Th2型γδ T细胞参与急性RSV感染所诱发的气道炎症反应
2017-01-03胡海燕王丹丹戚菲菲刘北星
徐 蕾, 胡海燕, 王丹丹, 戚菲菲, 曾 胜, 刘 静, 刘北星
(中国医科大学基础医学院 免疫学教研室,辽宁 沈阳 110122)
Th2型γδ T细胞参与急性RSV感染所诱发的气道炎症反应
徐 蕾, 胡海燕, 王丹丹, 戚菲菲, 曾 胜, 刘 静, 刘北星*
(中国医科大学基础医学院 免疫学教研室,辽宁 沈阳 110122)
γδ T细胞是机体重要的固有免疫细胞,参与肺组织炎性病变及哮喘的发生发展。但迄今为止,γδ T细胞在呼吸道合胞病毒感染所诱发的气道炎症反应中的作用尚不十分清楚。研究通过建立RSV急性感染的实验动物模型,采用HE染色、Real-timeRT-PCR、流式细胞术等实验方法,旨在揭示γδT细胞在感染性气道炎症发生中的作用及其相关作用机制。结果显示,RSV感染导致BALA/c鼠肺炎性细胞浸润,其中嗜酸性粒细胞增加明显;同时肺组织局部Th2型细胞因子IL-4、IL-13 mRNA表达升高;RSV感染后,肺组织γδT细胞总数,特别是活化的CD69+γδT细胞数量显著增加,其中分泌Th2型细胞因子IL-4和IL-13的γδT细胞数量增加明显,而分泌Th1型细胞因子IFN-γ的γδT细胞数量显著减少,证实γδ T细胞通过分泌Th2型细胞因子介导RSV感染诱发的气道炎症反应。
γδ T细胞;呼吸道合胞病毒;气道炎症;哮喘
哮喘是以Th2优势应答为主的,以气道炎症和气道高反应性为主要特征的呼吸道疾病[1-2]。诸多因素影响哮喘的发生发展,其中病毒感染尤其是呼吸道合胞病毒感染是诱发和加重哮喘的主要原因[3]。呼吸道合胞病毒(respiratory syncytial virus, RSV)是秋冬季节引起婴幼儿毛细支气管炎和肺炎的主要病原体。研究发现,婴幼儿期严重RSV感染与儿童期哮喘及过敏症密切相关[4]。RSV毛细支气管炎患儿外周血中Th2型细胞因子如IL-4以及总IgE水平明显升高, 而Th1型细胞因子IFN-γ水平有所下降,提示RSV感染可能通过诱导Th2优势应答影响哮喘的发生发展[5]。广泛分布于皮肤黏膜系统的γδ T细胞是机体重要的固有免疫细胞之一。呼吸道黏膜系统的γδT细胞位于免疫防御的第一道防线,在呼吸道黏膜局部抗感染免疫及免疫调节方面发挥重要作用。γδT细胞作为效应细胞和调节细胞影响感染及过敏性炎症反应的发生过程[6]。Aoyagi等[7]发现RSV严重毛细支气管炎患儿外周血中IFN-γ分泌型γδT细胞数量明显减少,并伴随感染早期Th2型细胞因子水平的上升。我们前期研究工作亦发现,致敏前RSV感染明显降低致敏鼠肺组织γδT细胞数量,降低肺组织Th2型细胞因子水平,提示γδT细胞可能在肺组织炎性病变及喘息发作方面发挥重要作用[8]。