川芎的化学成分与药理作用研究进展
2017-12-26韩炜
韩炜
(国家食品药品监督管理总局 药品审评中心,北京 100038)
·综述·
川芎的化学成分与药理作用研究进展
韩炜*
(国家食品药品监督管理总局 药品审评中心,北京 100038)
川芎为伞形科植物川芎LigusticumchuanxiongHort的干燥根茎,是一味常用的活血行气药,其化学成分包含苯酞及其二聚体、生物碱、有机酸酚、多糖以及脑苷脂和神经酰胺等类化合物。川芎中的活性成分对心脑血管系统、神经系统、呼吸系统等都具有多方面的药理活性。本文系统综述川芎有效成分和药理方面的研究进展,为今后川芎的研究开发提供参考。
川芎;苯酞类;生物碱类;有机酚酸类;药理作用
川芎为伞形科植物川芎LigusticumchuanxiongHort的干燥根茎,主产于四川省彭州、都江堰等地,为川产道地药材之一,其性温,味辛,归肝经、胆经、心包经,有活血行气、祛风止痛之功能。《神农本草经》将其列为上品,称其“主中风入脑头痛,寒痹,筋挛缓急,金创,妇女闭血无子”;《名医别录》载其可治疗“心腹坚痛,中恶,卒急肿痛,胁风痛,齿根出血”;《药性论》补录“活腰脚软弱,半身不遂,主胞衣不出”;《中华人民共和国药典》收载其为“活血行气,祛风止痛。用于胸痹心痛,胸胁刺痛,跌扑肿痛,月经不调,经闭痛经,癥瘕腹痛,头痛,风湿痹痛”,可见川芎入药历史悠久,临床应用广泛。本文对川芎的化学成分及其药理作用进行综述,以期为川芎的临床应用、新产品研究与开发提供依据。
1 川芎的化学成分
目前从川芎中分离得到的化学成分包含苯酞及其二聚体、生物碱、有机酸、多糖以及脑苷脂和神经酰胺等类成分,其中苯酞类化合物是其主要化学成分。
1.1 苯酞类化合物
苯酞类化合物是伞形科药用植物的特征性成分之一,主要存在藁本属、当归属、欧当归属、蛇床属、山芎属等植物中。苯酞类化合物也是川芎中的一种主要活性化合物,其主要包括两类,一类是含有一个苯酞母核结构的苯酞单量体化合物;另一类是含有两个苯酞母核结构的苯酞二聚体化合物。从20世纪80年代到目前为止,有研究[1-21]从川芎药材中大约分离鉴定70余个苯酞类化合物,其中包括苯酞类单体化合物(化合物1~42)和苯酞类二聚体化合物(化合物43~68)。苯酞单体类化合物分别为:Z-藁本内酯(Z-ligustilide,1);E-藁本内酯(E-ligustilide,1a);洋川芎内酯A~N、Q~S(senkyunolides A~N、Q~S,2~18);正丁基苯酞(butylphthalide,19);Z-丁烯基苯酞(Z-butylidenephthalide,20);3-丁烯基-7-羟基苯酞(3-butylidene-7-hydroxyphthalide,21);4-羟基-3-丁基苯酞(4-hydroxy-3-butylphthalide,22);4,7-二羟基-3丁基苯酞(4,7-dihydroxy-3-butylphthalide,23);川芎内酯(cnidilide,24);新蛇床内酯(neocnidilide,25);Z-6,7-环氧藁本内酯(Z-6,7-epoxyligustilide,26);3-羧乙基-苯酞(3-carboxyrthyl-phthalide,27);chuanxiongnolide R1(28);chuanxiongnolide