通过电阻抗断层成像技术观察体位对机械通气ARDS患者肺通气的影响
2017-12-19王玉光王宏伟王双双杨卫然
王玉光 王宏伟 王双双 杨卫然 叶 钢
(首都医科大学附属北京潞河医院急救医学部急诊重症监护病房,北京 101149)
·基础研究·
通过电阻抗断层成像技术观察体位对机械通气ARDS患者肺通气的影响
王玉光 王宏伟 王双双 杨卫然 叶 钢*
(首都医科大学附属北京潞河医院急救医学部急诊重症监护病房,北京 101149)
目的利用电阻抗断层成像技术(electrical impedance tomography,EIT)观测急性呼吸窘迫综合征 (acute respiratory distress syndrome,ARDS)患者机械通气时,在不同体位下患者的肺内气体分布情况,并观察氧分压、氧合指数、潮气量的变化情况。方法采用前瞻性随机对照研究方法,选择首都医科大学附属北京潞河医院急诊重症监护病房2015年1月至2017年6月收治行机械通气的ARDS患者作为研究对象,应用随机数字表法分为试验组和对照组。试验组设定为常规体位有效抬高30°的基础上,每日间断予患者采取90°端坐位8 h;对照组设定为体位持续抬高30°。比较2组患者入组时、体位有效保持72、96、120 h后,分别通过EIT收集2组患者的感兴趣区域(region of interest,ROI)值,同时收集患者潮气量、通过血气分析收集氧分压、氧合指数等参数,以及呼吸机使用时间和监护室住院时间。结果研究期间最终共60例患者纳入分析,其中试验组27例,对照组33例。2组患者性别、年龄、急性生理和慢性健康评分Ⅱ(acute physiology and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ,APACHEⅡ)评分以及导致ARDS的病因等比较差异无统计学意义。与对照组相比,试验组患者在体位有效保持96 h及120 h后PaO2及氧合指数明显高于对照组,2组比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),同时通过EIT观测试验组患者肺重力依赖区96 h及120 h ROI3值、ROI4值明显高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),试验组患者呼吸机使用时间及监护室住院时间明显低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),试验组与对照组患者在体位有效保持96 h及120 h后潮气量值差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),试验组与对照组患者体位有效保持72 h时比较,氧分压、氧合指数、潮气量差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论对于ARDS患者行机械通气期间,每日间断予患者采取90°端坐位8 h以上,在96 h后,能够有效改善重力依赖区的肺通气情况,有效改善患者的氧分压及氧合指数,促进患者早日成功脱机拔管。
电阻抗成像技术;体位;肺内气体分布;潮气量;氧分压
