粗隆间骨折内固定手术治疗的研究进展[J].解放军医学院学报,2017,38(2):171-174,178.
[4]田大为,万华,熊敏,等.PFNA治疗股骨粗隆间骨折内固定手术失败的原因分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(20):1830-1834.
[5] Yamamoto N,Tamura R,Inoue T,et al.Radiological findings and outcomes of anterior wall fractures in pertrochanteric fractures[J].J Orthop Sci,2021,26(2):247-253.
[6] İmerci A,Aydogan N H,Tosun K.A comparison of the InterTan nail and proximal femoral fail antirotation in the treatment of reverse intertrochanteric femoral fractures[J].Acta orthopaedica Belgica,2018,84(2):123-131.
[7] Bhowmick K,Matthai T,Boopalan P R J,et al.Decision making in the management of malunion and nonunion of intertrochanteric fractures of the hip[J].Hip Int,2020,30(6):793-798.
[8] Stahl I,Eidelman M.Three point fixation of pediatric proximal humerus fractures by prebent wave-shaped wires:technical notes[J].J Pediatr Orthop B,2017,26(1):1-4.
[9]刘瑾,荣悦彤,赵云.全髋关节置换术后不同时间开始康复训练对Harris评分的影响[J].中国医学创新,2021,18(14):71-75.
[10] Dlj M,Nightingale J M,Geoghegan J M,et al.Concurrent upper limb and hip fracture in the elderly[J].Injury,2020,51(4):1025-1030.
[11] Cheung Z B,Selveria N S,Barbera J,et al.The effect of nail diameter on proximal femoral shortening after internal fixation of pertrochanteric hip fractures with short cephalomedullary nails[J].J Orthop,2020,22(3):358-361.
[12] Yu X,Wang H,Duan X,et al.Intramedullary versus extramedullary internal fixation for unstable intertrochanteric fracture,a meta-analysis[J].Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc,2018,52(4):299-307.
[13] Shu W B,Zhang X B,Lu H Y,et al.Comparison of effects of four treatment methods for unstable intertrochanteric fractures:A network meta-analysis[J].Int J Surg,2018,60(2):173-181.
[14] Mandal S,Banerjee U,Mukherjee A S,et al.Results of “Trochanteric Femoral Nailing (TFN)” in comminuted unstable trochanteric fractures[J].Acta Orthop Belg,2019,85(4):525-534.
[15] Andalib A,Etemadifar M,Yavari P.Clinical Outcomes of Intramedullary and Extramedullary Fixation in Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures:A Randomized Clinical Trial[J].Arch Bone Jt Surg,2020,8(2):190-197.
[16] Cardile C,Cazzaniga C,Manzini B,et al.Intertrochanteric hip fracture in an arthrodesed hip treated by a LCP condylar plate[J/OL].Acta Biomed,2021,92(1):e2021039.
[17] Zhu Q L,Yan M H,Zhao L L,et al.Analysis of treatment of osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture of femur with the locking compression plate (LCP)[J].Zhongguo Gu Shang,2017,24(5):378-381.
[18] Baik J S,Kim K R,Park B H,et al.Outcomes of Wedge Wing in the Lag Screw for Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures in Elderly Patients[J].Hip Pelvis,2021,33(2):71-77.
[19] Diemar S S,Llehave L T,Quardon N,et al.Effects of age and sex on osteocalcin and bone-specific alkaline phosphatase-reference intervals and confounders for two bone formation markers[J].Arch Osteoporos,2020,15(1):26-37.
[20] Yokota Y,Nishimura Y,Ando A,et al.Clinical Application of the Ratio of Serum Bone Isoform to Total Alkaline Phosphatase in General Practice[J].Acta Med Okayama,2020,74(6):467-474.
(收稿日期:2021-07-19) (本文編辑:张明澜)