R2(29);3-hydroxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-6,7-dihydroxy-3-butylphthalide(30);6-羟基洋川芎内酯B(6-hydroxy-senkyunolide B,31);川芎苷A(chuanxiongoside A,32);川芎苷B(chuanxiongoside B,33);celephthalide A(34);藁本内酯苷A(ligusticoside A,35);藁本内酯苷B(ligusticoside B,36);(+)-chuanxiongin A(37);(-)-chuanxiongin A(37a);chuanxiongins B~F(38~42),结构见图1。
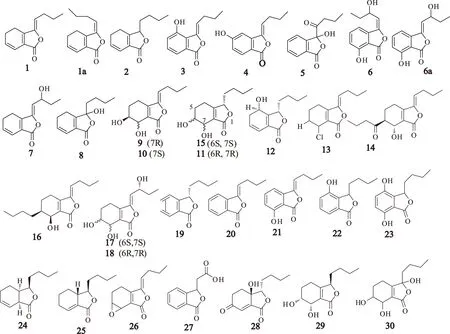
图1 川芎中苯酞单体类化合物的结构
苯酞类二聚体化合物分别为:洋川芎内酯O(senkyunolide O,43);洋川芎内酯P(senkyunolide P,44);欧当归内酯A(levistolide A,45);tokinolide B(46);ansaspirolide(47);3,8-二氢双藁本内酯(3,8-dihydrodiligustilide,48);riligustilide(49);Z,Z′-6,8′,7,3-双藁本内酯(Z,Z′-6,8′,7,3′-diligustilide,50);新当归内酯(angelicide,51);Z,Z′-3,3′,8,8′-双藁本内酯(Z,Z′-3,3′,8,8′ -diligustilide,52);Z-藁本内酯二聚体(Z-ligustilide dimer E-232,53);chuanxiongnolide A(54);chuanxiongnolide B(55);川芎萘呋内酯(wallichilide,56);chuanxiongdiolide A(57);chuanxiongdiolide B(58);chuanxiongdiolide R1(59);chuanxiongdiolide R2(60);chuanxiongnolides L1-L5(61~65);3,6,8,3a-二聚藁本内酯(3,6,8,3a-diligustilide,66);Z,Z-6′,6,7,3′a-二聚藁本内酯(Z,Z′-6,8′,7,3′-diligustilide,67);Z′-3,8-二氢-6,6′,7,3′a-二聚藁本内酯(Z′-3,8-dihydro-6,6′,7,3′a-diligustilide,68);(3′Z)-(3S,8S,3a′S,6′R)-4,5-dehydro-3.3a′,8.6′-diligustilide(69);(3′Z)-(3S,8R,3a′S,6′R)-4,5-dehydro-3.3a′,8.6′-diligustilide(70);chuanxiongdiolide R3(71),其结构见图2。
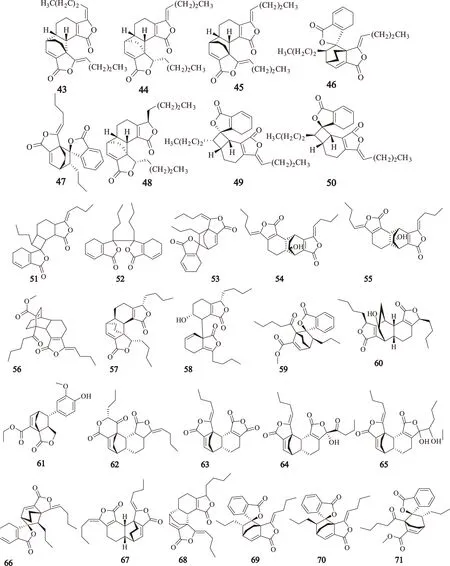
图2 川芎中苯酞二聚体类化合物的结构
1.2 有机酚酸类化合物
