二甲双胍对多囊卵巢综合征患者血清同型半胱氨酸水平影响的系统评价
2015-06-06肖西悦曾天舒陈璐璐
孔 雯, 肖西悦, 曾天舒, 陈璐璐△
华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院 1内分泌科 2妇产科,武汉 430022
二甲双胍对多囊卵巢综合征患者血清同型半胱氨酸水平影响的系统评价
孔 雯1, 肖西悦2, 曾天舒1, 陈璐璐1△
华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院1内分泌科2妇产科,武汉 430022
目的 系统评价二甲双胍对多囊卵巢综合征(polycystic ovary syndrome,PCOS)患者血清同型半胱氨酸水平的影响。方法 以“metformin”、“PCOS” 、“ homocysteine”为关键词全面检索SCI、PUBMED,EMBASE,Elsevier数据库,筛选出二甲双胍治疗多囊卵巢综合征文献进行Meta分析,比较二甲双胍治疗前后血清同型半胱氨酸水平的改变,结果以加权均数差(WMD)及95%可信区间(CI)表示。结果 共纳入8项研究。Meta分析结果显示二甲双胍明显降低多囊卵巢综合征患者同型半胱氨酸水平[WMD=-2.29,95%CI=(-2.65,-1.94),P<0.05]。亚组分析结果提示:二甲双胍治疗时程达3个月则可显著降低患者血清同型半胱胺酸水平,继续延长治疗时间并不会进一步降低血清同型半胱胺酸水平。此外,肥胖的PCOS患者在二甲双胍治疗后血清同型半胱氨酸水平下降更明显。结论 二甲双胍治疗能降低多囊卵巢综合征患者血清的同型半胱胺酸水平。
多囊卵巢综合征; 同型半胱氨酸; 二甲双胍; Meta 分析
多囊卵巢综合征(polycystic ovary syndrome,PCOS)是一种最常见的妇科内分泌疾病,影响着至少5%~10%的育龄期女性[1]。二甲双胍是一种能够改善PCOS患者代谢和内分泌紊乱的胰岛素增敏剂,被广泛应用于PCOS的治疗[2]。但有报道指出,长期服用二甲双胍的2型糖尿病患者可出现高同型半胱氨酸血症[3-4]。为了明确二甲双胍对PCOS患者同型半胱氨酸水平的影响,本研究搜集国内外有关二甲双胍治疗PCOS 的研究进行Meta分析,探讨二甲双胍治疗PCOS对血清同型半胱氨酸水平的影响,阐明二甲双胍与血清同型半胱氨酸水平之间的关系。
1 资料与方法
1.1 文献检索
以“polycystic ovary syndrome”、“metformin”、“homocysteine”为关键词检索SCI、PUBMED,EMBASE,Elsevier数据库,检索日期截止至2015年7月1日。
1.2 文献选择
纳入标准:①研究对象为多囊卵巢综合征;②年龄>18岁;③干预措施为接受二甲双胍治疗;④以用药前后脂联素水平为主要评价指标。排除标准:①其他药物联合二甲双胍治疗;②不能提供二甲双胍治疗前后的血清同型半胱氨酸值;③重复发表的文章(只选择最近发表的1篇);④综述及基础研究。
1.3 数据提取与方法学质量评价
由2名研究者独立进行文献筛选、数据提取和质量评价,而后交叉核对,必要时联系原文作者确定试验的实施过程,如遇分歧讨论解决。提取的资料项目包括一般信息(作者、发表年份等),血清同型半胱氨酸值,平均年龄,平均体质量指数(BMI),人数及治疗时间。
