超声在儿童尺桡骨远端骨折中的诊断价值
2020-08-27伍兴李雄涛夏敬冬
伍兴 李雄涛 夏敬冬
[摘要] 目的 評估超声在疑似儿童尺桡骨远端骨折中的诊断价值。 方法 收集2018年1~6月华中科技大学同济医学院附属武汉儿童医院骨科急诊收治的131例疑似尺桡骨远端骨折的儿童病例。急诊儿童骨科医师对疑似尺桡骨远端骨折的儿童首先进行超声检查,再完成常规X线检查。两种检查结果均采用盲法。以X线为标准对照,评估超声在儿童尺桡骨远端骨折诊断中的敏感性、特异性、准确性、阳性预测值、阴性预测值和受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)下面积。 结果 超声检查诊断证实55例尺桡骨远端骨折,其中桡骨远端骨折36例,尺桡骨远端双骨折16例,尺骨远端骨折3例。超声检查对尺桡骨远端骨折的诊断敏感性和特异性分别为93.1%和98.6%,准确性为96.2%,阳性预测值98.2%和阴性预测值94.7%。超声诊断阳性率与X线诊断阳性率比较,差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.8,P = 0.371),超声诊断和X线诊断结果一致性较好(Kappa = 0.922,P < 0.001)。超声ROC曲线下面积为0.959(95%CI = 0.917~1.000)。 结论 超声在诊断尺桡骨远端骨折具有高敏感性和特异性。因此,超声是诊断儿童尺桡骨远端骨折的一种可选择的诊断检查方式。
[关键词] 尺桡骨远端骨折;超声;X线;诊断
[中图分类号] R726.8 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2020)07(a)-0144-04
[Abstract] Objective To evaluate the diagnostic value of ultrasound in children with suspected fracture of the distal ulna and radius. Methods A total of 131 children with suspected fracture of the distal ulna and radius were admitted to the emergency Department of Orthopedics, Wuhan Children′s Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science & Technology, from January to June 2018. Emergency pediatric orthopedic surgeons performed ultrasound examination first and then completed routine X-ray examination of children with suspected fracture of the distal ulna and radius. The results of both tests were blind. The diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) of ultrasound in children′s fracture of the distal ulna and radius were evaluated using X-ray as the standard control. Results Ultrasound examination confirmed 55 cases of fracture of the distal ulna and radius, including 36 cases of fracture of distal radius, 16 cases of double of fracture of the distal ulna and radius and 3 cases of fracture