利用COⅠ基因序列和杂交实验分析鉴定桨角蚜小蜂属的本地种群
2015-11-22张毅波杨念婉张桂芬王进军万方浩
张毅波,杨念婉,张桂芬,王进军,万方浩*
(1.中国农业科学院植物保护研究所,植物病虫害生物学国家重点实验室,北京100193;2.西南大学植物保护学院,重庆500070)
烟粉虱Bemisia tabaci(Gennadius)因其分布范围广、危害严重、寄主谱广泛、生物型复杂、产卵量大、传播病毒种类多、抗药性强、扩张蔓延速度快等特点,成为世界各国竭力防控的目标(Brown et al.,1995;Pascual and Callejas,2004;De Barro et al.,2011;刘树生,2012)。其中,尤以中东-小亚细亚1(MEAM1)隐种和地中海 (MED)隐种更为突出,两者已成为制约我国蔬菜、观赏植物及经济作物等产业发展的重要瓶颈 (罗晨等,2006;Wan et al.,2010;高建昌等,2011)。目前,我国粉虱类害虫的防治主要依靠化学药剂。由于化学农药对非靶标天敌的危害和烟粉虱抗药性的快速发展,利用自然天敌的生物防治方法已逐渐成为控制烟粉虱危害的一项潜在有力措施 (Wan et al.,2009;Xu et al.,2013;Yang et al.,2014)。
自1850年Haldeman建立桨角蚜小蜂属以来,世界范围内已经鉴定并命名的桨角蚜小蜂达65种,其中以烟粉虱为寄主的达 24种 (Kirk et al.,2000;Naranjo et al.,2004;Zolnerowich and Rose,2008;孟瑞霞等,2008;皇甫伟国等,2010;王继红等,2011)。桨角蚜小蜂属寄生蜂是控制粉虱类(尤其是烟粉虱)害虫的重要天敌类群 (Rose et al.,1996)。然而,此类寄生蜂个体微小,成虫体长不足1 mm,而且外部形态极为相似,仅仅依据形态特征,包括雌蜂触角棒节形状和大小,产卵器形状和长度,前翅特征等外部特征(Haldeman,1850;Dozier,1932;Rose and Rosen,1991-1992;Rose and Zolnerowich,1997),很难快速准确区分。
2008年,中国农科院植保所从美国德克萨斯农工大学引进了海氏桨角蚜小蜂Eretmocerus hayati,用于烟粉虱生防防治研究 (Yang and Wan,2011;Yang et al.,2012,Xu et al.,2013)。热孜万古丽.阿布都哈尼等 (2013)在新疆维吾尔自治区吐鲁番地区棉田发现一种自然发生的桨角蚜小蜂属的地理种群。新疆种群能够在自然条件极为干旱、昼夜温差大的吐鲁番地区建立种群并大范围发生,我们猜测这种寄生蜂可能对极端气候具有很强的适应能力和大范围应用的生防潜力。同时,我们在中国农业科学院廊坊实验基地采集到一种自然发生桨角蚜小蜂种群。为了进一步利用本地桨角蚜小蜂生物防治粉虱类害虫,亟待对他们进行准确的物种鉴定。
当前,基于线粒体COⅠ基因序列的分子生物学物种快速鉴定手段在昆虫鉴定中得到广泛应用。这些研究主要涉及:叶甲类 (郑福山等,2007;代金霞和张大治,2010)、蝽类 (梁秋英,2009)、鳞翅目蛾类(杨聪慧等,2012;张桂芬等,2013)、蚜虫类 (王剑峰和乔格侠,2007;陈占秀和顾耘,2012)、蓟马类 (乔玮娜等,2012;Zhang et al.,2012)、介壳虫类 (田虎等,2013)等等。这种方法不仅能够准确快速区别和鉴定物种,也是发现、鉴定新种和隐种的有效手段 (Smith et al.,2005)。然而,新种的鉴定和命名不能仅仅依靠DNA分类的结果,片面依赖分子数据来区分物种是远远不够的,准确的物种鉴定还须与传统形态或生态等特征相结合 (Miller,2007;Ross et al.,2010;Yeates et al.,2011)。
生殖隔离是生物种定义中最基本的特征之一。种间杂交作为验证物种生殖隔离的最直接方法,在膜翅目寄生性天敌间被广泛的使用,并且为传统分类学的物种定名提供依据 (Pinto and Stouthamer,1994;Billah et al.,2008),比如赤眼蜂的鉴定 (Stouthamer et al.,2000;Pinto et al.,2003),短背茧蜂属果蝇寄生蜂 (Billah et al.,2008)等。桨角蚜小蜂大多营孤雌产雄生殖方式,不同种群间能否杂交并产生具有生殖能力的雌性后代就成为判断种群间基因能否交流的指标,也是鉴定是否为同物种的重要特征之一 (Hunter et al.,1996)。
