脂多糖刺激脐带间充质干细胞上调IL-1Ra分泌的研究*
2015-12-06范文跃
李 敏,胡 松,王 兰,范文跃
1.成都医学院 基础医学院(成都 610500);2.成都医学院 生物医学系(成都 610500)
间充质干细胞(mesenchymal stem cells,MSCs)是来源于中胚层的多能干细胞,具有自我更新和多向分化能力,可向三胚层细胞分化,如骨细胞、神经元细胞、心肌细胞、脂肪细胞和胰腺细胞等[1-5]。骨髓、脐带、脂肪组织、牙组织、羊水、外周血、和鼻甲[6-12]等机体组织均可分离培养出 MSCs。其中,以骨髓来源的MSCs最具代表性,但其培养到第6代后增殖能力减弱;而脐带华通胶来源的脐带MSCs(umbilical cord MSCs,UC-MSCs)自我更新及增殖能力均很强[13]。MSCs强表达CD13、CD29、CD105和 CD44,弱表达 CD106,不表达 CD14、CD34、CD11a、CD31、CD45与 HLAⅡ抗原,不表达或低表达HLAⅠ抗原。MSCs具有低免疫原性和免疫抑制特性,可抑制T细胞与B细胞增殖[14-15],抑制树突状细胞与自然杀伤细胞的免疫功能[16-17]。白介素1受体拮抗剂(interleukin-1receptor antagonist,IL-1Ra)是首个被发现天然存在的细胞因子拮抗剂,竞争性结合于IL-1受体后不引起IL-1生物学效应,从而起到抗炎作用[18]。IL-1Ra和MSCs都具有抑制炎症的作用,其共移植可改善临床疾病的治疗效果[19]。Toll样受体(Toll-like Receptors,TLRs)是参与固有免疫的一类重要蛋白质分子,也是连接固有免疫和适应性免疫的桥梁,其能特异识别病原相关分子模式。当微生物突破机体的物理屏障时,TLRs可识别相应的配体来激活机体产生免疫应答。脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide,LPS)是TLR4的特异性配体,LPS激活TLR4,可刺激免疫细胞分泌Ⅰ型IFNs和促炎因子,如TNF-α、IL-1β和IL-6。UC-MSCs高表达 TLR4[20]。
为探讨 MSCs的免疫机制,本研究选择UCMSCs,以IL-6为实验的阳性对照[21-22],采用 LPS激活TLR4,观察UC-MSCs对IL-1Ra分泌的影响,以期更深入地了解UC-MSCs免疫抑制功能与细胞因子分泌的关系。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试剂
胎牛血清(Millipore,USA);L-DMEM 培养基(HyClone,美国);LPS(Peprotech,美国);IL-1Ra和IL-6试剂盒(上海泛科实业有限公司,中国);胰蛋白酶(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司,中国);抗人单 克 隆 抗 体 CD14-PE、CD34-FITC、CD29-PE 和CD105-APC及其同型对照(eBiocsience,美国);引物合成(上海生工生物工程技术服务有限公司,中国);Trizol细胞裂解液和逆转录试剂盒(Takara,日本),EvaGreen Dye(Bio-Rad,美国)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 UC-MSCs原代培养 采用组织块法分离培养UC-MSCs:取新鲜脐带(来源于成都医学院第一附属医院产科,均取得产妇同意)置于培养皿中,用PBS冲去脐带外围血块,撕去外膜,拔掉2根动脉,沿静脉剪开,用眼科镊拨离静脉,剩余为华通胶。PBS冲洗掉剩余脐带组织上的血液,将其剪为约2mm2的组织块,装入T75塑料培养瓶内,加入5mL培养基,48h后加入3mL培养基,每3d换液并镜下观察。
