牙周病与慢性肾病相关性的Meta分析
2017-01-06张天夫王晓峰周文博史庆怡
刘 聪,王 婷,张天夫,王晓峰*,刘 新*,桑 雪,周文博 ,史庆怡,袁 琳
(1.吉林大学中日联谊医院 口腔科,吉林 长春130033;2.吉林大学护理学院,吉林 长春130000)
*通讯作者
牙周病与慢性肾病相关性的Meta分析
刘 聪1,王 婷2,张天夫1,王晓峰1*,刘 新1*,桑 雪1,周文博1,史庆怡1,袁 琳1
(1.吉林大学中日联谊医院 口腔科,吉林 长春130033;2.吉林大学护理学院,吉林 长春130000)
牙周病(periodontal disease,PD)是一种发生在牙周支持组织的疾病,其发病率在全世界范围内高达90%[1]。近几十年来,越来越多的研究发现PD与很多全身系统疾病有一定的相关性,例如糖尿病、心脑血管疾病、低体重早产儿等[2-5]。
慢性肾病(chronic kidney disease,CKD)被定义为肾脏损伤或不明原因引起的肾小球滤过率(GRF)<60ml/min/1.73 m2超过3个月[6]。全球发病率估计8%-16%,并逐年增高[7]。患有CKD的人群会增加终末期肾病、心血管事件和死亡的风险[8,9]。CKD的发病机制至今尚未完全明确,2005年,Kshirsagar等[10]在一项纳入了5537位参与者的横断面研究中首次发现,重度的PD与肾功能下降(GRF<60ml/min/1.73m2)呈明显的相关性。随后,众多学者对两者的相关性进行了多项临床研究,但并未得出一致的结论。本文按照MOOSE (Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology)标准对公开发表的探讨PD与CKD的相关性文献进行Meta分析,以期对公共卫生及临床通过防治PD减少CKD的发生提供参考。
1 资料与方法
1.1 纳入标准
纳入标准为:(1)探讨PD与CKD相关性的研究主题;(2) PD有明确的诊断标准;(3)结局指标GRF<60 ml/min/1.73 m2;(4)研究设计为观察性研究包括队列研究、病例-对照研究和横断面研究;(5)直接提供了相对危险度(relative risk,RR),比值比(odds ratio,OR)及95%可信区间(confidenceinterval,CI)或直接通过文中提供的数据进行计算。
1.2 文献检索及资料提取
由两位评价者独立检索 PubMed、Embase和Cochrane 数据库,检索时间均为从建库至2016年9月。同时,手工检索近期综述及纳入文献的参考文献;如试验报告不详或资料缺乏,尝试通过信件与作者取得联系获取,以使纳入文献资料更加全面。以PubMed为例,检索策略如表一。由两位评论者独立筛选并对符合纳入条件的文献进行资料提取,若遇到分歧邀请第三位评论者加入,通过讨论达成一致。资料提取内容包括:第一作者及发表时间,研究人群(年龄、性别、例数),国家,研究设计类型,PD与CKD的诊断标准,协变量的校正,RR或OR 及95%的CI等。
1.3 统计学质量评价及质量等级
由于纳入的文章包含横断面研究,由两名评论者遵照Chambrone等[11]改编的 Newcastle-Ottawa Scale(NOS)量表对所有纳入的文献进行质量评价。评价总分为14分,高质量:11-14分;中等质量:8-10分;低质量:<8分[10]。
1.4 统计学分析
采用Stata 12.0软件完成。对于队列研究计算合并RR或OR及95%的CI,横断面研究计算合并OR及95%的CI。首先采用Q检验与I2检验看研究间是否具有异质性,当P<0.1、I2≥50.0%时,说明研究间存在异质性,反之则同质性较好,同质性较好采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,反之则采用随机效应模型分析。其次,采用去除单项研究法敏感性对结果的稳健性进行检测。