本研究针对桨角蚜小蜂体型小、难以与其他同域近缘种寄生蜂快速准确区别的问题,以海氏桨角蚜小蜂 Eretmocerus hayati,古桥桨角蚜小蜂Eretmocerus furuhashii,未知桨角蚜小蜂属新疆吐鲁番种群Eretmocerus sp.XJ和未知桨角蚜小蜂属河北廊坊种群Eretmocerus sp.LF四种寄生蜂为研究对象,结合NCBI已发表的其他桨角蚜小蜂的基因序列,采用COⅠ基因序列分析明确两个未知桨角蚜小蜂种群的系统发育地位,进而利用亲缘关系相近种种间杂交方法联合鉴定未知物种。
1 材料与方法
1.1 供试虫源
海氏桨角蚜小蜂由中国农业科学院植物保护研究所生物入侵研究室2008年从美国德克萨斯农工大学引入 (上世纪90年代从巴基斯坦引入美国,Zolnerowich and Rose,2008),古桥桨角蚜小蜂种群由吉林农业大学昆虫研究所臧连生研究员提供,桨角蚜小蜂新疆种采自新疆维吾尔自治区吐鲁番地区棉花地,桨角蚜小蜂廊坊种群采自河北省廊坊市中国农业科学院植物保护研究所廊坊中试基地的棉花地,其中桨角蚜小蜂新疆种群和廊坊种群由福建农林大学黄建教授帮助鉴定到属。
1.2 DNA提取
寄生蜂DNA提取方法参照Teng et al.(2010)报道的方法并稍加改进。用软毛毛笔轻轻挑取单头寄生蜂成虫,置于滴有20μL提取缓冲液(50 mmol/L Tris-HCl, l mmol/L EDTA, 1%SDS,20 mmol/L NaCl,pH8.0)的 parafilm 膜上,以PCR管底部作为匀浆器充分研磨,匀浆液移入1.5 mL离心管;然后以200μL缓冲液分2次冲洗匀浆器、合并混匀;加入 5μL蛋白酶 K(20 mg/mL),充分混匀后于60℃水浴1 h(中途混匀1次);然后沸水浴5 min,加入220μL氯仿/异戊醇 (v∶v=24∶1),轻柔混匀后,冰浴30 min;然后于4℃ 12000 r/min离心20 min,取上清液,加入440μL预冷无水乙醇,轻柔混匀后于-30℃放置30 min;4℃ 12000 r/min离心15 min,小心弃去上清液。加入500μL预冷75%乙醇洗涤,4℃ 12000 r/min离心15 min,小心弃去上清液;然后将离心管倒扣于洁净滤纸上,自然干燥20 min。每管加入20μL超纯水,充分溶解后于-30℃保存备用。
1.3 PCR扩增、电泳检测以及序列测定
依据本实验室以往的经验和电泳谱带的多态性程度,选取引物 C1-J-2183(5'-CAAC ATTTATTTTGATTTTTTGG-3')和TL2-N-3014(5'-TCCAATGCACTAATCTGCCA TATT-3')(Simon et al.,1994),引物由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成。然后,以四种桨角蚜小蜂的DNA为模板,进行PCR扩增。
反应体系为25μL,其中超纯水 18.75μL,10×缓冲液 2.5 μL(包含镁离子),0.2 mmol/L dNTPs 0.5μL,Taq聚合酶2.5 μL,5 pmol/L 每种引物0.5μL,模板DNA 2μL。扩增程序为:95℃预变性3 min;35个循环:94℃ 45 s,53℃ 1 min,72℃ 2 min;最后72℃延伸2 min。扩增反应在ABI-9700 PCR基因扩增仪上运行。
取1μL PCR扩增产物,加1μL上样缓冲液(0.25% 溴酚兰,40% 蔗糖水溶液),以 DNA Marker为参照,在含有染色剂GoldView的1.5%的琼脂糖凝胶上进行电泳分离 (电泳液为0.5×TBE),105 V电泳25 min后,以GelDoc Universal Hood II型凝胶成像系统分析结果。将经电泳检测验证合格的PCR产物送上海生工生物工程有限公司双向测序,获得的序列利用MEGA 5.0软件进行拼接。根据标本数量及PCR产物的质量,海氏桨角蚜小蜂测序5头,古桥桨角蚜小蜂测序6头,桨角蚜小蜂新疆种群测序10头,桨角蚜小蜂廊坊种群测序5头。每种寄生蜂选取1条拼接序列录入美国国立生物技术信息中心 (National Center of Biotechnology Information,NCBI)数据库。
