周剂量多西他赛联合顺铂与周剂量多西他赛联合奥沙利铂治疗晚期胃癌的临床研究
2015-01-04
兰州大学第二医院 VIP外科,甘肃 兰州 730000
周剂量多西他赛联合顺铂与周剂量多西他赛联合奥沙利铂治疗晚期胃癌的临床研究
王涛,赵磊,李榆,宋爱琳
兰州大学第二医院 VIP外科,甘肃 兰州 730000
背景与目的:已有研究证实,多西他赛联合顺铂(docetaxel plus cisplatin,DP)或多西他赛联合奥沙利铂(docetaxel plus oxaliplatin,DO)治疗晚期胃癌具有较好的疗效。本研究旨在观察周剂量多西他赛联合顺铂与周剂量多西他赛联合奥沙利铂一线治疗晚期胃癌的疗效及不良反应。方法:76例胃癌患者随机分为两组,每组38例,DP组多西他赛35 mg/m2,静脉滴注,第1、8天,顺铂60 mg/m2,静脉滴注,第1天,21 d为1个周期;DO组多西他赛35 mg/m2,静脉滴注,第1、8天,奥沙利铂120 mg/m2,静脉滴注,第1天,21 d为1个周期。结果:DP组总有效率为37%,中位无进展生存期为4.9个月,中位生存期为9.7个月;DO组总有效率为41%,中位无进展生存期为4.4个月,中位生存期为12.3个月。两组的总有效率(P=0.707)、中位无进展生存期(P=0.324)、中位生存期(P=0.581)差异均无统计学意义。两组的3/4级不良反应都是中性粒细胞减少,DP组恶心、呕吐发生率较高(P<0.05),而DO组周围神经病变发生率较高(P<0.05);两组贫血、血小板减少、脱发、腹泻和肝功能损害等不良反应差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:DP和DO一线治疗晚期胃癌的疗效及不良反应相仿,值得临床进一步研究。
胃癌;化疗;多西他赛;顺铂;奥沙利铂
胃癌的发病率居全世界恶性肿瘤的第4位,死亡率居第2位,在我国其死亡率居所有恶性肿瘤的第3位[1]。虽然早期检测可发现一部分患者,但多数患者就诊时往往已经为晚期或出现转移,需要姑息性化疗。尽管联合化疗比单药化疗能延长患者的生存时间,提高生活质量[2],但目前全球还没有标准的联合方案作为胃癌一线治疗的推荐方案。虽然多西他赛联合顺铂(docetaxel plus cisplatin,DP)方案一直被作为进展期胃癌的一个推荐方案,但因研究证实,奥沙利铂比顺铂的交叉耐药性[3]和毒性低,且不需要静脉水化。因此,多西他赛联合奥沙利铂(docetaxel plus oxaliplatin,DO)的方案已作为进展期胃癌新的治疗方法[4]。然而多西他赛与铂类的联合,标准的3周给药会导致较严重的骨髓抑制。先前的研究已经表明,对非小细胞肺癌和乳腺癌,多西他赛每周给药可减少血液毒性,但保留治疗效果[5-6]。同样,近期的Ⅲ期临床试验表明,奥沙利铂取代顺铂治疗进展期胃癌疗效更优且毒性更低[7]。因此,本研究旨在评估每周DP或DO方案治疗晚期胃癌的疗效和安全性。
