摩擦对齿轮振动噪声影响的研究进展
2018-03-05南咪咪吴立言
刘 更, 南咪咪, 刘 岚, 吴立言, 赵 颖
(西北工业大学 陕西省机电传动与控制工程实验室,西安 710072)
齿轮摩擦引起的问题主要包括齿面磨损、齿面胶合、热损失、振动以及噪声。磨损、胶合及热损失的研究已有较丰富的研究成果[1]。本文主要对由摩擦引起的齿轮振动与噪声的研究进行综述。齿轮装置的振动噪声主要来自齿轮啮合产生的振动激励[2],早期的实验研究认为摩擦是引起齿轮噪声的主要原因之一[3]。齿面摩擦一方面增加了引起齿轮传动振动噪声的主要因素—传递误差[4-5],另一方面它还直接引起空气辐射噪声[6]。
本文从计入摩擦的齿轮动力学模型、齿轮系统动态响应、齿轮摩擦噪声和实验验证四个方面综述摩擦对齿轮系统振动噪声的研究现状,并指出现有研究中存在的问题及未来的研究方向。
1 计入摩擦的齿轮动力学模型
1.1 齿轮动力学模型
引入摩擦的齿轮系统动力学有其自身特点。以理想圆柱齿轮传动为例,轮齿在啮合点处通常存在相对滑动(节点除外)。随着齿轮的转动,相对滑动速度发生变化,并且节点附近相对滑动速度方向相反,进而导致齿面间的摩擦力方向改变。齿面摩擦力的脉动变化与轮齿载荷、齿面相对滑动速度、齿面摩擦因数、润滑条件以及齿面形貌等因素有关。
考虑摩擦的齿轮系统动力学模型可分为全有限元模型[7]和集中质量模型[8]。已有研究大多采用集中质量模型,如图1所示。学者们在研究摩擦动力学时多采用垂直啮合线方向(Off-Line of Action, OLOA)与啮合线方向(Line of Action, LOA)分别作为坐标系x与y方向[9-10],其中,无摩擦时OLOA方向不存在振动激励。采用该坐标系使得齿轮动力学方程推导简洁明了,能清楚地获得摩擦引起的振动情况,但少数文献会采用与图1中不同的坐标系,以便将数值计算与相应的实验作对比[11]。
齿轮系统的主要激励分为三类:刚度激励、误差激励以及齿轮侧隙引起的冲击激励。侧隙的存在可能会引起轮齿脱啮,而脱啮后齿面将不存在摩擦作用。因此现有研究摩擦影响的多数文献中,均假设啮合过程不出现脱啮或者不考虑侧隙影响。

图1 直齿圆柱齿轮集中质量模型Fig.1 The lumped parameter model of a spur gear pair
刚度激励主要取决于啮合刚度模型。现有齿轮动力学研究采用的啮合刚度模型主要分为五类:①均值刚度模型;②矩形波模型;③时变刚度模型;④动刚度模型;⑤计入摩擦效应的啮合刚度模型[12-15],即摩擦动力学特有的啮合刚度模型。前4种啮合刚度模型与一般齿轮动力学中所采用的无异。现有研究中误差激励的选取因人而异,通常取空载传递误差[16]、齿廓误差[17]或者综合啮合误差作为误差激励[18]。
一对齿轮啮合过程如图2所示。在驱动力矩T1与负载力矩T2作用下,齿轮啮合始于A点终于D点,图2中该对齿轮分别于B和C两点啮合,力F1与F2表示主动轮所受摩擦力,对应的摩擦力臂分别为NB和NC。
考虑齿面摩擦的齿轮动力学方程一般形式见式(1)~式(6)。

(1)
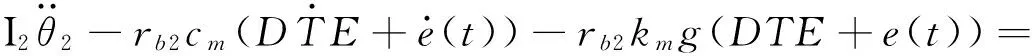
(2)

(3)
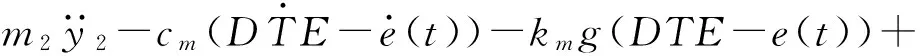
(4)
(5)
(6)
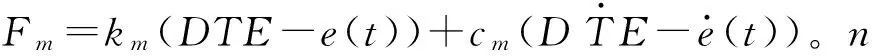
1.2 摩擦因数计算模型
齿面摩擦因数的计算常采用半经验公式,各种不同的半经验公式汇总见表1。
表1中公式1出处不明但在研究中多被采用,如文献[16],公式2用于计算摩擦因数均值,公式3改善了公式1在节点位置的突变,采用三角函数使摩擦因数连续变化,公式4、5、7、8是研究人员采用不同数学模型对圆盘实验结果进行拟合得到,式9建立了摩擦因数只与相对滑动速度相关时的计算方法。