of distal ulnar. The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound examination for the diagnosis of fracture of the distal ulna and radius were 93.1% and 98.6%, respectively, with an accuracy of 96.2%, a positive predictive value of 98.2% and a negative predictive value of 94.7%. There was no significant difference in the positive rate of ultrasound diagnosis and X-ray diagnosis (χ2=0.8, P = 0.371), and the consistency of ultrasound diagnosis and X-ray diagnosis was good (Kappa = 0.922, P < 0.001). The area under ultrasonic ROC was 0.959 (95%CI = 0.917-1.000). Conclusion Ultrasound has high sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing fracture of the distal ulna and radius. Therefore, ultrasound is an alternative diagnostic test for the diagnosis of fracture of the distal ulna and radius in children.
[Key words] Fracture of the distal radius and ulna; Ultrasound; X-ray; Diagnosis
尺桡骨远端骨折是儿童最常见的骨折,发病率约31.1%[1]。X线作为尺桡骨远端骨折诊断的金标准已经广泛应用。但是X线属于电离辐射,可能危害健康,如增加恶性肿瘤的患病风险[2-4]。
近年来,关于超声诊断儿童骨折的研究日益增多[5-8]。目前超声在诊断儿童尺桡骨远端骨折中的应用主要是干骺端[9-11]。超声已用于骨骺软骨成像[12]。华中科技大学同济医学院附属武汉儿童医院(以下简称“我院”)已经应用超声诊断儿童其他部位的骨骺骨折[13-14],但相关研究国内外较少。本研究目的是探讨超声检查诊断儿童尺桡骨远端骨折的诊断价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
收集2018年1~6月在我院骨科急诊收治的疑似尺桡骨远端骨折患者共131例。所有患者均签署知情同意书。纳入标准:年龄<15岁,疑似前臂远端骨折。排除标准:患者拒绝;开放性骨折;已行X线检查;畸形明显;合并前臂骨筋膜室综合征及神经血管损伤。其中男83例,女48例;年龄1.1~12.6岁,中位年龄8.3岁;平均就诊时间(1.94±0.62)d。本研究获得我院医学伦理审查委员会批准。
1.2 方法
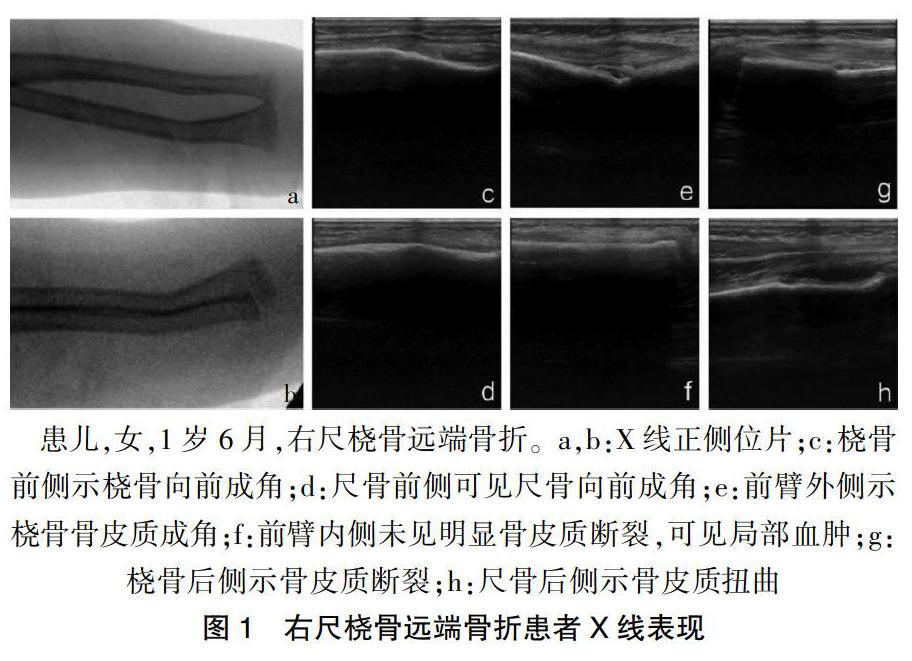
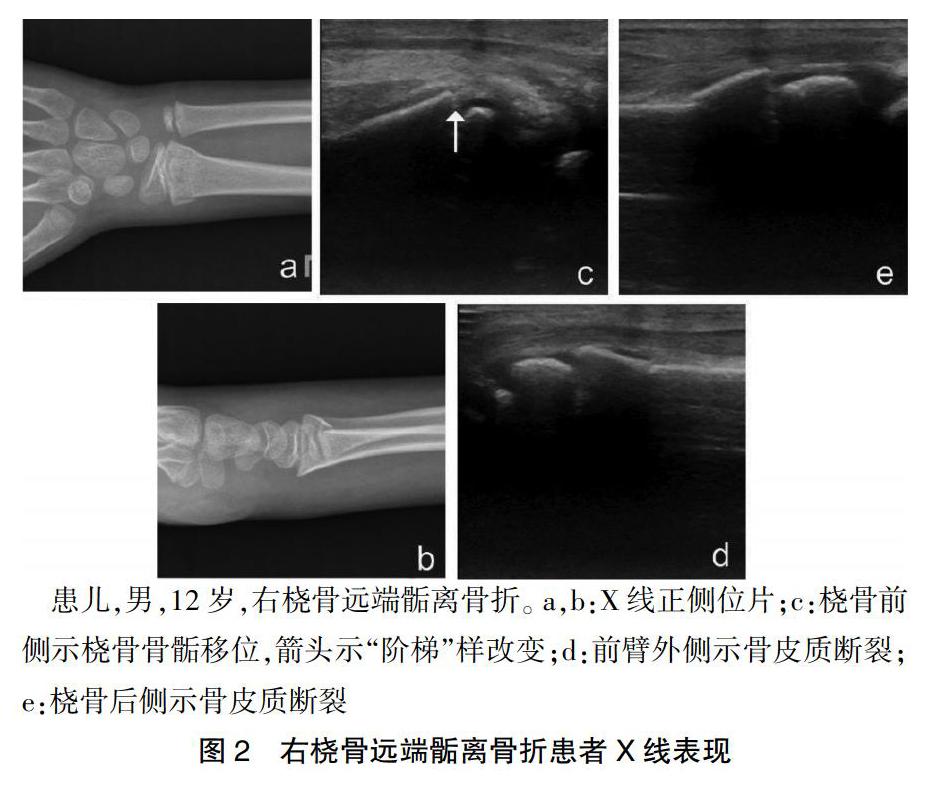
由超声医师对急诊儿童骨科医师进行1 h培训,培训内容为如何使用超声检测尺桡骨远端骨折的基本彩超图像及实际操作。检查设备为:GE LOGIQ e床边超声仪(美国GE公司)。对前臂远端进行了标准化6个平面检查(桡骨前侧、桡骨后侧、尺骨前侧、尺骨后侧、前臂内侧、前臂外侧)[15](图1)。前臂旋后位检查尺桡骨的前侧,前臂旋前位检查尺桡骨的后侧。探头与尺桡骨面保持垂直,抓取特征性的图像(图2)。超声判断骨折的标准[16]包括:高信号的骨皮质弯曲、扭曲变形或断裂。间接性诊断骨折的体征,如骨膜下血肿,因受专业技术限制不作为骨折判断依据。