有机酚酸类是川芎中的一种主要特征性成分,《中华人民共和国药典》规定干燥的川芎中阿魏酸(ferulic acid)含量不得少于0.10%。阿魏酸也是有机酚酸中的有效成分,到目前为止,共鉴定19个有机酚酸类[13-22]化合物,分别为阿魏酸(ferulic acid,72);咖啡酸(caffeic acid,73);原儿茶酸(protocatechuic acid,74);对羟基苯甲酸(p-hydroxybenzoic acid,75);香草酸(vanillic acid,76);香草醛(vanillin,77);瑟丹酸(sedanonic acid,78);没食子酸(gallic acid,79);大黄酚(chrysophanol,80);3-甲氧基-4-羟基苯乙烯(3-methoxy-4-hydroxystyrene,81);1-羟基-1-[3-甲氧基-4-羟苯基]乙烷(1-hydroxy-1-(3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)-ethane,82);绿原酸(chlorogenic acid,83);阿魏酸松柏酯(coniferyl ferulate,84);5-羟甲基-6-内-3-甲氧基-4-羟苯基-8-氧杂双环[3.2.1]辛-3-烯-2-酮(5-hydroxymethyl-6-endo-3-ethoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl-8-oxa-bicyclo[3.2.1]-oct-3-one,85);叶酸(folic acid,86);棕榈酸(palmitinic acid,87);亚油酸(linoleic acid,88);芥子酸(sinapic acid,89);ligubenzocycloheptanone A(90),其结构式见图3。
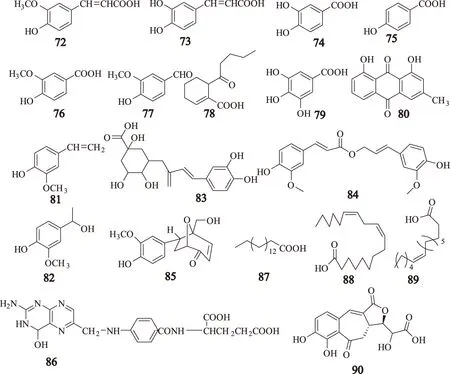
图3 川芎中有机酚酸类化合物的结构
1.3 生物碱类化合物
从川芎中分离得到11个生物碱类化合物[3-4,17],其中川芎嗪(tetramethylpyrazine)为川芎中特征性生物碱,这些生物碱分别为:川芎嗪(tetramethylpyrazine,91);L-异丁基-L缬氨酸酐(L-isobutyl-L-valine anhydride,92);L-缬氨酸-L缬氨酸酐(L-valine-L-valine anhydride,93);尿嘧啶(uracil,94);腺嘌呤(adenine,95);三甲胺(trimethylamine,96);胆碱(choline,97);1-乙酰基-β-卡啉(1-acetyl-β-carboline,98);1-β-丙烯酸乙酯基-7-醛基-β-卡啉(1-β-ethylacrylate-7-aldehydo-β-carboline,99);黑麦草碱(pelolyrine,100);腺苷(adenosine,101),其结构见图4。
1.4 神经酰胺和脑苷脂类化合物