1.2.2 流式细胞术检测UC-MSCs表面标志物 取胰蛋白酶消化UC-MSCs,1000rpm离心5min,以5×104个/管分装于1.5mL离心管中,分别加入抗人单克隆抗体 CD14-PE、CD34-FITC、CD29-PE和CD105-APC及其同型对照,流式细胞仪检测。
1.2.3 分组 设立实验组和对照组,分别以1、10、20μg/mL LPS刺激 UC-MSCs为实验组,未刺激UC-MSCs为对照组;采用1ug/mL LPS分别刺激UC-MSCs 3、8、24h为实验组,未刺激UC-MSCs为对照组。
1.2.4 qPCR法检测IL-1Ra和IL-6基因的表达
Trizol细胞裂解液裂解细胞并提取RNA,按照Takara试剂盒说明书逆转录成cDNA。引物信息如下(表1),设置GAPDH为内参基因,采用qPCR法检测IL-1Ra和IL-6的基因表达。10uL qPCR反应体系:cDNA 1μL,Primer 1μL,EvaGreen Dye 5μL,H2O 3μL。反应条件:95℃3min,1个循环;95℃5s,60℃10s(IL-1Ra 57℃),72℃15s,40个循环;72℃60s,1个循环。Bio-Rad qPCR仪检测。
1.2.5 ELISA法检测IL-1Ra和IL-6蛋白质的分泌 收集LPS不同剂量与时间刺激的细胞上清,未刺激的UC-MSCs上清为空白对照组。按照IL-1Ra和IL-6ELISA试剂盒说明书操作,检测各组上清中IL-1Ra和IL-6蛋白质分泌量。酶标仪测定其吸光度值,绘制标准曲线,并计算各样品的浓度值。
1.3 统计学方法
采用GraphPad Prism 5软件对所有数据进行分析,两两比较采用单因素方差分析Dunnett-t检验,结果以均数±标准差(±s)进行描述,检验水准α设定为0.05。
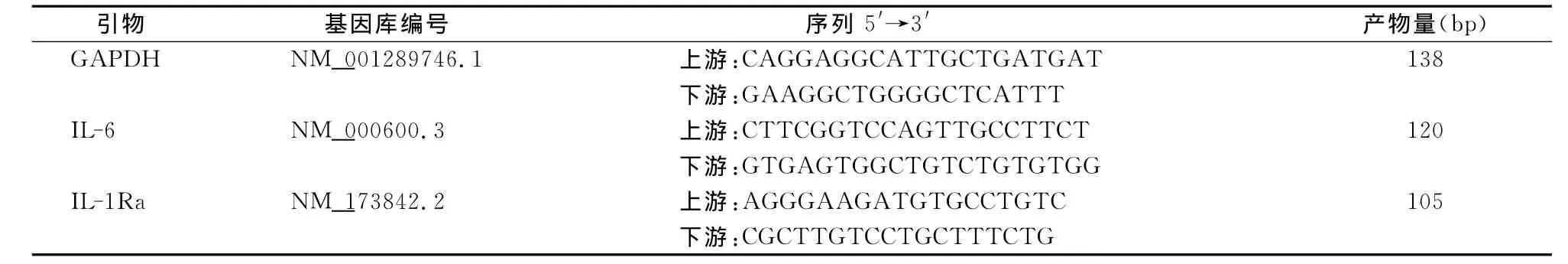
表1 qPCR引物信息
2 结果
2.1 原代培养及鉴定
采用脐带组织块贴壁法原代培养第7~10天,可见组织边缘有贴壁细胞,呈长梭形(图1)。流式细胞术检测UC-MSCs的标志性表面抗原,结果显示:UC-MSCs表达CD29和CD105,不表达CD14与CD34(图2)。根据其形状与流式细胞术结果,分离培养的细胞符合UC-MSCs的生物学特性。
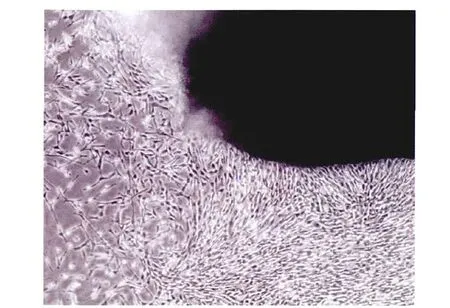
图1 UC-MSCs原代细胞培养13d(40×)
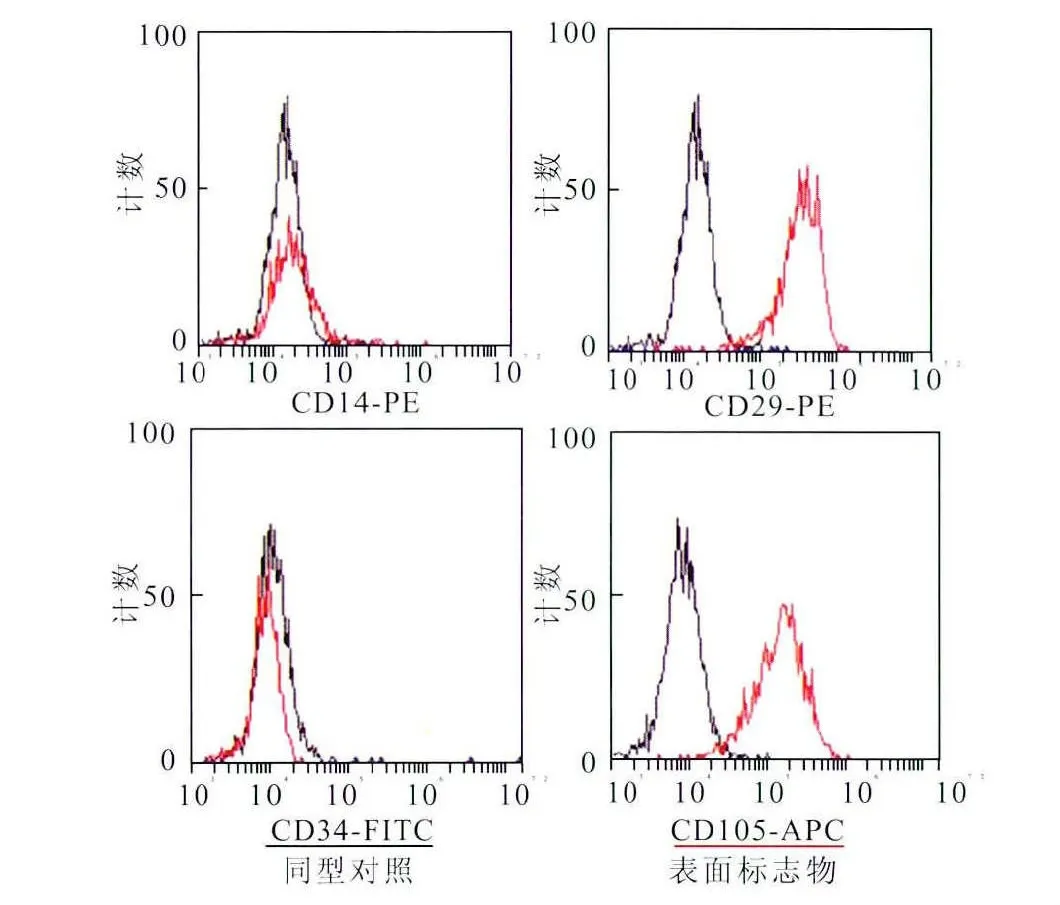
图2 流式细胞术检测UC-MSCs表面标志物
2.2 LPS激活TLR4对 UC-MSCs分泌IL-1Ra和IL-6的影响