为了更加准确反映齿轮传动的工作环境,近年来已有研究将弹流润滑理论应用于齿面摩擦计算中,包括光滑表面弹流模型[31]及粗糙表面的弹流模型[32-33]。Xu等根据粗糙表面弹流润滑理论得出计算摩擦因数的回归公式为
(7)
式中:
t=b1+b4|SR|Phlg(η)+b5e-|SR|Phlog10(η)+b9eS
式中:bi(i=1~9)为常系数,表征润滑状态。

表1 摩擦因数计算模型汇总
经验公式与回归公式均用于线接触齿轮的摩擦因数计算。对于其他齿轮形式只能适当调整近似使用。与表1中的摩擦因数计算公式相比,考虑弹流润滑的摩擦因数稍小。表1中的公式4、5、6、7和8在节点处失真,公式9与弹流润滑公式的变化趋势相近,即由于相对滑动速度为零,节点处为滚动摩擦,因而摩擦因数接近于0。动力学方程中摩擦项的正负可由摩擦因数模型体现或者由受力分析获得。而如何选取摩擦因数计算模型,学术界并没有定论,且时变摩擦模型与恒定摩擦模型对齿轮动力学影响的结论也不一致[34-36]。齿面摩擦模型的研究有赖于摩擦学发展,在此不赘述。
从表1中可见,摩擦因数模型除了可分为时变型与恒定型,还可分为与载荷耦合型和与载荷非耦合型。若摩擦因数与载荷不耦合,对方程(1)、(2)、(5)、(6)有两种处理方式,一是使用等分的准静态单齿啮合力近似替代时变单齿啮合力Nk[37],二是将齿轮动力学方程右端Nk项展开,与左端刚度项合并同类项得到与不考虑摩擦时形式一致的动力学方程及等效刚度[10,19,38]。Vaishya等[16,39]以第二种方式研究摩擦对齿轮系统动力学特性的影响。Fernandes等[37]对比了两种计入方式下摩擦动力学特性。此外,也有学者利用等效刚度研究摩擦对齿轮系统稳定性的影响[13,40]。
当摩擦因数与瞬态啮合力耦合,除上述两种近似方式外,Li等[33]建立了动力学与弹流润滑耦合模型精确计入齿面摩擦,但该耦合模型只能使用时域解法,方程求解较耗时。而前两种方式可以选择计算速度快的频域法求解[41]。
此外,还有文献考虑了由摩擦耗能造成的扭矩波动[42-43],对比计入摩擦的各种摩擦动力学模型[44]及对求解方法的探讨[45-46]。
2 齿轮系统动态响应
2.1 摩擦对齿轮动力学特性的影响
考虑齿面摩擦后,齿轮修形对齿轮动力学特性的影响会有所变化。Lundvall等的研究表明,有无摩擦对最优修形量的影响不大,但摩擦的计入减弱了修形后的减振效果。Kahraman等对比三种修形量下的齿轮动力学响应,也认为有无摩擦对最优修形量影响不大。He等考虑齿顶修形和摩擦对齿轮系统的影响,发现修形增大了摩擦在OLOA方向的激励作用。
同时考虑齿廓误差和摩擦在不同转速下齿轮动力学响应,发现摩擦对动力学响应的影响也不尽相同。已有研究一致认为在低速时,摩擦对传递误差和轴承力产生不可忽略的影响,该现象的产生可能是由于低速时润滑油膜难以成形引起摩擦因数增大所致[47],也可能由于系统的不稳定所致。而在中高速时,摩擦对于齿轮系统动态传递误差及轴承力的影响可以忽略。Gunda和Singh等研究了含有齿廓误差和摩擦的纯扭转单自由度直齿轮动力学响应,发现摩擦对于节点处传递误差有明显的影响。Wu 等采用考虑齿面摩擦的有限元模型进行研究,发现动态啮合力在节点出现下跌现象。李文良等[48]的研究结果表明节点附近摩擦力的反向会带来较大的振动及噪声,而且对于直齿轮的影响较斜齿轮更大。
现有研究表明,齿面摩擦对动力学响应同时具有阻尼或激励作用。Iida等[49]的研究发现摩擦在振动起初表现为激励作用,当振动幅值达到某一临界值时摩擦起阻尼作用。Liu等的研究认为摩擦力对LOA方向的振动和角加速度表现出阻尼的效果,摩擦因数越大这种能力越明显,但是计入齿廓误差后,摩擦力引起的阻尼效果不再明显。He等与张靖等[50]的研究结果表明摩擦对于OLOA方向的轴承力起到激励作用,而对LOA方向的轴承力与传递误差的激励作用不明显。
