Mechanism of exosomal microRNA-224 in development of hepatocellular carcinoma and its diagnostic and prognostic value
2019-05-08YaoCuiHaiFengXuMingYueLiuYuJieXuJunChuangHeYunZhouShunDongCang
Yao Cui, Hai-Feng Xu, Ming-Yue Liu, Yu-Jie Xu, Jun-Chuang He, Yun Zhou, Shun-Dong Cang
Abstrac t BACKGROUND Exosomes contain proteins, lipids, and biological molecules such as DNA and RNA. Nucleic acids in exosomes are a group of molecules that can act as biomarkers. Currently, there are many reports on exosomal microRNAs, which are ideal biomarkers for the early diagnosis of cancer. However, there are few reports on the role of exosomal microRNAs in the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).AIM To understand the mechanism of exosomal microRNA-224 (miR-224) in the development of HCC and evaluate its diagnostic and prognostic value.METHODS Cell culture and transfection of exosomal miRNA-224, real-time quantitative PCR, luciferase reporter assay, and other methods were used to find new biomarkers related to the development of HCC that can be used to diagnose HCC and predict HCC prognosis.RESULTSBy targeting glycine N-methyltransferase, incubating exosomes with miR-224 mimic resulted in a significant increase in cell proliferation compared to that of the control group, while incubation with the miR-224 inhibitor significantly reduced cell proliferation. The same results were obtained for the cell invasion assay. Serum exosomal miR-224 did have some ability to differentiate patients with HCC from healthy controls, with an area under the curve of 0.910, and HCC patients with higher serum exosomal miR-224 expression had lower overall survival.CONCLUSION Exosomal miR-224 is a tumor promotor and can be a marker of diagnosis and prognosis of HCC patients, however, its ability to distinguish liver diseases needs further verification.
Key words: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Serum; Exosome; MicroRNA-224; Biomarker
INTRODUCTION
Liver cancer is a malignant tumor with a high mortality rate in China[1]. Liver cancer has the fourth-highest incidence rate of all tumors, and the fatality rate ranks third[1].A total of 25% of the cancer cases are caused by carcinogenic infections such as hepatitis virus and human papillomavirus, and this figure includes a high proportion of patients in low-income and middle-income countries[2]. Therefore, early detection,diagnosis, and treatment are of great significance for the prognosis of patients with liver cancer. An early clinical diagnosis can effectively improve the survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)[3]. However, the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of current noninvasive indicators such as serum alpha-fetoprotein(AFP) and imaging studies for HCC, especially early HCC, still need to be improved[4].Therefore, new methods for diagnosing HCC need to be developed.
Exosomes are secreted and released by various types of cells and contain nanovesicles with various active factors[5]. Previous literature has reported that serum microRNAs (miRNAs) are mainly present in the exosomes formed from phospholipid membranes, thus avoiding degradation by RNase in circulation[6]. Exosomes have been shown to play an important role in tumorigenesis, development, metastasis,deterioration, and immune escape[7,8]. For example, Gu et al[9]found that exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells can promote the growth of gastric cancer cells,which indicated that exosomes can promote tumorigenesis and cancer development.Yu et al[10]found that exosomes secreted by breast cancer cells can promote tumor angiogenesis, growth, and proliferation, proving that exosomes can promote tumor cell metastasis. Exosomes secreted by breast cancer cells can also promote the proliferation of surround ing normal breast cells and inhibit their apoptosis. In addition, exosomes may also promote complications in cancer patients; for example,patients with pancreatic cancer often have diabetes[11].
Exosomes contain proteins, lipids, and biological molecules such as DNA and RNA[12]. Nucleic acids in exosomes are a group of molecules that can act as biomarkers. Currently, there are many reports on exosomal miRNAs, which are ideal biomarkers for the early d iagnosis of cancer[13-16]. How ever, there are few reports on the role of exosomal miRNAs in the d iagnosis and prognosis of HCC. In this study,cell culture and transfection of exosomal miRNA, real-time quantitative PCR (RTqPCR), luciferase rep orter assay, and other method s w ere performed to find new biomarkers related to the d evelopment of HCC and to determine if the biomarkers can be used for the diagnosis and prognosis of HCC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample collection
A total of 89 HCC and 50 normal serum samples w ere collected from 2014 to 2016,and the clinical information is shown in Table 1. The patients were not treated before the samples w ere collected, and the diagnosis of HCC w as confirmed by pathological analysis of tumor tissue. The analysis of the samples w as approved by the patients and the ethics committee.