qPCR法及ELISA法检测LPS不同剂量(1、10、20μg/mL)刺激 UC-MSCs 24h后IL-1Ra和IL-6的分泌。1μg/mL和10μg/mL实验组较对照组IL-1Ra基因表达均增加,20μg/mL实验组较对照组IL-1Ra基因表达下降;1μg/mL实验组与对照组比较,IL-1Ra基因表达差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(图3A),而10μg/mL实验组与对照组比较,IL-1Ra基因表达差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。1μg/mL和10μg/mL实验组较对照组IL-6基因均表达增加,其差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(图3B);20μg/mL实验组IL-6基因较对照组表达下降。1μg/mL和10μg/mL实验组较对照组IL-1Ra蛋白质分泌增加,20μg/mL实验组较对照组IL-1Ra蛋白质分泌下降;1μg/mL实验组与对照组比较,IL-1Ra蛋白质分泌差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)(图3C);而10μg/mL实验组与对照组比较,IL-1Ra蛋白质分泌差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。LPS 1μg/mL、10μg/mL和20μg/mL实验组较对照组IL-6蛋白质分泌均增加,其差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)(图3D)。
qPCR法及ELISA法检测LPS在3、8、24h刺激 UC-MSCs后IL-1Ra和IL-6表达为:3h、8h和24h实验组较对照组IL-1Ra基因表达增加,3h、8h实验组与对照组比较IL-1Ra基因表达差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)(图4A),而24h实验组与对照组比较IL-1Ra基因表达差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。3h、8h和24h实验组较对照组IL-6基因表达均增加,3h实验组较对照组比较,IL-6基因表达差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)(图4B);8h和24h实验组与对照组比较IL-6基因表达差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。3h、8h和24h实验组较对照组IL-1Ra蛋白质分泌增加,24h实验组与对照组比较IL-1Ra蛋白质分泌差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)(图4C),而3h、8h实验组与对照组比较,IL-1Ra蛋白质分泌差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。3h、8h和24h实验组较对照组IL-6蛋白质分泌均增加,其差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)(图4D)。
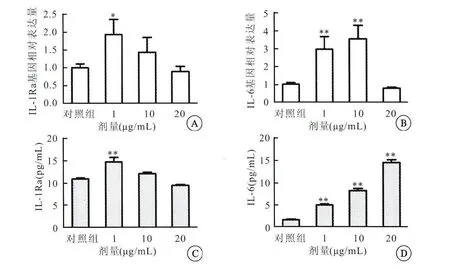
图3 LPS不同剂量刺激UC-MSCs后IL-1Ra和IL-6基因与蛋白质水平比较
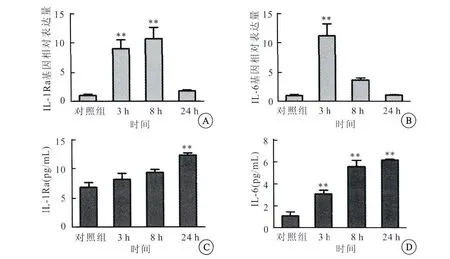
图4 LPS不同时间刺激UC-MSCs后IL-1Ra和IL-6基因与蛋白质分泌比较