1.4 COⅠ序列分析
以Bioedit软件读取序列,并对每条序列进行人工碱基读取和反复校对。校正后的碱基序列在NCBI上进行同源性比对,以确保获得的序列为目的基因片段。然后,结合NCBI中已公开的有效桨角蚜小蜂属寄生蜂的 COⅠ 序列 (表 1),用ClustalX进行COⅠ基因序列分析 (Herbert et al.,2004),用MEGA 5.0软件以Kimura双参数模型计算种内及种间遗传距离 (Kumar et al.,2004;Tamura et al.,2007),采用最大简约法 (Maximum parsimony,MP)和 最 大 似 然 法 (Maximum likelihood,ML)分别构建系统进化树,系统发育树分支的置信度采用自展法 (bootstrap analysis,BP)重复检测1 000次。为了检验样本种间遗传变异与种内个体间遗传变异的差异是否显著,使用MEGA 5.0软件计算种内及种间遗传距离并进行统计。
1.5 杂交试验
由于只有海氏桨角蚜小蜂和桨角蚜小蜂新疆种群的室内种群,所以我们针对两个种群开展了杂交实验。结合以上COⅠ基因序列比对结果,取相似性最大的海氏桨角蚜小蜂Er.hayati和桨角蚜小蜂新疆种Er.sp.XJ初羽化寄生蜂成虫,进行种间杂交试验,处理包括 (1)Er.hayati♀×Er.sp.XJ♂ (n=20),(2)Er.sp.XJ♀ × Er.hayati♂ (n=20),为证明两种寄生蜂是否具有孤雌产雌的能力,我们设置 (3)Er.hayati♀ (n=21),(4)Er.sp.XJ♀ (n=20)作为对照处理。
将每个杂交处理组合的成对寄生蜂成虫分别移入装有1钵棉花植株 (2株/钵)的正方体纱网(100目)养虫笼 (25 cm×25 cm×25 cm)中,棉花植株带有300-400头2-3龄烟粉虱若虫。5 d后,移除寄生蜂成虫,将每钵棉花苗编号并移至恒温人工智能气候箱 (28℃,70% ±5%RH,14∶10光周期,赛福智能人工气候箱)。8 d后,将棉花叶从植株上剪下并移至底部带有5%(w/v)琼脂溶液的玻璃培养皿 (直径9 cm)中,棉花叶背面朝上放置,同时依据棉花植株的编号对玻璃培养皿编号,便于接下来记录各处理寄生蜂后代羽化数据。此后,利用透明塑料保鲜膜将玻璃培养皿上口封好,置于室温 (26℃)下。每天10∶00调查一次寄生蜂后代的羽化情况直至所有寄生蜂羽化,记录羽化寄生蜂数和雌雄性比。
1.6 数据分析
因为杂交试验中各处理寄生蜂的后代羽化数均呈正态分布和具有方差同质性,所以单因素方差分析 (One-way ANOVA)结合最小显著差异t检验 (Least Significant Difference,LSD)直接用来分析各处理间寄生蜂的后代总体羽化数差异。各处理寄生蜂的后代雌雄性比经反正弦转化后同样利用单因素方差分析和LSD来分析各处理间寄生蜂后代性比间差异。数据分析采用的SAS 9.0版。
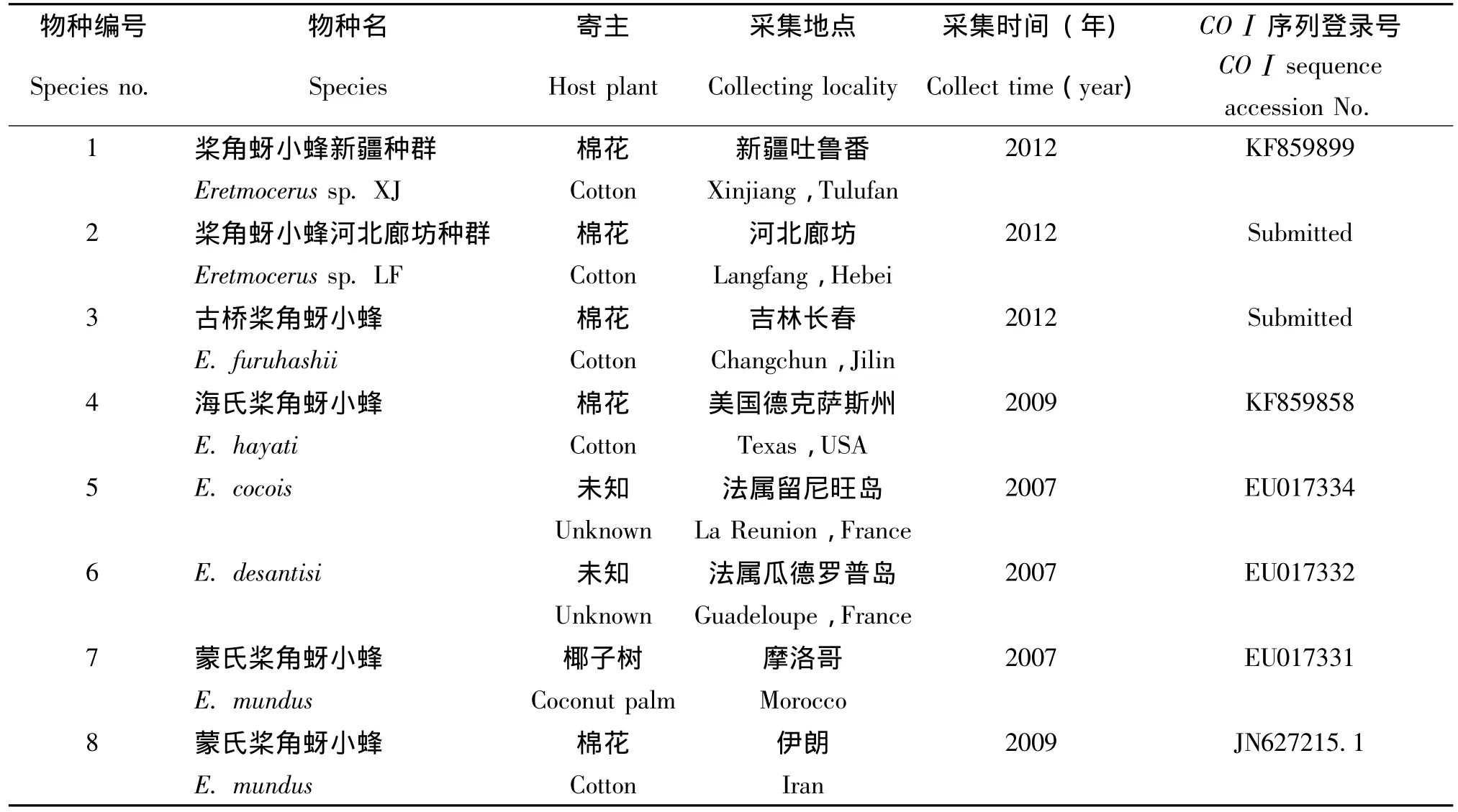
表1 本研究中用于COⅠ基因序列分析的桨角蚜小蜂种类Table 1 List of Eretmocerus parasitoids used for COⅠsequence analysis in this study
2 结果与分析
2.1 PCR扩增、电泳检测以及序列测定
每头寄生蜂均可扩增出长度约为860 bp的靶标片段,纯化测序后将目标基因片段修剪成长度为680 bp的片段进行分析,然后在NCBI中进行同源性比对。结果表明,4个桨角蚜小蜂种群的COⅠ碱基序列与数据库中已知的桨角蚜小蜂种类相对应的COⅠ基因片段的同源性为90%-95%,说明NCBI数据库中还没有本研究中测定的四种寄生蜂的COⅠ序列。其中,海氏桨角蚜小蜂与桨角蚜小蜂新疆种间基因相似度达98%,古桥桨角蚜小蜂与桨角蚜小蜂廊坊种群间相似度达99%。因此,将本研究测定的四种寄生蜂COⅠ序列提交NCBI,并获得相应登录号 (表1)。
