固相萃取-HPLC法测定辣椒油中偶氮染料
2017-07-01邢燕高慧刘玉栋王勤
邢燕,高慧,刘玉栋,王勤
(1.淄博市疾病预防控制中心,山东淄博255026;2.淄博市科学技术情报研究所,山东淄博255025)
固相萃取-HPLC法测定辣椒油中偶氮染料
邢燕1,高慧1,刘玉栋2,王勤1
(1.淄博市疾病预防控制中心,山东淄博255026;2.淄博市科学技术情报研究所,山东淄博255025)
建立一种基于大孔吸附树脂柱对辣椒油中苏丹红I-IV、苏丹红7B和对位红等6种偶氮染料进行的前处理方法。辣椒油样品经正己烷稀释,用自制大孔吸附树脂柱净化,用高效液相色谱-二极管阵列检测器检测,自制固相萃取柱经再生过程可重复使用。结果显示,6种染料在0.05 μg/mL~1.0 μg/mL浓度范围内线性关系良好,相关系数高于0.999 8,在3个加标浓度下,日内和日间的加标回收率在90.9%~104.3%之间,相对标准偏差(RSD)小于3.7%。
偶氮染料;辣椒油;固相萃取;液相色谱;大孔吸附树脂
近年来,非法添加和滥用合成染料已成为食品安全领域的主要隐患。偶氮类染料是印染工艺中应用最广泛的一类合成染料,由于其色泽鲜艳、着色稳定、价格低廉,近年来常被非法添加到食品中作为着色剂使用。由于偶氮类染料能分解产生致癌芳香胺,经过活化作用改变人体的DNA结构引起机体病变和诱发癌症,我国、美国和欧盟等国家严禁在食品中使用该类染料[1]。但利益驱使下仍有不法厂商在辣椒等食品中非法添加,因此加强对食品中偶氮类着色剂的检测十分必要。
目前偶氮类染料检测的预处理方法多是固相萃取[2-4]、液液萃取[5-7]、凝胶渗透色谱[8-9]、分子印迹固相萃取[10-12]、基质固相分散萃取[13-15]等方法。因固相萃取技术节省溶剂、操作简单,成本低廉,回收率高,目前已成为最受欢迎的样品前处理方法[16],而固相萃取吸附剂的选择是决定其富集效率最重要的因素之一。GB/T 19681-2005《食品中苏丹红染料的测定方法高效液相色谱法》中使用氧化铝固相萃取柱对样品进行了净化,并且仅针对食品中的苏丹红I-IV。大孔吸附树脂具有独特的吸附性能,具有机械强度高、耐酸碱、易于再生等特点。它被广泛应用于天然产物的分离与提纯,关于它的使用作为固相萃取吸附剂的研究较少。杨文翰等用大孔吸附树脂作为固相吸附剂,对食品中天然色素栀子黄进行测定,可重复使用10次以上[17],大孔树脂固相萃取柱的最大优势是再生性[18]。本文选用大孔吸附树脂作为固相吸附剂,建立了一种基于大孔吸附树脂固相萃取柱的前处理方法,用高效液相色谱-二极管阵列检测器检测辣椒油中苏丹红I-IV、苏丹红7B和对位红6种偶氮类染料,对试验条件,如洗脱溶剂,固相萃取柱再生次数,方法的检测限和适用性等进行研究。
1 材料与方法
1.1 仪器与试剂
Waters2695/2998系列高效液相色谱仪、二极管阵列检测器:美国Waters;N-EVAPTM 112型氮吹浓缩仪:美国Organomation公司;12位SPE固相萃取仪:美国Supelco公司。
甲醇、乙腈(色谱纯):上海安谱实验科技股份有限公司;乙酸乙酯、二氯甲烷、环己烷(农残级):迪马科技;甲酸(分析纯):天津巴斯夫化学公司;苏丹红I-IV标准品(纯度均为90%):西格玛–奥德里奇;苏丹红7B(纯度为89%)、对位红(纯度为98%):德国 Dr.Ehrenstorfer公司。6 mL SPE柱管(PP)、筛板(PE):上海安谱实验科技股份有限公司;大孔吸附树脂(LX-68):西安蓝晓科技有限公司。