3 讨论
IL-1Ra对很多炎症性疾病起到广谱抗炎作用,且可抑制移植排斥反应的发生与发展[23],协同MSCs的免疫抑制作用。IL-1Ra与 MSCs联合移植,可显著改善由氨基半乳糖诱导猪急性肝衰竭的肝功能,促进肝组织再生[19]。在大鼠爆发性肝衰竭模型中,IL-1Ra基因转导至羊水来源的MSCs移植于大鼠中,发现其可促进肝细胞再生,缓解爆发性肝衰竭的病情[24]。IL-1Ra与VEGF基因转导至骨髓MSCs,将其与胰腺进行共移植,发现其可改善移植的治疗效果[25]。 炎症环境可增加IL-1Ra的 分泌[26]。研究[27]发现,炎症环境培养的 MSCs分泌的IL-1Ra比常氧环境增加了10倍。IL-1Ra作用发挥与其竞争性结合IL-1受体,阻断IL-1信号级联反应有关。IL-1β是引发肺水肿起主要作用的炎症因子之一[28],而在LPS诱导的急性肺损伤模型中,MSCs灌注可提高该疾病的生存率,该作用与MSCs分泌IL-1Ra,进而减弱IL-1β诱导的促炎活动有关[29-30]。在本研究结果显示:LPS诱导的炎症环境可刺激UC-MSCs分泌IL-1Ra增多。
目前,在人类体内发现有10种TLRs(TLR1~10),在小鼠身上发现有13种 TLRs(TLR1~13)[31],均属于IL-1受体超家族成员。MSCs表达功能性TLR4,可促进其分化[1,20]、增殖[32]和 迁移[33]。有研究发现,激活TLR4可增强 MSCs免疫抑制能力,促使MSCs向抗炎型转变。在Sun等[34]采用LPS诱导小鼠急性肺损伤模型中,发现UCMSCs可快速迁移到炎症部位,减轻肺组织损伤和炎症反应,该作用与LPS刺激UC-MSCs增强CD4+CD25+FOX P3+Treg细胞免疫功能和增加抑炎因子IL-10分泌,并下调促炎因子 TNF-α、MIP-2和IFN-γ表达有关。关于激活TLR4对 MSCs免疫抑制能力影响的研究尚存争议。有研究[35-36]报道,激活TLR4使MSCs向促炎表型转变,也有研究[37-38]报道,激活TLR4对 MSCs的免疫抑制能力并没有影响或者使其作用减弱。本研究发现,LPS不同剂量与时间激活TLR4后,UC-MSCs均分泌IL-1Ra,在基因水平上,以1μg/mL刺激 UC-MSCs 3h和8h表达IL-1Ra差异显著;在蛋白质水平上,则以1μg/mL刺激UC-MSCs 24h表达IL-1Ra差异显著。由此表明,激活TLR4增加UC-MSCs对IL-1Ra的分泌,可能会增强或协同UC-MSCs的免疫抑制作用。
综上所述,UC-MSCs免疫作用发挥可能与炎症环境存在的炎症介质有关,LPS激活TLR4,可刺激UC-MSCs分泌IL-1Ra增加,该作用可能与MSCs免疫调节机制有关,可能协同或增强MSCs的免疫抑制作用。但该作用对炎症的负调控,也可能会增加机体对病原体的感染。因而,深入研究MSCs中TLR4的免疫调节机制,对MSCs临床应用的安全性、有效性和长期性是非常有意义的。
[1]Ebert R,Benisch P,Krug M,et al.Acute phase serum amyloid A induces proinflammatory cytokines and mineralization via toll-like receptor 4in mesenchymal stem cells[J].Stem Cell Res,2015,15(1):231-239.