2.2 COⅠ序列分析及系统发育树的构建
使用最大简约法和最大似然法以29条桨角蚜小蜂的COⅠ序列构建系统发育树,聚类分析结果如图1和图2所示,同时进一步比较分析了各样本间的遗传距离 (表2)。结果表明:桨角蚜小蜂新疆种群与海氏桨角蚜小蜂分别聚为不同分支,但两种群间支持率达100,进一步分析发现两者的种群内遗传距离分别为0.0023和0.000,种群间遗传距离0.024;桨角蚜小蜂廊坊种群与古桥桨角蚜小蜂聚为同一支,支持率也达100,两者的种内遗传距离分别为0.0029和0.0173,种间遗传距离为 0.011。

图1 利用最大简约法构建8种桨角蚜小蜂系统发育树Fig.1 Maximum parsimony tree based on the analysis of COⅠ gene sequences of the 8 Eretmocerus parasitoids


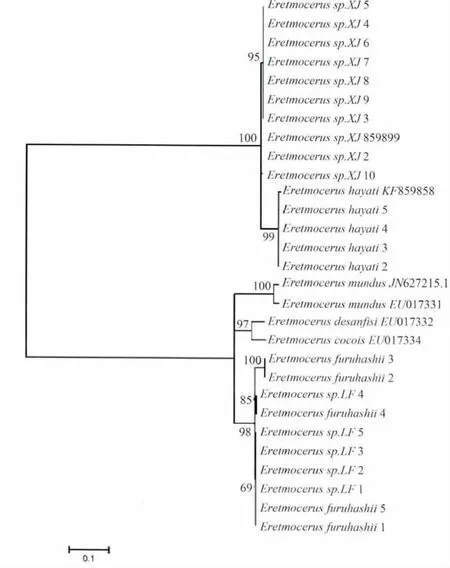
图2 利用最大似然法构建的8种桨角蚜小蜂系统发育树Fig.2 Maximum likelihood tree based on the analysis of COⅠ gene sequences of the 8 Eretmocerus parasitoids
2.3 种间杂交
桨角蚜小蜂新疆种群和海氏桨角蚜小蜂的初羽化处女蜂均不能产生雌性后代,表明两个寄生蜂种群均无孤雌产雌能力;两种寄生蜂间能够成功杂交,并能产生具有生殖能力的雌性后代,且杂交后寄生蜂雌蜂生殖力 (F3,76=1.28,P=0.2878,表3)和后代性比均没有显著性差异(F1,37=0.33,P=0.5686,表 3),表明寄生蜂种群间不具有生殖隔离特点。

表3 海氏桨角蚜小蜂与未知桨角蚜小蜂新疆种群的杂交结果Table 3 The results of the crossing tests between Eretmocerus hayati and Eretmocerus sp.XJ

续上表
3 结论与讨论
准确鉴定天敌的种类是生物防治得以成功应用的基础,对天敌种类的选择、适时释放以及效果评价等具有重要意义。多数寄生性天敌昆虫及其寄主,个体微小,形态相似,习性相近,且分布广泛,具有多型多态现象。因此借助一般的形态学方法进行种类鉴定往往比较困难,而结合分子生物学技术和生态杂交实验可以使上述问题得到解决 (Pinto,1998;De Barro et al.,2000)。
随着基因测序技术的飞速发展及成本的进一步降低,利用基因序列比对来快速鉴定物种的技术在膜翅目昆虫中得到广泛应用。De Barro et al.(2000)通过将核糖体基因的28 s区段、ITS(internal transcribed spacer,基因转录间隔区)区段以及线粒体COⅡ基因与外部形态相结合成功证实在澳大利亚存在3个桨角蚜小蜂种。Polaszek et al.(2004)通过将13个恩蚜小蜂近似种群的核糖体基因28 s(D2区域)序列与外部形态相结合证明:Encarsia californica和 E.dispersa为新种,而E.brasiliensis(Hempel)与E.bispida DeSantis为同种异名。Rugman-Jones et al.(2009)通过分析短背茧蜂属Psyttalia(茧蜂科:蝇茧蜂亚科)寄生蜂的28 s D2和COⅠ基因成功鉴定并区分10个来源于不同地区的相似复合种。利用COⅠ基因序列鉴定物种技术 (DNA条形码技术)的有效性必须满足两个条件:两个物种具有独特的DNA序列和种间基因差异应远大于种内差异 (Hebert et al.2004)。同时,Hebert et al.(2003)指出当种间差异小于0.02时,可以判定两者为同种。本研究表明在8个桨角蚜小蜂样本利用最大简约法和最大似然法构建的系统发育树上,所有已知种均各自聚成了一个独立分支。其中,桨角蚜小蜂廊坊种群与古桥桨角蚜小蜂聚为一支,而且种间遗传距离为0.011,本研究初步推测两者为同种。桨角蚜小蜂新疆种群与海氏桨角蚜小蜂分别聚为不同分支,但是种群间支持率达100,而且种群间种间遗传距离0.024,可定为近似种或同种。