1.2 色谱条件
Waters Symmetry C18柱(250 mm×4.6mm,5 μm)。流动相:乙腈-0.1%甲酸水溶液,(95∶5,体积比);柱温 30℃,流速 1 mL/min,进样量 10 μL。对位红,苏丹红I、II的检测波长为510 nm;苏丹III、苏丹红7B和苏丹IV的检测波长为480 nm。
1.3 标准曲线
标准贮备液:分别称取苏丹红Ⅰ、苏丹红Ⅱ、苏丹红Ⅲ、苏丹红Ⅳ、苏丹红7B和对位红各10.0 mg(按实际含量折算),用乙酸乙酯溶解后用乙腈分别定容至100 mL,苏丹红Ⅰ、苏丹红Ⅱ、苏丹红Ⅲ、苏丹红Ⅳ、苏丹红7B和对位红的浓度为100 μg/mL。
标准系列:吸取标准储备液 0、5、10、50、100 μL,用乙腈定容至 10 mL,此标准系列浓度为 0、0.05、0.1、0.5、1.0 μg/mL。
1.4 大孔树脂固相萃取柱的制备及再生
3 g的LX-68大孔树脂(相当于1.8 g干树脂)添加到6 mL SPE柱管(底部预先放置一块筛板),上端用微孔筛板固定。
使用过的固相萃取柱用10 mL乙醇去除残留二氯甲烷,然后用10 mL的水除去乙醇。用5 mL 5%盐酸洗涤,用水洗至中性,再用5 mL 5%氢氧化钠洗涤,重新用水洗至中性,固相萃取柱进行再生完成。
1.5 样品预处理
称取0.2g辣椒油于1.5 mL的离心管中,加入1 mL正己烷稀释样品,以备过柱。用5 mL 1%甲酸-甲醇活化固相萃取柱,上样后用4 mL正己烷淋洗,除去油中的脂肪等杂质,用8 mL二氯甲烷洗脱,收集洗脱液并用氮气吹至近干。用0.5 mL乙酸乙酯溶解残渣,经0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤后经HPLC分析。此外,在整个净化过程中,溶剂流速保持在约1 mL/min。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 色谱条件的优化
试验考察了不同流动相对偶氮染料的分离行为,包括甲醇,乙腈和不同比例的乙腈-乙酸水溶液。在相同的检测波长下,染料在乙腈流动相中的峰面积大于甲醇流动相,目标物的保留时间也缩短。当流动相为乙腈-1%甲酸水溶液(95∶5,体积比)时,目标分析物可以达到基线分离。1 μg/mL的6种偶氮染料标准的HPLC色谱图如图1(A)所示。图1(B)为加标辣椒油样品的色谱图。在试验条件下,染料的峰形良好,并且能达到基线分离。
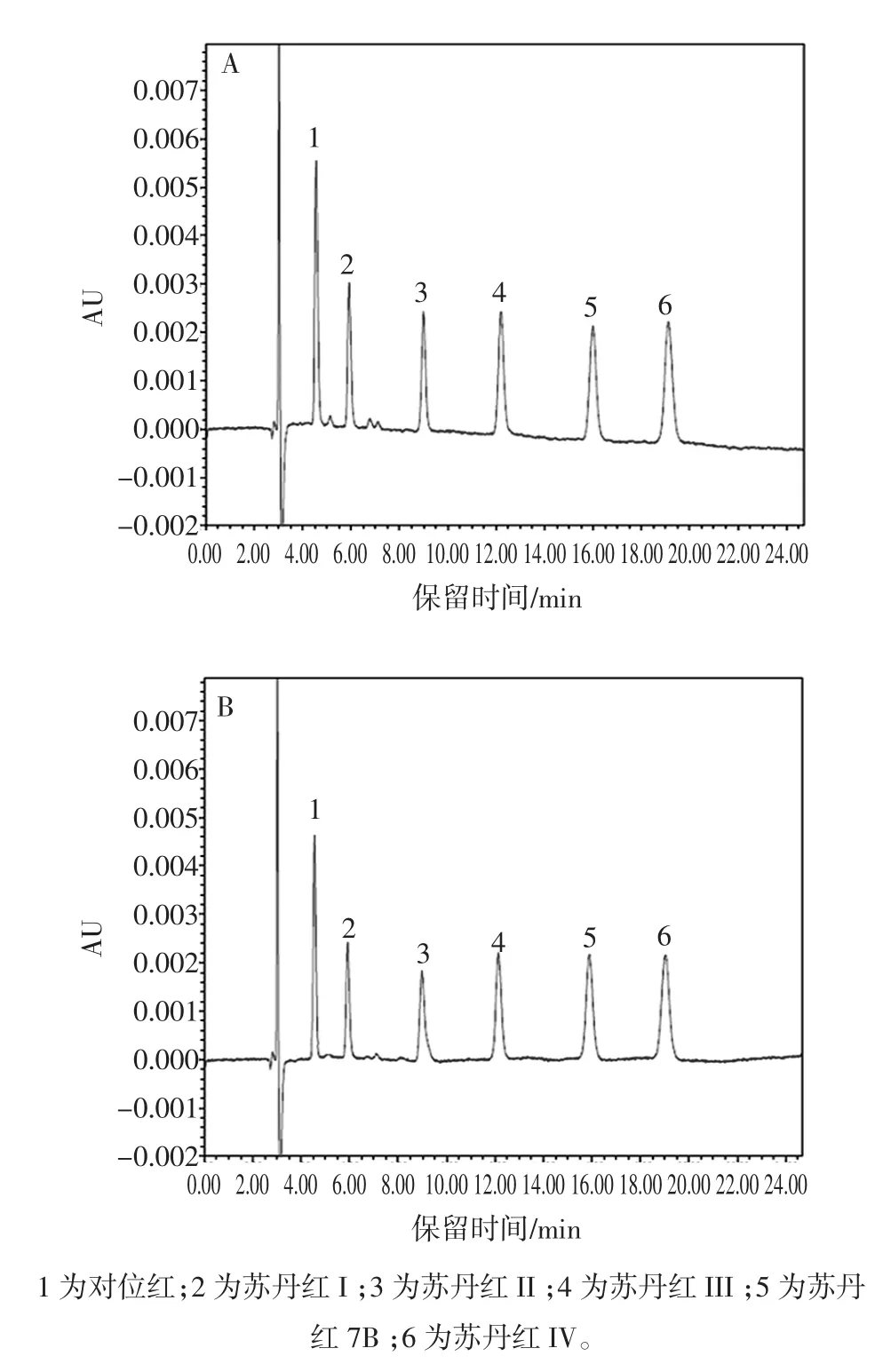
图1 6种偶氮染料的HPLC色谱图1.0 μg/mL(A);加标辣椒油样品的HPLC色谱图(B)Fig.1 HPLC chromatograms of 6 kinds azo dyes standards 1.0 μg/mL(A);Sample spiked with azo dyes standards(B)
2.2 固相萃取条件的优化
试验对LX-68大孔吸附树脂柱的活化溶剂、淋洗溶剂、洗脱溶剂和洗脱溶剂体积等条件进行了优化,用于优化试验的样品为0.4 μg/mL的加标辣椒油样品,样品取样质量为0.2 g。
