Ghrelin对小鼠认知功能的影响及机制探讨
2015-12-02陈任方姝晨宁宇范里陈家禄
陈任,方姝晨,宁宇,范里,陈家禄
Ghrelin对小鼠认知功能的影响及机制探讨
陈任1,方姝晨2,宁宇2,范里1,陈家禄1
目的:探讨Ghrelin对小鼠认知功能的影响及机制。方法:野生型(WT)组和CGRP基因敲除(CGRP-/-)组小鼠各10只,且各分为对照亚组和实验亚组各5只,均腹腔注射100μL含0.1μg/LGherlin的PBS试液(实验亚组)或空白PBS试液(对照亚组),进行Morris水迷宫实验及记忆探索实验,并测定其海马趾组织中CGRP、IGF-1及IGF-1mRNA含量。结果:WT组中,实验亚组与对照亚组比较,逃避潜伏期时间缩短,目标区域停留时间百分比增加,CGRP、IGF-1及IGF-1mRNA的含量较高(P<0.05);CGRP-/-组中,实验亚组与对照亚组相比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);与CGRP-/-组实验亚组比较,WT组实验亚组注射第4、5天的逃避潜伏期较低,目标区域停留时间百分比较高,CGRP、IGF-1及IGF-1mRNA含量较高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:Gherlin可能通过促进海马体释放CGRP,使得海马的IGF-1产量增加,由此提高小鼠的认知能力。
Ghrelin;胰岛素样生长因子-1;认知功能
Ghrelin是一种28个氨基酸组成的酰化肽,其最早从大鼠胃组织中分离纯化出来,并被认为是生长素促分泌物受体-1a(growth hormone secretagogue receptor-1a,GHSR-1a)的内源性配体[1]。Ghrelin能调节细胞增殖和生存[2],并有增加摄食量、增强胃肠道活动、促进胃酸分泌、引发肥胖和增重等作用[3]。除这些生物活性外,Ghrelin可通过作用于海马趾的神经元从而提高空间学习能力,并且可诱导海马CA1区中新的突触结构形成[4]。已有实验证明,刺激小鼠感觉室周器官(circumventricular organs,CVOs)后,CVOs中神经元通过释放降钙素基因相关肽(calcitonin gene-related peptide,CGRP)可促进海马趾产生胰岛素样生长因子-1(insulin-like growth factor-1,IGF-1)。CGRP是一种由降钙素基因选择性剪切转录形成37个氨基酸组成的神经肽[5],广泛分布于中央及周围神经系统[6]。
为了验证Ghrelin是否可以刺激感觉神经元,从而促进海马中CGRP的释放,进而增加IGF-1的含量,最终提高小鼠的认知功能,本文将CGRP基因敲除型(CGRP-knockout,CGRP-/-)小鼠(其CVOs中神经元无法正常合成CGRP)与野生型(wild-type,WT)小鼠进行对照试验,报告如下。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 实验动物 C57BL/6品系WT小鼠(WT组)和该品系CGRP基因敲除小鼠[7](CGRP-/-组)各10只,鼠龄10~12周,体质量21~24 g,均在23℃~25℃温控、12 h白天-黑夜循环控制及自由、充足摄食条件下饲养。每组小鼠采用随机数字表法分为实验亚组和对照亚组各5只。
1.1.2 实验试剂及仪器 C18反向色谱柱(购于英国Amersham公司);酶免疫测定试剂盒(购于法国SPI-BIO公司);polytron型匀浆机(购于瑞士Kinematica公司);酶免疫测定试剂盒(购于美国Diagnostic Systems Laboratories公司);Trizol试剂(购于美国Invitrogen公司);7700型测序仪(购于日本Perkin Elmer Applied Biosystems公司);Taqman PCR试剂盒(购于美国Applied Biosystems公司);