急性呼吸窘迫综合征 (acute respiratory distress syndrome,ARDS)[1]是临床常见的急性呼吸系统疾病,常继发于严重感染、休克、创伤及烧伤等多种疾病,病死率高达30%~40%[2]。对于发生ARDS的患者,行有创机械通气是挽救患者生命的有效手段。但是,气管插管的置入也是并发呼吸机相关性肺炎(ventilator associated pneumonia,VAP)等致命合并症的主要途径,如何在“肺保护性通气”和“肺开放”(open lung)及“维持肺开放”(keep lung open)等通气策略[3]的基础上辅以物理的肺康复治疗方案,使患者的病情尽快得到有效的控制,是近年来重症监护医护人员关注的重点。那么对于ARDS行机械通气的患者在不同体位时,肺内气体是如何分布的以及对患者的治疗效果有什么样的影响呢,笔者采取间断予患者采取90°端坐位作为实施肺康复的主要措施,取得了很好的结果,现报道如下。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2015年1月至2017年6月入住首都医科大学附属北京潞河医院急诊重症监护病房行机械通气的患者。纳入标准:①年龄≥18周岁;②符合ARDS柏林标准[4]的有创机械通气患者;③给予有创机械通气超过48 h的患者。排除标准:①体内安装有永久或临时心脏起搏器者;②中、大量胸腔积液者;③血流动力学严重不稳、椎骨或骨盆疾患,骨科术后体位特殊要求者;④体质量指数(body mass index,BMI)>30 kg/m2的患者。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 实验方法
采用前瞻性随机对照研究方法,选择本院急诊重症监护病房2015年1月至2017年6月收治行机械通气的ARDS患者作为研究对象,所有患者在入室病情平稳后,应用随机数字表法分为试验组(Group 1)和对照组(Group 2)。Group 1设定为常规体位有效抬高30°的基础上每日间断予采取90°端坐位8 h;Group 2设定为体位持续抬高30°。 研究方案得到本院伦理委员会的核准,患者及家属均知情,并签订知情同意书。患者入组时收集患者一般资料,包括姓名、性别、年龄、诊断、住院号、身高、体质量、有创机械通气模式和参数、BMI、第一个24 h急性生理和慢性健康评分Ⅱ(acute physiology and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ,APACHEⅡ)和生命体征;分别于患者入组时、体位有效保持72 h(Time 1)、96 h(Time 2)、120 h(Time 3)后记录患者的感兴趣区域(region of interest,ROI)值及氧分压、氧合指数、潮气量等数值。
1.2.2 电阻抗断层成像技术(electrical impedance tomography,EIT)所得参数
EIT是通过绑缚在患者胸廓上的一条电极带连续发射阻抗波、并根据其在胸腔内穿透不同组织后的衰减程度、进而构建成图像的一项新技术。具有无创、实时、可连续观测的特点,并可对肺组织的不同区域分层或段ROI观察,进而了解肺在不同状态下的通气变化[5]。使用时根据患者的胸围给予佩戴合适型号的EIT(Drager C500,德国德尔格公司)电极带(图1)。调整EIT基线,待基线平稳后,设置为4层模式,即ROI1~ROI4(图2),将ROI3~ROI4区认定为重力依赖区,2组患者体位有效保持72、96、120 h后记录10 min EIT数据。在整个实验的过程中,不对患者行强刺激操作,呼吸机(Drager V500,德国德尔格公式)参数保持不变。
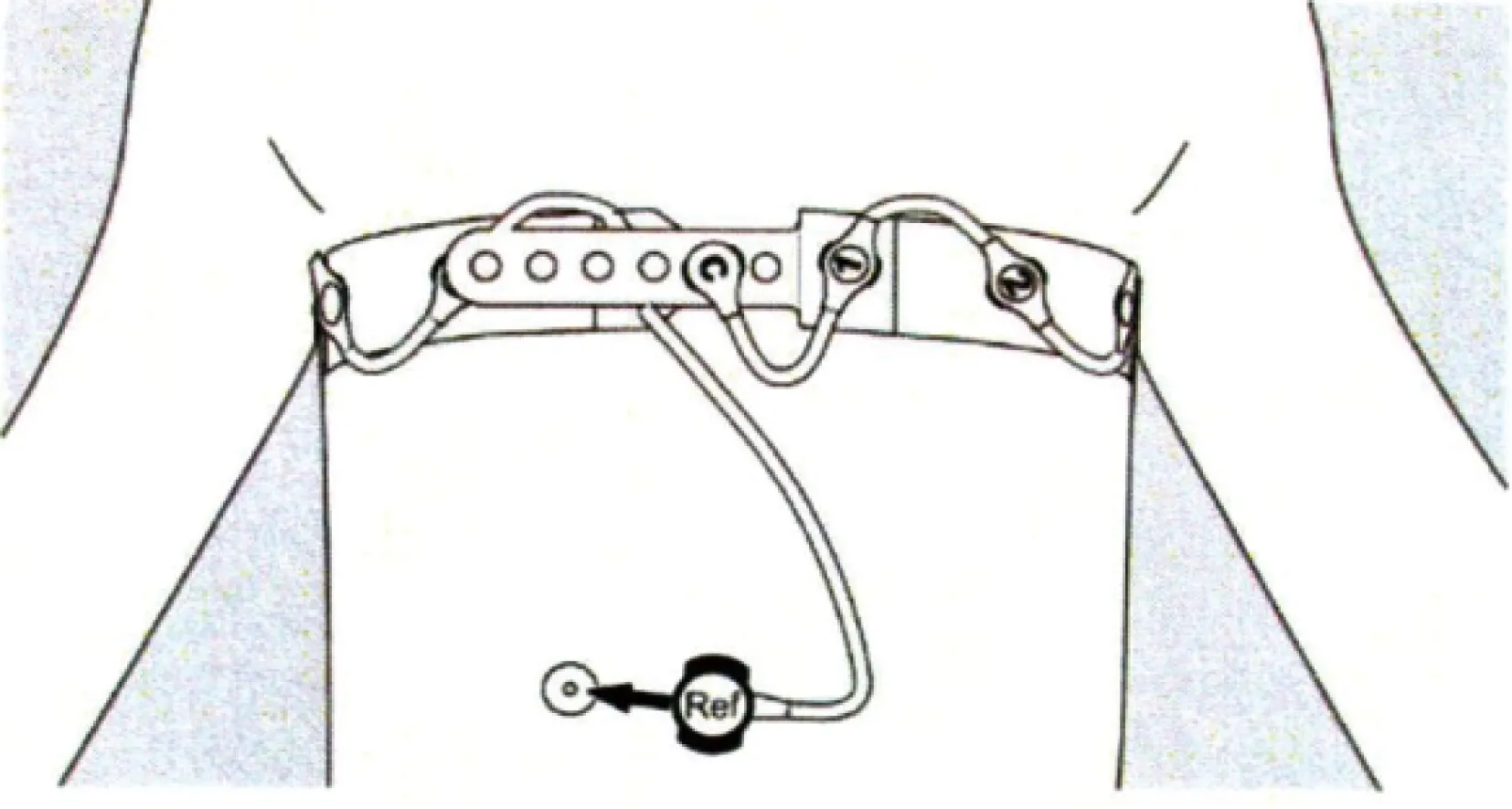
图1 EIT绑带的具体位置Fig.1 Location of the EIT bind
EIT:electrical impedance tomography.