种间杂交是鉴定相似种的重要辅助手段在膜翅目昆虫中广泛的应用 (Pinto,1998)。杂交实验显示,海氏桨角蚜小蜂种群能够与桨角蚜小蜂新疆种群成功杂交,且杂交后能产雌性后代。这进一步证明相似种海氏桨角蚜小蜂与桨角蚜小蜂新疆种为同种寄生蜂。相似的,Pinto et al.(2003)通过对北美洲两种难以从形态上鉴定和区分的赤眼蜂Trichogramma minutum Riley和Trichogramma platneri Nagarkatti间进行了103对种内和种间的杂交试验证明两种寄生蜂具有较强的生殖隔离水平,可以定义为不同的物种。Hunter et al.(1996)研究发现来源于亚利桑那,加利福尼亚和德克萨斯的三个桨角蚜小蜂本地种群雌蜂具有相似的形态特征,区分非常困难。然而,亚利桑那和加利福尼亚种群间能成功杂交,而与德克萨斯种群间却存在明显的生殖隔离。基于这个结论及对三种群寄生蜂雄峰特征的分析,Rose and Zolnerowich(1997)将三个不同种群分别鉴定命名为Eretmocerus eremicus(Arizona and California)和Eretmocerus tejanus(Texas)。然而,由于对新疆种桨角蚜小蜂的起源及传入方式并不是很清楚,我们暂时只能称之为海氏桨角蚜小蜂新疆自然发生种群。
另外,由于部分寄生蜂会营孤雌生殖(Werren,1997;Zchori-Fein et al.,2001),有些桨角蚜小蜂属寄生蜂也有此特性。比如:De Barro et al.(2000)在澳大利亚发现一种蒙氏桨角蚜小蜂Eretmocerus mundus的孤雌生殖品系。Rose and Zolnerowich(2003)在美国也发现了一种孤雌品系的桨角蚜小蜂,但是并没有进一步对其鉴定。因此,我们在杂交试验中设计了处女蜂处理。研究结果显示,海氏桨角蚜小蜂两个种群的处女蜂均不具有产雌能力,不营孤雌产雌生殖,不会对海氏桨角蚜小蜂种群间杂交结果产生影响。
目前对利用COⅠ基因序列鉴定物种的技术还存在一些问题和争议。有人质疑单个短片段的序列不能提供物种水平上的可靠信息,所以结合种间杂交试验来共同鉴定未知桨角蚜小蜂,不仅可以提高鉴定准确度,更能一定程度上弥补分子鉴定手段可能存在的缺陷。利用COⅠ基因序列分析种群间遗传距离,进而选取遗传距离最近 (接近判定为同种的水平,0.02)的种群进行杂交实验,验证是否为同种。这种研究方法可以为其他个体微小,形态类似昆虫的快速鉴定提供参考。尽管还不清楚这种寄生蜂从何处以何种方式传入我国,但是他们能够在自然条件如此恶劣和特殊的新疆(干旱,昼夜温差大等)地区建立种群并大范围发生,预测这种寄生蜂对极端气候具有很强的适应能力。因此,围绕此种寄生蜂对烟粉虱的生防控制潜力的研究将成为下一步的研究重点。
References)
Abuduhani R,Abulimiti M,Jamali R,et al.Population dynamics and spatial distribution of Bemisia tabaci and dominant parasitic wasp Eretmocerus sp.from the field of Jujube intercropping with cotton[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,2013,50(10):1842-1849.[热孜万古丽·阿布都哈尼,买合甫皮古丽·阿不力米提,热孜万古丽·加马力,等.枣棉套作田烟粉虱及优势寄生蜂桨角蚜小蜂的种群动态及空间分布规律[J].新疆农业科学,2013,50(10):1842-1849]
Billah MK,Kimani-Njogu SW,Wharton RA,et al.Cross mating studies among five fruit fly parasitoid populations:potential biological control implications for tephritid pests[J].Biocontrol,2008,53:709-724.