在由急诊儿童骨科医师做出超声诊断之后,常规前臂的正侧位X线片,由独立的放射科医师出具诊断报告。以X线为标准对照,评估超声在儿童尺桡骨远端骨折的诊断敏感性、特异性、准确性、阳性预测值、阴性预测值和ROC曲线下面积。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS 13.3统计学软件对所得数据进行分析,计算超声检查与X线诊断骨折的敏感性、特异度、阳性预测值和阴性预测值,阳性似然比和阴性似然比,采用配对χ2检验判断一致性。诊断效能采用受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)分析。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 超声诊断结果一般情况
超声检查诊断证实55例尺桡骨远端骨折的患儿共71个骨折,其中桡骨远端骨折36例,尺桡骨远端双骨折16例,尺骨远端骨折3例。
2.2 超声诊断的敏感性和特异性
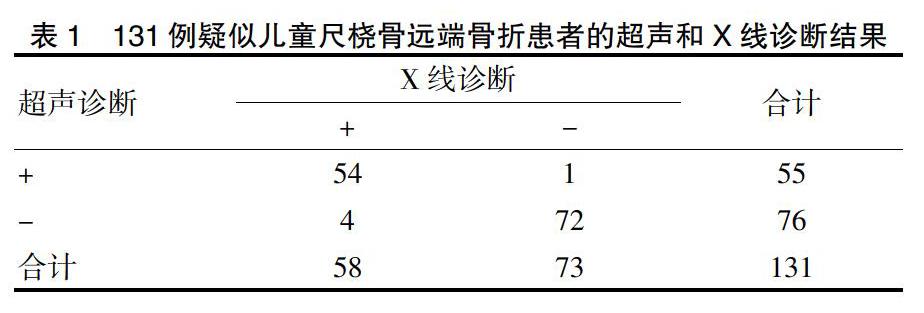
超声检查尺桡骨远端骨折假阴性4例。4例假阴性分别为2例桡骨远端骨折,1例尺骨远端骨折和1例尺骨远端骺离骨折。超声检查与X线诊断结果见表1。超声检查对尺桡骨远端骨折的诊断敏感性和特异性分别为93.1%和98.6%,准确性为96.2%,阳性预测值为98.2%和阴性预测值为94.7%,阳性似然比为68.00和阴性似然比为0.07。
2.3 超声与X线诊断的相关性
超声诊断阳性率为42.0%,X线诊断阳性率为44.3%。超声诊断阳性率与X线诊断阳性率比较,差异无统计学意义(χ2 = 0.8,P = 0.371),超声诊断和X线诊断结果一致性较好(Kappa = 0.922,P < 0.001)。
2.4 超声诊断的特异度和敏感度
以X线诊断为金标准,超声诊断尺桡骨远端骨折,ROC曲线下面积为0.959(95%CI=0.917~1.00)。
3 讨论。
X线是儿童尺桡骨远端骨折的首选常规检查方式。Alzen等[17]回顾性分析2006例疑似骨折的患儿X线片,发现仅354例(17.2%)患儿确诊为骨折。该研究表明了合理选择放射学检查的重要性。而超声是一种无电离辐射、性价比高的辅助诊断方法。本研究证实超声是儿童尺桡骨远端骨折一种可选择的诊断方式,包括尺桡骨远端骺离骨折的诊断。
超声诊断的敏感度和特异性与是否包含关节骨折相关。Hübner等[18]报道超声诊断桡骨远端骨折的敏感率为98.3%,因为包含了关节骨折,特异性仅为69.3%。Hübner等[18]认为超声不适合诊断近关节的骨折和无移位的骺离骨折。本研究结果显示,超声对儿童尺桡骨远端骨折诊断的敏感率和特异性为93.1%和98.6%,与既往文献报道一致[16]。超声已经用于骨骺骨折的诊断,例如:肱骨遠端骺离骨折[19-20],肱骨外髁骨折[7]等。Chen等[21]同样的报道3例桡骨远端Salter Harris 1型骺离骨折,在X线未发现异常,而超声提示骨骺损伤。因此,本研究的高敏感率和特异性提示超声可以用于诊断尺桡骨远端骺离骨折。
本研究中超声诊断有4例假阴性结果。超声不能穿透骨皮质,仅能在骨皮质形成高回声线。此回声线的连续性断裂或可见低回声带才能直接判断骨折。由于儿童青枝骨折的特征,仅表现局部皮质不平整,超声只能发现局部骨膜下血肿,难以区分骨折或单纯的软组织损伤。本研究中未采用单纯骨膜下血肿诊断骨折,从而导致病例漏诊。因此,非超声专科使用超声诊断骨折需要一定学习曲线,健侧的超声对比有利于准确的判断骨骺损伤。
本研究显示,超声是一种诊断儿童尺桡骨远端骨折的可靠方法。超声检查与X线检查比较具有较高的敏感性和特异性,是一种替代X线的诊断方式。
[参考文献]
[1] Randsborg PH,Gulbrandsen P,Saltyte Benth J,et al. Fractures in children:epidemiology and activity-specific fracture rates [J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am,2013,95(7):e42.