测定了甲醇、0.5%甲酸-甲醇、1%甲酸-甲醇和2%甲酸-甲醇作为活化溶剂时,大孔吸附树脂柱对6种染料的回收效果,结果见图2。
由图2可知,1%甲酸-甲醇作为淋洗液时偶氮染料的回收率最高。
为了获得可靠、重复性高的结果,除杂是固相萃取中的一个关键因素。样品加到固相萃取柱上以后,需要用合适的溶剂洗涤除去脂肪和极性较小的类胡萝卜素等杂质,这样可以保证得到干净无干扰的色谱图,并且使洗脱液可以氮吹至近干,试验验证了正己烷、乙酸乙酯、甲醇的除杂效果,发现正己烷的除杂效果最好,且不影响偶氮染料的回收率。试验考察不同极性溶剂(甲醇、丙酮、乙腈、二氯甲烷)对偶氮染料的洗脱效果,不同洗脱溶剂对辣椒油样品加标回收率的影响如图3所示。
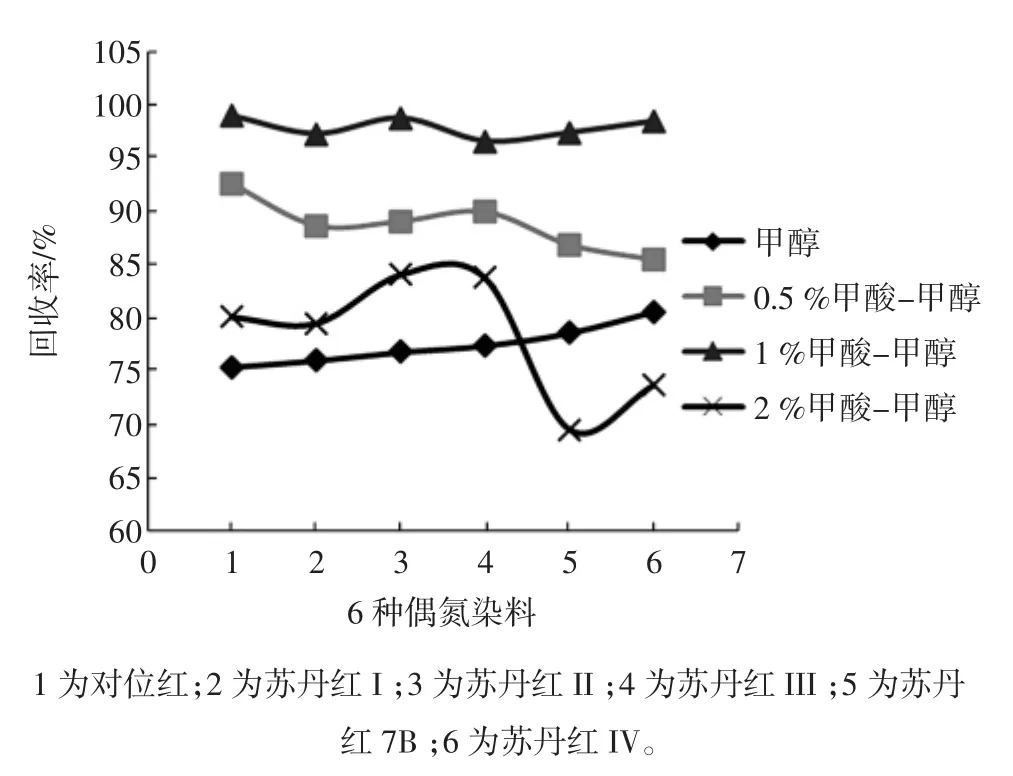
图2 不同活化溶剂对染料回收率的影响Fig.2 Effects of different pre-elution solvents on the recoveries of azo dyes

图3 不同洗脱溶剂对染料回收率的影响Fig.3 Effects of different eluent solvents on the recoveries of azo dyes
图3中试验数据表明二氯甲烷进行回收率比较高,用8 mL二氯甲烷作为洗脱溶剂可以使目标化合物得到满意的回收率。
2.3 回收率、精密度
在最佳试验条件下,6种染料在0.05 μg/mL~1.0 μg/mL浓度范围内线性关系良好,相关系数高于0.999 8,试验数据见表1。定量限(LOQ)以10倍信噪比计算,在0.008 mg/kg~0.023 mg/kg之间(按取样量0.2 g计算),结果一同列于表1中。对辣椒油中6种染料进行高、中、低3个浓度的加标提取试验,加标浓度为0.05、0.25、0.40 mg/kg,用外标法定量。每个加标水平做6组平行试验,次日重复加标样品试验,试验结果列于表2中。在不同的加标浓度下,日内和日间的加标回收率在90.9%~104.3%之间,相对标准偏差(RSD)小于3.7%,用大孔吸附树脂柱萃取辣椒油中偶氮染料方法准确可靠。加标样品的回收率和精密度见表2。

表1 6种偶氮染料的线性范围、线性回归方程和相关系数Table 1 Linear regression parameters of 6 kinds of azodyes
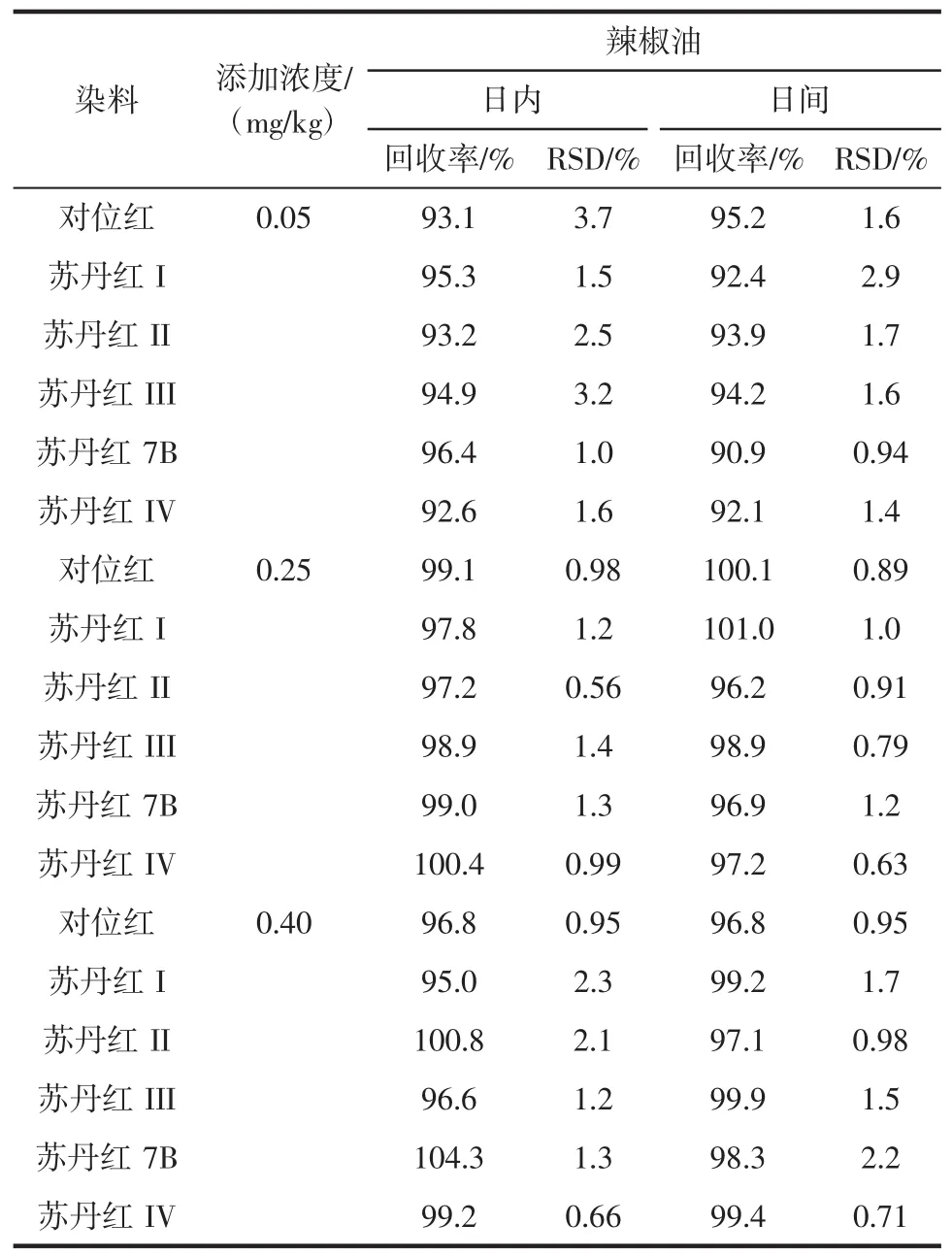
表2 加标样品的回收率和精密度Table 2 Analytical parameters for assessing the feasibility of the method
2.4 大孔吸附树脂柱的再生次数
大孔吸附树脂柱的再生按照1.4的方法,使用加标辣椒油样品(0.40 mg/kg添加水平)检测再生后树脂柱的萃取效果,同时做3个平行试验,再生次数为5次。大孔吸附树脂柱再生后对加标样品中偶氮染料的回收率见图4。
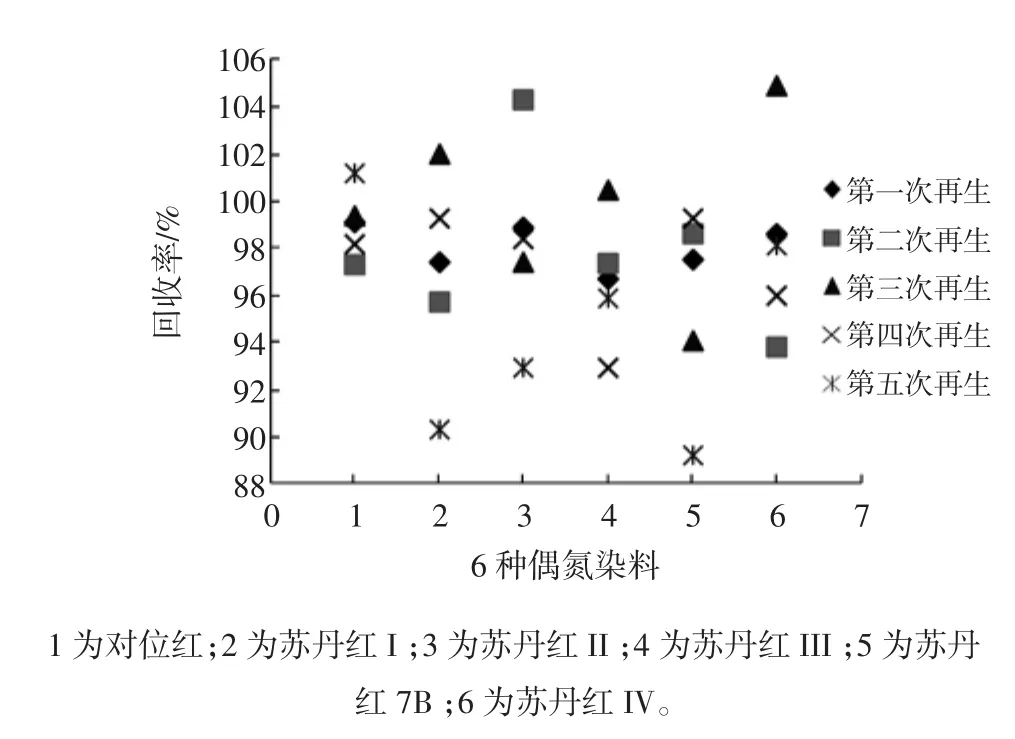
图4 大孔吸附树脂柱再生后对加标样品的萃取效果Fig.4 The extract effectiveness of regeneration macroporous resin for spiking sample