2009年,Yang等[23]从川芎中分离得到3个神经酰胺类化合物(102~104)和2个脑苷脂类化合物(105和106),其中化合物102和103是新的神经酰胺类化合物,这些化合物分别为:(2R)-2-hydroxy-N-[(2S,3S,4R,8E)-1,3,4-trihydroxypentadec-8-en-2-yl]heptacosanamide(102);(2R)-2-hydroxy-N-{(3S,4S,5S)-4-hydroxy-5-[(4E)-undec-4-en-1-yl]tetrahydrofuran-3-yl}heptacosanami de(103);(2R)-2-hydroxy-N-[(2S,3S,4R,8E)-1,3,4-trihydroxyicos-8-en-2-yl]tetracosanamide(104);(2R)-N-[(2S,3R,4E,8E)-1-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3-hydroxydodeca-4,8-dien-2-yl]-2-hydroxydocosanamide(105);(2R)-N-[(2S,3S,4R,8E)-1-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3,4-dihydroxyoctadec-8-en-2-yl]-2-hydroxyhexadecanamide(106),其结构见图5。
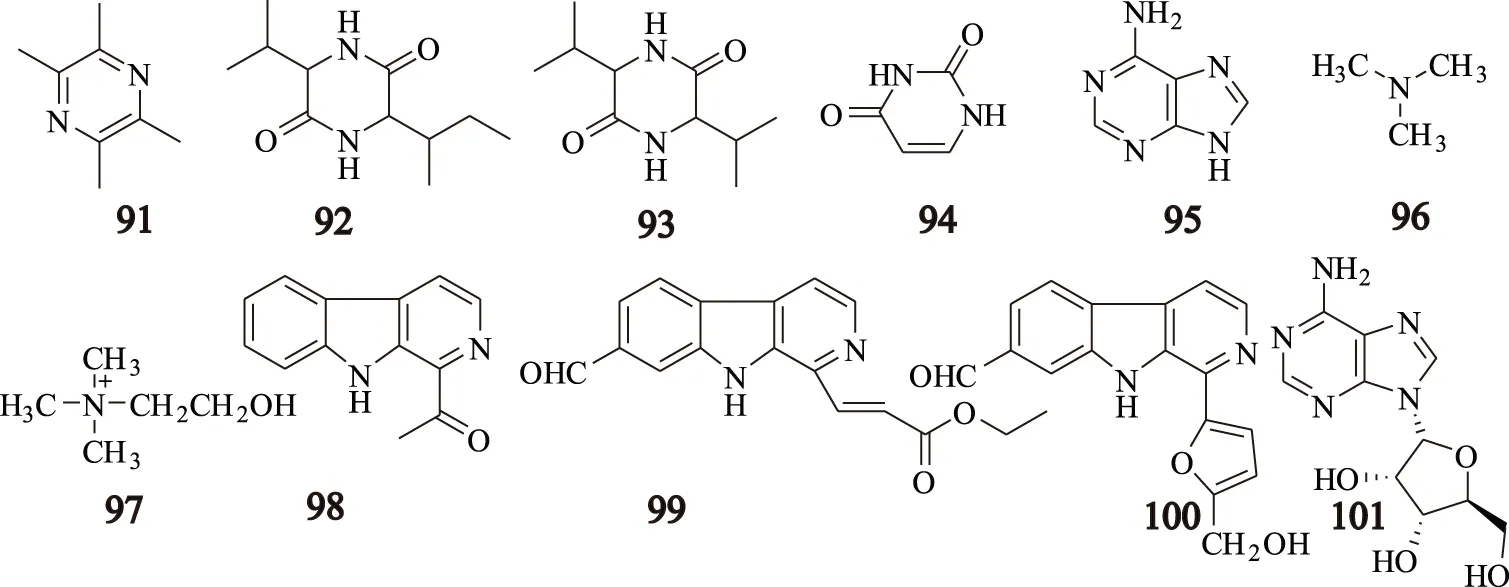
图4 川芎中生物碱类化合物的结构
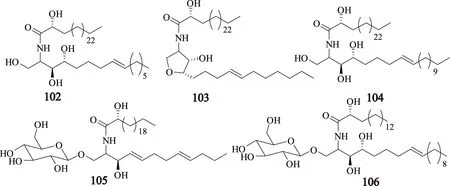
图5 川芎中神经酰胺和脑苷脂类化合物的结构
1.5 多糖类化合物
范智超等[24]采用DEAE-纤维素柱色谱和凝胶渗透色谱从川芎中得到4个均一多糖组分LCP-1、LCP-2、LCP-3和LCP-4,其相对分子质量分别为3.1×104、5.2×104、9.0×104、3.6×104。Yuan J F等[25]从川芎中也分离得到3个多糖组分LCA、LCB、LCC。
1.6 其他类化合物
除了以上成分,川芎还含有其他成分。Nie等[26]从川芎中分离得到化合物东莨菪内酯(scopoletin,107);大豆苷元(daidzein,108);二十四烷酸(lignoceric acid,109);紫云英苷(astragalin,111);金色酰胺醇酯(aurantiamide acetate,112);过氧化麦角甾醇(ergosterol peroxide,113)。Li等[10]首次从川芎中分离得到化合物淫羊藿次苷(icariside F2,110);Miao等[7]从川芎中分离得到化合物菜油甾-4-烯-3-酮(campest-4-en-3-one,114)和(-)-alloaromadendrane-4β,10α,13,15-tetrol(117);肖永庆等[15]从川芎中分离得到一个新的川芎三萜化合物xiongterpene(115),另外还有化合物4-pentylcyclohex-3-ene-1α,2β-diol(116)[6]和孕甾烯醇酮(118)progesterone[16],这些化合物的结构见图6。
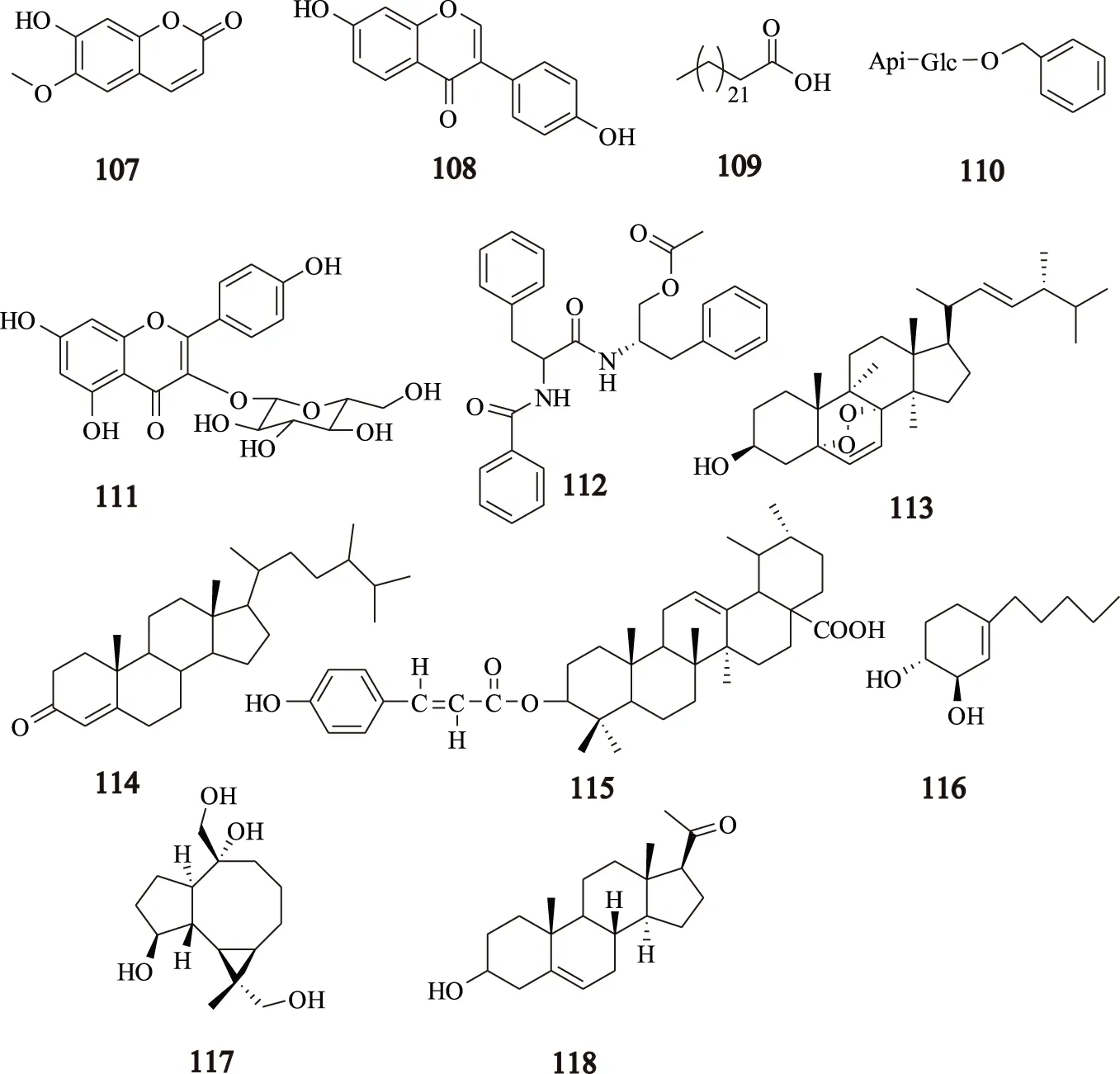
图6 川芎中其他类化合物的结构
2 川芎的药理作用
川芎具有活血行气、散瘀止痛、祛风燥湿的功能,属于“血中之气药”。现代药理研究表明,川芎中的活性成分对心脑血管系统、神经系统、呼吸系统以及肝、肾等都具有多方面的药理活性。
2.1 苯酞类化合物的药理作用