为进一步明确RSV感染所诱发的气道炎症反应过程中γδ T细胞的作用, 本研究利用RSV急性感染BALB/c鼠模型,通过HE染色、Real-time RT-PCR、流式细胞术等实验技术,探讨在RSV感染导致BALB/c鼠气道炎症的发展过程中,γδT细胞可能作为效应细胞和调节细胞发挥重要作用。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 实验动物 6~8周龄雌性BALB/c鼠,购自北京华阜康生物科技股份有限公司,在中国医科大学实验动物中心SPF级动物饲养室内常规饲养。
1.1.2 病毒 人类呼吸道合胞病毒A2 型(RSV A2),Hep-2细胞增殖病毒,30%蔗糖超速离心法分离病毒粒子,-80 ℃冰箱保存。病毒滴度用组织细胞半数感染量50% (50% tissue culture infections dose, TCID50)表示。
1.1.3 试剂 RNA提取试剂盒、逆转录试剂盒和荧光实时定量PCR试剂盒购自TAKARA公司。小鼠流式检测抗体FITC-anti-TCRγδmAb、APC-anti-CD3 mAb、PEcy7-anti-CD69 mAb及PE标记的细胞因子抗体(IFN-γ、IL-4、IL-13)购自Biolenged公司。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 RSV感染 小鼠给予水合氯醛麻醉后,经鼻黏膜感染20 μL含2×106TCID50RSV的病毒悬液,感染后第4天收集实验标本,进行相关检测。
1.2.2 肺组织病理标本制作及染色 感染后第4天的小鼠肺组织浸泡于4%多聚甲醛中固定,随后经过石蜡包埋、切片后进行HE染色分析小鼠肺组织炎症反应。
1.2.3 Real-timeRT-PCR技术检测细胞因子mRNA的表达 用RNAisoplus试剂盒提取细胞总RNA,PrimeScriptTM逆转录试剂盒合成cDNA。按照SYBR Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ试剂盒说明,采用Real-time RT-PCR技术检测肺组织局部Th1型细胞因子IFN-γ和Th2型细胞因子IL-4、IL-13的mRNA表达水平。引物设计:IFN-γ-F,5′-TATCTGGAGGAACTGGCAAA-3′, IFN-γ-R, 5′-GGTGTGATTCAATGACGCTT-3′;IL-13-F, 5′-AGCATGGTATGGAGTGTGGA-3′, IL-13-R,5′-TTGCAATTGGAGATGTTGGT-3′;IL-4-F, 5′-TGTACCAGGAGCCATATCCA-3′,IL-4-R,5′-TTCTTCGTTGCTGTGAGGAC-3′;β-actin-F, 5′-CAACGAGCGGTTCCGATG-3′, β-actin-R, 5′-GCCACAGGATTCCATACCCA-3′。