从图4可以看出,再生树脂与新树脂具有相同的吸附、洗脱性能。因此,大孔树脂固相萃取柱可以通过再生步骤重复使用至少5次。
3 结论
将自制的大孔吸附树脂柱成功应用于辣椒油中偶氮染料的检测,提供了一个非常简单,快速,灵敏和环保的前处理方法。辣椒油样品经正己烷稀释,用自制大孔吸附树脂柱净化,用高效液相色谱-二极管阵列检测器检测,外标法定量。结果表明,6种染料在0.05 μg/mL~1.0 μg/mL 浓度范围内线性关系良好,相关系数高于0.999 8,在不同的加标浓度下,日内和日间的加标回收率在90.9%~104.3%之间,相对标准偏差小于3.7%,用大孔吸附树脂柱萃取辣椒油中偶氮染料方法准确可靠。
参考文献:
[1] Ahlström L H,Sparr Eskilsson C,Björklund E.Determination of banned azo dyes in consumer goods[J].TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2005,24(1):49-56
[2] Qi P,Zeng T,Wen Z,et al.Interference-free simultaneous determination of Sudan dyes in chili foods using solid phase extraction coupled with HPLC-DAD[J].Food Chemistry,2011,125(4):1462-1467
[3] Yan H,Wang H,Qiao J,et al.Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography for determination of Sudan dyes in preserved beancurds[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2011,1218(16):2182-2188
[4] Yan H,Gao M,Qiao J.New ionic liquid modified polymeric microspheres for solid-phase extraction of four Sudan dyes in foodstuff samples[J].J Agric Food Chem,2012,60(27):6907-6912
[5] Long C,Mai Z,Yang X,et al.A new liquid-liquid extraction method for determination of 6 azo-dyes in chilli products by high-performanceliquidchromatography[J].Food Chemistry,2011,126(3):1324-1329
[6] Sun S,Wang Y,Yu W,et al.Determination of sudan dyes in red wine and fruit juice using ionic liquid-based liquid-liquid microextraction and high-performance liquid chromatography[J].Journal of Separation Science,2011,34(14):1730-1737
