全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置设计与试验
2017-12-20栗晓宇耿爱军侯加林张智龙
栗晓宇,耿爱军,2※,侯加林,张 姬,张智龙
全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置设计与试验
栗晓宇1,耿爱军1,2※,侯加林1,张 姬1,张智龙1
(1. 山东农业大学机械与电子工程学院,泰安 271000;2. 山东省园艺机械与装备重点实验室,泰安 271000)
针对目前大蒜播种机械自动化程度低、蒜种鳞芽朝上率低的现状,基于种盒式大蒜播种方式,设计了一种全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置。该装置主要包括机架、地轮、地轮轴、测速编码器、光电传感器、控制箱、输送装置和提取投放装置,能够实现蒜种盒自动给进、准确抓取、平稳输送、精确投放等功能。设计了机械臂和机械手结构,通过理论分析建立了各关键部件参数数学模型,确定了机械臂和机械手工作参数,探明了机组行进速度对各舵机工作参数的影响规律,明确了影响蒜种盒投放间隙的因素。为了测试蒜种盒投放效果影响进行了试验,结果表明当机组行进速度为0.90 km/h,中心舵机、辅助舵机、控距舵机转速分别为26.04、26.04、13.89 r/min时蒜种盒投放后衔接间隙平均值为5.6 mm,投放效果较优,满足大蒜播种要求。该文研究结果可为实现大蒜播种自动化提供参考。
农业机械;设计;农作物;大蒜播种;蒜种盒;提取投放;自动化
0 引 言
大蒜是中国主要经济作物之一,2016年主产区种植面积达到37.3~40.0万hm2[1-2]。大蒜播种时要求“根下芽上、直立播种”,长期以来一直依靠人工种植,劳动强度大,工作效率低。
国内外高校及科研机构对大蒜播种机及蒜种定向装置进行了诸多研究。Benjaphragairat等[3]基于10行大蒜播种机设计了一种排种器及其控制系统,该播种机根据株距要求确定了排种器参数和作业速度,其田间适应性受到限制,且蒜种入土姿态随机,出芽率仅为74.57%;Bakhtiari等[4]研发了一种大蒜播种机并进行田间试验,结果表明漏播率为12.23 %,伤种率为1.14 %,但没有解决蒜种定向问题;Brajesh等[5]设计了自走式大蒜播种机,适用于小地块播种,漏播率为2.67%,重播率为8%,播种机生产率为0.065 hm2/h,不具备蒜种定向机构,蒜种鳞芽朝向随机,不符合我国播种农艺要求;Труфляк等[6]发明了一种手扶式大蒜精密播种机,蒜种定向效果好,但工作效率低、劳动强度大。Bakhitiari[7]基于对大蒜物理和气动特性的研究研制了一种气吸式大蒜精密排种器,试验表明该排种器能够解决单粒取种的问题,但不具备鳞芽定向机构,其工作特性需进一步试验和优化等[8]研制了一种手动式大蒜播种机,田间试验表明其工作效率可达到理论值84.79%,该播种机自动化程度低。Zhang Dengquan等[9]研制了一种大蒜直立栽种机构,直立率70.6%,尚未实现成果转化;赵丽清等[10]基于机器视觉技术,利用机械臂实现蒜种定向投放,维护成本较高,蒜瓣定向识别技术仍待优化;王丹阳等[11]研制了一种半自动大蒜播种机,采用种盒式大蒜播种方式,针扎式取蒜方式,实际应用中易受外界环境约束;谢学虎等[12-13]设计了一种大蒜播种机种植机构,主要解决蒜种鳞芽直立度和弓背面朝向一致的问题,其应用受限于蒜种品种不同,需要进一步研究;耿爱军等[14-15]提出了种盒式大蒜播种方式,研制了种盒式大蒜播种机,自动化程度仍待提高;魏玉珍等[16-17]提出了3种直立方案,鳞芽朝上率均低于种盒式大蒜播种方式,该装置结构有待完善。针对上述现状,本文设计了一种全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置,介绍了其工作原理和主要部件设计并进行了试验,以期为实现大蒜播种自动化发展提供参考。