苯酞类化合物具有广泛的药理作用,包括调节心脑血管系统和神经系统,舒张平滑肌,抑制平滑肌细胞增殖,抑制学习记忆力损伤,诱导血红素氧合酶-1的表达以及抗菌、抗真菌和抗病毒等活性[27-31]。Z-藁本内酯(1)被认为是这些苯酞类化合物中主要的活性化合物。研究表明,其具有扩张血管[32]、平喘[33]、抗血小板聚集[34]、镇痛[35]、抗血栓形成和抗增殖作用[36]。可集中作用于肌肉松弛剂[37]、中枢去甲肾上腺素或γ-氨基丁酸[38]。另外,有关研究[39-41]也表明,Z-藁本内酯对短暂性前脑缺血、永久性局部脑缺血、慢性脑缺血等具有显著的神经保护作用。通过对文献归纳整理,苯酞类化合物与药理作用见表1。
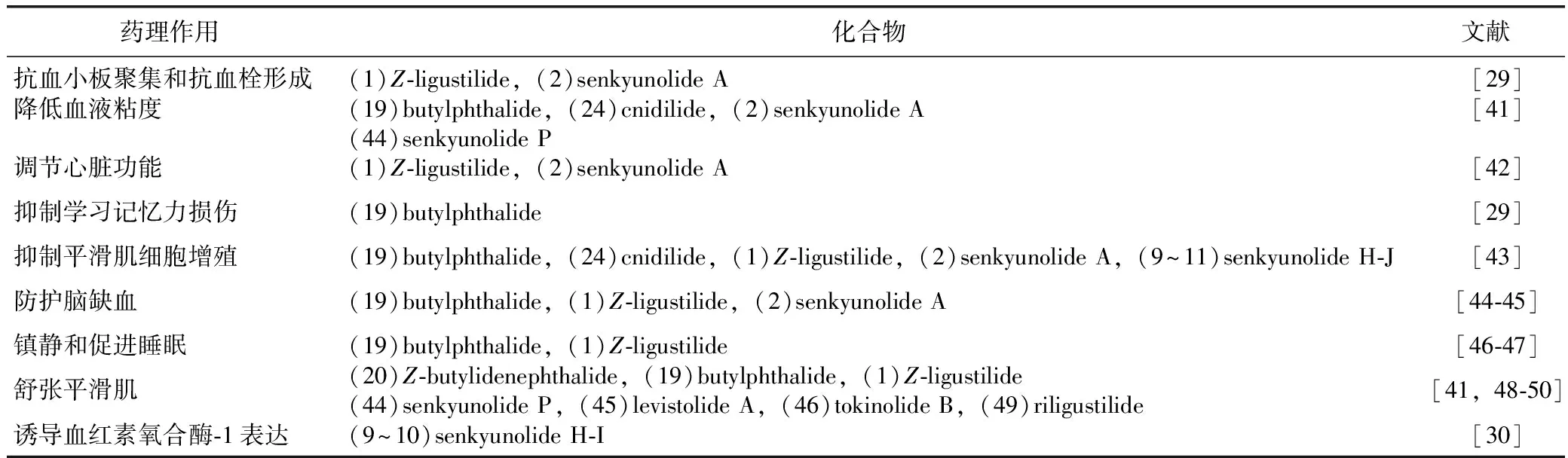
表1 川芎中苯酞类化合物的药理作用
2.2 有机酚酸类化合物的药理作用
川芎中有机酚酸类化合物的药理作用研究主要集中在阿魏酸(72)、咖啡酸(73)以及绿原酸(83)等化合物上。对阿魏酸的药理研究表明,阿魏酸可以显著改善血液流动性,抑制血小板聚集,降低血脂,预防血栓形成,保护嗜铬细胞瘤样神经元(PC12)以及具有较强的抗氧化活性[44],在国内临床上已用于治疗心绞痛和高血压[51]。绿原酸能调节葡萄糖-6-磷酸酶参与葡萄糖代谢过程,降低低密度脂蛋白-胆固醇和总胆固醇的氧化来降低心血管疾病的风险[52]。
2.3 生物碱类化合物的药理作用
川芎嗪(91)被认为是川芎的有效成分,对其药理研究较为广泛,现代药理研究表明,川芎嗪具有抗血小板聚集、扩张血管、抗门静脉高血压[53-55],同时还具有抗动脉粥样硬化、抗心肌炎和心肌肥厚等。
3 结语
川芎LigusticumchuanxiongHort作为一味常用的活血行气、祛风止痛的中药,其主要含有苯酞、有机酚酸、生物碱以及多糖等类多种化学成分。现代药理研究表明,川芎对心脑血管系统、神经系统、呼吸系统等都具有多方面的药理活性,其中苯酞类和有机酚酸类是川芎主要活性成分。川芎嗪(tetramethylpyrazine)常被认为是川芎的有效成分,然而在药材中其含量甚微,不能作为川芎质量控制的指标性成分,所以对于川芎中川芎嗪的认识存在争议,需要做进一步的研究。通过本综述系统阐述了川芎有效成分和药理方面的研究进展,为今后川芎的研究开发提供了参考。
[1] Wang P,Gao X,Wang Y,et al.Phthalides from the rhizome ofLigusticumwallichii[J].Phytochemistry,1984,23(9):2033-2038.
[2] Naito T,Katsuhara T,Niitsu K,et al.Two phthalides fromLigusticumchuanxiong[J].Phytochemistry,1992,31(2):639-642.
[3] Naito T,Ikeya Y,Okada M,et al.Two phthalides fromLigusticumchuanxiong[J].Phytochemistry,1996,41(1):233-236.
[4] Li S L,Chan S S,Lin G,et al.Simultaneous analysis of seventeen chemical ingredients ofLigusticumchuanxiongby on-line high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector-mass spectrometry[J].Planta Med,2003,69(5):445.