2 结果
2.1 检测结果
初检出3623篇相关文献,通过EndNote X7剔除重复264篇文献,阅读题目和摘要排除不相关文章及综述排除3320篇文献,对剩余的39篇文献全文进行仔细阅读,最终纳入3个队列研究[12-15]、5个横断面研究[10,16-19]。
2.2 纳入文献的质量评价结果及质量等级
6篇文献为高质量文献(得分11-12分),2篇文献为中等质量文献(得分9-10分)。
2.3 PD与CKD的相关性
队列研究间同质性较好(I2=44.6%,P=0.125),所以采用固定效应模型进行 Meta 分析。合并结果提示PD人群与牙周状况健康的人群,有更高的CKD的发病风险(RR=1.913,95%CI:1.418-2.579),见图1。依次剔除各研究进行敏感性分析,发现结果无实质性变化,说明Meta 分析结果稳健性好。由于研究个数少,未进行亚组分析。
横断面研究间同质性好(I2=0%,P=0.586),所以采用固定效应模型进行 Meta 分析。合并结果提示 PD人群与牙周状况健康的人群,有更高的CKD的发病风险(RR=1.564,95%CI:1.325-1.846),见图2。依次剔除各研究进行敏感性分析,发现结果无实质性变化,说明Meta 分析结果稳健性好。
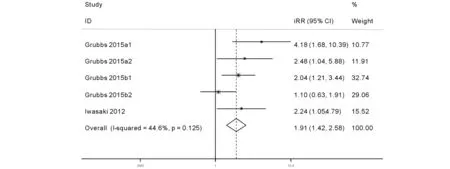
图1 队列研究的Meta分析结果
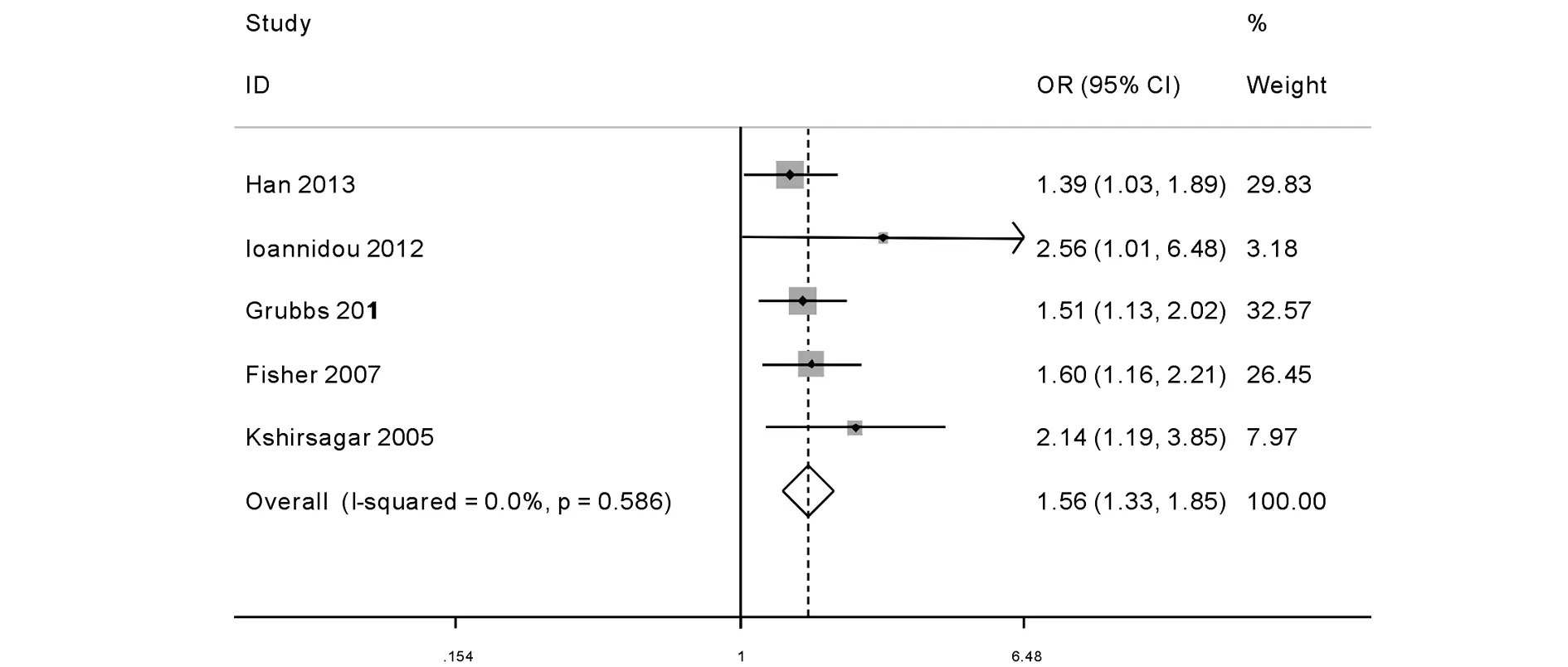
图2 横断面研究的Meta分析结果
3 讨论
3.1 相关性分析
根据先前的报道,对于肾脏疾病有以下几种危险因素:年龄[20],蛋白尿[21],高血压[22],糖尿病[23],异常血脂症[24],肥胖[25]和吸烟[26]。但这些传统的因素不能完全解释CKD的发生,2005年,Kshirsagar等[10]首次报道了重度的PD是肾功能下降(GRF<6 0 ml/min/1.73 m2)的危险因素。此后,美国的Fisher等[16]在第三次健康和营养调查中筛选出12947位成年人进行横断面调查,结果发现PD是美国成年人CKD一种潜在的非传统的危险因素。PD是一种全身系统的炎症负担来源[27-29]。研究证明慢性的炎症反应会导致高血压和糖尿病,且两者是心血管疾病和CKD的主要危险因素[30]。关于PD与CKD之间的相关性,许多学者开展了观察性研究力图进行证明,但还没有一致的结论。本Meta分析基于队列研究的结果显示,PD可以增加CKD发生风险的1.913倍,且各研究间同质性较好,敏感性分析结果稳健性好;基于横断面研究的结果显示PD可以增加CKD发生风险的1.564倍,且各研究间无异质性,敏感性分析结果稳健性好。
3.2 纳入文献的特征和质量
本 Meta 分析共纳入8篇观察性研究的文献(3篇队列研究,5篇横断面研究),均为国外发表的英文文献。所有的文献均对危险因素如年龄、性别、高血压、吸烟等进行了校正,改编的NOS评分质量较高(2篇9分、1篇10分、5篇11分、1篇12分,平均10.75分),总之,纳入文献总体质量较高,结果论证强度较强。
3.3 本研究的局限性
本研究虽然对于探讨PD与CKD之间的相关性的文献进行了全面的检索,且结果论证强度较强,但还是有以下局限性:①纳入文献数目较少且都是观察性研究,5篇为横断面研究,论证强度最高的队列研究只有3篇。②纳入文献较少且都是公开发表的国外文献,可能会导致发表偏倚。③各研究间对PD的定义及严重程度不统一,无法进行“剂量-效应分析”。④Meta分析属于二次文献,本身具有一定局限性。
3.4 临床指导意义