Cell culture
The hepatocyte lines WRL68, Hep G2, and SKHEP1 were selected and cultured in RPMI-1640 (Sigma) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gibco) at 37 °C in 5%CO2. An miRNA mimic or inhibitor was transfected into cells with preincubated exosomes or Lipofectamine 2000.
Exosome isolation
The cells were starved in serum-free medium overnight and then centrifuged for 3 min at 2000 rpm, followed by filtration. The exosomes in the cell culture medium and in patient serum were extracted using the Total Exosome Isolation Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The resulting precipitate was observed under a transmission electron microscope as described previously[17].
RT-qPCR
Exosomal RNA in serum or cell culture medium was extracted with Trizol (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The expression of exosomal miRNA was detected on the Quant Stud io 7 Flex RT PCR System (Applied Biosystems) using a hydrolysis probe according to the manufacturer's instructions. All experiments were performed in triplicate, and a mixture of let-7i, let-7g, and let-7d (let-7d/g/i) w as used as endogenous controls to calculate the relative concentration of miRNA[18-20].
Cell proliferation and invasion
A Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) assay (Dojindo, Japan) follow ed by measuring the spectrophotometric absorbance at 450 nm was used to estimate cell proliferation. All experiments w ere performed in triplicate, and data are presented as the mean. A total of 2 × 105cells were cultured for 48 h in serum-free medium, w hile the lower chamber w as filled w ith med ium containing 10% FBS to analyze the invasion abilities of the cells; the cancer cells in the lower chamber were ultimately counted[21].
Luciferase reporter assay
MicroRNA-224 (miR-224) mimic, glycine N-methyltransferase (GNMT) w ild- or 3'-untranslated region (UTR) mutant-type, and controls were cotransfected into SKHEP1 cells in 24-w ell plates for 24 h. The harvested cells w ere analyzed for fluorescence intensity using a dual luciferase reporter assay kit as indicated.
Statistical analysis
Differences between groups were analyzed by t-tests using GraphPad Prism 6.0. The receiver op erating characteristic (ROC) curve w as constructed using SPSS 22.0 software, and the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated to assess the specificity and sensitivity of the pred iction of HCC cases and controls. A P-value < 0.05 w as consid ered significant. The Kap lan-Meier survival curve w as used to analyze the survival of the patients.