[2]Marrelli M,Paduano F,Tatullo M.Human periapical cystmesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neuronal cells[J].J Dent Res,2015,94(6):843-852.
[3]Zhu L,Ruan Z,Yin Y,et al.Expression and significance of DLL4--Notch signaling pathway in the differentiation of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocytes induced by 5-azacytidine [J].Cell Biochem Biophys,2015,71(1):249-253.
[4]Li CJ,Cheng P,Liang MK,et al.MicroRNA-188regulates age-related switch between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation[J].J Clin Invest,2015,125(4):1509-1522.
[5]Sawangmake C,Nowwarote N,Pavasant P,et al.A feasibility study of an in vitro differentiation potential toward insulinproducing cells by dental tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2014,452(3):581-587.
[6]Zhang X,Yamaoka K,Sonomoto K,et al.Local delivery of mesenchymal stem cells with poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid nanofiber scaffold suppress arthritis in rats[J].PLoS One,2014,9(12):114621.
[7]Zhao X,Liu D,Gong W,et al.The toll-like receptor 3ligand,poly(I:C),improves immunosuppressive function and therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cells on sepsis via inhibiting MiR-143[J].Stem Cells,2014,32(2):521-533.
[8]Maumus M,Manferdini C,Toupet K,et al.Adipose mesenchymal stem cells protect chondrocytes from degeneration associated with osteoarthritis [J].Stem Cell Res,2013,11(2):834-844.
[9]Tomic S,Djokic J,Vasilijic S,et al.Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental pulp and dental follicle are susceptible to activation by toll-like receptor agonists[J].Stem Cells Dev,2011,20(4):695-708.
[10]Zheng YB,Zhang XH,Huang ZL,et al.Amniotic-fluidderived mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing interleukin-1 receptor antagonist improve fulminant hepatic failure [J].PLoS One,2012,7(7):41392.
[11]Kota DJ,DiCarlo B,Hetz RA,et al.Differential MSC activation leads to distinct mononuclear leukocyte binding mechanisms[J].Sci Rep,2014,4:4565.
[12]Dumitru CA,Hemeda H,Jakob M,et al.Stimulation of mesenchymal stromal cells(MSCs)via TLR3reveals a novel mechanism of autocrine priming[J].FASEB J,2014,28(9):3856-3866.
[13]Mitchell KE,Weiss ML,Mitchell BM,et al.Matrix cells from Wharton′s jelly form neurons and glia[J].Stem Cells,2003,21(1):50-60.
[14]Pijnappels DA,Schalij MJ,Ramkisoensing AA,et al.Forced alignment of mesenchymal stem cells undergoing cardiomyogenic differentiation affects functional integration with cardiomyocyte cultures[J].Circ Res,2008,103(2):167-176.
[15]François M,Romieu-Mourez R,Li M,et al.Human MSC suppression correlates with cytokine induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and bystander M2macrophage differentiation[J].Mol Ther,2012,20(1):187-195.
[16]Ghannam S,Boui C,Djouad F,et al.Immunosuppression by mesenchymal stem cells:mechanisms and clinical applications[J].Stem Cell Research and Therapy,2010,1(1):2.
[17]Chiesa S,Morbelli S,Morando S,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells impair in vivo T-cell priming by dendritic cells[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2011,108(42):17384-17389.
[18]Weber A,Wasiliew P,Kracht M.Interleukin-1beta(IL-1beta)processing pathway[J].Sci Signal,2010,3(105):165.