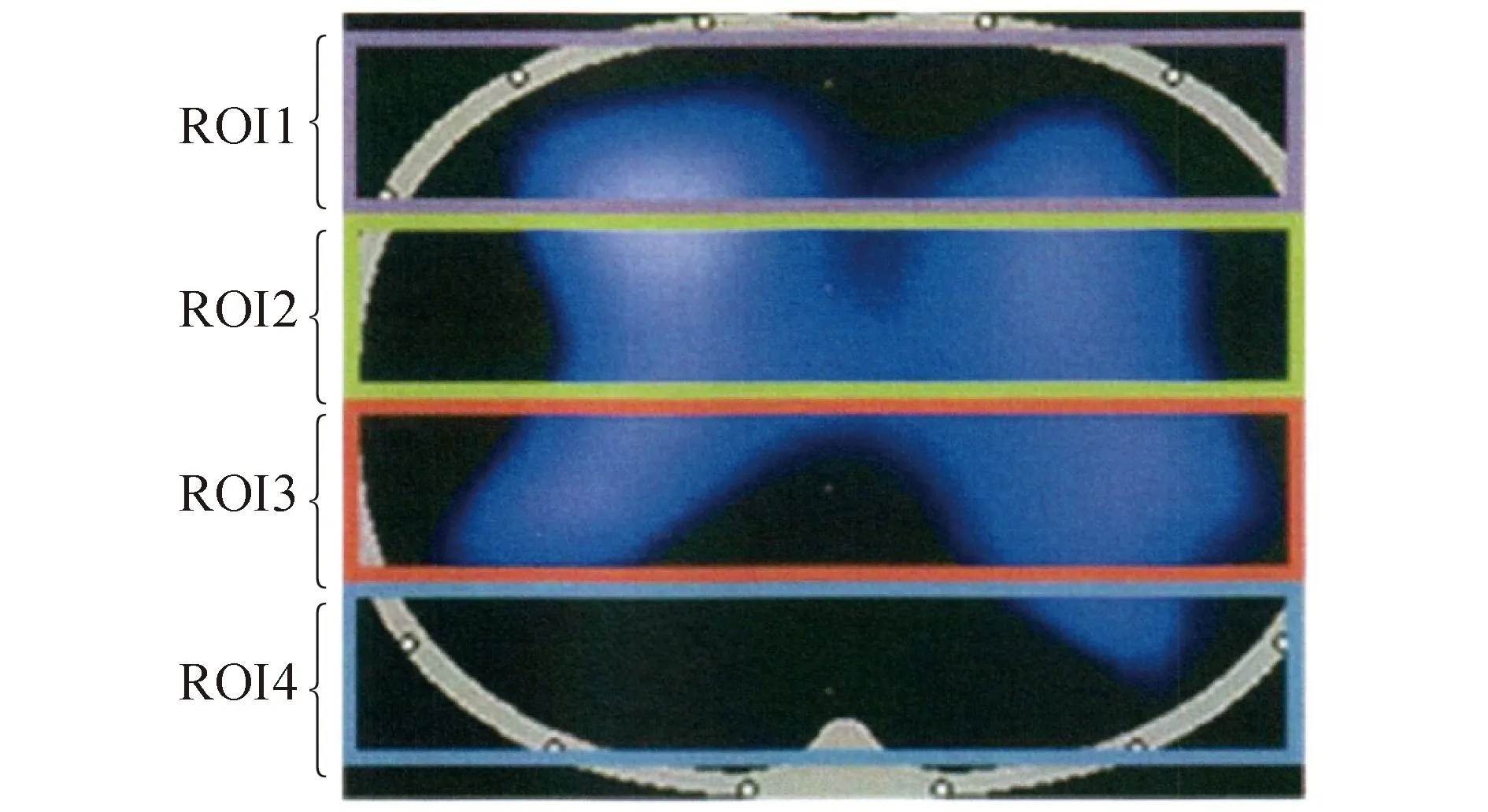
图2 EIT图像分区示意图Fig.2 EIT image partition diagram
ROI1,ROI2,ROI3 and ROI4 were respectively from top to bottom.From left to right,right lung and left lung;ROI:region of interest.