RESULTS
Exosome separation and validation
The morphological characteristics of the exosomes in the cell culture medium were observed under a transmission electron microscope. The exosomes showed a vesicular structure with a diameter of approximately 50-150 nm, which is consistent with theliterature[22].
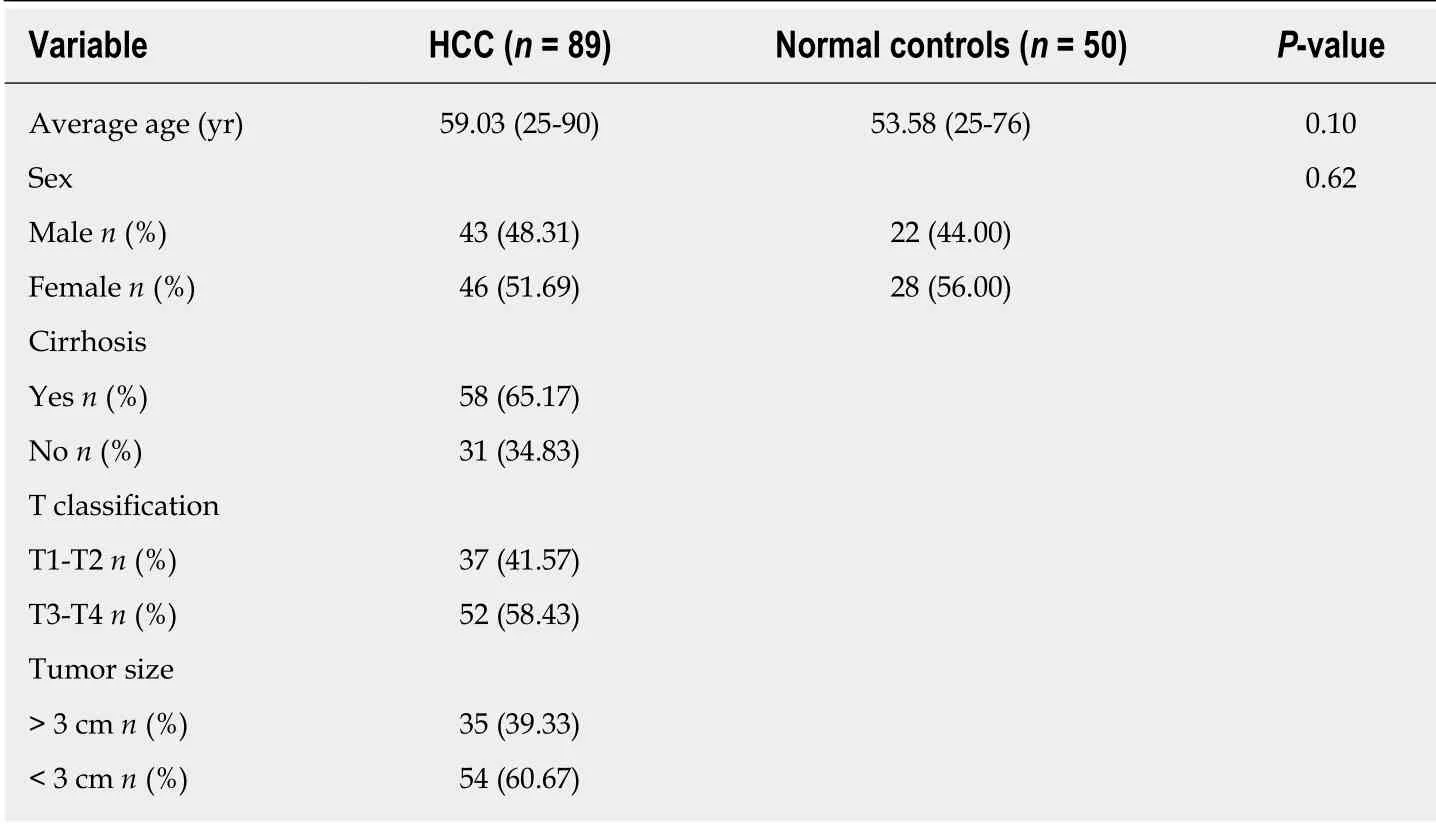
Table 1 Clinical information of the patients
Based on previous experimental results, w e found that the expression level of miR-224 in the HCC tissues w as significantly higher than that in the normal controls. In this stud y, we verified the expression of miR-224 in the exosomes of WRL68, Hep G2,and SKHEP1 cell lines by RT-qPCR. The expression level of exosomal miR-224 w as significantly increased in the tw o liver cancer cell lines, Hep G2 and SKHEP1,compared to that of the normal hepatic cell line, WRL68 (Figure 1).
Exosomal miR-224 stimulates the proliferation and invasion of HCC cells
Exosomes incubated w ith miR-224 mimic or inhibitor w ere ad d ed to Hep G2 and SKHEP1 cells to measure cell p roliferation. The results show ed that exosomes incubated w ith the miR-224 mimic resulted in a significant increase in cell proliferation compared to the proliferation in the control group, w hile the exosomes incubated with the miR-224 inhibitor exhibited significantly reduced cell proliferation(Figure 2A and B). These results ind icated that exosomal miR-224 can promote the proliferation of liver cancer cells. The same results w ere obtained for the cell invasion assay (Figure 2C and D). Exosomes incubated w ith the miR-224 mimic resulted in more cells passing through the insert membranes to the low er chamber, indicating that the exosomal miR-224 can also promote liver cancer cell invasion.
MiR-224 targets GNMT
It has been reported that miR-224 can affect cancer development by targeting glycine N-methyltransferase (GNMT)[23], so we used a luciferase reporter assay to verify whether miR-224 can directly interact with GNMT. As shown in Figure 3A, the wildtype GNMT reporter gene combined w ith the miR-224 mimic exhibited low er luciferase activity in the Hep G2 cell line than that of the control group. However,when the 3'-UTR of the GNMT gene was mutated, this reduction could be eliminated.The siGNMT was added to Hep G2 cells to knock out GNMT mRNA, w hich can reduce the expression of GNMT. The results show ed that the proliferation and invasion of cells increased notably (Figure 3B and C). It is suggested that miR-224 may directly target GNMT to promote the proliferation and invasion of liver cancer cells.