Brown JK,Frohlich DR,Rosell RC.The sweetpotato or silverleaf whiteflies:Biotypes of Bemisia tabaci or a species complex [J].Annual Review of Entomology,1995,40:511-534.
Chen ZX,Gu Y.Study on application of COⅠgene in the Homoptera Aphididae[J].Journal of Qingdao Agricultural University(Natural Science),2012,29:261-266.[陈占秀,顾耘.线粒体COⅠ基因在同翅目蚜科昆虫种类鉴定中的应用研究[J].青岛农业大学学报 (自然科学版),2012,29:261-266]
Dai JX,Zhang DZ.Discussion on the phylogeny of partial Chrysomelidae insects based on COⅠ gene sequences[J].Journal of Ningxia Univerisity(Natural Science Edition),2010,31(1):78-81.[代金霞,张大治.从COⅠ基因序列探讨叶甲科部分昆虫的系统关系 [J].宁夏大学学报 (自然科学版),2010,31(1):78-81]
De Barro PJ,Driver F,Naumann ID,et al.Descriptions of three species of Eretmocerus Haldeman(Hymenoptera:Aphelinidae)parasitising Bemisia tabaci(Gennadius)(Hemiptera:Aleyrodidae)and Trialeurodes vaporariorum(Westwood)(Hemiptera:Aleyrodidae)in Australia based on morphological and molecular data[J].Australian Journal of Entomology,2000,39(4):259-269.
De Barro PJ,Liu SS,Boykin LM,et al.Bemisia tabaci:a statement of species status[J].Annual Review of Entomology,2011,56:1-19.
Dozier HL.The identity of certain whitefly parasites of the genus Eretmocerus Hald.,with descriptions of new species(Hymenoptera:Aphelinidae)[J].Proceedings of the Entomological Society of Washington,1932,34:112-122.
Gao JC,Guo GJ,Guo YM,et al.Development and reproduction of Bemisia tabaci biotype B on wild and cultivated tomato accessions[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2011,31(23):7211-7217.[高建昌,郭广君,国艳梅,等.不同番茄材料对B型烟粉虱个体发育和繁殖能力的影响[J].生态学报,2011,31(23):7211-7217]
Kirk AA,Lacey LA,Brown JK,et al.Variation in the Bemisia tabaci s.l.species complex(Hemiptera:Aleyrodidae)and its natural enemies leading to successful biological control of Bemisia biotype B in the USA [J].Bulletin of Entomological Research,2000,90:317-327.
Kumar S,Tamura K,Nei M.MEGA3:Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment [J].Briefings in Bioinformatics,2004,5(2):150-163.
Haldeman SS.On four new species of Hemiptera of the genera Ploiaria,Chermes,Aleurodes,and two new Hymenoptera,parasitic on the last named genus[J].American Journal of Science,1850,IX:108-111.
Hebert PDN,Penton EH,Burns JM,et al.Ten species in one:DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the neotroical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2004,101(41):14812-14817.
Hebert PDN,Ratnasingham S,De Waard JR.Barcoding animal life:cytochrome coxidase subunit I divergences among closely related species[J].Proceedingsof the Royal Society B Biological Sciences,2003,270(1):S96-S99.
Huangfu WG,Dong S,Gao MQ,et al.Bemisia tabaci(Gennadius)and its hymenopteran parasitoids in Ningbo,China[J].Journal of Environmental Entomology,2010,32(3):375-379.[皇甫伟国,董帅,高明清,等.宁波地区烟粉虱及其寄生蜂调查[J].环境昆虫学报,2010,32(3):375-379]
Hunter MS,Antolin MF,Rose M.Courtship behavior,reproductive relationships,and allozyme patterns of three North American populations of Eretmocerus nr.californicus (Hymenoptera:Aphelinidae)parasitizing the whitefly Bemisia sp.,tabaci complex(Homoptera:Aleyrodidae)[J].Proceedings of the Entomological Society of Washington,1996,98:126-137.