在ABI 7500系统下进行实时荧光定量PCR扩增。结果采用2-ΔΔCT(fold change)进行统计分析。
1.2.4 小鼠肺组织单细胞悬液制备 取小鼠肺组织并剪碎,用10 mL含有collagenaseD (200 μg/mL)和DNAseⅠ(40 μg/mL)的10%FBSvRPMI1640重悬组织块,在37 ℃水平摇床上孵育90 min。300目钢网过滤经酶消化后的肺组织,收集细胞悬液并用淋巴细胞分离液分离,RPMI1640调整细胞浓度至1×106/mL用于荧光抗体染色。
1.2.5 流式细胞术检测细胞表面分子 向细胞悬液中加入封闭抗体CD16/CD32(ebioscience),4 ℃避光孵育15 min;2%FBS-PBS洗涤1次后进行表面染色,加入FITC-anti-TCRγδmAb、APC-anti-CD3mAb及PEcy7-anti-CD69 mAb(Biolenged),4 ℃避光孵育30 min;2%FBS-PBS洗涤1次,300 μL 2%FBS-PBS重悬细胞,上机检测。
1.2.6 流式细胞术检测细胞内细胞因子 细胞经表面染色后,2%FBS-PBS洗涤1次;向细胞悬液中加入2 μL/mL的Cell Activation Cocktail(Biolenged)37 ℃温箱孵育1 h后,加入2 μmol/L蛋白转运抑制剂(Monensin),继续孵育4 h;2%FBS-PBS洗涤2次,加入250 μL Fixation and Permeabilization Solution(BD),4 ℃避光孵育20 min;Perm/Wash Buffer(BD)和2%FBS-PBS洗涤后,加入PE标记的细胞因子抗体(IFN-γ、IL-4、IL-13)或同种型抗体,4 ℃避光孵育30 min;2% FBS-PBS洗涤2次, 300 μL 2%
FBS-PBS重悬细胞,上机检测。
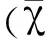
2 结果与分析
2.1 RSV感染诱发BALB/c鼠急性气道炎症
用RSV经鼻感染BALB/c鼠,感染后第4天取肺组织,HE染色发现,与正常对照组相比,RSV感染鼠肺组织细支气管周围明显出现炎性细胞浸润(图1)。肺泡灌洗液中炎性细胞总数明显增加,其中以嗜酸性粒细胞、淋巴细胞及中性粒细胞数量增加尤为显著(图2),提示经鼻感染RSV可诱导BALB/c鼠气道炎症应答。