[7] Schummer C,Sassel J,Bonenberger P,et al.Low-level detections of Sudan I,II,III and IV in spices and Chili-containing foodstuffs using UPLC-ESI-MS/MS[J].J Agric Food Chem,2013,61(9):2284-2289
[8] Zhu Y,Zhao B,Xiao R,et al.Simultaneous determination of 14 oilsoluble synthetic dyes in chilli products by high performance liquid chromatography with a gel permeation chromatography clean-up procedure[J].Food Chemistry,2014,145(15):956-962
[9] Oplatowska M,Stevenson Paul J,Schulz C,et al.Development of a simple gel permeation clean-up procedure coupled to a rapid disequilibrium enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA)for the detection of Sudan I dye in spices and sauces[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2011,401(4):1411-1422
[10]Yan H,Qiao J,Pei Y,et al.Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography for determination of Sudan dyes in preserved beancurds[J].Food Chemistry,2012,132(1):649-654
[11]Zhang Z,Xu S.Li J,et al.Selective solid-phase extraction of Sudan I in chilli sauce by single-hole hollow molecularly imprinted polymers[J].J Agric Food Chem,2012,60(1):180-187
[12]Yan H,Qiao J,Wang H,et al.Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction combined with ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquidliquid microextraction for the determination of four Sudan dyes in sausage samples[J].Analyst,2011,136:2629-2634