1.2.3 患者体位有效性的观察
本科室使用的电动床上配有量角器,能够直观查看到患者体位抬高的角度,本研究负责人随时查看患者体位的有效性。
1.3 统计学方法

2 结果
2.1 一般资料
本研究共调查68例患者,因病情导致试验不能进行、放弃治疗及96 h内死亡患者8例,最终共60例患者纳入分析,其中试验组(Group 1)27例,对照组(Group 2)33例。患者的一般资料详见表1。
2.2 在不同体位、不同时间时,相关呼吸力学指标情况
本研究显示,ARDS患者在行机械通气期间,90°端坐位有利于促进肺功能的恢复,随着端坐时间的延长,患者的呼吸力学指标明显恢复,患者采取间断90°端坐位72 h及与保持体位持续抬高30°72 h(Time 1)比较,2组患者的氧分压、氧合指数、潮气量差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),间断端坐96 h(Time 2)与120 h(Time 3),2组患者的氧分压、氧合指数差异有统计学意义(P值分别为0.042,0.006和0.002,0.000),而潮气量差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),详见表2。
2.3 不同体位肺部不同区域气体分布情况
本研究发现端坐更有利于患者重力依赖区肺通气的改善,患者采取间断90°端坐位72 h及与保持体位持续抬高30°72 h(Time 1)比较,2组患者肺部ROI1、ROI2、ROI3、ROI4 4个区域气体分布情况差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),而给予患者采取间断90°端坐位96、120 h后,患者重力依赖区气体分布与体位持续抬高30°96 h(Time 2)、120 h(Time 3)比较,肺部ROI1、ROI2、ROI3、ROI4 4个区域气体分布情况差异有统计学意义(P值分别为0.042;0.022,0.000;0.046,0.010;0.035,0.000)。详见表3。
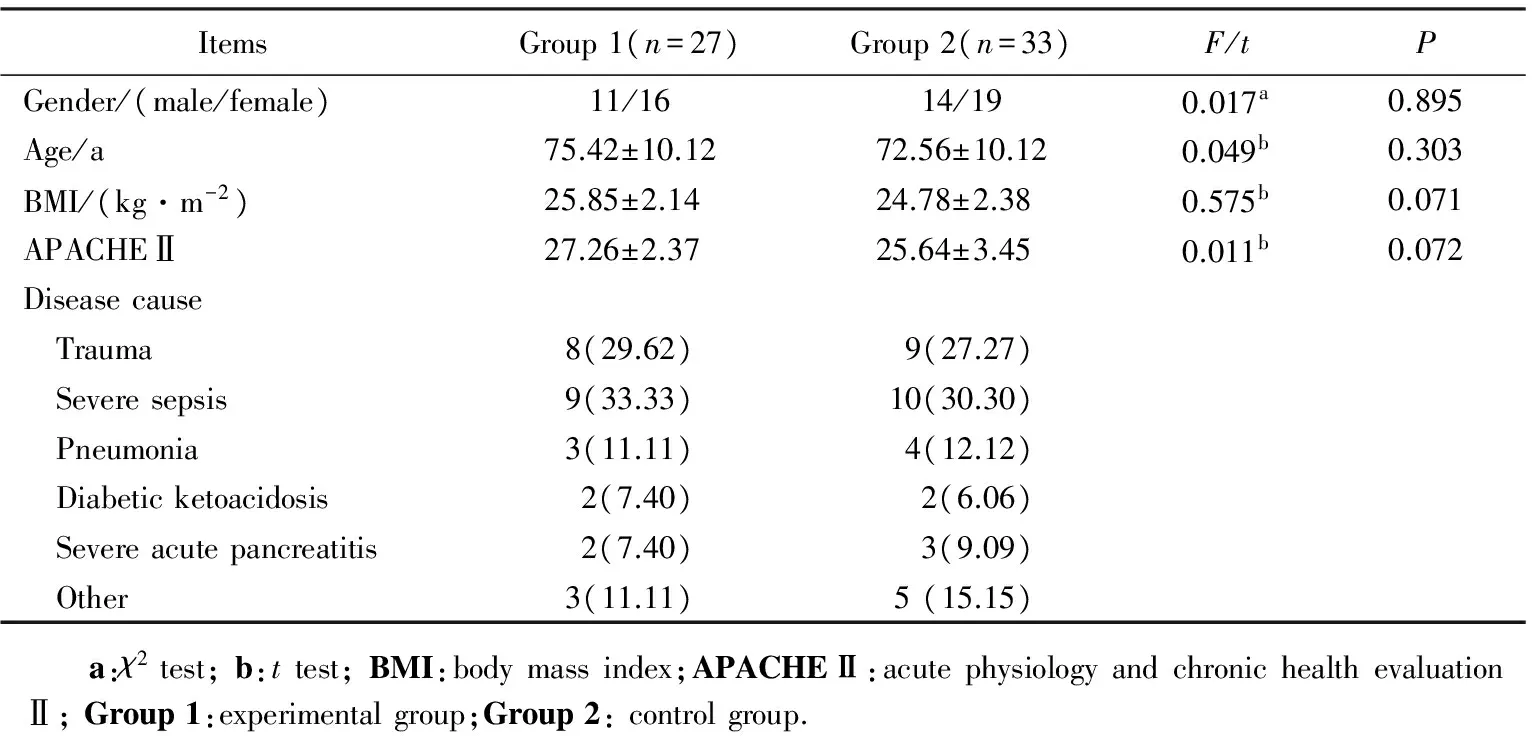
表1 2组患者一般资料比较 Tab.1 Baseline data comparison n(%)
表2 患者在不同体位不同时间时氧分压、氧合指数及潮气量的情况Tab.2 The oxygen partial pressure,oxygenation index and tidal volume of patients in different positions
1 mmHg=0.133 kPa;*P<0.05vsgroup 2;Time1:72 h;Time2:96 h;Time3:120 h;Group1:experimental group;Group2: control group.
试验组及对照组肺通气示意图详见图3。
2.4 呼吸机使用时间及监护室住院时间