1.4 统计与分析
采用R软件进行统计分析。采用χ2检验对纳入文献进行异质性检验,若P<0.1各研究间存在异质性,则采用随机效应模型。反之,则采用固定效应模型进行合并分析。本次Meta分析涉及数据为数值变量资料,选择加权均数差(WMD)为合并统计量,结合95%置信区间(95%CI)进行分析。并以二甲双胍的用药疗程(短于或等于3个月和长于3个月)、患者BMI(BMI<25和≥25)进行亚组分析。此外,二甲双胍治疗对患者BMI的影响也进行了分析,以明确其可能的作用途径。
2 结果
2.1 文献检索结果
通过文献检索获得可能相关文献13篇。其中2篇文献为二甲双胍联合叶酸或维生素B12治疗,故未纳入。3篇文献仅用图表表明同型半胱氨酸的改变,无具体数值,与作者联系也无回信。最终纳入分析的研究为8项[5-12],纳入研究的基本特征见表1。
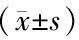
表1 纳入本次Meta分析8项研究的PCOS患者基本特征
2.2 Meta分析结果
2.2.1 同型半胱氨酸水平分析结果 表1纳入的8项研究,比较了PCOS患者应用二甲双胍前后同型半胱氨酸水平的变化,共159例。各研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.3,I2=16%),采用固定效应模型。结果显示,二甲双胍治疗后PCOS患者同型半胱氨酸水平显著降低[WMD=-2.29,95%CI(-2.65,-1.94),P<0.05],见图1。
2.2.2 亚组分析 ①二甲双胍的用药疗程小于或等于3个月的亚组同型半胱氨酸水平明显下降,[WMD=-2.30,95%CI(-2.67,-1.94),P<0.05]。治疗时间长于3个月的亚组同型半胱氨酸水平并未更进一步下降[WMD=-2.06,95%CI(-3.75,-0.37),P<0.05]。即二甲双胍可显著降低PCOS患者同型半胱氨酸水平,但其程度并无时间依赖性。见图2。
②平均BMI小于或等于25 kg/m2的亚组同型半胱氨酸水平无明显改变,[WMD=0.28,95%CI(-2.08,2.64),P>0.05]。平均BMI大于25的亚组同型半胱氨酸水平下降更显著[WMD=-2.35,95%CI(-2.71,-1.99),P<0.05]。即二甲双胍治疗后,仅肥胖的PCOS患者同型半胱氨酸的水平下降明显。见图3。
2.2.3 二甲双胍对BMI的影响 此外,将PCOS患者服用二甲双胍治疗前后的BMI进行比较分析,结果发现二甲双胍并未显著减轻患者BMI[WMD=0.52,95%CI(-0.15,1.19),P>0.05],见图4。
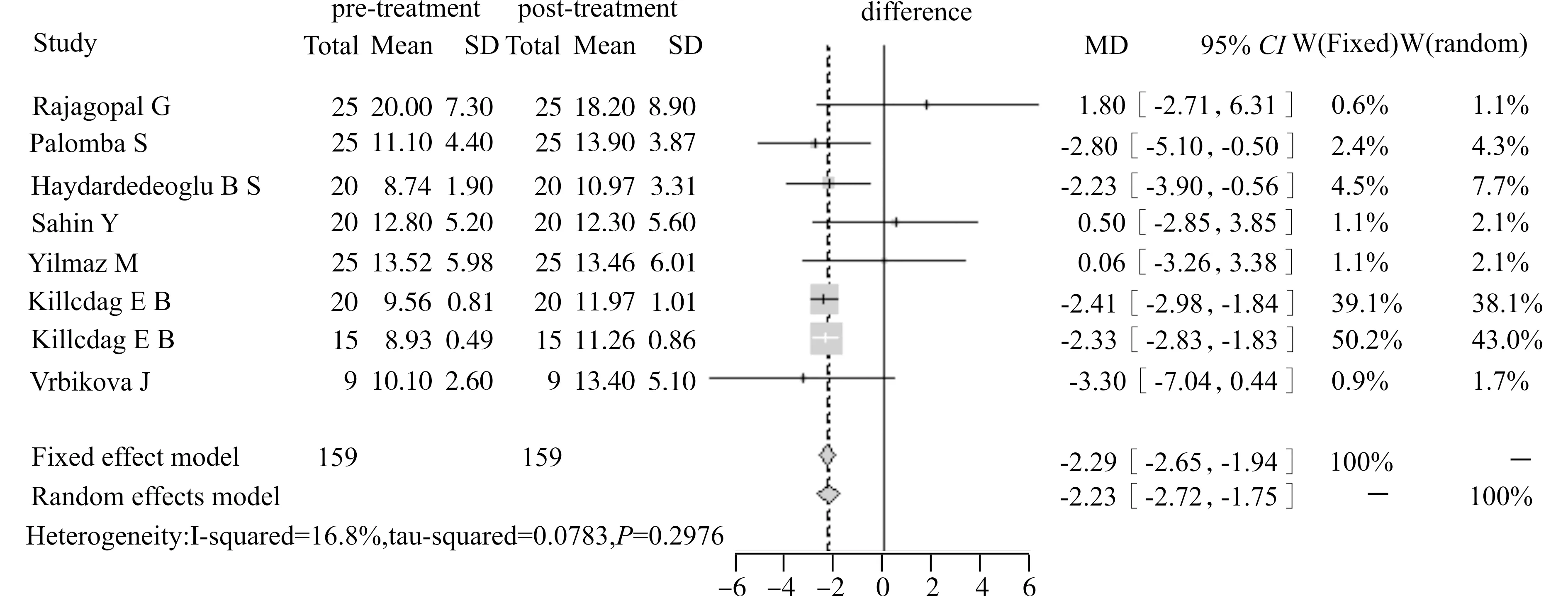
图1 8项研究中二甲双胍治疗PCOS患者前后同型半胱氨酸水平变化的Meta分析(森林图)Fig.1 Meta-analysis of homocysteine levels before and after metformin therapy in the eight included studies (forest plot)