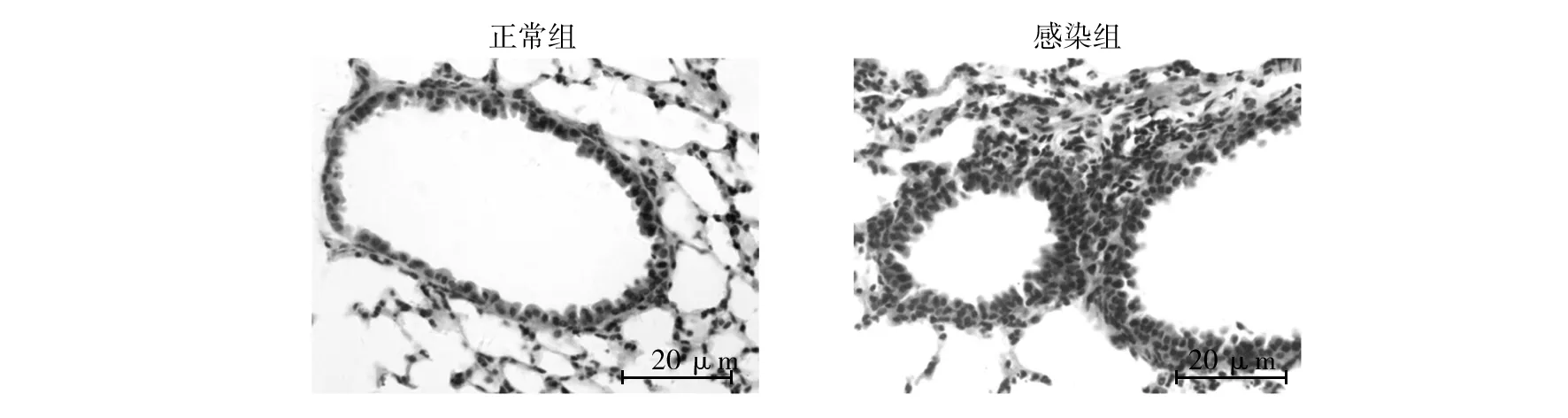
图1 RSV感染导致BALB/c小鼠肺组织内炎性细胞浸润Fig.1 Infection with RSV resulted in a massive inflammation in the lungs of BALB/c mice
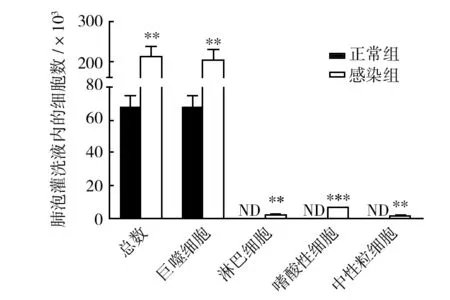
图2 RSV感染对BALB/c小鼠肺泡灌洗液 中炎性细胞数量的影响Fig.2 Infection with RSV influence the number of inflammatory cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of BALB/c mice *P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,下图同 *P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,the following figure with
2.2 RSV感染增强BALB/c鼠肺组织局部Th2型细胞因子mRNA表达
Real-timeRT-PCR技术检测小鼠肺组织Th1/Th2型细胞因子mRNA表达。结果发现RSV感染不仅能增强肺组织局部Th2型细胞因子IL-4、IL-13 mRNA的表达,Th1型细胞因子IFN-γ水平与对照组相比亦有所升高。推测本研究中升高的干扰素可能参与机体对RSV病毒的抑制和清除,介导机体的抗感染免疫(图3)。
2.3 RSV感染增加小鼠肺组织局部γδ T细胞总数及活化的γδ T细胞数量
在对RSV感染与过敏性哮喘相关性的研究中发现,致敏前感染RSV可能通过影响γδ T细胞的活性,进而影响哮喘的发展进程[8]。为进一步证实RSV感染对肺组织局部γδ T细胞的影响,分离了小鼠肺组织淋巴细胞,利用流式细胞术分析小鼠肺组织γδ T细胞总数及其活化的γδ T细胞数量。结果显示,RSV感染导致肺组织局部γδ T细胞总数以及活化γδ T细胞(细胞表面标记为CD69+γδ T细胞)的百分比和细胞数均明显增加,提示RSV感染通过影响γδ T细胞的数量和活性左右气道炎症反应的发生发展(图4)。
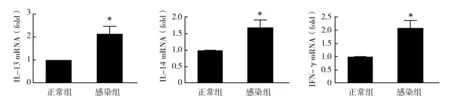
图3 RSV感染影响BALB/c鼠肺组织局部细胞因子mRNA表达Fig.3 Infection with RSV influence the expression of cytokine mRNA in the lungs of BALB/c mice