[13]Hou X,Li Y,Cao S,et al.Analysis of para red and sudan dyes in egg yolk by UPLC-MS-MS[J].Chromatographia,2010,71(1/2):135-138
[14]Enríquez-Gabeiras L,Gallego A,Garcinuño R M,et al.Interference-free determination of illegal dyes in sauces and condiments by matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD)and liquid chromatography(HPLC-DAD)[J].Food Chemistry,2012,135(1):193-198
[15]Liu R,Hei W,He P,et al.Simultaneous determination of fifteen illegal dyes in animal feeds and poultry products by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography B,2011,879(24):2416-2422
[16]Soylak M,Unsal Y E,Yilmaz E,et al.Determination of rhodamine B in soft drink,waste water and lipstick samples after solid phase extraction[J].Food Chem Toxicol,2011,49(8):1796-1799
[17]Yang W,Wang J,Li X,et al.A new method research for determination of natural pigment crocin yellow in foods by solid-phase extraction ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography[J].J Chromatogr A,2011,1218(11):1423-1428
[18]Liu Y,Bai Q,Lou S,et al.Adsorption characteristics of(-)-epigallocatechin gallate and caffeine in the extract of waste tea on macroporous adsorption resins functionalized with chloromethyl,amino,and phenylamino groups[J].J Agric Food Chem,2012,60(6):1555-1566
Determination of Azo Dyes in Chilli Oil by SPE Coupled with HPLC