此外,摩擦对于不同类型齿轮的动力学特性影响不同。对于直齿圆柱轮的影响较斜齿圆柱齿轮的影响更大,对弧齿锥齿轮的影响较准双曲面齿轮明显。考虑不同重合度时摩擦对齿轮系统动力学的影响没有统一的规律;考虑斜齿轮不同安装错位形式时,得到滑动摩擦对系统振动的影响不同;考虑表面特性,研究了包含摩擦与表面波纹度对齿轮系统振动和结构噪声的作用[51];同时考虑滑动摩擦及齿面磨损对齿轮动力学的影响,发现磨损初期产生类似修形的减振效果,后期会迅速加剧系统的振动[52];考虑齿面缺陷[53]或齿根裂纹[54]与齿面摩擦作用对振动的影响,结果表明在多数情况下齿面摩擦对故障齿轮系统振动的影响相较由故障引起的齿轮系统振动的影响小。
2.2 摩擦非线性动力学
齿轮摩擦非线性动力学主要研究齿面摩擦对齿轮系统混沌分叉等非线性特性的影响。由于非线性表现与参数的选取密切相关,因此这方面的研究没有普遍的一致性结论。
齿面摩擦会使齿轮系统提前进入混沌并且使混沌的程度有所降低[55-57]。对于功率分流式齿轮传动系统摩擦也使得系统提前进入混沌,并且增加了跳跃次数,使得轮齿间的碰撞更加严重[58]。当齿面摩擦分别与固定间隙、简谐时变间隙或随机间隙共同作用[59],系统未出现脱啮时,摩擦使得传递误差略微增加,当出现脱啮时摩擦会加剧系统的振动[60],并且低速时会增加响应的高频成分[61]。
Vaishya和Singh等采用时变摩擦因数,分别建立了纯扭转线性和非线性齿轮动力学模型,对比了两种模型在不同重合度与不同转速下的动态响应。结果表明非线性模型的失稳区域小于线性模型的失稳区域,在共振之外的区域两种模型计算的动态响应基本相同。
Liu和Parker等建立了考虑摩擦力矩对轮齿弯曲作用的直齿轮动力学模型,啮合刚度计入齿面摩擦的弯曲作用。结果表明计入摩擦后激起高阶谐波共振,并且会导致模态耦合失稳并且整数重合度时出现参数失稳。Li等[62]认为在考虑摩擦时,阻尼和载荷越大,系统越稳定。
从上述文献可以看出,摩擦对齿轮系统非线性动态特性的影响不可忽略。而研究齿轮非线性动力学特性的意义在于对混沌或分叉的控制[63]。因此,研究摩擦对于系统混沌或分叉的控制是很有必要的。
3 齿轮摩擦噪声
摩擦噪声的研究有很多,但主要是对盘摩擦噪声的实验探究[64-65],而针对齿轮摩擦噪声研究却屈指可数。齿面摩擦除了影响齿轮传动动力学特性外,也直接产生空气噪声。Theodossiades等[66]建立了轻载时齿轮空气噪声的分析模型,并在半消音室进行了试验,仿真与实验结果吻合较好。齿轮空气噪声中包含了摩擦噪声的成分,但该实验并未对摩擦噪声进行分离单独研究。
Kim等[67]建立了齿面滑动摩擦噪声源模型,研究由齿面时变摩擦引起的空气噪声。其理论依据公式(8)所示的悬臂梁声源声波方程。图3为齿面摩擦引起噪声的示意图。使用该模型进行研究,结果表明转速越高,粗糙度越大时产生的噪声越大。
(8)
式中各参数的含义详见文献[67]。
Aziz等[68]考虑齿面粗糙度与最小油膜厚度共同决定的接触状态,采用相对声压级研究干摩擦与考虑润滑摩擦噪声之间的关系。
He等[69]建立了LOA和OLOA两个方向的振动路径。其中,LOA方向的激励是传递误差,而OLOA方向的激励是齿面摩擦,利用仿真软件分别计算了两种传递路径产生的辐射噪声。结果表明OLOA路径传递的辐射噪声占总噪声的比例不可忽视。
摩擦噪声涉及的领域相当广泛[70],而关于齿轮摩擦噪声的研究目前尚不完善。一方面实验研究时干扰因素多,难以隔离出齿面摩擦噪声成分。另一方面理论研究模型不易建立。因此齿轮摩擦噪声的研究亟待发展。
4 实验研究
