神经突触核蛋白-γ、骨形态发生蛋白2、基质金属蛋白酶9在口腔颌面部鳞癌中的表达情况及相关性分析
2019-01-08齐晓宇
齐晓宇

[摘要]目的 分析神经突触核蛋白-γ(SNCG)、骨形态发生蛋白2(BMP-2)、基质金属蛋白酶9(MMP-9)在口腔颌面部鳞癌中的表达情况及相关性。方法 选取2016年1月21日~2017年1月21日我院存档的70例口腔颌面部鳞癌组织蜡块标本作为肿瘤组织,另选择70例癌旁组织与70例正常组织进行参照。依据肿瘤细胞的分化程度,将70例肿瘤组织标本分为高分化组(15例),中分化组(33例)及低分化组(22例)。依据是否出现淋巴结转移情况,将70例肿瘤组织标本分为淋巴结转移(30例)及淋巴结未转移(40例)。比较三组不同组织部位标本中的SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9表达情况;比较不同分化程度肿瘤组织中SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9的表达阳性率;分析淋巴结转移对肿瘤组织中SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9表达阳性率的影响;分析SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9三者之间的相关性。结果 肿瘤组织中的SNCG、MMP-9的阳性率高于癌旁组织和正常组织,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);癌旁组织与正常组织的SNCG、MMP-9阳性率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。肿瘤组织和癌旁组织中的BMP-2的阳性率高于正常组织,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);癌旁组织与肿瘤组织的BMP-2阳性率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。高、中、低分化组肿瘤组织中的BMP-2与MMP-9阳性率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);高分化组肿瘤组织中的SNCG阳性率低于低、中分化组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);低、中分化组肿瘤组织中的SNCG阳性率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。出现淋巴结转移组织中的SNCG、MMP-9阳性率高于淋巴结未转移组织,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。SNCG与BMP-2蛋白成正相关性(r=0.420,P<0.05),BMP-2与MMP-9成正相关性(r=0.390,P<0.05),SNCG与MMP-9成正相关性(r=0.561,P<0.05)。结论 在口腔颌面部鳞癌中,SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9三者互成正相关性,具有高表达特征,可作为该类肿瘤疾病的常用檢测指标。
[关键词]口腔颌面部;鳞癌;神经突触核蛋白-γ;骨形态发生蛋白2;基质金属蛋白酶9;表达;相关性
[中图分类号] R739.81 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-4721(2019)11(b)-0144-04
Expression of synuclein-γ, bone morphogenetic protein-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in oral and maxillofacial squamous cell carcinoma and their correlation analysis
QI Xiao-yu
Department of Ophthalmology and Otorhinolaryngology, Iron and Coal General Hospital of Liaoning Health Industry Group, Liaoning Province, Tieling 112700, China
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the expression and correlation of synuclein-γ (SNCG), bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in oral and maxillofacial squamous cell carcinoma. Methods From January 21, 2016 to January 21, 2017, 70 cases of oral and maxillofacial squamous cell carcinoma wax specimens archived in our hospital were selected as tumor tissues. Another 70 cases of adjacent tissues and 70 normal tissues were selected for reference. According to the degree of differentiation of tumor cells, 70 tumor tissue samples were divided into high differentiation group (15 cases), medium differentiation group (33 cases) and low differentiation group (22 cases). According to the presence or absence of lymph node metastasis, 70 tumor tissue samples were divided into lymph node metastasis (30 cases) and no lymph node metastasis (40 cases). The expression of SNCG, BMP-2 and MMP-9 in three different tissues were compared. The positive expression rates of SNCG, BMP-2 and MMP-9 in tumor tissues with different differentiation degrees were compared. The effect of lymph node metastasis on the positive expression rates of SNCG, BMP-2 and MMP-9 in tumor tissues was analyzed. The correlation among SNCG, BMP-2 and MMP-9 were analyzed. Results The positive rates of SNCG and MMP-9 in tumor tissues were higher than those in adjacent tissues and normal tissues, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the positive rate of SNCG and MMP-9 between the adjacent tissues and normal tissues (P>0.05). The positive rate of BMP-2 in tumor tissues and adjacent tissues were higher than that in normal tissues, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the positive rate of BMP-2 between the adjacent tissues and tumor tissues (P>0.05). The positive rates of BMP-2 and MMP-9 in the tumor tissues of the high, medium and low differentiation groups were not statistically significant (P>0.05). The positive rate of SNCG in tumor tissues in the high differentiated group was lower than that in the low and medium differentiated groups, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in SNCG positive rate between low and medium differentiation groups (P>0.05). The positive rate of SNCG and MMP-9 in lymph node metastasis tissues was higher than that in no lymph node metastasis tissues, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). SNCG was positively correlated with BMP-2 (r=0.420, P<0.05), BMP-2 was positively correlated with MMP-2 (r=0.390, P<0.05), and SNCG was positively correlated with MMP-2 (r=0.561, P<0.05). Conclusion In oral and maxillofacial squamous cell carcinoma, SNCG, BMP-2 and MMP-9 are positively correlated and have high expression characteristics, which can be used as a common detection indexes for such tumor diseases.