1 资料和方法
1.1 临床资料
收集2011年1—12月兰州大学第二医院收治的76例胃癌患者,随机分为每周DP方案(DP组)和每周DO方案(DO组),每组38例。所有患者按AJCC第七版TNM分期均为Ⅳ期。纳入标准:①组织学证实为胃腺癌;②不能手术的局部晚期,复发或出现转移的患者;③PS评分0~2,血常规、肝肾功能正常,心电图无明显异常,无化疗禁忌证;④未行姑息性化疗,估计生存期≥3个月;⑤未行紫杉烷类(多西他赛和紫杉醇)药物治疗;⑥签署化疗知情同意书(表1)。
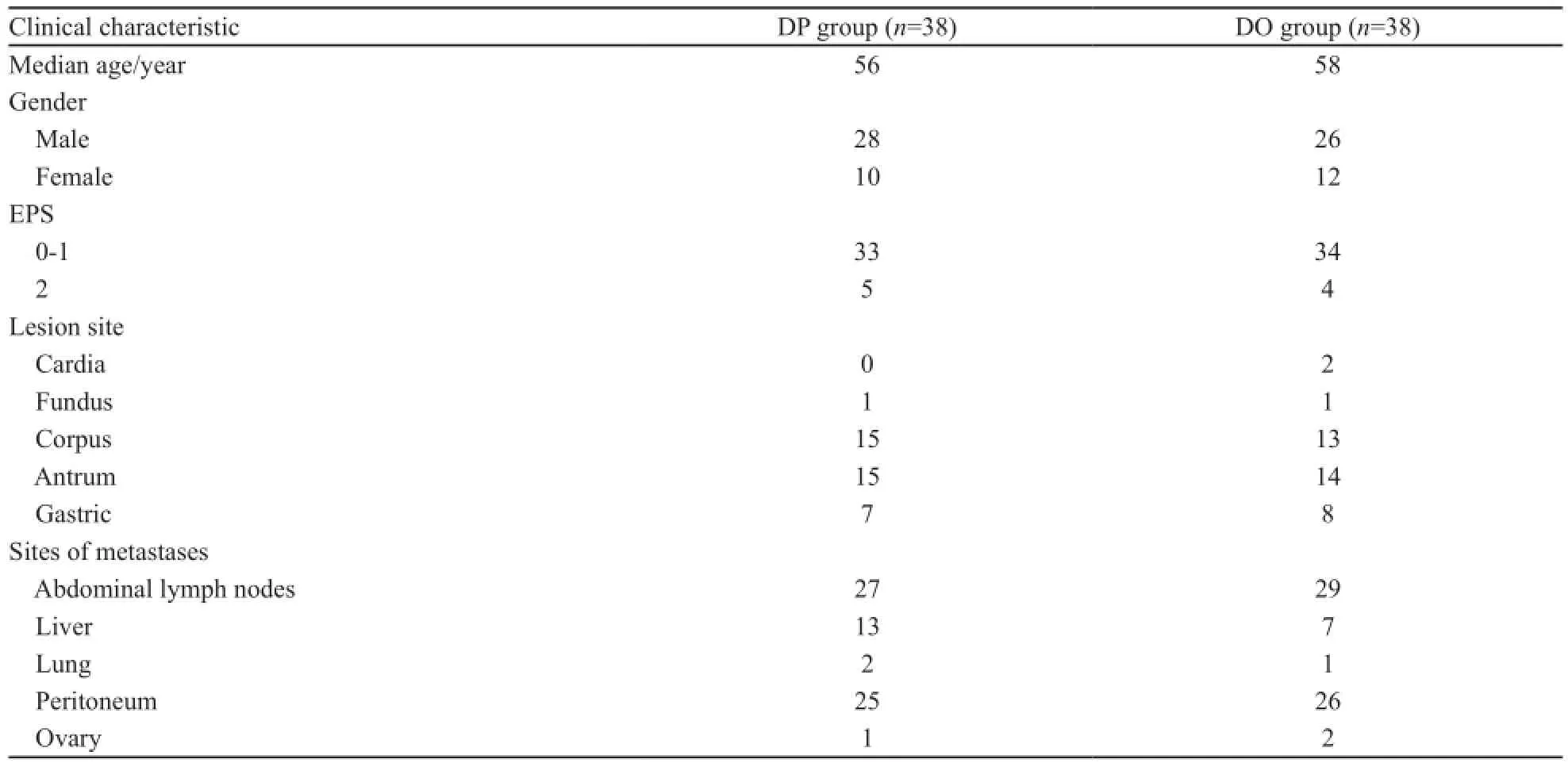
表1 两组患者的一般资料Tab. 1 The clinical characteristics of two groups
1.2 治疗方法
DP组:多西他赛35 mg/m2,静脉滴注,第1、8天;顺铂60 mg/m2,静脉滴注,第1天。21 d为1个周期。DO组:多西他赛35 mg/m2,静脉滴注,第1、8天;奥沙利铂120 mg/m2,静脉滴注,第1天。21 d为1个周期。每例患者在使用多西他赛前静脉给予10 mg地塞米松,以防止体液潴留及过敏反应。顺铂静脉输注前后水化,化疗期间常规止吐升白,每周复查血常规,每个周期化疗后复查肝、肾功能。
1.3 疗效及不良反应评价
近期客观疗效按WHO标准评价,分为完全缓解(complete remission,CR)、部分缓解(partial remission,PR)、稳定(stable disease,SD)、进展(progression disease,PD),有效率(response rate,RR)=(CR+PR)%,无进展生存期(progression-free survival,PFS)和总生存期(overall survival,OS)。依据美国国立癌症研究所不良反应事件通用标准3.0版评价不良反应。神经毒性反应按注射用奥沙利铂专用神经毒性反应分级法评定。
1.4 统计学处理
采用SPSS19.0版统计软件处理数据,计数资料比较用Fisher精确概率法,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 化疗完成情况
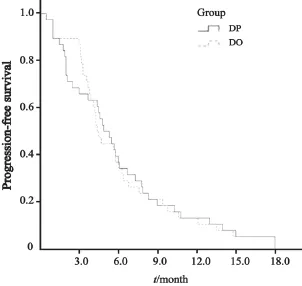
图1 两组无进展生存期比较Fig. 1 The progression-free survival of two groups
DP组化疗的中位周期数为3个(1~12个周期);DO组化疗的中位周期数为5个(范围1~8个周期)。
2.2 两组疗效比较