1 全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置设计
1.1 全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置结构
全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置如图1所示。该装置主要包括机架、地轮、地轮轴、测速编码器、光电传感器、控制箱、输送装置和提取投放装置。编码器用于检测机组行进速度[18-21];光电传感器安装在机架前端一侧,用于检测蒜种盒位置信息[22-25];控制箱包括自动控制系统[26-28]、蓄电池和行程开关等部件;输送装置安装在机架横向两端,由步进电机驱动,实现蒜种盒自动给进功能;提取投放装置主要包括底座、舵盘、中心舵机、机械臂、辅助舵机和机械手,底座固定在机架后端一侧,位于光电传感器正前方,机械臂通过舵盘与安装在底座上中心舵机的动力输出轴连接,机械手通过安装在机械臂上端中央的辅助舵机与机械臂连接,如图2所示。
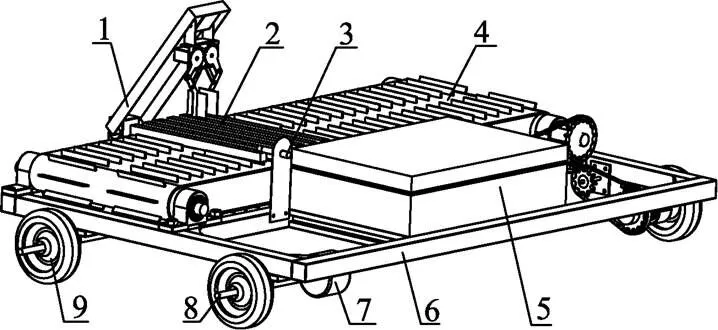
1. 提取投放装置 2. 蒜种盒 3. 光电传感器 4. 输送装置 5. 控制箱 6. 机架 7. 测速编码器 8. 地轮轴 9. 地轮
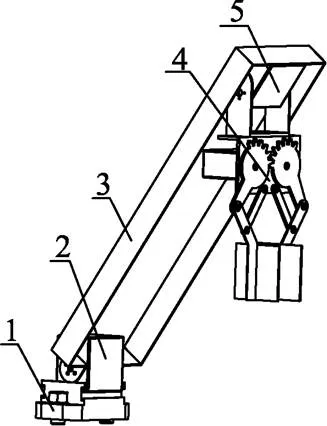
1. 底座 2. 中心舵机 3. 机械臂 4. 机械手 5. 辅助舵机
1.2 全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置工作原理
全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置适用于种盒式大蒜播种方式,由步进电机提供动力,单片机系统根据测速编码器检测到的地轮转速来控制各舵机的转速。当光电传感器检测到蒜种盒时输送带停止运输,同时机械臂摆动到蒜种盒上方,机械手垂直抓住蒜种盒后机械臂向后摆动,此过程中心舵机与辅助舵机协调配合使蒜种盒始终平行于地面;此时传感器没有检测到蒜种盒,输送装置继续运输蒜种盒,直到下一蒜种盒到位时停止。当机械臂达到指定转角时停止摆动,机械手张开,蒜种盒投放至地面,随后机械臂立刻回摆,抓取下一蒜种盒;投放后的蒜种盒与上一蒜种盒首尾衔接。
2 全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置关键部件
2.1 机械手参数设计
机械手主要包括U形旋转架、L形安装板、控距舵机、异形齿盘、连架杆、连接臂和爪片,如图3所示。爪片尺寸根据蒜种盒高度、重心位置等参数确定,尺寸为 40 mm´30 mm´2 mm,内侧涂覆有橡胶层,目的是增大爪片与蒜种盒间摩擦,防止在运输过程中掉落。连架杆、齿柄与连接臂铰接安装,三者构成自由度为1的平行四边形连杆机构。控距舵机动力输出轴与异形齿盘连接,通过驱动连杆机构运动使机械手实现闭合、张开动作。以异形齿盘分度圆圆心为原点,建立坐标系如图4所示。
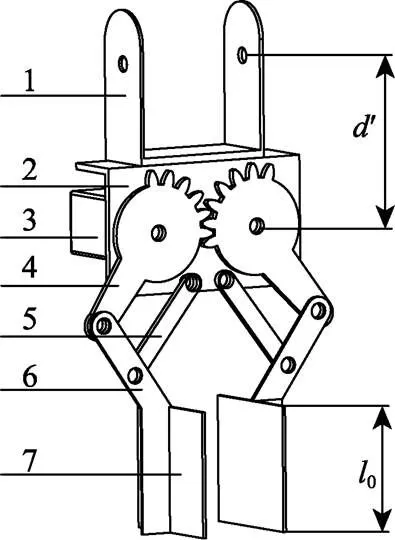
1. U形旋转架 2. L形安装板 3. 控距舵机 4. 异形齿盘 5. 连架杆 6. 连接臂 7. 爪片
1. U shape rotating frame 2. L shape mounting panel 3. Distance controlling actuator 4. Special shaped gear disk 5. Connecting rod 6. Connecting arm 7. Claw
注:为控距舵机动力输出轴安装距离,mm;0为爪片高度,mm,30 mm。
Note:represents installing distance of distance controlling actuator power output shaft, mm;0represents claw height; mm, 30 mm.