1.2 方法
所有小鼠均腹腔注射 100μL含0.1μg/LGherlin的PBS试液(实验亚组)或空白PBS试液(对照亚组)。从制模当天起连续5 d每天9点与15点各注射一次,每天进行一次Morris水迷宫实验,最后一次实验后2 h进行空间记忆探索实验,记录结果。在最后一次实验后30~60m in内将动物处死,快速取脑,进行海马中CGRP、IGF-1、IGF-1mRNA的测定。
1.2.1 Morris水迷宫实验及记忆探索实验[8]水迷宫由一个直径150 cm的圆形池及一个小鼠站台组成,池中控制水恒温30℃,池中放置一个易辨别的圆形塑料小鼠平台,直径12 cm。将小鼠站台放置于池的东南角,没入水面下1 cm。每只放入水迷宫的小鼠有90 s的时间去寻找并爬上站台。若小鼠爬上站台后,使其在站台上停留10 s。记录小鼠找到平台所需时间,即逃避潜伏期。若小鼠未在90 s内找到站台,实验者将小鼠引向站台,同样停留10 s,潜伏期记录为90 s。每只小鼠每天进行一次Morris水迷宫实验,共进行5 d。最后一次实验后2 h进行空间记忆探索实验。将水池中的站台移除后,将小鼠放入水池中90 s,将原站台中点为中心半径30 cm的水域划分为目标区域。记录每只小鼠在目标区域内所停留的时间,计算其占总时间的百分比。
1.2.2 海马中CGRP、IGF-1、mRNA的测定方法 实验结束后处死动物,快速取脑,细心分离出海马,冷冻后等待处理。①海马CGRP含量的测定:海马组织称重后,在0.5m L的2mol/L醋酸中混合均匀,将混合物置于90℃水浴中20m in,然后4 500 g离心10m in(4℃)。用C18反向色谱柱将CGRP从上清液中萃取(柱的制备:先用5m L甲醇自上而下冲洗柱体,然后20m L 0.1%三氟乙酸冲洗,最后在氮气环境中使冲洗溶剂挥发)。使用专用的酶免疫测定试剂盒测定,CGRP的测定敏感度为10 pg/m L。②海马IGF-1含量的测定:将组织加入1m L 1mol/L醋酸中,使用Polytron型匀浆机将海马组织切碎(2次,每次15 s),并使其混匀,然后4 500g离心分离10 min,取上清液于-80℃冷藏器中保存,使用专用的酶免疫测定试剂盒测定IGF-1浓度。③mRNA定量分析:组织称重后浸入液氮中,所有的mRNA均按照制造商的说明用Trizol试剂从海马组织中萃取。在每50~100mg组织加入1m L Trizol,于4℃12 000 rpm离心10m in,取上样品会分成三层:黄色的有机相、中间层和无色的水相,mRNA主要在水相中,把水相(通常可吸取550μL)转移到新管中。由于cDNA是以mRNA为模板逆转录而来,故通过样品cDNA的测定来计算mRNA含量。样品cDNA放大所需条件:7700型测序仪、引物、双标记基因探针、Taqman PCR试剂盒。温度控制95℃、10min使其失活,随后95℃、15 s使其变性,60℃、1m in退火并解链,循环40次。标本的IGF-1与β肌动蛋白的比值作为作为衡量mRNA含量的标准。
1.3 统计学处理
2 结果
2.1 学习记忆能力比较
WT组中,实验亚组与对照亚组比较,逃避潜伏期时间缩短,目标区域停留时间百分比增加(P<0.05);CGRP-/-组中,实验亚组与对照亚组相比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);与CGRP-/-组实验亚组比较,WT组实验亚组注射第4、5天的逃避潜伏期较低,目标区域停留时间百分比较高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1。
表1 各组小鼠学习记忆能力比较(±s)