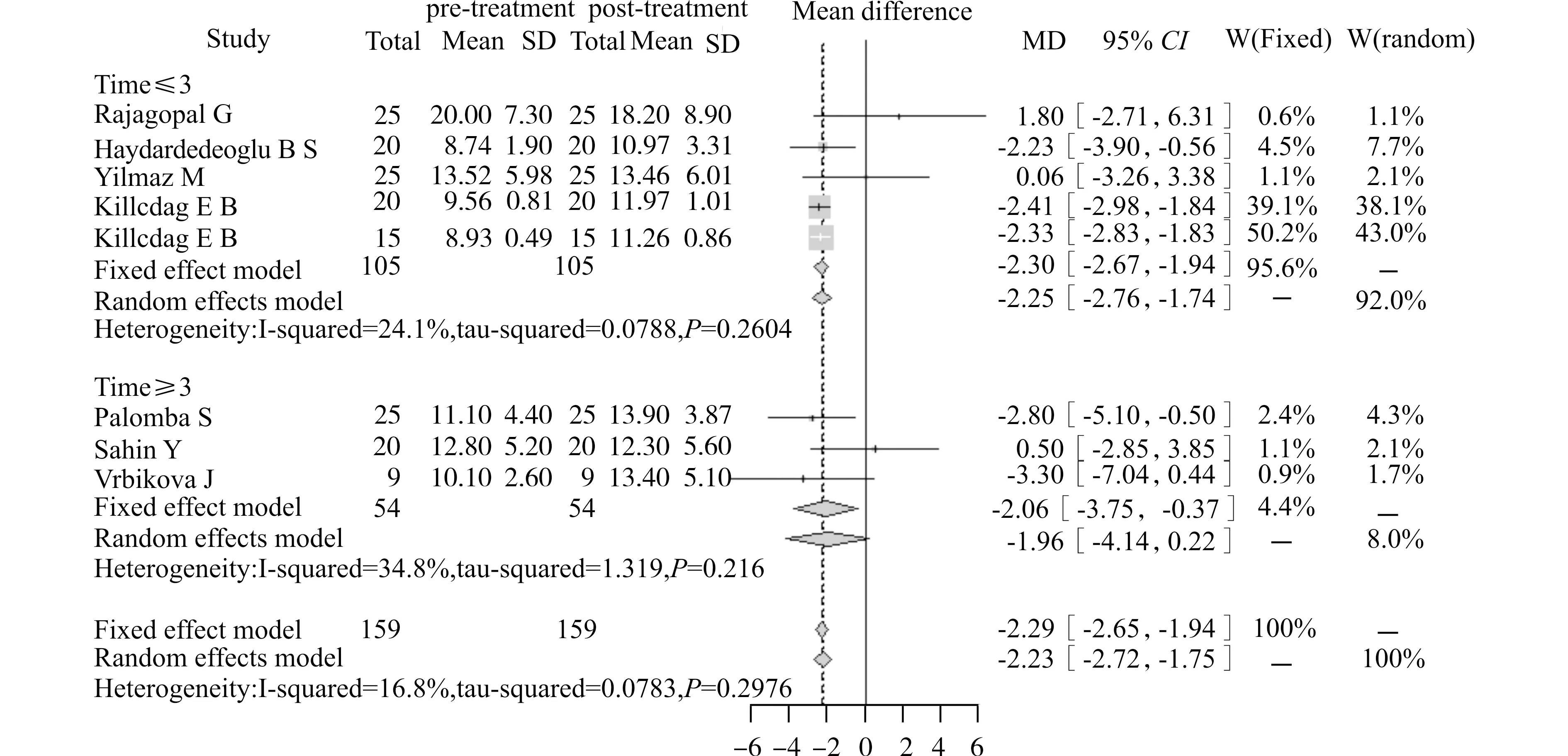
图2 二甲双胍治疗疗程的亚组分析Fig.2 Subgroup analysis of the duration of metformin therapy
图3 二甲双胍治疗PCOS患者平均BMI的亚组分析Fig.3 Subgroup analysis of the average BMI of PCOS patients after metformin therapy
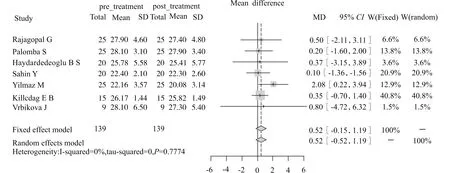
图4 8项研究中二甲双胍治疗前后患者BMI的改变(森林图)Fig.4 Meta-analysis of the changes of BMI in PCOS patients before and after metformin treatment in the eight included studies (forest plot)
2.3 偏倚分析
对纳入文献绘制漏斗图。结果显示,图中散点集中分布在无效线两侧,漏斗图基本对称,提示纳入的文献存在发表偏倚的可能性小,见图5。
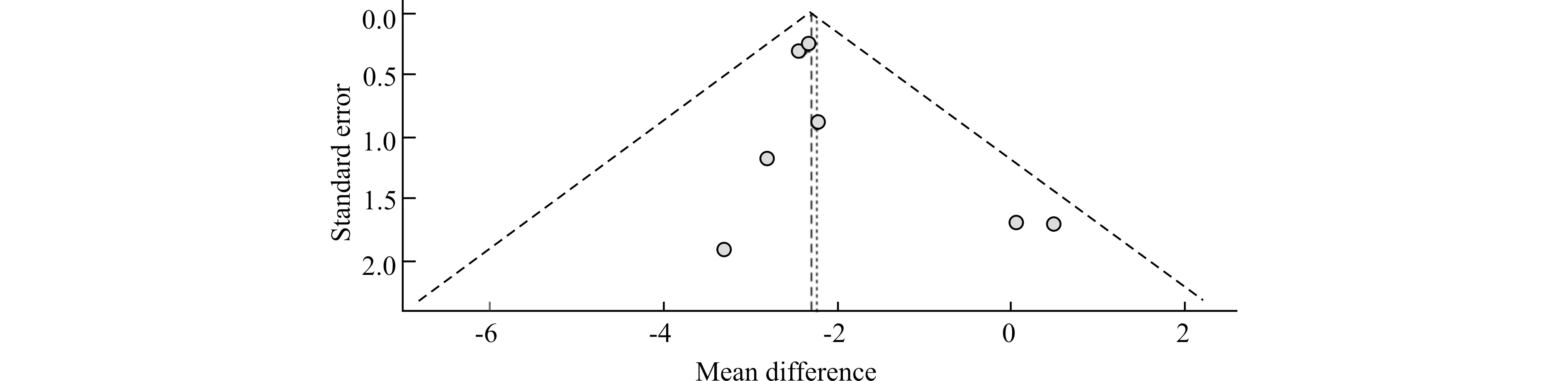
图5 8项研究中二甲双胍治疗PCOS患者前后同型半胱氨酸水平变化的Meta分析(漏斗图)Fig.5 Meta-analysis of homocysteine levels before and after metformin therapy in the eight included studies (funnel plot)
3 讨论
近来,高半胱氨酸血症被认为是心血管疾病的独立危险因子[13-16],PCOS患者也被发现有增加心血管疾病的风险。而且,高同型半胱氨酸血症与流产、低体重新生儿、妊娠期糖尿病等孕期不良结局密切相关[17-19]。因此,越来越多的学者开始研究PCOS与高同型半胱氨酸血症的关系[9,20-21]。二甲双胍虽然是治疗多囊卵巢综合征的首选药物,但对同型半胱氨酸水平的影响不清楚。因此,本研究系统评价了相关文献,纳入8项研究。结果显示,二甲双胍治疗能显著改善PCOS患者高同型半胱氨酸血症。大量研究也发现长期的二甲双胍治疗并不足以导致维生素B12及叶酸的缺乏,更不会造成高同型半胱氨酸血症[22-23]。其原因可能是机体中约50%的维生素B12均储存于肝脏,通过胆汁排泄。而排泄的维生素B12又经过肠肝循环被有效吸收。因此,维生素B12的浓度在较长的时间内可以维持基本不变。
为明确高同型半胱氨酸血症的改善与二甲双胍治疗疗程的关系,本研究进行了时间疗程亚组分析,结果发现其疗效与二甲双胍治疗时间并无线性关系。近来,Palomba等[6]的研究也发现二甲双胍改善胰岛素抵抗的作用在使用12个月后开始减弱。提示,二甲双胍可能并不适合PCOS患者作为单药长期使用。
PCOS患者一半以上肥胖,为了解二甲双胍是否对非肥胖PCOS患者一样有效,本研究进行了BMI亚组分析。结果发现,二甲双胍治疗仅能降低肥胖PCOS患者的同型半胱氨酸水平,但并不改变患者的BMI水平。说明二甲双胍改善高同型半胱氨酸血症并不是通过减轻患者体重达到的。Yilmaz等[9]的研究也发现,持续6个月给予POCS患者每天2 550 mg二甲双胍并不减轻患者体重。但二甲双胍被许多实验证实有减轻体重的作用[24-26]。众多研究结果不一致的原因可能在于二甲双胍仅对约一半的PCOS患者有效[27]。