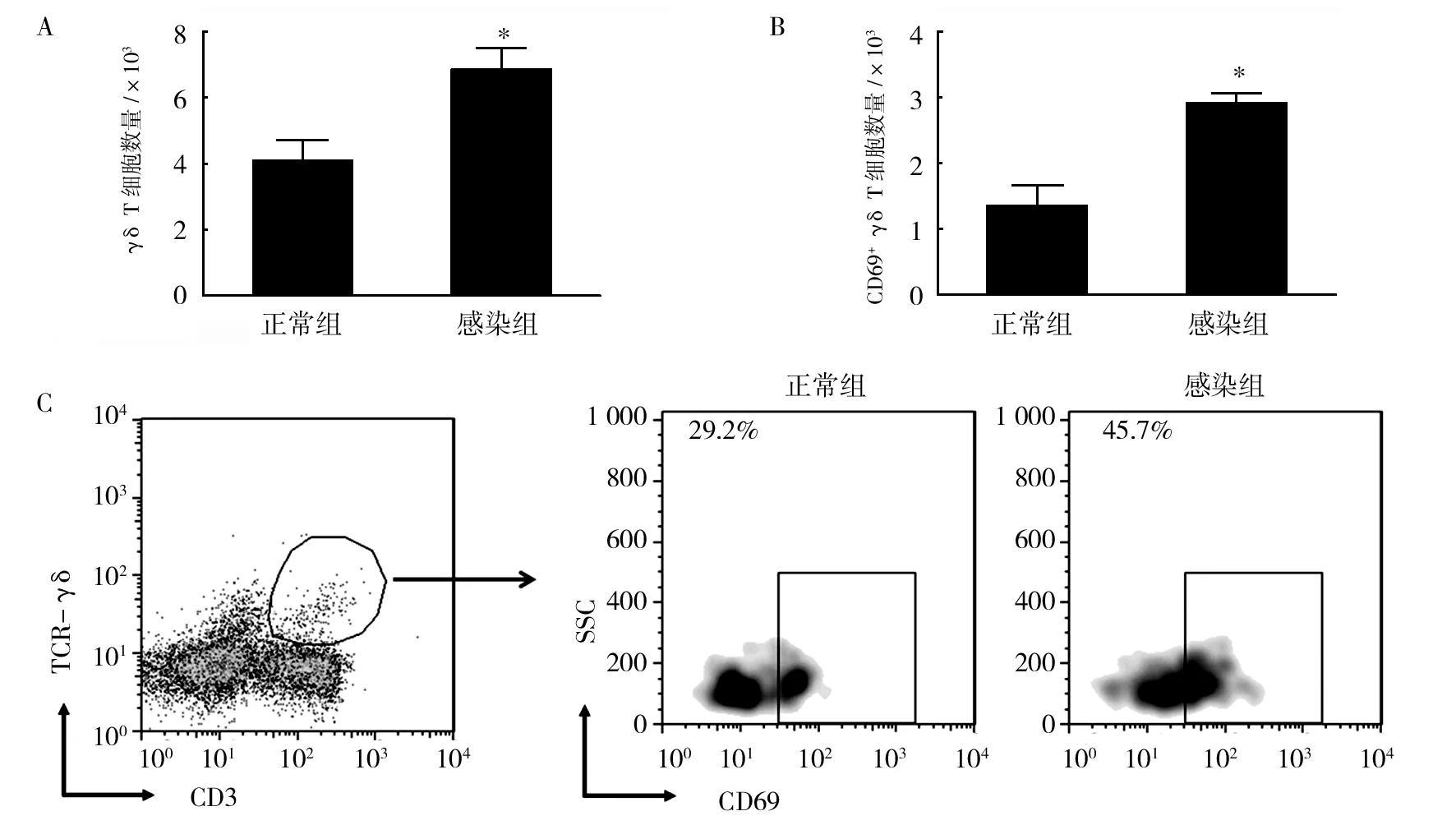
图4 RSV感染增加小鼠肺细胞中γδ T细胞总数及活化γδ T细胞数量Fig.4 RSV infection increased the number of γδ T cells as well as CD69+ γδ T cells in the lungs of miceA:肺组织γδ T细胞总数;B:肺组织CD69+ γδ T细胞数量;C:肺组织CD69+ γδ T细胞流式散点图A:γδ T cellsin the lungs; B:CD69+ γδ T cellsin the lungs;C:representative flow cytometry plots for CD69+ γδ T cells
2.4 RSV感染增加小鼠肺组织内Th2型γδ T细胞数量
流式细胞术检测细胞内细胞因子,分析小鼠肺组织局部Th1/Th2型γδ T细胞数量。结果发现,分泌Th2型细胞因子的γδ T细胞,如IL-13+γδ T细胞、IL-4+γδ T细胞数量在感染后明显增加。然而,分泌Th1型细胞因子的γδ T细胞,如IFN-γ+γδ T细胞数量却显著降低(图5)。Th2型细胞因子IL-4与IL-5可以协同诱导嗜酸性细胞的活化与分化,增加血清中IgE含量,诱发实验鼠气道炎症,导致Th2样反应[9-10]。结果显示,分泌Th2型细胞因子的γδ T细胞在RSV感染诱发的气道炎症中发挥重要作用。
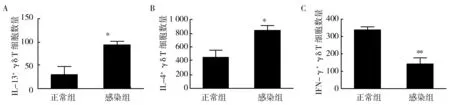
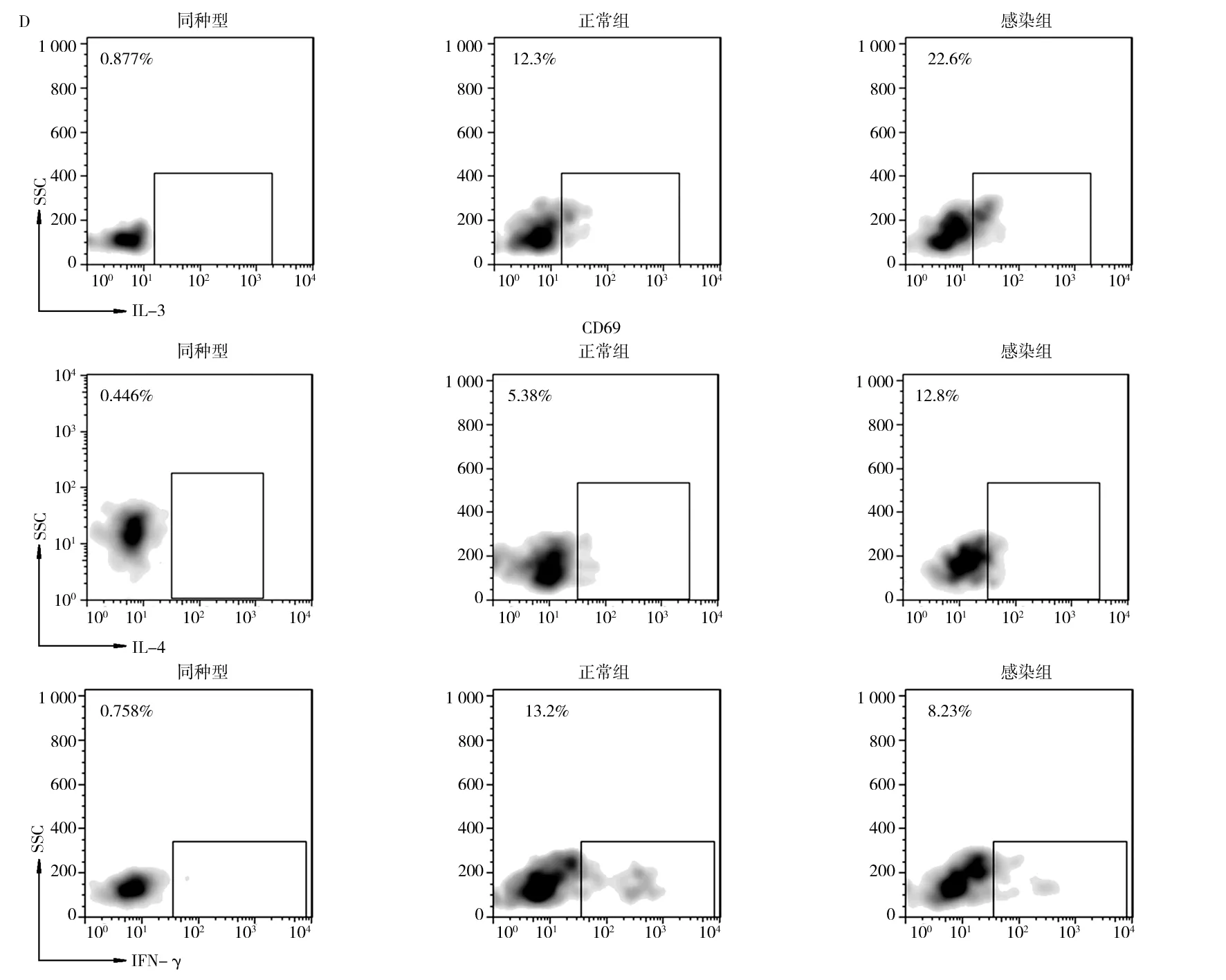
图5 RSV感染影响小鼠肺组织局部Th1/Th2型γδ T细胞数量Fig.5 Infection with RSV influence the number ofTh1/Th2-associated γδ T cells in the lungs of miceA:肺组织IL-13+ γδ T细胞数量;B:肺组织IL-4+ γδ T细胞数量;C:肺组织IFN-γ+ γδ T细胞数量;D:分泌IL-4、IL-13和IFN-γ的γδT细胞的流式散点图A:IL-13+ γδ T cells in the lungs; B:IL-4+ γδ T cells in the lungs;C:IFN-γ+ γδ T cells in the lungs;D:representative flow cytometry plots demonstrating IL-13、IL-4 and IFN-γ expression by γδ T cells
3 讨 论