图3 机械手结构示意图
Fig.3 Schematic diagram of manipulator structure
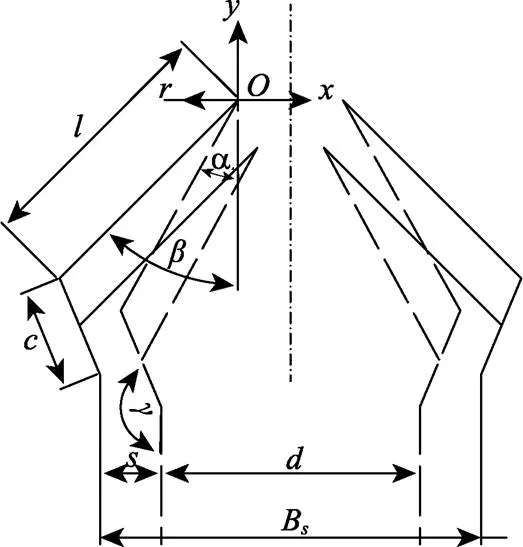
注:O为坐标原点;r为异形齿盘分度圆半径,取12 mm;l为连架杆长度,mm;c为连接臂长度,mm;d为蒜种盒宽度,mm;s为爪片张开和闭合时的距离差,mm;α为控距舵机初始角,(°);β为控距舵机终止角,(°);γ为连接臂与爪片夹角,取150°;BS为机械手张开后宽度,mm。
以机械手为研究对象,其主要结构参数计算方法如下
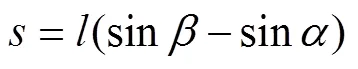
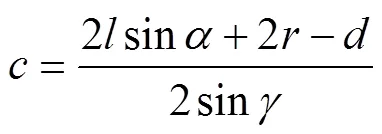
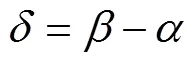
式中为控距舵机转角,(°)。
根据式(1)和式(2),连接臂长度范围20~40 mm,连架杆长度范围30~50 mm时,控距舵机初始角变化趋势如图5所示,控距舵机初始角随着连接臂长度增大而增大,随着连架杆长度的减小而增大。平行四连杆机构中,以连接臂为最短杆,以连架杆为最长杆,为满足杆长条件,保证机构良好的传力性能,选取连接臂长度为30 mm,连架杆长度为40 mm,此时26.75°。实际操作中要求爪片牢固抓紧蒜种盒以防止滑落,控距舵机初始角应略小于理论值,因此初始角取25°。同时,由于输送带上均匀分布有种盒定位板,爪片张开和闭合时的距离差过大或过小都无法使机械手准确抓取蒜种盒,当距离差在10~15 mm范围内即可满足工作要求。取控距舵机终止角=45°,将已知参数代入式(1)计算得距离差=11.38,符合设计要求。
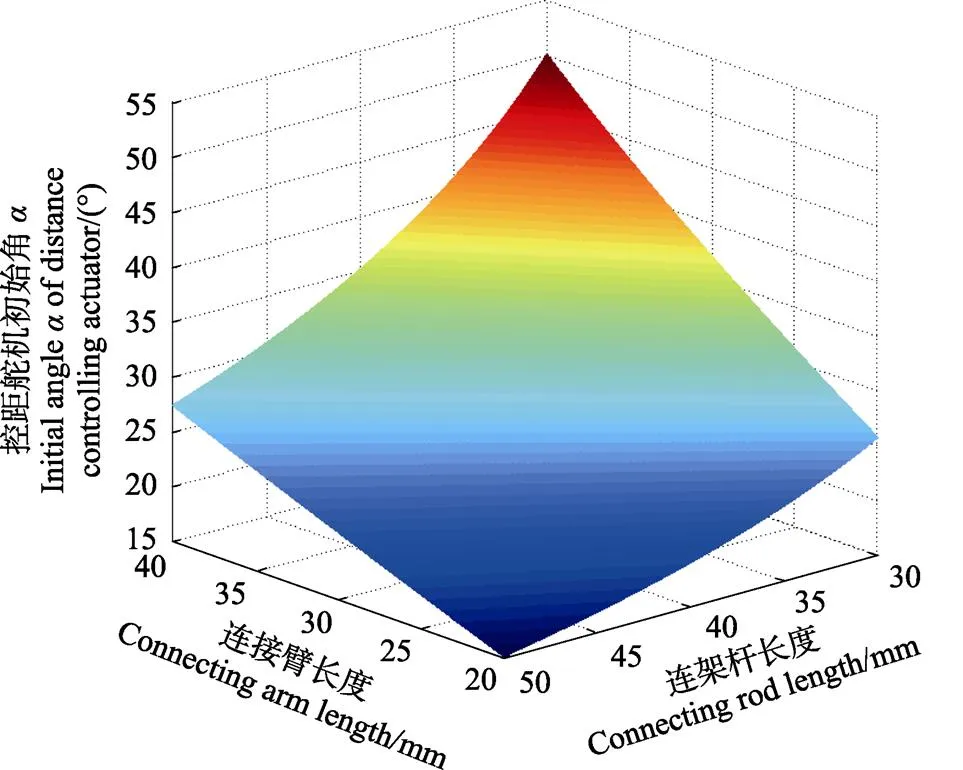
图5 连接臂长度与连接杆长度对控距舵机初始角α的影响