系统评价纳入的8个研究均为自身前后对照,发生偏倚风险较低,故所得结论较可靠。但文章存在局限性。首先,文章检索时限定文献语种为英文;其次研究纳入文章数量及样本量有限。
综上所述,二甲双胍可以显著降低PCOS患者同型半胱氨酸水平,但仍需开展高质量、大样本、长期的研究进一步论证。
[1] Glintborg D,Andersen M.An update on the pathogenesis,inflammation,and metabolism in hirsutism and polycystic ovary syndrome[J].Gynecol Endocrinol,2010,26(4):281-296.
[2] Naderpoor N,Shorakae S,de Courten B,et al.Metformin and lifestyle modification in polycystic ovary syndrome:systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Hum Reprod Update,2015,21(5):560-574.
[3] Liu Q,Li S,Quan H,et al.Vitamin B12 status in metformin treated patients:systematic review[J].PLoS One,2014,9(6):e100379.
[4] Bouchoucha M,Uzzan B,Cohen R.Metformin and digestive disorders[J].Diabetes Metab,2011,37(2):90-96.
[5] Rajagopal G,Reddy A P,Venkata Harinarayan C,et al.Effect of lifestyle modification and metformin therapy on emerging cardiovascular risk factors in overweight Indian women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J].Metab Syndr Relat Disord,2012,10(4):273-279.
[6] Palomba S,Falbo A,Russo T,et al.Insulin sensitivity after metformin suspension in normal-weight women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2007,92(8):3128-3135.