[5] Li Y H,Peng S L,Zhou Y,et al.Two new phthalides fromLigusticumchuanxiong[J].Planta Med,2006,72(7):652-656.
[6] Chang X L,Jiang Z Y,Ma Y B,et al.Two new compounds from the roots ofLigusticumchuanxiong[J].J Asian Nat Prod Res,2009,11(9):805-810.
[7] Miao C,Wu S,Luo B,et al.A new sesquiterpenoid fromLigusticumchuanxiongHort[J].Fitoterapia,2010,81(8):1088-1090.
[8] Huang J,Lu X Q,Lu J,et al.Two new phthalides with BuChE inhibitory activity fromLigusticumchuanxiong[J].J Asian Nat Prod Res,2013,15(12):1237-1242.
[9] Huang J,Lu X Q,Zhang C,et al.Anti-inflammatory ligustilides fromLigusticumchuanxiongHort[J].Fitoterapia,2013,91(8):21-27.
[10] Li L J,Su Y F,Yan S L.Three new phthalide glycosides from the rhizomes ofLigusticumchuanxiong[J].Phytochem Lett,2016,17(9):14-17.
[11] Yang J,Feng X L,Yang Y,et al.Novel phthalide derivatives identified fromLigusticumchuanxiong(Chuanxiong)[J].Chin Med,2016,11(10):1-7.
[12] Wei W,Wu X W,Yang X W.Novel phthalide derivatives from the rhizomes ofLigusticumchuanxiongand their inhibitory effect against lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells[J].RSC Adv,2016:6(66),61037-61046.
[13] Kaouadji M,Pachtere F D,Pouget C,et al.Three additional phthalide derivatives,an epoxymonomer and two dimers,fromLigusticumwallichiirhizomes[J].J Nat Prod,2004,49(5):872-877.