Correlation between serum exosomal miR-224 and liver cancer
Using RT-qPCR, we determined that the expression levels of exosomal miR-224 in the 89 HCC samples were significantly higher than those in the 50 healthy controls(Figure 4A). In addition, according to the clinical characteristics of the sample group,the levels of exosomal miR-224 in the serum of patients with large tumors or latestage tumors were significantly higher (Figure 4B and C). In the ROC curve analysis,serum exosomal miR-224 showed an ability to differentiate HCC patients from healthy controls, with an AUC of 0.910 (Figure 4D). These results indicated that serum exosomal miR-224 can be used as a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of HCC.
In addition, we analyzed the overall survival of the followed patients. Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed that HCC patients with higher serum exosomal miR-224 expression had lower overall survival (Figure 5), suggesting that serum exosomal miR-224 can be an independent prognostic factor for HCC.
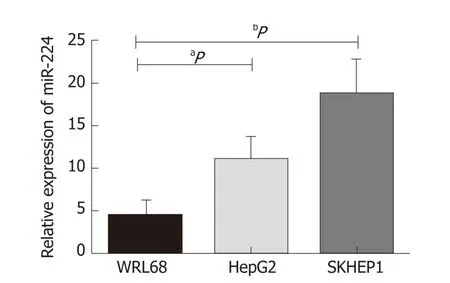
Figure 1 Relative expression of exosomal microRNA-224 in the hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines compared to that of the control.a P < 0.05, b P < 0.01. miR-224: MicroRNA-224.
DISCUSSION
In this study, w e id entified that the expression level of exosomal miR-224 in the liver cancer cell lines Hep G2 and SKHEP1 w as significantly higher than that in the healthy liver cell line WRL68 using gene chip and RT-qPCR. We also determined that the high expression of exosomal miR-224 can promote the proliferation and invasion of liver cancer cells. In ad d ition, low er luciferase activity w as observed w hen the miR-224 mimic and the GNMT w ild type were cotransfected into the Hep G2 cell line, w hile this phenomenon did not occur when the GNMT 3'-UTR was mutated, indicating that miR-224 can directly target the 3'-UTR of GNMT mRNA. In ad dition, siGNMT w as ad ded to the Hep G2 cell line, and as a result, the proliferation and invasion of the cancer cells increased. Therefore, miR-224 can directly target GNMT to promote the proliferation and invasion of cancer cells.
We verified that miR-224 can directly target GNMT to increase the proliferation and invasion of liver cancer cells. In colorectal cancer, miR-224 targets caspase-3 and caspase-7, and this inverse relationship w as evid ent from the earliest p hases of transformation in the intestinal mucosa[24]. In ad d ition, miR-224-5p inhibited autophagy by targeting Smad4 in breast cancer cells, suggesting a novel regulatory netw ork contributing to the metastasis of breast cancer[25]. Both miR-224 overexp ression and PTX3 silencing p romoted cell p roliferation, migration, and invasion, w hereas the aforementioned properties w ere reduced w hen miR-224 w as inhibited, ind icating that miR-224 inhibition may significantly p revent cervical carcinoma p rogression by targeting the PTX3 gene[26]. MiR-224 inversely regulated thiored oxin-interacting p rotein (TXNIP) by bind ing d irectly to its 3'-UTR, w hich resulted in the activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), w hile either TXNIP re-expression or HIF-1α depletion abolished the effects of miR-224 on the proliferation and migration of PDAC cells in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that TXNIP is a target of miR-224[27]. HIF-1α inhibits the NCR1/NKp46 p athw ay by up regulating miR-224,w hich affects the killing capability of natural killer cells in prostate cancer, thus ind ucing the immune escap e of tumor cells[28]. In summary, miR-224 may play an important role in the development and occurrence of tumors. Furthermore, miR-224 has many target genes, suggesting that miR-224 may participate in different pathways for cancer regulation, which requires further exploration.
We collected preop erative serum from HCC patients and healthy controls and isolated exosomes w ith high and stable p urity. The exp ression level of serum exosomal miR-224 in HCC p atients w as significantly higher than that in healthy controls, as determined by RT-qPCR. The ability of serum exosomal miR-224 as a biomarker to d istinguish HCC patients from healthy controls was confirmed by the ROC curve analysis. In add ition, the relationship betw een tumor size and stage and miR-224 expression in HCC patients w as analyzed, and we found that the expression of serum exosomal miR-224 w as higher in p atients w ith larger tumors and later stages. In ad d ition, w e also analyzed the relationship betw een the exp ression of exosomal miR-224 and the overall survival of p atients. The Kap lan-Meier survival curve show ed that the higher the exp ression level of serum exosomal miR-224, the shorter the patient's overall survival, suggesting that serum exosomal miR-224 can be used as a prognostic factor in patients w ith HCC. How ever, in this study w e only compared the expression of exosomal miR-224 in the serum of HCC patients and healthy controls. It is not clear w hether the expression of exosomal miR-224 in cirrhosis, hepatitis, or other liver cancer type is different, so the ability of miR-224 to distinguish between HCC and other liver diseases needs further verification.