所有患者均可评价近期疗效。两组均无CR患者,DP组,中位PFS4.9个月(95%CI:3.5~6.3个月,图1):中位OS 9.7个月(95%CI:6.2~13.2个月)(图2);DO组:中位PFS 4.4个月(95%CI:3.8~5.0个月),中位OS 12.3个月(95%CI:8.5~16.1个月);两组RR的差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,表2)。
2.3 不良反应
两组的不良反应均能耐受,最常见的3级或4级血液学不良反应为中性粒细胞减少。DP组恶心、呕吐发生率较高(P<0.05),而DO组周围神经病变发生率较高(P<0.05)两组间其他如贫血、血小板减少、脱发、腹泻和肝功能损害等不良反应差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,表3)。
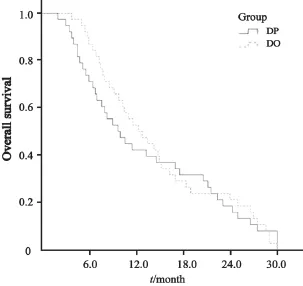
图2 两组总生存期比较Fig. 2 The overall survival of two groups

表2 两组患者疗效比较Tab. 2 The efficacy of two groups
3 讨 论
胃癌的发病率及死亡率较高,但其早期缺乏特异性表现,检出率低,多数患者就诊时已为进展期,治疗以手术为主,但失去手术机会和术后局部复发、远处转移的患者通常以全身联合化疗为主。现有的治疗方案,氟尿嘧啶类和铂类为基础的联合方案被广泛使用,但治疗效果仍然不理想。已有研究证实,多西他赛无论是单药还是用于联合化疗治疗进展期胃癌均有效[8-9]。Roth等[10]的Ⅱ期研究结果显示,DP方案每3周1次的化疗方案,治疗进展期胃癌的有效率为18%~56%,中位生存期为9~11个月。然而,用于治疗结直肠癌的奥沙利铂,也已证明在治疗进展期胃癌上是有效和安全的[11-13]。因此,DO方案被用于进展期胃癌。陈绍俊等[14]报道周剂量DO方案治疗48例晚期胃癌,有效率为56.5%,初治有效率为61.29%,复治有效率为47.06%,中位PFS为5.6个月,中位OS为11.8个月。邓文静等[15]报道DP方案治疗晚期胃癌的有效率为58.8%。本研究结果显示,两种化疗方案都具有明显的抗肿瘤活性,且其疗效和不良反应与国内外所报道的每3周多西他赛联合铂类治疗晚期胃癌的结果相仿。每3周多西他赛联合顺铂中位OS为10.5~11.0个月。在本研究中,DP方案组有相似的结果(中位PFS为4.9个月;位OS 9.7个月)。每3 周多西他赛联合奥沙利铂RR为34%~45%,中位OS为8.5~11.6个月,本研究中DO方案组亦有相似结果(RR为42%和中位OS为12.3个月)。然而每3周多西他赛联合顺铂方案,其骨髓抑制比较明显,尤其是在老年患者。