[14] 常新亮,马云保,张雪梅,等.川芎化学成分研究[J].中国中药杂志,2007,32(15):1533-1536.
[15] 肖永庆,李丽,游小琳,等.川芎化学成分研究[J].中国中药杂志,2002,27(7):519-522.
[16] 郝淑娟,张振学,田洋,等.川芎化学成分研究[J].中国现代中药,2010,12(3):22-25.
[17] Li W,Tang Y,Chen Y,et al.Advances in the chemical analysis and biological activities of chuanxiong[J].Molecules,2012,17(9):10614-10651.
[18] Bing H,Xu Z,Feng Z M,et al.Ligubenzocycloheptanone A,a novel tricyclic butenolide with a 6/7/5 skeleton fromLigusticumchuanxiong[J].Scientific Reports,2016,6:28783-28787.
[19] 王文祥,顾明,蒋小岗,等.川芎化学成分研究[J].中草药,2002,33(1):4-5.
[20] 杨丽红,谢秀琼,万丽,等.川芎化学成分研究[J].时珍国医国药,2007,18(7):1576-1577.
[21] Wei W,Xu W,Yang X W.Two new phthalide dimers from the rhizomes ofLigusticumchuanxiong[J].J Asian Nat Prod Res,2017,19(7):704-711.
[22] 王普善,高宣亮,福山爱保,等.中药川芎的化学成分研究—六种酚类化合物[J].中草药,1985,16(5):45-47.
[23] Yang N Y,Ren D C,Duan J A,et al.Ceramides and Cerebrosides fromLigusticumchuanxiongHort[J].Helv Chim Acta,2010,92(2):291-297.
[24] 范智超,张志琪.川芎中多糖的研究[J].中草药,2006,37(7):973-976.
[25] Yuan J F,Zhang Z Q,Fan Z C,et al.Antioxidant effects and cytotoxicity of three purified polysaccharides fromLigusticumchuanxiongHort[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2012,74(4):822-827.
[26] Nie H D,Hao R.Study of the chemical constituents of the Chuanxiong ground par[J].Med Inform,2011,326(1/3):326-328.
[27] Gijbels M J M,Scheffer J J C,Svendsen A B.Analysis of phthalides from umbelliferae by combined liquid-solid and gas-liquid chromatography[J].Chromatographia,1981,14(8):452-454.
[28] Almeida C,Kehraus S,Prudêncio M,et al.Marilones A-C,phthalides from the sponge-derived fungusStachylidiumsp.[J].Beilstein J Org Chem,2011,7(1):1636-1642.
[29] Beck J,Chou S.The structural diversity of phthalides from the Apiaceae[J].J Nat Prod,2007,70(5):891-900.
[30] Lin G,Chan S K,Chung H S,et al.Chemistry and biological activities of naturally occurring phthalides[J].Studies in Natural Products Chemistry,2005,32(5):611-669.
[31] Qi H Y,Shiuon S,Yan C,et al.Senkyunolides reduce hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in human liver HepG2 cells via induction of heme oxygenase-1[J].Chemico-Biological Interactions,2010,183(3):380-389.
[32] Cao Y X,Zhang W,He J Y,et al.Ligustilide induces vasodilatation via inhibiting voltage dependent calcium channel and receptor-mediated Ca2+influx and release[J].Vascular Pharmacology,2006,45(3):171-176.
[33] 陶静仪,阮于平,梅其炳,等.当归成分藁本内酯平喘作用的实验研究[J].药学学报,1984,19(8):561-565.
[34] Lian Z,Du J R,Jin W,et al.Z-ligustilide extracted from Radix Angelica sinensis decreased platelet aggregation induced by ADP ex vivo and arterio-venous shunt thrombosis in vivo in rats[J].Yakugaku Zasshi,2014,134(3):855-859.
[35] Du J,Yu Y,Ke Y,et al.Ligustilide attenuates pain behavior induced by acetic acid or formalin[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2007,112(1):211-214.
[36] Lu Q,Qiu T Q,Yang H.Ligustilide inhibits vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation[J].Eur J Pharmacol,2006,542(1/3):136-140.
[37] Ozaki Y,Sekita S,Harada M.Centrally acting muscle relaxant effect of phthalides(ligustilide,cnidilide and senkyunolide)obtained fromCnidiumofficinaleMakino[J].Yakugaku Zasshi,1989,109(6):402-406.
[38] Matsumoto K,Kohno S,Ojima K,et al.Effects of methylenechloride-soluble fraction of Japanese angelica root extract,ligustilide and butylidenephthalide,on pentobarbital sleep in group-housed and socially isolated mice[J].Life Sci,1998,62(23):2073-2082.