早期研究齿轮摩擦的实验多简化为圆盘对滚实验,并通过大量实验数据来获取计算摩擦因数的经验公式。Drozdov等通过圆盘对滚实验研究滚滑运动下摩擦情况,并得到摩擦因数计算经验公式。NASA[71]测试了齿轮传动系统的振动和噪声。其中,振动位移通过箱体表面加速度计测得,而系统的噪声通过布置于箱体外一定距离处的麦克风获得。该实验获取的是整个系统的振动与噪声情况,尚无法得知齿面摩擦对系统振动噪声单独的影响。NASA Army Research Laboratory测量了齿面摩擦力的大小[72]。实验中使用变速电机和电涡流加载器,设计缺齿齿轮进行单齿摩擦力的测量。测量结果表明摩擦因数约为0.04~0.06,并且在节点处摩擦因数光滑连续变化。该测量结果多次被齿面摩擦研究者引用,佐证其所建动力学模型的有效性,如文献[34]。
He等采用了图4所示的齿轮装置对直齿圆柱齿轮轴承力进行测量,对比了动态传递误差及OLOA和LOA方向振动位移的测量值与计算值。两者变化趋势比较吻合,误差在10%左右。

图4 轴承力测试现场图Fig.4 Experiments rigs of a gear pair
Velex等对齿轮摩擦动力学进行了理论与实验研究,实验使用电扭矩加载器,对象为大传动比的直齿轮副和斜齿轮副。测量了低转速下轴承水平方向和铅垂方向的动载荷,实验结果与理论计算的趋势基本一致。
总体而言,涉及齿面摩擦的实验包括三类,齿面摩擦因数测定实验,摩擦引起的结构振动实验及摩擦噪声实验。结构振动实验受限于实验条件,如不能测量高速时的摩擦力对动响应的影响。摩擦噪声实验由于测量得到的噪声是整个系统总噪声,通常难以准确判断出齿面摩擦噪声所占的比例及变化情况。
5 结 论
通过对国内外相关文献分析与总结,可见齿面摩擦对齿轮振动噪声影响的研究尚不成熟。涉及的齿轮类型多限于圆柱齿轮,并且齿面摩擦因数模型差异较大。摩擦产生的噪声随着相对滑动速度的增加而增大,但目前缺乏相应的实验对比。并且已有的研究结论表明中高速时齿面摩擦对齿轮振动的影响很小,低速时摩擦的影响不可忽略,并且摩擦对齿轮非线性表现影响较为显著。此外,对于齿轮摩擦空气噪声的研究非常欠缺。为了完善齿轮摩擦振动噪声的研究体系,还需从以下几个方面进行深入研究:
(1) 全面考虑摩擦对齿轮系统的影响。应考虑摩擦对齿轮啮合刚度的影响,在动力学方程中体现摩擦引起的能量损失等。由于问题的复杂性,现有研究多不考虑以上因素,今后研究应完善齿轮含摩擦振动动力学的研究。
(2) 应用弹流润滑理论研究齿面摩擦因数及啮合阻尼。目前动力学方程中采用经验公式对齿面摩擦因数及啮合阻尼进行近似计算,而将弹流润滑理论用于齿轮系统可得到更为准确的齿面摩擦力及啮合阻尼。
(3) 齿轮摩擦空气噪声的实验与理论研究。现有相关的文献相对较少,有关表面摩擦引起噪声的模型大多比较简单,不具有齿轮啮合的特征,需要建立合理可靠的齿面摩擦噪声模型。关于齿轮摩擦噪声的实验由于真实齿轮箱中摩擦噪声难以分离,可以考虑建立具有啮合过程中滑动速度变化等特点的简化实验装置进行专项研究。
[ 1 ] MARTIN K F. A review of friction predictions in gear teeth [J]. Wear, 1978, 49(2): 201-238.
[ 2 ] WELBOURN D B. Fundamental knowledge of the gear noise-a survey [C]. Conference on Noise and Vibrations of Engines and Transmission, Cranfield, 1979: 9-14.
[ 3 ] ATTIA A Y. Noise of involute helical gears [J]. Journal of Engineering for industry, 1969(1): 165-171.
[ 4 ] HOUSER D. The root of gear noise: Transmission error [J]. Power Transmission Design, 1986: 27-30.