本Meta分析结果显示PD与CKD之间具有一定正相关性。这就提示,口腔医生面对PD的患者,在治疗患者牙周病提高其口腔卫生质量的基础上,也要对患者肾脏功能加强重视,并口腔卫生宣教OHI(oral hygiene instruction)做好口腔卫生的预防工作。对于肾内科医生也要注重CKD患者的口腔卫生状况,必要时联合口腔医生对患有PD的CKD患者进行洁治或刮治辅助治疗。迄今,世界上还没有一篇关于此研究高质量的RCT,中国台湾chen等[31]研究发现PD对于eGFR下降≥30%是一种危险因素,但中国大陆尚无此研究,因此,未来有必要对此研究进行更多的研究,尤其是高质量RCT的研究。
综上所述,本研究结果表明PD与CKD的发生具有一定相关性,未来还需要更多研究对此结论加以证明。
[1]Pihlstrom B L,Michalowicz B S,Johnson N W.Periodontal diseases[J].Lancet,2005,366(9499):1809.
[2]Simpson T,Needleman I,Wild S H,et al.Treatment of periodontal disease for glycaemic control in people with diabetes[J].Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews,2010,5(5):472.
[3]Preshaw P M,Alba A L,Herrera D,et al.Periodontitis and diabetes:a two-way relationship[J].Diabetologia,2012,55(1):21.
[4]Friedewald V E,Kornman K S,Beck J D,et al.The American Journal of Cardiology and Journal of Periodontology Editors' Consensus:Periodontitis and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease?[J].Journal of periodontology,2009,80(7):1021.
[5] Madianos P N,Lieff S,Murtha A P,et al.Maternal periodontitis and prematurity.Part II:Maternal infection and fetal exposure[J].Annals of Periodontology,2001,6(1):175.
[6]Levey A S,Eckardt K U,Tsukamoto Y,et al.Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease:A position statement from Kidney Disease:Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO)[J].Kidney International,2005,67(6):2089.
[7]Jha V,Garcia-Garcia G,Iseki K,et al.Chronic kidney disease:global dimension and perspectives[J].The Lancet,2013,382(9888):260.
[8]Weiner D E,Tighiouart H,Amin M G,et al.Chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality:A pooled analysis of community-based studies[J].Journal of the American Society of Nephrology Jasn,2004,15(5):1307.