[39] Wu X M,Qian Z M,Zhu L,et al.Neuroprotective effect of ligustilide against ischaemia-reperfusion injury via up-regulation of erythropoietin and down-regulation of RTP801[J].British J Pharmacol,2011,164(2):332-343.
[40] Peng H Y,Du J R,Zhang G Y,et al.Neuroprotective effect ofZ-ligustilide against permanent focal ischemic damage in rats[J].Biol Pharm Bull,2007,30(2):309-312.
[41] Kuang X,Yao Y,Du J R,et al.Neuroprotective role ofZ-ligustilide against forebrain ischemic injury in ICR mice[J].Brain Res,2006,1102(1):145-153.
[42] Naito T,Kubota K,Shimoda Y,et al.Effects of constituents in a Chinese crude drug,Ligustici Chuanxiong Rhizoma on vasocontraction and blood viscosity[J].Nat Med,1995,49(3):288-292.
[43] Nakazawa K,Fujimori K,Inoue K,et al.Effects of extract from a herbal drug,cnidium rhizome(senkyu),on contraction,heart rates and membrane potentials of isolated guinea pig atria[J].Yakugaku Zasshi,1989,109(9):662-671.
[44] Kobayashi S,Mimura Y,Naitoh T,et al.Chemical structure-activity of cnidium rhizome-derived phthalides for the competence inhibition of proliferation in primary cultures of mouse aorta smooth muscle cells[J].Jap J Pharmacol,1993,63(3):353-359.
[45] 董高翔,冯亦璞.丁基苯酞对大鼠局部脑缺血再灌注损伤皮层钙凋磷酸酶和钙蛋白酶活性的影响[J].药学学报,2000,35(10):790-792.
[46] Or T C,Yang C L,Law A H,et al.Isolation and identification of anti-inflammatory constituents fromLigusticumchuanxiongand their underlying mechanisms of action on microglia[J].Neuropharmacology,2011,60(6):823-831.
[47] Matsumoto K,Kohno S,Ojima K,et al.Effects of methylenechloride-soluble fraction of Japanese angelica root extract,ligustilide and butylidenephthalide,on pentobarbital sleep in group-housed and socially isolated mice[J].Life Sci,1998,62(23):2073-2082.
[48] Bjeldanes L F,Kim I S.Sedative activity of celery oil constituents[J].J Food Sci,2010,43(1):143-144.
[49] Tsi D,Tan B K H.Cardiovascular pharmacology of 3-n-butylphthalide in spontaneously hypertensive rats[J].Phytother Res,1997,11(8):576-582.
[50] Chan S,Cheng T G.Relaxation effects of ligustilide and senkyunolide A,two main constituents ofLigusticumchuanxiong,in rat isolated aorta[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2007,111(3):677-680.
[51] Hou Y Z,Yang J,Zhao G R,et al.Ferulic acid inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation induced by angiotensin II[J].Eur J Pharmacol,2004,499(2):85-90.
[52] Nardini M,D′Aquino M,Tomassi G,et al.Inhibition of human low-density lipoprotein oxidation by caffeic acid and other hydrocinnamic acid derivatives[J].Free Rad Biol Med,1995,19(5):541-552.
[53] Sheu J R,Kan Y C,Hung W C,et al.The antiplatelet activity of tetramethylpyrazine is mediated through activation of NO synthase[J].Life Sci,2000,67(8):937-947.
[54] Pang P K,Shan J J,Chiu K W.Tetramethylpyrazine,a calcium antagonist[J].Planta Med,1996,62(5):431-435.
[55] Huang Y T,Chang F C,Chen K J,et al.Acute hemodynamic effects of tetramethylpyrazine and tetrandrine on cirrhotic rats[J].Planta Med,1999,65(2):130-134.
AdvancesinChemicalConstituentsandPharmacologicalEffectsofLigusticumchuanxiong
HAN Wei*
(Centerfordrugevaluation,CFDABeijing100038,China)
Chuanxiong Rhizoma (Chuan-Xiong, CX), the dried rhizome ofLigusticumchuanxiongHort., is used as one of Chinese medicine for activating blood and promoting the circulation of Qi.Modern research indicates that phthalides, organic acids, alkaloids, polysaccharides, ceramides and cerebrosides are main components responsible for the properties of CX.The pharmacological effects of CX, its main chemical fraction and monomer are related to multiple systems, such as cardiovascular system, nervous system and respiratory system, etc.This paper summarizes domestic and foreign reports on the pharmacological activities and active ingredients for the further research.
Ligusticumchuanxiong;phthalides;alkaloids;organic acids;pharmacological effects
10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.2017.9.027
*
韩炜,副主任药师,高级审评员,研究方向:中药新药的药学评价;Tel:(010)68921239,E-mail:hanw@cdc.org.cn
2017-07-12)