[ 5 ] ERITENEL T, PARKER R G. Three-dimensional nonlinear vibration of gear pairs [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2012, 331(15): 3628-3648.
[ 6 ] YOON K. Analysis of gear noise and design for gear noise reduction[D]. Purdue University, 1993.
[ 7 ] WU Y, WANG J, HAN Q. Contact finite element method for dynamic meshing characteristics analysis of continuous engaged gear drives [J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2012, 26(6): 1671-1685.
[ 8 ] KAHRAMAN A, LIM J, DING H. A dynamic model of a spur gear pair with friction[C]. Proceedings of the 12th IFToMM world congress, Besancon, France, 2007.
[ 9 ] HE S, GUNDA R, SINGH R. Inclusion of sliding friction in contact dynamics model for helical gears[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2007,129(1): 48-57.
[10] HE S, GUNDA R, SINGH R. Effect of sliding friction on the dynamics of spur gear pair with realistic time-varying stiffness[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2007, 301(3/4/5): 927-949.
[11] VELEX P, CAHOUET V. Experimental and numerical investigations on the influence of tooth friction in spur and helical gear dynamics [J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2000, 122(4): 515-522.
[12] LUNDVALL O, STR-MBERG N, KLARBRING A. A flexible multi-body approach for frictional contact in spur gears [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2004, 278(3): 479-499.
[13] LIU G, PARKER R G. Impact of tooth friction and its bending effect on gear dynamics [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration ,2009, 320(4/5): 1039-1063.
[14] 苟向锋, 祁常君, 陈代林. 考虑齿面接触温度的齿轮系统非线性动力学建模及分析[J]. 机械工程学报,2015, 51(11): 71-77.