之前的研究,每3周多西他赛联合顺铂的方案,3/4级中性粒细胞减少发生率为76%~85%。本研究中每周给药可降低严重中性粒细胞减少为45%。然而,每周多西他赛的给药比3周多西他赛给药其剂量强度相对增加,会导致患者感明显乏力,这表明每周多西他赛联合治疗方案在疗效和耐受性方面没有比3周多西他赛治疗方案有明显优势。本研究结果得到之前如非小细胞肺癌或乳腺癌的随机对照研究的支持。
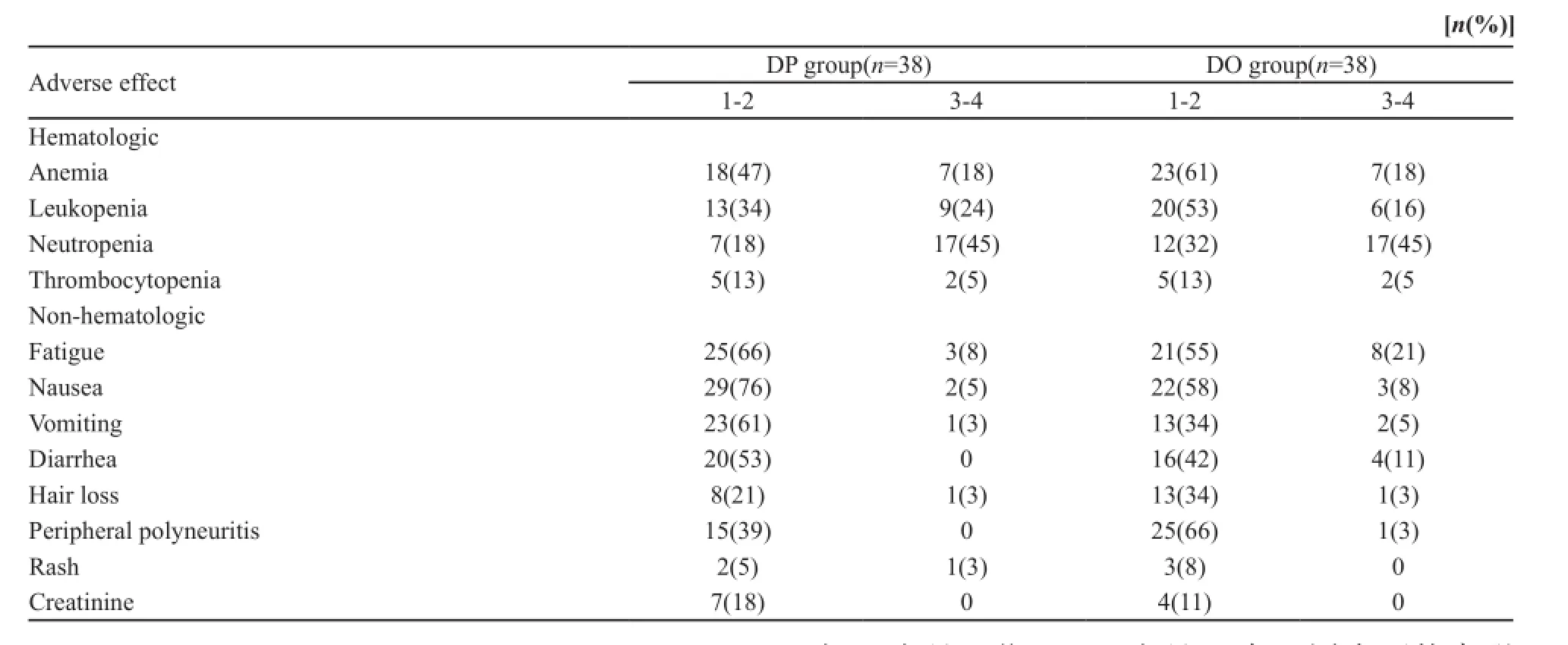
表3 两组患者的不良反应Tab. 3 Adverse effects of two groups
已有研究表明,奥沙利铂可以代替顺铂[16]。与顺铂相比,奥沙利铂的交叉耐药性和毒性较低[3],且不需要静脉水化。本研究结果显示,两组患者的生存率和不良反应发生率差异无统计学意义。DP组呕吐和肾毒性的发生率比DO组高,DO组外周神经病变发生率比DP组高,但DO组总体的不良反应比DP组低。总之,两种化疗方案治疗晚期胃癌的疗效和安全性虽然相似,但是否将多西他赛联合DO作为晚期胃癌的推荐方案或标准化疗方案,需要进一步研究及评估。
[参 考 文 献]
[1] 郑朝旭, 郑荣寿, 陈万青. 中国2009年胃癌发病与死亡分析[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2013, 22: 327-332.
[2] WAGNER A D, GROTHE W, HAERTING J, et al. Chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis based on aggregate data[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2006, 24(18): 2903–2909.
[3] RIXE O, ORTUZAR W, ALVAREZ M,et al. Oxaliplatin, tetraplatin, cisplatin, and carboplatin: spectrum of activity in drug-resistant cell lines and in the cell lines of the National Cancer Institute's Anticancer Drug Screen Panel[J]. Biochem Pharmacol,1996, 52(12): 1855–1865.
[4] RICHARDS D, MCCOLLUM D, WILFONG L, et al. PhaseⅡ trial of docetaxel and oxaliplatin in patients with advanced gastric cancer and/or adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction[J]. Ann Oncol, 2008, 19(1): 104–108.
[5] CHEN Y M, SHIH J F, PERNG R P, et al. A randomized trial of different docetaxel schedules in non-small cell lung cancer patients who failed previous platinum-based chemotherapy[J]. Chest, 2006, 129(4): 1031–1038.
[6] TABERNERO J, CLIMENT M A, LLUCH A, et al. A multicentre, randomised phase Ⅱ study of weekly or 3-weekly docetaxel in patients with metastatic breast cancer[J]. Ann Oncol, 2004, 15(9): 1358–1365.
[7] AL-BATRAN S E, HARTMANN J T, PROBST S. Phase Ⅲtrial in metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil, leucovorin plus either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: a study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2008, 26(9): 1435–1442.
[8] AJANI J A, MOISEYENKO V M, TJULANDIN S, et al. Clinical benefit with docetaxel plus fluorouracil and cisplatin compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil in a phase Ⅲ trial of advanced gastric or gastroesophageal cancer adenocarcinoma: the V-325 Study Group[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2007, 25(22): 3205-3209.