[9]Ninomiya T,Kiyohara Y,Kubo M,et al.Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease in a general Japanese population:The Hisayama Study[J].Kidney International,2005,68(1):228.
[10]Kshirsagar A V,Moss K L,Elter J R,et al.Periodontal disease is associated with renal insufficiency in the Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities (ARIC) study[J].American Journal of Kidney Diseases,2005,45(4):650.
[11]Chambrone L,Foz A M,Guglielmetti M R,et al.Periodontitis and chronic kidney disease:a systematic review of the association of diseases and the effect of periodontal treatment on estimated glomerular filtration rate[J].Journal of clinical periodontology,2013,40(5):443.
[12]Chambrone L,Pannuti C M,Guglielmetti M R,et al.Evidence grade associating periodontitis with preterm birth and/or low birth weight:II.A systematic review of randomized trials evaluating the effects of periodontal treatment[J].Journal of clinical periodontology,2011,38(10):902.
[13]Iwasaki M,Taylor G W,Nesse W,et al.Periodontal Disease and Decreased Kidney Function in Japanese Elderly[J].American Journal of Kidney Diseases,2012,59(2):202.
[14]Grubbs V,Vittinghoff E,Taylor G,et al.The association of periodontal disease with kidney function decline:a longitudinal retrospective analysis of the MrOS dental study[J].Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation,2016,31(3):466.
[15]Grubbs V,Vittinghoff E,Beck J D,et al.Association Between Periodontal Disease and Kidney Function Decline in African Americans:The Jackson Heart Study[J].Journal of periodontology,2015,86(10):1126.
[16]Fisher M A,Taylor G W,Shelton B J.Periodontal disease and other nontraditional risk factors for CKD[J].American Journal of Kidney Diseases the Official Journal of the National Kidney Foundation,2008,51(1):45.
[17]Grubbs V,Plantinga L C,Crews D C,et al.Vulnerable populations and the association between periodontal and chronic kidney disease[J].Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology,2011,6(4):711.
[18]Han S S,Shin N,Lee S M,et al.Correlation between periodontitis and chronic kidney disease in Korean adults[J].Kidney research and clinical practice,2013,32(4):164.
[19]Effie Ioannidou DDS MS,Yoshio Hall M D,Swede H,et al.Periodontitis associated with chronic kidney disease among Mexican Americans[J].Journal of Public Health Dentistry,2013,73(2):112.
[20]Neugarten J,Gallo G,Silbiger S,et al.Glomerulosclerosis in aging humans is not influenced by gender[J].American Journal of Kidney Diseases,1999,34(5):884.
[21]Ruggenenti P,Schieppati A,Remuzzi G.Progression,remission,regression of chronic renal diseases[J].The Lancet,2001,357(9268):1601.
[22]Klag M J,Whelton P K,Randall B L,et al.Blood pressure and end-stage renal disease in men[J].New England Journal of Medicine,1996,334(1):13.
[23]Iseki K,Oshiro S,Tozawa M,et al.Prevalence and correlates of diabetes mellitus in a screened cohort in Okinawa,Japan[J].Hypertension Research,2002,25(2):185.
[24]Schaeffner E S,Kurth T,Curhan G C,et al.Cholesterol and the risk of renal dysfunction in apparently healthy men[J].Journal of the American Society of Nephrology,2003,14(8):2084.
[25]Fox C S,Larson M G,Leip E P,et al.Predictors of new-onset kidney disease in a community-based population[J].Jama,2004,291(7):844.
[26]Orth S R.Smoking and the kidney[J].Journal of the American Society of Nephrology,2002,13(6):1663.
[27]Fisher M A,Taylor G W.A prediction model for chronic kidney disease includes periodontal disease.[J].Journal of Periodontology,2009,80(1):16.
[28]Loos B G.Systemic markers of inflammation in periodontitis.[J].Journal of Periodontology,2005,76(11 Suppl):2106.
[29]Offenbacher S,Beck J D.A perspective on the potential cardioprotective benefits of periodontal therapy[J].American Heart Journal,2005,149(6):950.
[30]Tonelli M,Pfeffer M A.Kidney disease and cardiovascular risk[J].Annu.Rev.Med.,2007,58:123.
[31]Chen Y T,Shih C J,Ou S M,et al.Periodontal disease and risks of kidney function decline and mortality in older people:a community-based cohort study[J].American Journal of Kidney Diseases,2015,66(2):223.
1007-4287(2016)12-2087-04
2016-02-17)