GOU Xiangfeng, QI Changjun, CHEN Dailin. Nonlinear dynamic modelling and analysis of gear system with tooth contact temperature [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(11): 71-77.
[15] SAXENA A, PAREY A, CHOUKSEY M. Time varying mesh stiffness calculation of spur gear pair considering sliding friction and spalling defects [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2016, 70: 200-211.
[16] VAISHYA M, SINGH R. Sliding friction-induced non-linearity and parametric effects in gear dynamics [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2001, 248(4): 671-694.
[17] GUNDA R, SINGH R. Dynamic analysis of sliding friction in a gear pair[C]∥ Proceedings of Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Chicago, USA, September 2-6, 2003, ASME, C2003:1-8
[18] CHANG Lehao, LIU Geng, WU Liyan. A robust model for determining the mesh stiffness of cylindrical gears [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2015, 87: 93-114.
[19] CHINMAYA K, MOHANTY A R. An algorithm for determination of time-varying frictional force and torque in a helical gear system [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2007, 42(4): 482-496.
[20] LIU C, QIN D, LIAO Y. Dynamic model of variable speed process for herringbone gears including friction calculated by variable friction coefficient[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2014, 136: 041006-1-041006-12.
[21] FENG Z, WANG S, LIM T C, et al. Enhanced friction model for high-speed right-angle gear dynamics [J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2011, 25 (11): 2741-2753.
[22] SONG C, ZHU C, LIU W. Sliding friction on dynamics of crossed beveloid gears with small shaft angle[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2013, 27 (5): 1255-1263.
[23] 圆柱齿轮、锥齿轮和准双曲面齿轮 胶合承载能力计算方法 第1部分:闪温法:GB/Z 6413.1-2003 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社,2003.
[24] DUAN C, SINGH R. Dynamics of a 3DOF torsional system with a dry friction controlled path [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, 289 (4/5): 657-688.
[25] DROZDOV Y N, GAVRIKOV Y A. Friction and scoring under the conditions of simultaneous rolling and sliding of bodies[J]. Wear, 1967(11): 291-302.
[26] O’DONOGHUE J P, CAMERONA. Friction and temperature in rolling sliding contacts [J]. ASLE Transactions, 1966, 9: 186-194.
[27] Calculation of Scuffing Load Capacity of Cylindrical,Bevel and Hypoid Gears-Part 1: Flash Temperature Method: NEN NPR ISO/TR 13989-1:2000[S]. ISO copyright office, Geneva, Switzerland.
[28] BENEDICT G H, KELLY B W. Instantaneous coefficients of gear tooth friction[J]. Transactions of ASLE, ASLE Lubrication Conference, 1961, 4(1): 59-70.
[29] KELLEY B, LEMANSKI A. Lubrication of involute gearing [C]. Proceedings of Institution of Mechanical Engineers 1967, 182: 173-184.
[30] BUCKINGHAM E. Analytical mechanics of gears [M]. New York, Dover Publications, 1949.
[31] CHEON G. Analysis of the nonlinear behavior of gear pairs considering hydrodynamic lubrication and sliding friction [J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2009 , 23(8): 2125-2137.
[32] XU H, KAHRAMAN A, ANDERSON N E, et al. Prediction of mechanical efficiency of parallel-axis gear pairs [J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2007, 129(1): 58-68.
[33] LI S, KAHRAMAN A. A Tribo-dynamic model of a spur gear pair [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration,2013, 332(20): 4963-4978.
[34] HE S, CHO S, SINGH R. Prediction of dynamic friction forces in spur gears using alternate sliding friction formulations [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 309(3/4/5): 843-851.
[35] DIAB Y, VILLE F, VELEX P. Prediction of power losses due to tooth friction in gears [J]. Tribology Transactions, 2006, 49(2): 260-270.