Liang QY.Molecular phylogeny analysis of 9 species of Pentatoma(Hemioptera:Pentatomidae)inferred from COⅠgene sequence[J].Entomotaxonomia,2009,31(2):105-114.[梁秋英 .基于COⅠ基因序列的九种真蝽属昆虫的分子系统学研究 (半翅目:蝽科)[J].昆虫分类学报,2009,31(2):105-114]
Liu SS.Bemisia tabaci:a species complex [J].Chinese Journal of Biological Control,2012,28(4):466.[刘树生.烟粉虱是一个物种复合体 [J].中国生物防治学报,2012,28(4):466]
Luo C,Guo XJ,Yue M,et al.Host plant effects on the morphological and biological characteristics of Bemisia tabaci(Gennadius)biotype B[J].Biodiversity Science,2006,14(4):333-339.[罗晨,郭晓军,岳梅,等.寄主植物对B型烟粉虱形态学和生物学特性的影响 [J].生物多样性,2006,14(4):333-339]
Meng RX,Zhang QW,Liu XX.Progress in the application of biological control of Bemisia tabaci[J].Chinese Journal of Biological Control,2008,24(1):80-84.[孟瑞霞,张青文,刘小侠.烟粉虱生物防治应用现状 [J].中国生物防治,2008,24(1):80-84]
Miller SE.DNA barcoding and the renaissance of taxonomy[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2007,104(12):4775.
Naranjo SE,Ellsworth PC,Hagler JR.Conservation of natural enemies in cotton:role of insect growth regulators in management of Bemisia tabaci[J].Biological Control,2004,30:52-72.
Pascual S,Callejas C.Intra-and interspecific competition between biotypes B and Q of Bemisia tabaci(Hemiptera:Aleyrodidae)from Spain[J].Bulletin of Entomological Research,2004,94:369-375.
Pinto JD.Systematics of the North American species of Trichogramma Westwood(Hymenoptera:Trichogrammatidae)[M].Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Washington,1998,22:1-287.
Pinto JD, Platner GR, Stouthamer R. The systematic of the Trichogramma minutum species complex (Hymenoptera:Trichogrammatidae),a group of important North American biological control agents:the evidence from reproductive compatibility and allozymes [J].Biological Control,2003,27:167-180.
Pinto JD,Stouthamer R.Systematics of the Trichogrammatidae with emphasis on Trichogramma.In:Wajnberg E,Hassan SA,eds.Biological Control with Egg Parasitoids[M].Wallingford:CAB International,1994,1-36.
Polaszek A,Manzari S,Quicke DLJ.Morphological and molecular taxonomic analysis of the Encarsia meritoria species-complex(Hymenoptera, Aphelinidae), parasitoids of whiteflies(Hemiptera,Aleyrodidae)of economic importance[J].Zoologica Scripta,2004,33:403-421.
Qiao WN,Wan FH,Zhang AB,et al.Application of DNA barcoding technology for species identification of common thrips(Insect:Thysanoptera)in China [J].Acta Entomologia Sinica,2012,55(3):344-356.[乔玮娜,万方浩,张爱兵,等.DNA条形码技术在田间常用蓟马种类识别中的应用[J].昆虫学报,2012,55(3):344-356]
Rose M, Rosen D.Eretmocerus debachi n. sp. (Hymenoptera:Aphelinidae),an effective parasite of Parabemisia myricae(Homoptera:Aleyrodidae)[J].Israel Journal of Entomology,1991-1992,25-26:199-207.
Rose M, Zolnerowich G.Eretmocerus Haldeman (Hymenoptera:Aphelinidae)in the United States,with descriptions of new species attacking Bemisia(tabaci complex)(Homoptera:Aleyrodidae)[J].Proceedings of the Entomological Society of Washington,1997,99:1-27.
Rose M,Zolnerowich G.Eretmocerus picketti new species(Hymenoptera:Chalcidoidea:Aphelinidae),reared from Tetraleurodes acaciae(Quaintance)(Homoptera:Aleyrodidae:Aleyrodinae)[J].Pan.Pacific.Entomologist,2003,79:119-127.
Rose M,Zolnerowich G,Hunter MS.Systematics,Eretmocerus,and Biological Control.In:Gerling D,ed.Bemisia:Taxonomy,Biology,Damage and Management[M].Hants:Intercept,1995.
Ross KG,Gotzek D,Ascunce MS,et al.Species delimitation:a case study in a problematic ant taxon [J].Systematic Biology,2010,59(2):162-184.
Rugman-Jones PF,Wharton R,van Noort T,et al. Molecular differentiation of the Psyttalia concolor(Szepligeti)species complex(Hymenoptera:Braconidae)associated with olive fly,Bactrocera oleae(Rossi)(Diptera:Tephritidae),in Africa[J].Biological Control,2009,49:17-26.