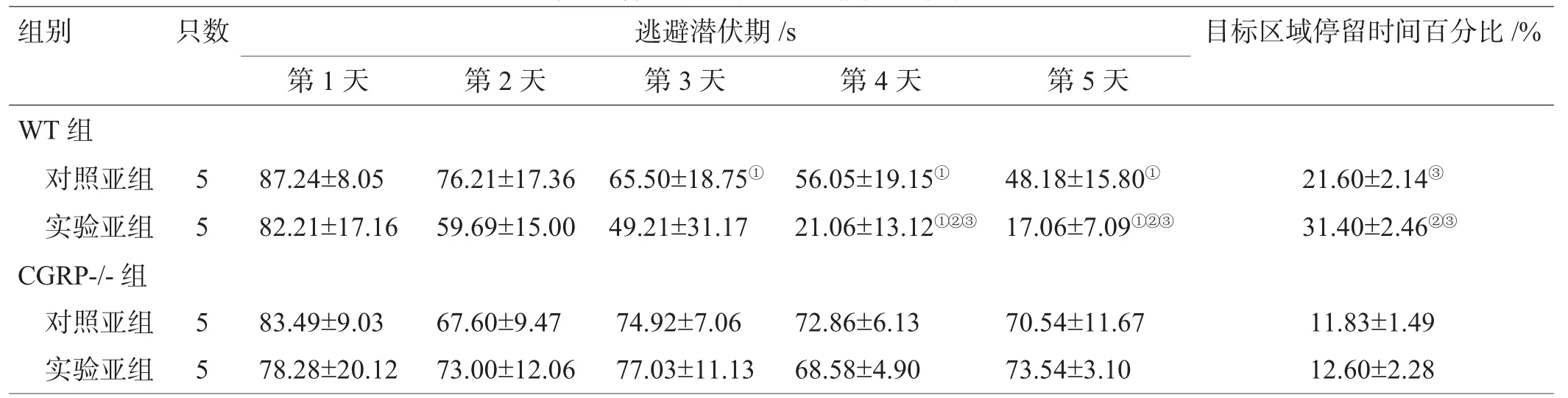
表1 各组小鼠学习记忆能力比较(±s)
注:与第1天比较,①P<0.05;与同组对照亚组比较,②P<0.05;与CGRP-/-组实验亚组比较,③P<0.05
组别 只数 逃避潜伏期/s 目标区域停留时间百分比/% 第1天 第2天 第3天 第4天 第5天WT组对照亚组 5 87.24±8.05 76.21±17.36 65.50±18.75① 56.05±19.15① 48.18±15.80① 21.60±2.14③实验亚组 5 82.21±17.16 59.69±15.00 49.21±31.17 21.06±13.12①②③ 17.06±7.09①②③ 31.40±2.46②③CGRP-/-组对照亚组 5 83.49±9.03 67.60±9.47 74.92±7.06 72.86±6.13 70.54±11.67 11.83±1.49实验亚组 5 78.28±20.12 73.00±12.06 77.03±11.13 68.58±4.90 73.54±3.10 12.60±2.28
2.2 海马中CGRP、IGF-1、mRNA含量比较
CGRP-/-组中CGRP、IGF-1及IGF-1 mRNA含量低于WT组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);WT组中,实验亚组的CGRP、IGF-1及IGF-1mRNA的含量高于对照亚组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);CGRP-/-组中,2亚组的 CGRP、IGF-1及IGF-1mRNA含量差异无统计学意义,见表2,说明Ghrelin可通过促进小鼠神经元释放CGRP从而提高海马的IGF-1产量。
表2 各组小鼠海马趾中CGRP、IGF-1、IGF-1mRNA的含量比较(±s)

表2 各组小鼠海马趾中CGRP、IGF-1、IGF-1mRNA的含量比较(±s)
注:与同组对照亚组比较,①P<0.05;与WT组对应亚组比较,②P<0.05
组别 只数 CGRP(ng/mL) IGF-1(ng/m L) IGF-1mRNA WT组对照亚组 5 125.36±8.47 125.57±9.47 1.02±0.18实验亚组 5 197.55±15.23① 192.44±12.40① 1.86±0.23①CGRP-/-组对照亚组 5 6.40±2.10② 101.07±9.57 0.70±0.08②实验亚组 5 7.44±2.20② 100.46±14.03② 0.72±0.08②
3 讨论
IGF-1是一种由70个氨基酸组成的碱性肽,广泛分布于各组织与细胞中。IGF-1可调节生长激素的促生长作用,影响后天的生长和发育[9]。IGF-1被证实可提高海马CA1区中突触传递的兴奋性,并通过海马中神经形成的增加来提高空间认知能力[10]。相反地,当无外源性IGF-1注入小鼠时,血浆中的IGF-1含量偏低,小鼠的空间认知能力相对变差[11]。有研究证实,给予IGF-1抗体后小鼠学习记忆能力显著下降[12]。这提示,在成熟个体中血浆IGF-1含量与认知功能存在紧密的联系[13]。本文也证实IGF-1可以拮抗认知功能的下降。
Steen等[14]发现阿尔兹海默病(A lzheimer’s disease,AD)患者早期的IGF-1基因表达降低,IGF-1产生过少,最终导致AD。Okereke等[15]发表的一项长期随访报道则显示整体认知功能和词汇记忆均与血浆IGF-1水平呈正相关,表明受试者血浆IGF-1水平越高,认知功能越好,对晚发型AD有预测作用。