[9] NISHIYAMA M, WADA S. Docetaxel: its role in current and future treatments for advanced gastric cancer[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2009, 12(3): 132–141.
[10] ROTH A D, FAMIO N, STUPP R, et al. Docetaxel, cisplatin,and fluorouracil; docetaxel and cisplatin; and epirubicin, cisplatin, and fluorouracil as systemic treatment for advanced gastric carcinoma: a randomized phase Ⅱ trial of the Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research[J].J Clin Oncol, 2007, 25(22): 3217–3223.
[11] KIM G M, JEUNG H C, RHA S Y, et al. A randomized phaseⅡ trial of S-1-oxaliplatin versus capecitabine-oxaliplatin in advanced gastric cancer[J].Eur J Cancer, 2012, 48(4): 518–526.
[12] LORDICK F, LORENZEN S, STOLLFUSS J. Phase Ⅱ study of weekly oxaliplatin plus infusional fluorouracil and folinic acid (FUFOX regimen) as first-line treatment in metastatic gastric cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2005, 93(2): 190–194.
[13] LOUVET C, ANDRE T, TIGAUD J M, et al. Phase Ⅱ study of oxaliplatin fluorouracil, and folinic acid in locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer patients[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2002, 20(23): 4543–4548.
[14] 陈绍俊, 黄海欣, 李桂生. 周剂量多西他赛联合奥沙利铂治疗48例晚期胃癌[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2008, 18(10): 775-777.
[15] 邓文静, 余更生, 吕华珠, 等. 多西他赛联合顺铂治疗晚期胃癌的临床观察[J].辽宁医学院学报, 2014, 35(1): 24-26.
[16] CUNNINGHAM D, STARLING N, RAO S, et al. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2008, 358(1): 36–46.
Weekly docetaxel combined with cisplatin versus weekly docetaxel combined with oxaliplatin in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer
WANG Tao, ZHAO Lei, LI Yu, SONG Ailin (Department of VIP Surgery, the Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou Gansu 730000, China)
SONG ailin E-mail: 2015956568@qq.com
Background and purpose:It has confirmed that docetaxel, in combination with cisplatin or oxaliplatin have good effect in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer. This study in order to observe the clinical efficacy and adverse reaction of weekly docetaxel combined with cisplatin (DP) versus weekly docetaxel combined with oxaliplatin (DO) as the firrst-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer.Methods:A total number of 76 cases of advanced gastric cancer were randomly assigned 2 arms, 38 per arm. DP regimen group (docetaxel 35 mg/m2, ivgtt, dl, d8 combined with cisplatin 60 mg/m2, ivgtt, dl, repeated every 3 weeks) and DO regimen group(docetaxel 35 mg/m2, ivgtt, dl, d8 combined with oxaliplatin 120 mg/m2ivgtt, dl, repeated every 3 weeks).Results:No significant difference was found between DP regimen group and DO regimen group on the objective RR(37% vs 41%),PFS (4.9 vs 4.4 months) and OS (9.7 vs 12.3 months). The main grade 3 or 4 toxicity in the DP and DO groups was neutropenia, DO was less associated with nausea and vomiting, but more associated with peripheral neuropathy than DP group. No signifcant difference was found between DP regimen group and DO regimen group on the anemia, thrombocytopenia, diarrhea, alopecia (P>0.05).Conclusion:Weekly docetaxel combined with cisplatin (DP) shows similar effcacy and toxicity compared with weekly docetaxel combined with oxaliplatin (DO) as the frst-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer and worthy of further study.
Gastric cancer; Chemotherapy; Docetaxel; Cisplatin; Oxaliplatin
10.3969/j.issn.1007-3969.2015.02.012
R735.2
A
1007-3639(2015)02-0150-05
2014-07-31
2014-09-15)
宋爱琳 E-mail:2015956568@qq.com