[7] Haydardedeoglu B,Simsek E,Kilicdag E B,et al.Metabolic and endocrine effects of metformin and metformin plus cyclic medroxyprogesterone acetate in women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J].Int J Gynaecol Obstet,2009,105(1):32-35.
[8] Sahin Y,Unluhizarci K,Yilmazsoy A,et al.The effects of metformin on metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors in nonobese women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J].Clin Endocrinol (Oxf),2007,67(6):904-908.
[9] Yilmaz M,Bukan N,Ayvaz G,et al.The effects of rosiglitazone and metformin on oxidative stress and homocysteine levels in lean patients with polycystic ovary syndrome[J].Hum Reprod,2005,20(12):3333-3340.
[10] Kilicdag E B,Bagis T,Tarim E,et al.Administration of B-group vitamins reduces circulating homocysteine in polycystic ovarian syndrome patients treated with metformin:a randomized trial[J].Hum Reprod,2005,20(6):1521-1528.
[11] Kilicdag E B,Bagis T,Zeyneloglu H B,et al.Homocysteine levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome treated with metformin versus rosiglitazone:a randomized study[J].Hum Reprod,2005,20(4):894-899.
[12] Vrbikova J,Bicikova M,Tallova J,et al.Homocysteine and steroids levels in metformin treated women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J].Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes,2002,110(2):74-76.
[13] Petrisor B A,Keating J,Schemitsch E.Grading the evidence:levels of evidence and grades of recommendation[J].Injury,2006,37(4):321-327.