本研究显示间断予患者采取90°端坐位,能够促进患者肺部炎性反应的局限,促进尽早脱机拔管。试验组(Group 1)患者在呼吸机使用时间方面和监护室住院时间方面,均少于对照组(Group 2)患者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),详见表4。
3 讨论
3.1 EIT技术能够有效监测有创机械通气患者肺通气的情况
既往主要是通过计算机断层扫描(computed tomography,CT)来了解患者肺损伤的情况,但是,需要患者外出到CT室进行检查,这使得重症患者在转运的过程中存在一定的风险性,使得该项检查存在一定的局限性。近年来用于评价肺内气体分布的新兴手段是EIT[6]。它通过监测肺内通气引起的胸内阻抗变化,可以提供ARDS局部肺组织的力学特征,较之于金标准CT来说,它的优点是无创、床边、实时、无辐射[7-8]。它的原理在于不同的组织导电率不同,进而形成不同的影像学资料。然而,EIT的分辨率比CT要低得多,因此不能用于肺形态学的准确表示[9]。就临床护理而言,EIT能够于床旁通过直观的影像学资料,实时客观的反映出患者在保持不同体位时,肺内气体分布的具体情况,能够有效的反映出患者肺部通气质量差的区域,从而指导护士重点加强该区域物理治疗的手段,进而能够起到有效预防肺不张、促使炎性反应局限等作用。
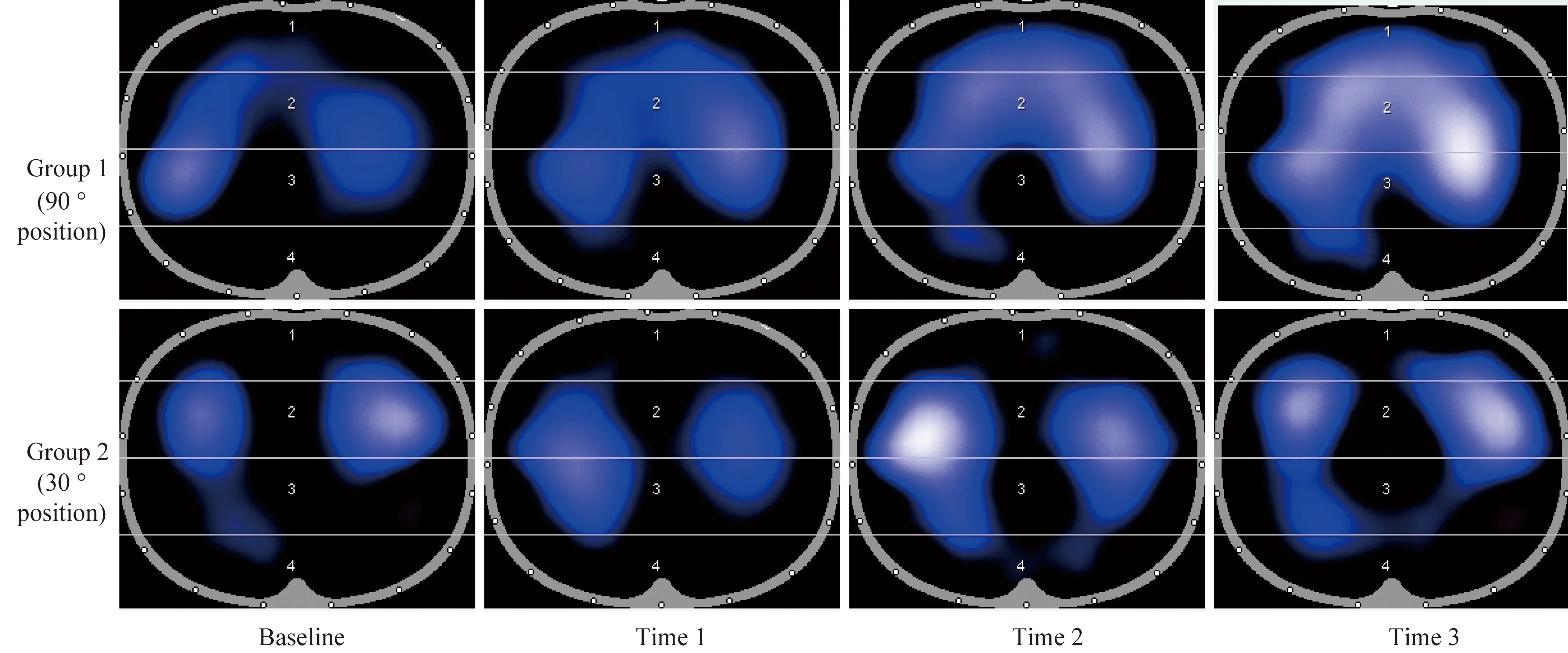
图3 肺通气情况Fig.3 Pulmonary position
Group1:experimental group;Group2: control group;Time1: 72 h EIT;Time2: 96 h EIT;Time3: 120 h EIT;EIT:electrical impedance tomography.
表3 患者肺的四个区域气体分布情况Tab.3 Distribution of the four areas of the patient’s lungs (%,)
The cross section of the lung was divided into four equal parts from the ventral side to the dorsal side,which were respectively ROIl,Rol2,ROI3 and ROI4 regions.The data measured were the percentage of the total ventilation in different positions and regions; 1 mmHg=0.133 kPa;*P<0.05vsGroup 2;Time1: 72 h;Time2: 96 h;Time3: 120 h;Group1:experimental group;Group2: control group;ROI:region of interest.
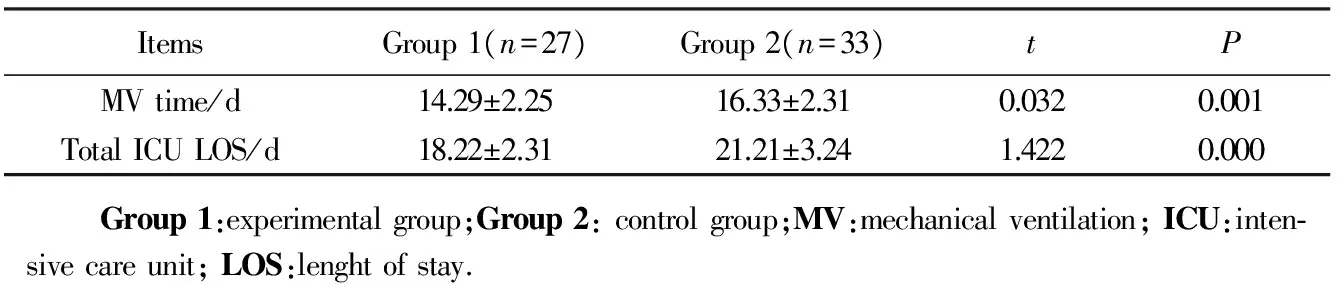
表4 患者呼吸机使用时间及住监护室时间Tab.4 MV time and total ICU length of stay
3.2 端坐卧位可有效改善患者重力依赖区部位的肺内气体分布