[2] Mulvihill DJ,Jhawar S,Kostis JB,et al. Diagnostic Medical Imaging in Pediatric Patients and Subsequent Cancer Risk [J]. Acad Radiol,2017,24(11):1456-1462.
[3] Lubin JH,Adams MJ,Shore R,et al. Thyroid Cancer Following Childhood Low-Dose Radiation Exposure:A Pooled Analysis of Nine Cohorts [J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2017,102(7):2575-2583.
[4] Bibbo G. Effective doses and standardised risk factors from paediatric diagnostic medical radiation exposures: Information for radiation risk communication [J]. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol,2018,62(1):43-50.
[5] 陈小亮,周治国,伍兴,等.超声技术在儿童股骨髁上骨折闭合复位内固定手术中的应用价值[J].临床小儿外科杂志,2019,18(1):30-33.
[6] 伍兴,李雄涛,夏敬冬,等.超声引导闭合复位内固定治疗轻度移位的儿童肱骨外髁骨折[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2019,40(10):939-943.
[7] Li XT,Shen XT,Wu X,et al. A novel transverse ultrasonography technique for minimally displaced lateral humeral condyle fractures in children [J]. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res,2019,105(3):557-562.
[8] Lee SH,Yun SJ. Diagnostic Performance of Ultrasonography for Detection of Pediatric Elbow Fracture:A Meta-analysis [J]. Ann Emerg Med,2019,74(4):493-502.
[9] Galletebeitia Laka I,Samson F,Gorostiza I,et al. The utility of clinical ultrasonography in identifying distal forearm fractures in the pediatric emergency department [J]. Eur J Emerg Med,2019,26(2):118-122.
[10] Rowlands R,Rippey J,Tie S,et al. Bedside Ultrasound vs X-Ray for the Diagnosis of Forearm Fractures in Children [J]. J Emerg Med,2017,52(2):208-215.
[11] Poonai N,Myslik F,Joubert G,et al. Point-of-care Ultrasound for Nonangulated Distal Forearm Fractures in Children: Test Performance Characteristics and Patient-centered Outcomes [J]. Acad Emerg Med,2017,24(5):607-616.
[12] Supakul N,Hicks RA,Caltoum CB,et al. Distal humeral epiphyseal separation in young children: an often-missed fracture-radiographic signs and ultrasound confirmatory diagnosis [J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol,2015,204(2):W192-198.
[13] 李雄涛,沈先涛,伍兴,等.超声检查在移位较小或没有移位的儿童肱骨外髁骨折中的应用[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2017,38(12):927-931.
[14] 沈先涛,陈小亮,李雄涛,等.婴幼儿肱骨远端骨折超声诊断及辅助治疗的临床意义[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2015, 36(2):141-144.
[15] Herren C,Sobottke R,Ringe MJ,et al. Ultrasound-guided diagnosis of fractures of the distal forearm in children [J]. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res,2015,101(4): 501-505.
[16] Hedelin H,Tingstr?觟m C,Hebelka H,et al. Minimal training sufficient to diagnose pediatric wrist fractures with ultrasound [J]. Crit Ultrasound J,2017,9(1):11.
[17] Alzen G,Duque-Reina D,Urhahn R,et al. Radiographic examination of injuries in children. Clinical and legal considerations about indications [J]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr,1992,117(10):363-367.
[18] Hübner U,Schlicht W,Outzen S,et al. Ultrasound in the diagnosis of fractures in children [J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br,2000,82(8):1170-1173.
[19] 周治國,陈小亮,李雄涛,等.超声对儿童肱骨远端Ⅰ型骨骺损伤的诊断价值[J].放射学实践,2017,32(9):977-980.
[20] 杨史珍,王海峰,廖芳娟,等.超声对桡骨远端骨折的治疗价值分析[J].中国医药科学,2019,9(3):131-133, 199.
[21] Chen L,Kim Y,Moore CL. Diagnosis and guided reduction of forearm fractures in children using bedside ultrasound [J]. Pediatr Emerg Care,2007,23(8):528-531.
(收稿日期:2019-12-09)