过敏性哮喘是与Th2型免疫应答密切相关的气道炎症性病变,表现为嗜酸性粒细胞肺组织浸润,Thl/Th2型细胞因子比例失衡和气道高反应性等[11]。病毒感染影响过敏原致敏及哮喘的发生。引起婴幼儿毛细支气管炎和肺炎的主要病原体呼吸道合胞病毒,可导致感染患儿出现喘鸣,气道堵塞等哮喘样临床病症,故RSV感染与支气管哮喘相关性研究受到普遍重视。大量的研究证实RSV感染与Th1和Th2细胞分泌的细胞因子比例失衡有关。有研究显示,RSV感染时外周血Th2细胞亚群增加,伴随IL-4水平轻微增加;IL-5和IL-10水平明显增高,而Th1细胞亚群及IFN-γ显著下降[5,12]。
作为固有免疫细胞,γδ T细胞是影响机体Thl/Th2均衡性的重要因素之一。γδ T细胞在接受抗原刺激后,可以分泌多种细胞因子,包括Th1型细胞因子IL-2和IFN-γ;Th2型细胞因子IL-4、IL-5和IL-13[13-14]。在抗感染免疫的初次应答中,γδ T细胞可因抗原性质的不同而分泌不同类型的细胞因子,进而调控免疫应答的类型。流式细胞术分析证实过敏性哮喘患者痰细胞中γδ T细胞比例明显升高,并表达高水平的细胞因子IL-4和IL-10[15]。有研究表明,去除γδ T细胞的哮喘模型鼠肺泡灌洗液中Th2型细胞因子IL-13水平下降,IL-10水平明显升高,气道反应性亦明显下降[16],提示γδ T细胞在气道变态炎症反应过程中不可忽视的生物学作用。我们研究结果显示,RSV感染鼠支气管周围炎性细胞浸润增加,尤其是嗜酸性粒细胞,并伴随肺组织γδ T细胞总数及CD69+γδ T细胞增加。流式细胞术检测细胞内细胞因子,其中IL-4、IL-13分泌型γδ T细胞数量显著增加,同时IFN-γ分泌型γδ T细胞数量明显减少,提示γδ T细胞通过分泌Th2型细胞因子参与RSV感染诱发的气道炎症反应。
本研究利用Real-time RT-PCR、流式细胞术等实验技术,证实RSV感染过程中,分泌Th2型细胞因子的γδ T细胞水平明显增高,提示某些固有免疫细胞可能在RSV感染诱发的气道炎症应答中发挥重要作用。
[1] Savelkoul HF, NeijensHJ.Immune responses during allergic sensitization and the development of atopy[J].Allergy,2000,55(11):989-997.
[2] Ma L, Zeng J, Mo B, et al.ANP/NPRA signaling preferentially mediates Th2 responses in favor of pathological processes during the course of acute allergic asthma[J].Int J ClinExp Med,2015,8(4):5121-5128.