对于接受有创机械通气的患者,中华医学会曾建议将重症患者的床头抬高30~45°[10],但对于不同角度卧位下,患者肺内气体分布的具体情况,多年来相关的研究并不多,且没有提供足够的证据。EIT的临床应用填补了这一项的空白,相关的临床实验数据[11-13]显示,在肺内气体分布方面,EIT与CT之间存在着良好的相关性,它通过监测肺内通气引起的胸内阻抗变化而显像。在临床使用的过程中,常将EIT设定为四层模式,并将ROI3~ROI4区认定为重力依赖区,患者端坐位时,由于重力的作用,患者的膈肌下降,胸腔范围增大,肺活动的空间增大。通过实验发现,当患者处于端坐卧位时,可能因为膈肌下降,肺内重力依赖区气体分布随膈肌的下移而增加。当患者端坐达到96 h以上时,患者原重力依赖区因为体位的改变不再是重力依赖区,使得有效参与呼吸的肺泡数量明显增多,同时使肺内气体分布更加均匀。
3.3 端坐卧位可有效改善机械通气患者呼吸力学的相关指标
肺康复是近年来逐步引起大家重视的一个领域,对于ARDS的患者,由于病情进展快、肺的渗出液比较多,患者的氧分压和氧合指数很难维持,目前国内外主要的治疗手段之一是利用不同的方法进行肺复张。比较推崇的是俯卧位通气,但是俯卧位通气的过程中存在的风险比较大,包括皮肤压力性损伤、管路滑脱、气道梗阻、心律失常等[14-16]。对于机械通气期间行俯卧位通气,不仅需要极大的人力,对患者来说也存舒适度极差等弊端。国内外大型医院予患者采取直立位作为肺康复的手段[17],但需要多科室人员共同参与才能保证患者的安全。对于人力、设备等条件均有限的情况,可尝试采用床上端坐位来替代直立位为患者进行肺康复。笔者通过实验发现,当间断予患者采取90°端坐位96 h后,患者的氧分压、氧合指数、潮气量明显改善。在治疗方案相同的情况下,患者端坐时间越长,患者上述呼吸力学指标的改善越明显。进而缩短了呼吸机的使用时间,同时减少了患者的监护室住院时间。
3.4 结论
EIT技术能够实时监测患者肺通气的情况,是一种安全、可靠的临床技术方法,对于机械通气的ARDS患者,端坐卧位能够有效的改善患者肺重力依赖区的通气,减少肺不张等的发生,能够有效改善患者的呼吸力学等参数,进而促进患者的脱机拔管,减少患者的监护室住院时间,端坐位是对机械通气患者肺康复的有效的方案之一。
由于本研究为单中心,样本量有限,所获得的结果有一定的局限性,有待于将来联合多中心、大样本进行进一步研究,以探讨其可推广性和临床实用性。
[1] ARDS Definition Task Force,Ranieri V M,Rubenfeld G D,et al.Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition[J].JAMA,2012,307(23):2526-2533.
[2] Bellani G,Laffey J G,Pham T,et al.Epidemiology,patterns,and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries [J].JAMA,2016,315(8):788-800.