本文观察到对WT组小鼠腹膜内注射Ghrelin可提高其海马趾中CGRP、IGF-1及 IGF-1 mRNA的组织含量。CGRP-/-组小鼠海马趾内初始的CGRP、IGF-1及IGF-1mRNA含量明显低于WT组小鼠,且注射Ghrelin后,其CGRP、IGF-1以及IGF-1mRNA含量并未提高,证明在WT组小鼠中,Ghrelin可通过促进海马趾内CGRP的释放从而提高IGF-1的水平。Aberg等[10]提出假说认为,Ghrelin可明显提高WT组小鼠的空间学习能力,而对CGRP-/-组小鼠无明显影响。也有报道称Ghrelin能直接作用于海马从而提高空间学习能力,但William 等[16]证实Ghrelin无法直接通过血脑屏障,而是通过某种介质发挥作用,笔者认为CGRP在这过程中起关键作用。
综上所述,本文证实Ghrelin可刺激神经元,从而促进海马中CGRP的释放,CGRP进而增加IGF-1的含量,可能最终提高小鼠的认知功能。
[1]Kojima M,Hosoda H,Date Y,etal.Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach[J].Nature,1999,402:656-660.
[2]M iao Y,Xia Q,Hou Z,etal.Ghrelin protects cortical neuron against focal ischemia/reperfusion in rats[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2007,359:795-800.
[3]Masuda Y,Tanaka T,Inomata N,etal.Ghrelin stimulates gastric acid secretion and motility in rats[J].Biochem BiophysRes Commun,2000, 276:905-908.
[4]Diano S,Farr SA,Benoit SC,et al.Ghrelin controls hippocampal spine synapse density and memory performance[J].NatNeurosci,2006,9: 381-388.
[5]Narimatsu N,Harada N,Kurihara H,et al. Donepezil improves cognitive function in m ice by increasing the production of insulin-like growth factor-I in the hippocampus [J].J PharmacolExp Ther,2009,330:2-12.
[6]Dobolyi A,Irwin S,Makara G,et al.Calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing pathways in the rat forebrain[J].JComp Neurol,2005,489: 92-119.
[7]Oh-hashiY,Shindo T,Kurihara Y,etal.Elevated sympathetic nervous activity in mice deficient in alphaCGRP [J].Circ Res,2001,89: 983-990.
[8]Ryan SH,Williams JK,Thomas JD.Choline supplementation attenuates learning deficits associated with neonatal alcohol exposure in the rat: effects of varying the timing of choline administration[J].Brain Res,2008,1237:91-100.