[36] JIANG H, SHAO Y, MECHEFSKE C K, et al. The influence of mesh misalignment on the dynamic characteristics of helical gears including sliding friction [J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2015, 29(11): 4563-4573.
[37] FERNANDES P, RODRIGUES J, SEABRA J, et al. Influence of friction on gear dynamic [C]. 5th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Porto-Portugal, 24-26 July, 2006: 1-21.
[38] CHINMAYA K, MOHANTY A R. Determination of time-varying contact length, friction force, torque and forces at the bearings in a helical gear system [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 309(1/2): 307-319.
[39] VAISHYA M, SINGH R. Analysis of periodically varying gear mesh systems with coulomb friction using floquet theory[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2001, 243(3): 525-545.
[40] GHOSH S, CHAKRABORTY G. Parametric instability of a multi-degree-of-freedom spur gear system with friction[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2015, 354: 236-253.
[41] 常乐浩. 平行轴齿轮传动系统动力学通用建模方法与动态激励影响规律研究[D]. 西安:西北工业大学, 2014.
[42] VELEX P, SAINSOT P. An analytical study of teeth friction excitations in errorless spur and helical gears [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2002, 37(7): 641-658.
[43] 徐辅仁. 渐开线齿轮机构输出扭矩波动率与齿间滑动摩擦因数及齿数之关系[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2000(5): 37-39.
XU Furen. The relationships between the fluctuation rate of the output torque of the involute gearing and both the sliding friction coefficient between teeth and tooth numbers [J]. Machinery Design and Manufacture, 2000(5): 37-39.
[44] VAISHYA M, SINGH R. Strategies for modeling friction in gear dynamics [J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2003, 125(2): 383-393.
[45] HE S, SINGH R. Dynamic transmission error prediction of helical gear pair under sliding friction using floquet theory[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2008,130(5): 052603- 1-052603-9.
[46] HE S, ROOK T, SINGH R. Construction of semianalytical solutions to spur gear dynamics given periodic mesh stiffness and sliding friction functions[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2008, 130(12): 122601-1-122601-9.
[47] DE SANTOS E G P G, DE WIT C C. Velocity dependence in the cyclic friction arising with gears [J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2002, 21(9): 761-771.
[48] 李文良, 王黎钦, 常山, 等. 斜齿轮齿面摩擦力对动力学的弯曲效应[J]. 船舶力学, 2013, 17(8): 937-943.
LI Wenliang, WANG Liqin, CHANG Shan, et al. Tooth friction bending effect of helical gear on gear dynamics [J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2013, 17(8): 937-943.
[49] IIDA H, TAMURA A, YAMADA Y. Vibrational characteristics of friction between gear teeth [J]. Bull. JSME, 1985, 28(241): 1512-1519.
[50] 张靖, 陈兵奎, 康传章, 等. 计及齿面摩擦的直齿轮动力学分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2012, 31(21): 126-132.
ZHANG Jing, CHEN Bingkui, KANG Chuanzhang, et al. Dynamic analysis for spur gears considering friction effect [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(21): 126-132.
[51] SUNDAR S, SINGH R, JAYASANKARAN K, et. al. Effect of the tooth surface waviness on the dynamics and structure-borne noise of a spur gear pair [J]. Journal of Passenger Cars-Mechanical System 2013, 6(2): 1087-1093.
[52] KUANG J H, LIN A D. The Effect of tooth wear on the vibration spectrum of a spur gear pair [J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 2001, 123: 311-317.
[53] JIANG H, SHAO Y, MECHEFSKE C K. Dynamic chara-cteristics of helical gears under sliding friction with spalling defect [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2014, 39: 92-107.
[54] HOWARD I, JIA S, WANG J. The dynamic modelling of a spur gear in mesh including friction and a crack[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2001, 15(5): 831-853.
[55] 陆凤霞,王浩飞,朱如鹏,等.基于齿面摩擦的人字齿轮副动力学特性分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2016, 35(9): 204-212.