[3] Meade M O,Cook D J,Guyatt G H,et al.Ventilation strategy using low tidal volumes,recruitment maneuvers,and high positive end-expiratory pressure for acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome:a randomized controlled trial[J].JAMA,2008,299(6):637-645.
[4] Ferguson N D,Fan E,Camporota L,et al.The Berlin definition of ARDS: an expanded rationale,justification,and supplementary material[J].Intensive Care Med,2012,38(10):1573-1582.
[5] Walsh B K,Smallwood C D.Electrical impedance tomography during mechanical ventilation [J].Respir Care,2016,61(10):1417-1424.
[6] He X,Jiang J,Liu Y,et al.Electrical impedance tomography-guided PEEP titration in patients undergoing laparoscopic abdominal surgery:[J].Medicine (Baltimore),2016,95(14):e3306.
[7] Pfurtscheller K,Ring S,Beran E,et al.Effect of body position on ventilation distribution during PEEP titration in a porcine model of acute lung injury using advanced respiratory monitoring and electrical impedance tomography[J].Intensive Care Med Exp,2015,3(1):38.
[8] Rausch S M,Haberthür D,Stampanoni M,et al.Local strain distribution in real three-dimensional alveolar geometries[J].Ann Biomed Eng,2011,39(11):2835-2843.
[9] Bellani G,Amigoni M,Pesenti A.Positron emission tomography in ARDS: a new look at an old syndrome[J].Minerva Anestesiol,2011,77(4):439-447.
[10] 中华医学会重症医学分会.呼吸机相关性肺炎预防,诊断和治疗指南(2013)[J].中华内科杂志,2013,52(6):524-526.