[9]Okajima K,Harada N.Promotion of insulin-like growth factor-I production by sensory neuron stimulation;molecular mechanism(s)and therapeutic implications[J].Curr Med Chem, 2008,15:3095-3112.
[10]Aberg MA,Aberg ND,Hedbacker H,et al. Peripheral infusion of IGF-I selectively induces neurogenesis in the adult rat hippocampus[J].J Neurosci,2000,20:2896-2903.
[11]Trejo JL, Llorens-Martin MV, Torres- Aleman I. The effects of exercise on spatial learning and anxiety-like behavior are mediated by an IGF-I-dependent mechanism related to hippocampal neurogenesis [J]. Mol Cell Neurosci, 2008, 37: 402-411.
[12]Lupien SB,Bluhm EJ,Ishii DN.System ic insulin-like growth factor-I adm inistration prevents cognitive mpairment in diabetic rats,and brain IGF regulates learning/memory in normal adult rats[J].JNeurosciRes,2003,74:512-523.
[13]Landi F,Capoluongo E,Russo A,etal.Free insulin-like growth factor-I and cognitive function in older persons living in community.[J] Grow th Horm IGFRes,2007,17:58-66.
[14]Steen E,Terry BM,Rivera EJ,et al.Impaired insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling machanisms in Alzheimer's disease-is this type 3 diabetes?[J].J Alzheimers Dis,2005,7:63-80.
[15]Okereke OI,Kang JH,Ma J,et al.Midlife plasma insulin-like growth factor Iand cognitive function in older men [J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2006,91:4306-4312.
[16]BanksWA,Tschöp M,Robinson SM,et al. Extent and direction of ghrelin transport across the blood-brain barrier is determ ined by its unique primary structure[J].J Pharmacol Exp Ther,2002,302:822-827.
(本文编辑:王晶)
Effect and Mechanism of Ghrelin on Cognitive Function in Mice
CHEN Ren,FANG Shu-chen,NING Yu,FAN Li,CHEN Jia-lu.Department of Spinal surgery,Renm in Hospital ofWuhan University Hubei General Hospital,Wuhan 430000,China
Objective:To explore the effect and mechanism of Ghrelin on the cognitive function in mice. Methods: Ten wild-type mice (WT group) and 10 CGRP-gene knockout mice (CGRP-/- group)were equally divided as the control subgroup (n=5) and the examination subgroup (n=5). Mice were treated by intraperitoneal injection of 100 μL of 0.1 μg/L Ghrelin solution dissolved in PBS (examination subgroup) or with PBS alone (control subgroup). The Morris maze task and probe test were examined in both groups, and then the tissue levels of CGRP, IGF-1 and IGF-1 mRNA in the hippocampus were determined. Results: In the WT group, the escape latency of the examination subgroup was shortened, the time spent in the target area of the examination subgroup was significantly enhanced, the tissue levels of CGRP, IGF-1 and IGF-1 mRNA were significantly up-regulated (P<0.05) compared to those in the control subgroup. There was no statistically significance between the two subgroups in CGRP-/- group (P>0.05). Compared with the examination subgroup of CGRP-/- group, the escape latency of the examination subgroup of WT group was shorter on days 4 and 5, and the time spent in the target area was longer, and the tissue levels of CGRP, IGF-1 and IGF-1 mRNA were significantly higher (P<0.05). Conclusion: Ghrelin may increase the hippocampal expression of IGF-1 via increase of CGRP release from the hippocampus, thus cognitive function was improved.
Ghrelin;insulin-likegrowth factor-1;cognitive function
R741;R741.02
A DOI 10.3870/sjsscj.2015.06.001
1.武汉大学人民医院脊柱外科 武汉430000 2.苏州市吴江区中医医院骨科 苏州215200 3.湖北中医药大学针灸骨伤学院 武汉430065
2015-04-13
陈任 darkdance-cr@qq.com