[14] Guzick D S,Talbott E O,Sutton-Tyrrell K,et al.Carotid atherosclerosis in women with polycystic ovary syndrome:initial results from a case-control study[J].Am J Obstet Gynecol,1996,174(4):1224-1232.
[15] Pierpoint T,McKeigue P M,Isaacs A J,et al.Mortality of women with polycystic ovary syndrome at long-term follow-up[J].J Clin Epidemiol,1998,51(7):581-586.
[16] Wild S,Pierpoint T,McKeigue P,et al.Cardiovascular disease in women with polycystic ovary syndrome at long-term follow-up:a retrospective cohort study[J].Clin Endocrinol (Oxf),2000,52(5):595-600.
[17] de la Calle M,Usandizaga R,Sancha M,et al.Homocysteine,folic acid and B-group vitamins in obstetrics and gynaecology[J].Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol,2003,107(2):125-134.
[18] Cermik D,Selam B,Taylor H S.Regulation of HOXA-10 expression by testosteroneinvitroand in the endometrium of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2003,88(1):238-243.
[19] Seghieri G,Breschi M C,Anichini R,et al.Serum homocysteine levels are increased in women with gestational diabetes mellitus[J].Metabolism,2003,52(6):720-723.
[20] Yarali H,Yildirir A,Aybar F,et al.Diastolic dysfunction and increased serum homocysteine concentrations may contribute to increased cardiovascular risk in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome[J].Fertil Steril,2001,76(3):511-516.
[21] Loverro G,Lorusso F,Mei L,et al.The plasma homocysteine levels are increased in polycystic ovary syndrome[J].Gynecol Obstet Invest,2002,53(3):157-162.
[22] Palomba S,Falbo A,Giallauria F,et al.Effects of metformin with or without supplementation with folate on homocysteine levels and vascular endothelium of women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J].Diabetes Care,2010,33(2):246-251.
[23] Heutling D,Schulz H,Nickel I,et al.Asymmetrical dimethylarginine,inflammatory and metabolic parameters in women with polycystic ovary syndrome before and after metformin treatment[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2008,93(1):82-90.
[24] Tan S,Hahn S,Benson S,et al.Metformin improves polycystic ovary syndrome symptoms irrespective of pre-treatment insulin resistance[J].Eur J Endocrinol,2007,157(5):669-676.
[25] Harborne L R,Sattar N,Norman J E,et al.Metformin and weight loss in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome:comparison of doses[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2005,90(8):4593-4598.
[26] Legro R S,Barnhart H X,Schlaff W D,et al.Clomiphene,metformin,or both for infertility in the polycystic ovary syndrome[J].N Engl J Med,2007,356(6):551-566.
[27] Kahn S E,Prigeon R L,McCulloch D K,et al.Quantification of the relationship between insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in human subjects.Evidence for a hyperbolic function[J].Diabetes,1993,42(11):1663-1672.
(2015-09-08 收稿)
Effect of Metformin on Homocysteine Levels in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome:An Meta-analysis
Kong Wen1,Xiao Xiyue2,Zeng Tianshu1etal
1DepartmentofEndocrinology,2DepartmentofGynecologyandObstetrics,UnionHospital,TongjiMedicalCollege,HuazhongUniversityofScienceandTechnology,Wuhan430022,China
Objective To systematically evaluate the effect of metformin therapy on serum homocysteine levels in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).Methods The SCI,PUBMED,EMBASE,and Elsevier databases were searched for relevant literatures concerning metformin therapy for meta-analysis,with key words “metformin”,“PCOS” and “homocysteine” used.The changes of homocysteine levels were compared between before and after metformin administration.Weighted mean differences (WMD) and 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) were calculated.Results A total of 8 studies were included.Meta-analysis showed that metformin administration decreased serum homocysteine concentrations in PCOS women [WMD=-2.29,95%CI=(-2.65,-1.94),P<0.05].Subgroup analysis exhibited that homocysteine was decreased after 3-month therapy,and it was no further reduced beyond 3 months.Meanwhile,the analysis also reveals that homocysteine levels were decreased significantly in obese PCOS patients after the therapy.Conclusion Metformin administration decreases serum homocysteine concentrations in PCOS women.
polycystic ovary syndrome; homocysteine; metformin; meta-analysis
R711.75
10.3870/j.issn.1672-0741.2015.05.010
孔 雯,女,1983年生,主治医师,E-mail:wenly-kong@163.com
△通讯作者,Corresponding author,E-mail: cheria_chen@126.com