2.2 机械臂设计
机械臂依靠中心舵机的驱动实现前后摆动。机械手抓取蒜种盒时长度和机械手张开后宽度对机械臂的结构参数有直接影响。工作时爪片抓取在蒜种盒的中间位置,如图6所示。
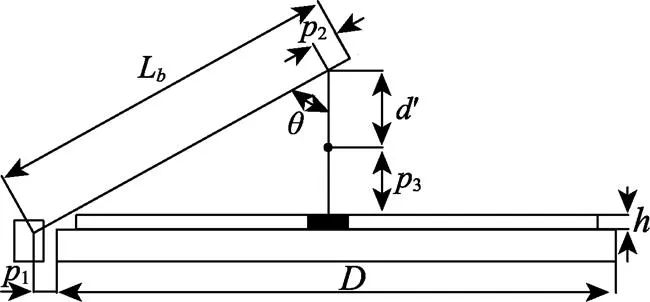
注:h为蒜种盒高度,30 mm;p1为中心舵机动力输出轴到输送装置边缘的距离,mm;p2为辅助舵机动力输出轴到机械臂顶端的距离,30 mm;p3为机械手提取蒜种盒时长度,mm;D 为输送带宽度,600 mm;Lb为机械臂的长度,mm;θ为提取蒜种盒时机械臂与机械手的夹角,(°)。
为防止机械手和蒜种盒在运动过程中与机械臂发生碰撞,保证机械臂运动过程中的稳定性,机械臂结构参数应满足以下条件
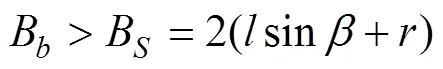
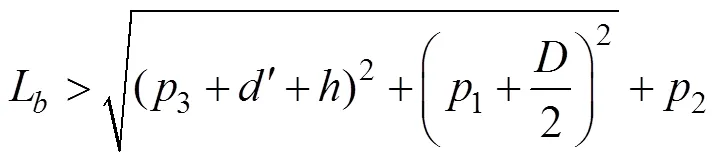
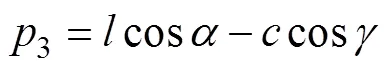
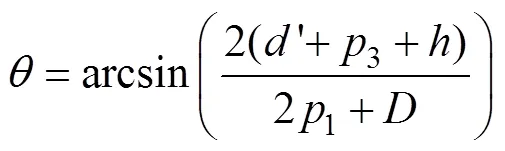
式中B为机械臂的宽度,mm;B为机械手张开后宽度,mm。
考虑到单片机系统便于设置控制中心舵机和辅助舵机转角,设定=60°。将已知参数代入式(4)~(7)中得到3=54.3,¢=201.5,B=80.6,L>427.8。结合实际需要,确定机械臂宽度B为85 mm,机械臂长度L为435 mm。根据计算获得机械臂的参数,以及实际承重能力,选择型号为LF-20MG 舵机,其基本参数为额定电压6.6 V,扭矩1.96 N·m。
2.3 自动控制系统设计
自动控制系统的核心是单片机系统,如图7所示,主要包括信号处理单元[29]、步进电机控制单元[30]、舵机控制[31]单元、模数转换单元等。自动控制系统工作流程如图8所示。