[11] Bikker I G,Leonhardt S,Bakker J,et al.Lung volume calculated from electrical impedance tomography in ICU patients at different PEEP levels[J].Intensive Care Med,2009,35(8):1362-1367.
[12] Bikker I G,Preis C,Egal M,et al.Electrical impedance tomography measured at two thoracic levels can visualize the ventilation distribution changes at the bedside during a decremental positive end-expiratory lung pressure trial[J].Criti Care,2011,15(4):R193.
[13] Meier T,Luepschen H,Karsten J,et al.Assessment of regional lung recruitment and derecruitment during a PEEP trial based on electrical impedance tomography[J].Intensive Care Med,2008,34(3):543-550.
[14] Gattinoni L,Tognoni G,Pesenti A,et al.Effect of prone positioning on the survival of patients with acute respiratory failure[J].N Engl J Med,2001,345(8):568-573.
[15] Guérin C.Prone positioning acute respiratory distress syndrome patients[J].Ann Transl Med,2017,5(14):289.
[16] Guerin C,Gaillard S,Lemasson S,et al.Effects of systematic prone positioning in hypoxemic acute respiratory failure: a randomized controlled trial[J].JAMA,2004,292(19):2379-2387.
[17] TEAM study investigators,Hodgson C,Bellomo R,et al.Early mobilization and recovery in mechanically ventilated patients in the ICU: a bi-national,multi-centre,prospective cohort study[J].Crit Care,2015,19(1):1-10.
Throughtheelectricalimpedancetomographytechnology(EIT)toobservethepositionoftheeffectsofmechanicalventilationinpatientswithARDSlungventilation
Wang Yugang,Wang Hongwei,Wang Shuangshuang,Yang Weiran,Ye Gang*
(EmergencyIntensiveCareUnit,BeijingLuheHospital,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing101149,China)
ObjectiveTo use electrical impedance tomography technology(EIT) to observe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) patients with mechanical ventilation,in the distribution of gas in the lungs of patients with different position,and to observe the oxygen partial pressure,oxygenation index,changes of the tidal volume.MethodsThe prospective randomized study method will be used,the patients with ARDS in the Emergency Intensive Care Unit,Beijing Luhe Hospital,Capital Medical University in January 2015 to June 2017 were tested with lines of mechanical ventilation as the research objects,and vis application of random grouping method,the tests were divided into trial group and control group.Experimental group will be set to normal position effectively to raise 30 degrees,on the basis of daily 8 hours continuously to patients with 90 degrees of sitting position.The control group was set up 30 degrees continuously for the position.The two groups of patients were compared,position effectively maintains 72,96,120 hours,respectively which were collected by electrical impedance imaging region of interest (ROI) values of two groups of patients,patients which were collected through breathing machine tidal volume,through the blood gas analysis to collect oxygen partial pressure,oxygenation index parameters,such as breathing machine and use time and care in the hospital.ResultsFinally,a total of 60 patients were included in the analysis of 27 cases of test group and control group 33 cases.Two groups of patients with gender,age,acute physiology and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ (APACHEⅡ) scores and lead to the causes of ARDS was no statistically significant difference.Compared with the control group,experimental group patients in position effectively maintain 96 hours and 120 hours after PaO2and oxygenation index was significantly higher than the control group,differences were statistically significant (P<0.05),at the same time,through the observation of EIT technology experimental group patients gravity ROI3 values depend on the area for 96 hours and 120 hours,ROI4 value was significantly higher than the control group (P<0.05).Patients in the experimental group were significantly lower in ventilator use time and in the hospital than in the control group (P<0.05);the experimental group compared with the control group in position effectively maintain 96 hours and 120 hours after,tidal volume no significant change (P>0.05).Position effectively maintain 72 hours,the experimental group compared with the control group patients of oxygen partial pressure,oxygenation index,tidal volume,the difference were statistically significant (P>0.05).ConclusionFor patients with ARDS line during invasive ventilation,daily continuously to 90 degrees patients keep sitting more than 8 hours,after 96 hours,can effectively improve the gravity depend on the changes of pulmonary ventilation,effectively improve the patient’s oxygen partial pressure and oxygenation index,promote patients of pulmonary rehabilitation,promote patients successfully weaning tube drawing at an early date.
electrical impedance tomography;position;the distribution of gas in the lungs;tidal volume;oxygen partial pressure
*Corresponding author,E-mail:Steelye@126.com
时间:2017-12-13 21∶09
http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3662.R.20171213.2109.034.html
10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2017.06.027]
R459.7
2017-10-20)
编辑 孙超渊