[19]施晓雷,檀家俊,肖江强,等.白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂联合骨髓问充质干细胞移植治疗猪急性肝衰竭 [J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(10):1930-1933.
[20]van den Berk LC,Jansen BJ,Siebers-Vermeulen KG,et al.Toll-like receptor triggering in cord blood mesenchymal stem cells[J].J Cell Mol Med,2009,13(9):3415-3426.
[21]Kota DJ,DiCarlo B,Hetz RA,et al.Differential MSC activation leads to distinctmononuclear leukocyte binding mechanisms[J].Sci Rep,2014,4:4565.
[22]Deng Y,Yi S,Wang G,et al.Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells instruct dendritic cells to acquire tolerogenic phenotypes through the IL-6-mediated upregulation of SOCS1[J].Stem Cells Dev,2014,23(17):2080-2092.
[23]Yuan J,Liu Y,Huang W,et al.The experimental treatment of corneal graft rejection with the interleukin-1receptor antagonist(IL-1ra)gene[J].PLoS One,2013,8(5):60714.
[24]Zheng YB,Zhang XH,Huang ZL,et al.Amniotic-fluidderived mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing interleukin-1 receptor antagonist improve fulminant hepatic failure [J].PLoS One,2012,7(7):41392.
[25]Mundra V,Wu H,Mahato RI.Genetically modified human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells for improving the outcome of human islet transplantation[J].PLoS One,2013,8(10):77591.
[26]Zapata-Tarrés M,Arredondo-García JL,Rivera-Luna R,et al.Interleukin-1receptor antagonist gene polymorphism increases susceptibility to septic shock in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J].Pediatr Infect Dis J,2013,32(2):136-139.
[27]Goolaerts A,Pellan-Randrianarison N,Larghero J,et al.Conditioned media from mesenchymal stromal cells restore sodium transport and preserve epithelial permeability in an in vitro model of acute alveolar injury[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2014,306(11):975-985.
[28]Howard M,Roux J,Iles KE,et al.Activation of the heat shock response attenuates the interleuk9(2):in 1β-mediated inhibition of the amiloride-sensitive alveolar epithelial ion transport[J].Shock,2013,3 189-196.
[29]Németh K,Leelahavanichkul A,Yuen PS,et al.Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10production[J].Nat Med,2009,15(1):42-49.
[30]Ortiz LA,Dutreil M,Fattman C,et al.Interleukin 1receptor antagonist mediates the antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect of mesenchymal stem cells during lung injury[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2007,104(26):11002-11007.
[31]Bujak M,Frangogiannis NG.The role of TGF-beta signaling in myocardial infarction and cardiac remodeling [J].Cardiovasc Res,2007,74(2):184-195.
[32]Hwang SH,Cho HK,Park SH,et al.Toll like receptor 3 &4 responses of human turbinate derived mesenchymal stem cells:stimulation by double stranded RNA and lipopolysaccharide[J].PLoS One,2014,9(7):101558.
[33]Yang ZH,Wang XB,Wang J,et al.[Influence of TLR2and TLR4agonists on migration of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells][J].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi,2014,22(1):183-186.
[34]Sun J,Han ZB,Liao W,et al.Intrapulmonary delivery of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuates acute lung injury by expanding CD4+CD25+ Forkhead Boxp3(FOXP3)+regulatory T cells and balancing anti-and pro-inflammatory factors[J].Cell Physiol Biochem,2011,27(5):587-596.
[35]Waterman RS,Tomchuck SL,Henkle SL,et al.A new mesenchymal stem cell(MSC)paradigm:polarization into a pro-inlammatory MSC1or an immunosuppressive MSC2 phenotype[J].PLoS One,2010,5(4):10088.
[36]Mei YB,Zhou WQ,Zhang XY,et al.Lipopolysaccharides shapes the human Wharton′s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro[J].Cell Physiol Biochem,2013,32(2):390-401.
[37]Lombardo E,Delarosa O,Mancheno-Corvo P,et al.Toll-like receptor-mediated signaling in human adipose-derived stem cells:implications for immunogenicity and immunosuppressive potential[J].Tissue Engineering A,2009,15(7):1579-1589.
[38]Raicevic G,Rouas R,Najar M,et al.Inflammation modifies the pattern and the function of toll-like receptors expressed by human mesenchymal stromal cells[J].Human Immunology,2010,71(3):235-244.