[Key words] Oral and maxillofacial; Squamous cell carcinoma; Synuclein-γ; Bone morphogenetic protein-2; Matrix metalloproteinase-9; Expression; Correlation
口腔颌面部鳞癌患者占据该部位肿瘤的发病率超过80%[1-2],以口腔黏膜作为主要病变区域,可选择手术治疗、放射治疗等方案进行干预,但是考虑到该类疾病的复发率与转移率较高,导致实际治疗难以获得良好的效果,术后5年生存率在50%左右。关于肿瘤细胞转移分子机制的报道较多,得知黏附分子、细胞因子、生长因子、蛋白溶酶等分子和肿瘤转移具有紧密的关联性[3]。许多学者研究报道[4],神经突触核蛋白-γ(SNCG)、骨形态发生蛋白2(BMP-2)、基质金属蛋白酶9(MMP-9)均与肿瘤的发生发展具有关联性,但是SNCG、BMP-2在口腔颌面部鳞癌中的研究相对较少,且3种蛋白表达目前尚未明确其相关性。本研究选取我院存档的70例口腔颌面部鳞癌组织蜡块标本,另选择70例癌旁组织与70例正常组织进行参照,分析SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9在口腔颌面部鱗癌中的表达情况及三者之间的相关性,以期为今后临床研究提供相关的参考资料,现报道如下。
1资料与方法
1.1一般资料
选取2016年1月21日~2017年1月21日我院存档的70例经过病理诊断后确诊的口腔颌面部鳞癌组织蜡块标本作为肿瘤组织,另计算机随机选择70例肿瘤边缘组织作为癌旁组织(距离病灶0~2 cm)与70例正常组织(无肿瘤情况)进行参照。口腔颌面部鳞癌组织蜡块标本中,男37例,女33例;年龄22~69岁,平均(45.12±3.22)岁。癌旁组织标本中,男38例,女32例;年龄21~69岁,平均(44.96±3.45)岁。正常组织标本中,男36例,女34例;年龄21~68岁,平均(45.10±3.20)岁。三组的一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。本研究经我院医学伦理委员会审核及同意。
纳入标准:①所有标本对象均为于我院就诊者;②所有标本的基本资料完整;③所有标本对象对本次研究知情同意。排除标准:①其他恶性肿瘤者;②以往有精神疾病史者;③存在认知障碍情况者;④妊娠与哺乳期女性[5-6]。
另外,依据肿瘤细胞的分化程度,将70例肿瘤组织标本分为高分化组(15例),中分化组(33例)及低分化组(22例)。依据是否出现淋巴结转移情况,将70例肿瘤组织标本分为淋巴结转移(30例)及淋巴结未转移(40例)。
1.2方法
将三组标本均给予甲醛固定(4%)、石蜡包埋后切成3~4 μm的薄片,之后给予HE染色,并给予免疫组化分析。选择鼠抗人SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9单克隆抗体,并选择免疫组织化学试剂。
给予免疫组化处理:选择En Vision二步法进行免疫组织化学染色处理,严格依照试剂说明书上的内容进行操作,选择磷酸盐缓冲液作为阴性对照一抗,选择阳性组织切片标本作为阳性对照组,选择生理盐水与PBS分别替代实验一抗。
1.3观察指标及评价标准
比较三组不同组织部位标本中的SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9表达情况;比较不同分化程度肿瘤组织中SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9的表达阳性率;分析淋巴结转移对肿瘤组织中SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9表达阳性率的影响;分析SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9三者之间的相关性。
SNCG、BMP-2表达主要存在于细胞核与胞浆内,MMP-9表达主要存在于细胞胞浆内,若为染色阳性结果,则表示呈现出较深的颜色或者棕色。依据着色细胞数评定积分与细胞着色强度对其表达情况进行评价。若不存在细胞染色,表示阴性(-);若着色细胞占比<10%,表示弱阳性(+);若着色细胞数占比在10%~50%,表示中等阳性(++);着色细胞数>50%,表示强阳性(+++)。之后依据染色强度进行细化分类,(-)至(+)表示阴性表达,(++)至(+++)表示阳性表达[7-8]。
1.4统计学方法
采用SPSS 21.0统计学软件进行数据分析,计量资料用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验;计数资料采用率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验;相关性采用Pearson相关性分析,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
2.1不同组织部位SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9表达阳性率的比较
肿瘤组织中的SNCG、MMP-9的阳性率高于癌旁组织和正常组织,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);癌旁组织与正常组织的SNCG、MMP-9阳性率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。肿瘤组织和癌旁组织中的BMP-2的阳性率高于正常组织,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);癌旁组织与肿瘤组织的BMP-2阳性率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(表1)。
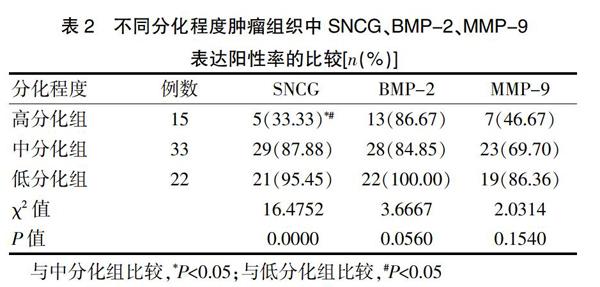
2.2不同分化程度肿瘤组织中SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9表达阳性率的比较
高、中、低分化组肿瘤组织中的BMP-2与MMP-9阳性率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);高分化组肿瘤组织中的SNCG阳性率低于低、中分化组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);低、中分化组肿瘤组织中的SNCG阳性率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(表2)。
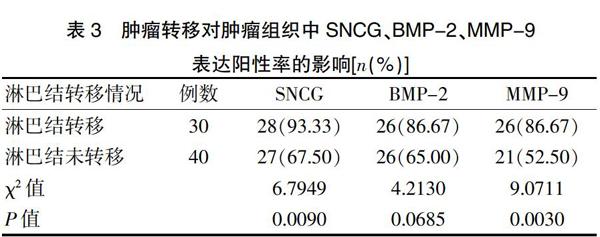
2.3淋巴结转移对肿瘤组织中SNCG、BMP-2、MMP-9表达阳性率的影响
出现淋巴结转移组织中的SNCG、MMP-9阳性率高于淋巴结未转移组织,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。淋巴结转移和淋巴结未转移组织中的BMP-2阳性率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(表3)。