XING Yan1,GAO Hui1,LIU Yu-dong2,WANG Qin1
(1.Zibo Municipal Center for Disease Control and Prevention,Zibo 255026,Shandong,China;2.Science and Technology Information Research Institute,Zibo 255025,Shandong,China)
An innovative pretreatment method for 6 kinds of azo dyes,such as Sudan I-IV,Sudan 7B,Para red,in chilli oil based on homemade macroporous resin solid-phase extraction(SPE)cartridge was established.The chilli oil samples were diluted by n-hexane and purified by a self-made macroporous resin cartridge,determined by high performance liquid chromatography(HPLC)coupled with diode array detector(DAD).The homemade SPE cartridge simplified the preparation procedure of samples and could be reused by regeneration steps.Results showed that the recoveries of 6 azo dyes added to the chilli products had a good linear in the rang from 0.05 μg/mL-1.0 μg/mL.The correlation coefficients were more than 0.999 8 for all experimental batches.Under three spiking levels,the recovery rates of intra-day and inter-day were ranged from 90.9%to 104.3%,and the relative standard deviations(RSDs)were lower than 3.7%.
azo dyes;chilli oil;solid-phase extraction;HPLC;macroporous resin
2016-07-26
山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2015PH035);山东省医药卫生科技发展计划项目(2013WS0028);浙江省科技厅分析测试项目(2015C37009)
邢燕(1982—),女(汉),主管技师,博士,从事食品、环境中有机污染物检测研究。
10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.13.029