Smith MA,Fisher BL,Hebert PDN.DNA barcoding for effective biodiversity assessment of a hyperdiverse arthropod group:the ants of Madagascar[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London,Series B,Biological Sciences,2005,360(1462):1825-1834.
Stouthamer R, Jochemsen P, Platner GR, et al. Crossing incompatibility between Trichogramma minutum and T.platneri(Hymenoptera:Trichogrammatidae):Implications for application in biological control[J].Environmental Entomology,2000,29(4):832-837.
Tamura K,Dudley J,Nei M,et al.MEGA 4:Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis(MEGA)software version 4.0 [J].Molecular Biology and Evolution,2007,24(8):1596-1599.
Teng X,Wan FH,Chu D.Bemisia tabaci Biotype Q dominates other biotypes across China[J].Florida Entomologist,2010,93(3):363-368.
Tian H,Li XF,Wan FH,et al.Identification of Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley(Heimiptera:Pseudococcidae)with species-specific COⅠ(SS-CO Ⅰ )primers[J].Acta Entomologia Sinica,2013,56(6):689-696.[田虎,李小凤,万方浩,等.利用种特异性COⅠ引物 (SS-COⅠ)鉴别扶桑绵粉蚧 [J].昆虫学报,2013,56(6):689-696]
Wan FH, Zhang GF, Liu SS, et al. Invasive mechanism and management strategy of Bemisia tabaci(Gennadius)biotype B:progress report of 973 program on invasive alien species in China[J].Science in China Series C:Life Science,2009,25:88-95.
Wang JF,Qiao GX. Application of DNA barcoding to Aphidinea(Insecta:Hemiptera)studies[J].Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica,2007,32(1):153-159.[王剑峰,乔格侠.DNA条形编码在蚜虫类昆虫中的应用[J].动物分类学报,2007,32(1):153-159]
Wang JH,Zhang F,Li YX.Diversity of species and reproductive mode of Bemisia tabaci parasitoids[J].Chinese Journal of Biological Control,2011,27(1):115-123.[王继红,张帆,李元喜.烟粉虱寄生蜂种类及繁殖方式多样性[J].中国生物防治,2011,27(1):115-123]
Werren JH.Biology of Wolbachia[J].Annual Review of Entomology,1997,42:587-609.
Xu HY, Yang NW, Wan FH. Competitive interactions between parasitoids provide new insight into host suppression[J].PLoS ONE,2013,8(11):e82003.
Yang NW,Wan FH.Host suitability of different instars of Bemisia tabaci biotype B for the parasitoid Eretmocerus hayati[J].Biological Control,2011,59(2):313-317.
Yang NW,Ji LL,Lövei GL,et al. Shifting preference between oviposition vs.host-feeding under changing host densities in two Aphelinid parasitoids[J].PLoSONE,2012,7(7):e41189.
Yang NW,Zang LS,Wang S,et al.Biological pests management by predators and parasitoids in greenhouse vegetable in China[J].Biological Control,2014,92-102.
Yang CH,Han HL,Chi MY,et al.Species identification of Noctuidae moths(Insecta:Lepidoptera)from Baihuashan,Beijing,China with DNA barcoding [J].Acta Entomologica Sinica,2012,55(9):1082-1092.[杨聪慧,韩辉林,等.DNA条形码技术在北京百花山地区夜蛾科物种鉴定中的应用[J].昆虫学报,2012,55(9):1082-1092]
Yeates DK,Seago A,Nelson L, et al. Integrative taxonomy,or iterative taxonomy[J].Systematic Entomology,2011,36(2):209-217.
Zheng FS,Du YZ,Wang ZJ,et al.Molecular phylogeny of Galerucella spp.(Coleoptera:Chrysomelidae:Galerucinae)based on mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I gene[J].Acta Entomologica Sinica,2007,50(5):501-507.[郑福山,杜予洲,王志杰,等.基于线粒体COⅠ基因序列的小萤叶甲属部分种类分子系统学研究 (鞘翅目:叶甲科:萤叶甲亚科)[J].昆虫学报,2007,50(5):501-507]
Zhang GF,Liu WX,Guo JY,et al.Species-specific COⅠ primers for rapid identification of Tuta absoluta(Meyrick),a significant,potential alien species[J].Journal of Biosafety,2013,22(2):80-85.[张桂芬,刘万学,郭建洋,等.重大潜在入侵害虫番茄潜叶蛾的SS-COⅠ快速检测技术[J].生物安全学报,2013,22(2):80-85]
Zhang GF,Meng XQ,Min L,et al.Rapid diagnosis of the invasive species,Frankliniella occidentalis(Pergande):a species-specific COⅠ marker[J]. Journal of Applied Entomology,2011,136(6):410-420.
Zchori-Fein E,Gottlieb Y,Kelley SE,et al.A newly discovered bacterium associated with parthenogenesis and a change in host selection behavior in parasitoid wasps[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2001,98:12555-12560.