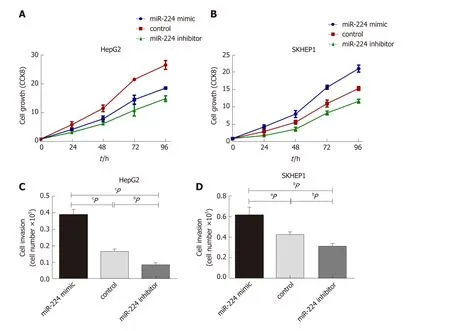
Figure 2 Exosomal microRNA-224 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion. A and B: MicroRNA-224 (miR-224) promoted cell growth as measured by the Cell Counting Kit 8 assay in HepG2 and SKHEP1 cell lines. C and D: MiR-224 can promote cell invasion in HepG2 and SKHEP1 cell lines. a P <0.05, b P < 0.01, c P < 0.001. CCK8: Cell Counting Kit 8; miR-224: MicroRNA-224.
In conclusion, exosomal miR-224 can decrease the expression of GNMT by d irectly targeting the 3'-UTR of GNMT mRNA to promote the proliferation and invasion of HCC cells, which may provide a new method for HCC treatment. In addition, serum exosomal miR-224 may be used as a biomarker for the d iagnosis of HCC and a prognostic factor for patients with HCC.
ARTICLES HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a malignant tumor with a high mortality rate.Exosomes have been show n to play an important role in tumorigenesis, cancer development, metastasis, deterioration, and immune escape.
Research motivation
We aimed to research the mechanism of exosomal microRNA-224 (miR-224) and its target in the development and invasion of HCC, and we also evaluated the diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-224 for patients with HCC.
Research methods
Cell culture and transfection of exosomal miR-224, its mimics, and its inhibitor; realtime quantitative PCR; and luciferase reporter assay w ere used to explore the mechanism of exosomal miR-224. HCC patients and healthy controls were used to assess the value of exosomal miR-224 in diagnosing HCC and predicting HCC prognosis.
Research results
Serum exosomes incubated w ith the miR-224 mimic showed a significant increase in cell proliferation and invasion w hen compared to the control group, w hile those incubated with the inhibitor showed a significant reduction. For discriminating HCC from healthy controls, serum exosomal miR-224 showed an area under the ROC curve of 0.910. Higher serum exosomal miR-224 expression levels in HCC patients w ere associated w ith low er overall survival.
Research conclusions
The results showed that exosomal miR-224 directly targets the 3'-UTR of glycine Nmethyltransferaseto and impacts the proliferation and invasion of HCC, and exosomal miR-224 may be used as a potential diagnostic and prognostic factor for patients with HCC.
Research perspectives
Our study provides novel insight into the mechanism of exosomal miR-224 in the development and invasion of HCC and may provide a potential biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of HCC.
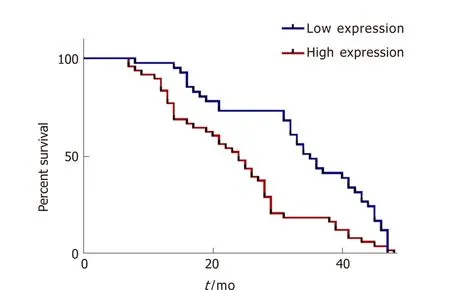
Figure 5 Kaplan-Meier overall survival analysis of microRNA-224.
杂志排行
World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Repurposing drugs to target nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- Central role of Yes-associated protein and WW-domain-containing transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif in pancreatic cancer development
- Considerations of elderly factors to manage the complication of liver cirrhosis in elderly patients
- Lysyl oxidase and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α: biomarkers of gastric cancer
- Predictive and prognostic implications of 4E-BP1, Beclin-1, and LC3 for cetuximab treatment combined with chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer with wild-type KRAS: Analysis from real-world data
- Extract of Cycas revoluta Thunb. enhances the inhibitory effect of 5-f luorouracil on gastric cancer cells through the AKT-mTOR pathway