[3] Schwarze J, GelfandEW.Respiratory viral infections as promoters of allergic sensitization and asthma in animal models[J].Eur. Respir J,2002,19:341-349.
[4] Backman K, Piippo-Savolainen E, Ollikainen H, et al.Adults face increased asthma risk after infant RSV bronchiolitis and reduced respiratory health-related quality of life after RSV pneumonia[J].Acta Paediatr,2014,103(8):850-855.
[5] Bendelja K, Gagro A, Bace A, et al.Predominant type-2 response in infants with respiratory syncytial virus(RSV)infection demonstrated by cytokine flow cytometry[J].ClinExp Immunol,2000,121(2):332-338.
[6] Cook L, Miyahara N, Jin N, et al.Evidence that CD8+dendritic cells enable the development of gammadelta T cells that modulate airway hyperresponsiveness[J].J Immunol,2008,181(1):309-319.
[7] Aoyagi M, Shimojo N, Sekine K, et al.Respiratory syncytial virus infection suppresses IFN-gamma production of gammadelta T cells[J]. ClinExpImmunol,2003,131(2):312-317.
[8] Liu B, Kimura Y.Respiratory syncytial virus protects against the subsequent development of Japanese cedar pollen-induced allergic responses[J].J Med Virol,2007,79(10):1600-1605.