LU Fengxia, WANG Haofei, ZHU Rupeng, et al. Dynamic characteristics analysis of double helical gear paris considering teeth surface sliding friction [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(9): 204-212.
[56] 王三民, 沈允文, 董海军. 含摩擦和间隙直齿轮副的混沌与分叉研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2002, 38(9): 8-11.
WANG Sanmin, SHEN Yunwen, DONG Haijun. Chaos and bifurcation analysis of a spur gear pair with combined friction and clearance [J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2002, 38(9): 8-11.
[57] WANG J, ZHENG J, YANG A. An analytical study of bifurcation and chaos in a spur gear pair with sliding friction [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2012, 31: 563-570.
[58] 郜浩冬, 张以都. 含摩擦的汇流传动齿轮非线性动力学分析[J]. 振动、测试与诊断, 2014, 34(4): 737-782.
GAO Haodong, ZHANG Yidu. Nonlinear dynamics analysis of convergent transmission gear containing friction [J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement and Diagnosis, 2014, 34(4): 737-782.
[59] 陈思雨, 唐进元. 间隙对含摩擦和时变啮合刚度的齿轮系统动力学响应的影响[J]. 机械工程学报, 2009, 45(8): 119-124.
CHEN Siyu, TANG Jinyuan. Effect of backlash on dynamics of spur gear pair system with friction and time-varying stiffness [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(8): 119-124.
[60] 刘长钊, 秦大同, 廖映华. 考虑齿面变摩擦因数的斜齿轮传动变速过程动力学分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2014, 33(24): 150-157.
LIU Changzhao, QIN Datong, LIAO Yinghua. Dynamic model for a parallel-axis helical gears transmission system based on variable friction coefficient between contact teeth [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(24): 150-157.
[61] CHEN S, TANG J, LUO C, et al. Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of geared rotor bearing systems with dynamic backlash and friction [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2011, 46(4): 466-478.
[62] LI X, SUN D, LIANG Y, et al. Stability study of gear meshing area considering friction of tooth surface [J]. International Journal of Industrial and Systems Engineering, 2016, 22(4): 466-483.
[63] SAGHAFI A, FARSHIDIANFAR A. An analytical study of controlling chaotic dynamics in a spur gear system [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2016, 96: 179-191.
[64] 张立军, 刁坤, 孟德建, 等. 摩擦引起的振动和噪声的研究现状与展望[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2013, 41(5): 765-772.
ZHANG Lijun, DIAO Kun, MENG Dejian, et al. Friction-induced vibration and noise research: the status quo and its prospect [J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2013, 41(5): 765-772.
[65] WANG D W, MO J L, WANG Z G, et al. Numerical study of friction-induced vibration and noise on groove-textured surface [J]. Tribology International, 2013, 64:1-7.
[66] THEODOSSIADES S, DE LA CRUZ M, RAHNEJAT H. Prediction of airborne radiated noise from lightly loaded lubricated meshing gear teeth [J]. Applied Acoustics, 2015, 100: 79-86.
[67] KIM S, SINGH R. Gear surface roughness induced noise prediction based on a linear time-varying model with sliding friction [J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2007, 13(7): 1045-1063.
[68] AZIZ S, SEIREG A. A parametric study of frictional noise in gears [J]. Wear, 1994, 176: 25-28.
[69] HE S, SINGH R, PAVIC G. Effect of sliding friction on gear noise based on a refined vibro-acoustic formulation [J]. Noise Control Engineering Journal, 2008, 56(3): 164-175.
[70] AKAY A. Acoustics of friction [J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2002, 111(4): 1525-1548.
[71] CHOY F K, QIAN W, ZAKRAJSEK J, et. al. Vibration and noise analysis of a gear transmission system[C]. NASA Technical Memorandum 106162.
[72] REBBECHI B, OSWALD F B, TOWNSEND D P. Measurement of gear tooth dynamic friction [C]. ASME Power Transmission and Gearing Conference proceedings, 1996, 88: 355-363.