[9] Psarras S, Papadopoulos NG, Johnston SL.Pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis-related wheezing[J].PaediatrRespir Rev,2004,5 SupplA:S179-184.
[10]Maggi E, Biswas P, Del Prete G, et al.Accumulation of Th-2-like helper T cells in the conjunctiva of patients withvernal conjunctivitis[J]. J Immuno,1991,146(4):1169-1174.
[11]Cakir M, Akcay S, Karakas T, et al.Prevalence of atopy in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus, hepatitis B virus carriers, and healthy children: role of T helper 1 (Th1)-type immune response[J].Allergy Asthma Proc,2008,29(2):166-170.
[12]Panuska JR, Merolla R, Rebert NA , et al.Respiratory syncytial virus induces interleukin-10 by human alveolar macrophages. Suppression of early cytokine production and implications for incomplete immunity[J].J Clin Invest,1995,96(5):2445-2453.
[13]Krug N, Erpenbeck VJ, Balke K, et al.Cytokine profile of bronchoalveolar lavage-derived CD4(+), CD8(+), and gammadelta T cells in people with asthma after segmental allergen challenge[J].Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol,2001,25(1):125-131.
[14]Kim K, Han J, Lee TR, et al.Comparative Analysis of Human Epidermal and Peripheral Blood γδ T Cell Cytokine Profiles[J].Ann Dermatol,2014,26(3):308-313.
[15]Hamzaoui A, Kahan A, Ayed K, et al. T cells expressing the gammadelta receptor are essential for Th2-mediated inflammation in patients with acute exacerbation of asthma[J].Mediators Inflamm,2002,11(2):113-119.
[16]Hahn YS, Taube C, Jin N, et al.Different potentials of gamma delta T cell subsets in regulating airway responsiveness: V gamma 1+cells, but not V gamma 4+cells, promote airway hyperreactivity, Th2 cytokines, and airway inflammation[J].J Immunol,2004,172(5):2894-2902.
Airway Inflammation Reaction Induced by Acute Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection Participated with Th2-γδ T Cells
XU Lei, HU Hai-yan, WANG Dan-dan, QI Fei-fei, ZENG Sheng, LIU Jing, LIU Bei-xing
(Teach. &Res.Div.ofImmunol.,Schl.ofBasicMed.Sci.,ChinaMed.Uni.,Shenyang110122)
γδ T cells are important innate immune cells in organism, they participate pulmonary inflammatory pathology and the occurrence and development of asthma. However, the effect of γδ T cells on respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)-induced airway inflammation remains unknown so far. In present study, through the establishment of an experimental animal model with acute RSV infection and the adoption of HE staining, RT-PCR, as well as flow cytometry and other methods were used aiming at the revealing the role of γδ T cells in the infective airway inflammation and related effective mechanism. The results showed that RSV infection caused BALA/c mice pneumonic cells infiltration, of them acidophilic granulocyte significantly increased; at the same time the expression of local Th2 cytokine IL-4, IL-13mRNA of pulmonary tissue raised; after RSV infection, total number of γδ T cells of pulmonary tissue, particularly the amount of the activated CD69+γδ T cells obviously increased, of them the amount of γδ T cells that secrete Th2 cytokine IL-4 and IL-13 increased significantly, however, the amount of γδ T cells that secrete Th1 cytokine IFN-γ decreased significantly, and proved that γδ T cells mediately induced RSV to infect the airway inflammation reaction through the secretion of Th2 cytokine.
γδ T cells; respiratory syncytial virus (RSV); airway inflammation; asthma
国家自然科学基金面上项目(81273239/H1005)
徐蕾 女,硕士研究生。主要从事病毒与哮喘研究。E-mail:xuleispace@126.com
* 通讯作者。女,教授,博士生导师。主要从事病毒与哮喘方面的研究。E-mail:bxliu@mail.cmu.edu.cn
2015-09-10;
2015-11-16
Q939.93;R392
A
1005-7021(2016)05-0032-06
10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2016.05.006