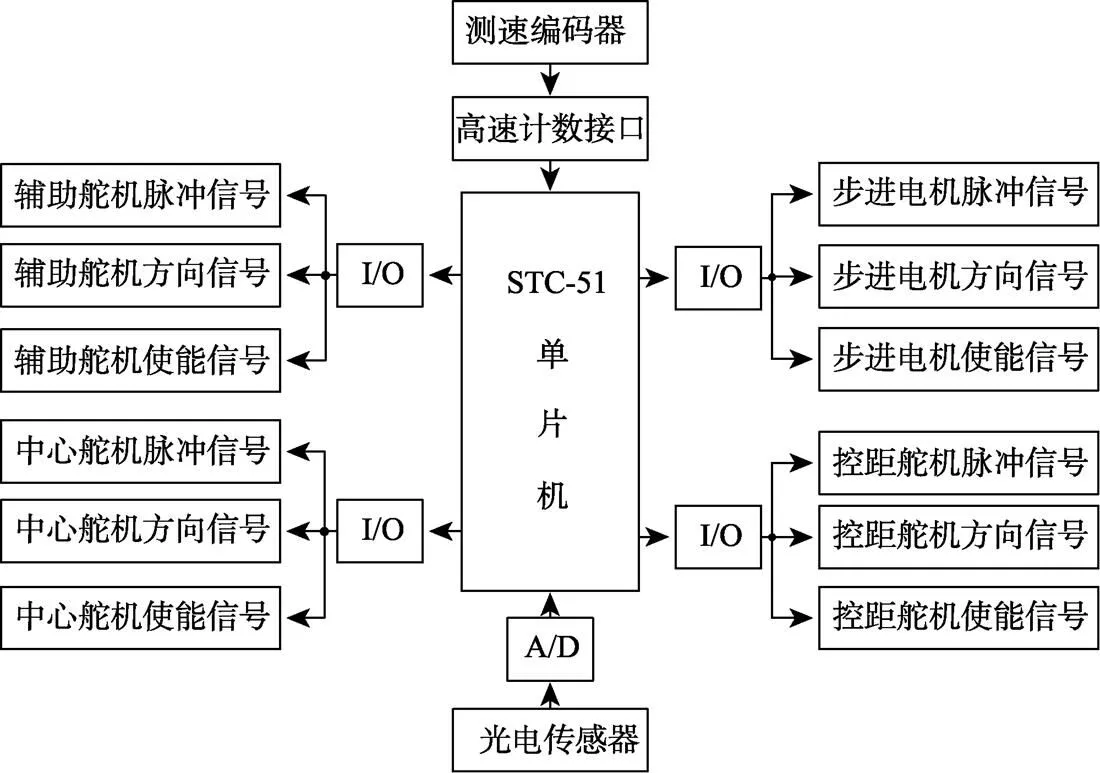
注:A/D为模数转换模块;I/O为信号输入/输出端口。
本控制系统硬件部分主要包括 STC 5A60S2 单片机、ADC0832 转换器、1 个电源开关、1个行程开关、1 个舵机控制板、1 个电机驱动器、2 个步进电机以及电源电路、放大电路等。系统工作时,光电传感器检测蒜种盒有无,若有蒜种盒,传感器输出电信号,经过 A/D 转换输出低电平送入单片机,命令驱动输送装置的步进电机停止转动;同时测速编码器将位移信息通过逻辑电路转化为脉冲信号送入单片机,单片机设定中心舵机、辅助舵机和控距舵机转角,发出运转指令;若无蒜种盒,单片机持续接收高电平,命令步进电机继续转动。
为使蒜种盒在运输过程中始终保持水平状态,中心舵机和辅助舵机设定为转速相同、转向相反。1个完整的工作周期包括机械臂往复摆动所用时间1和机械手提取投放蒜种盒用时2,时间内机组行进距离等于1个蒜种盒长度,工作周期内机械臂与机械手工作时间比为,各工作参数计算公式如下
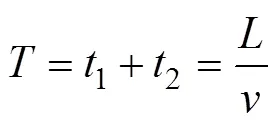
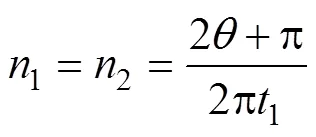
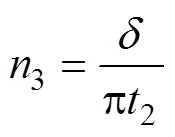
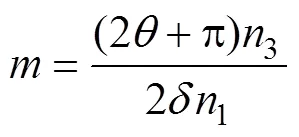
式中为机组行进速度,km/h;n为中心舵机转速,r/min;n为辅助舵机转速,r/min;n为控距舵机转速,r/min。
在不同工作条件下(如蒜种盒长度、行进速度等),可以通过改变1、2、的取值调整各舵机转速。当蒜种盒长度=600 mm时,中心舵机和控距舵机转速随机组行进速度变化规律如图9所示,可知中心舵机转速随行进速度变化的幅度较明显,为实际舵机操作提供理论依据。
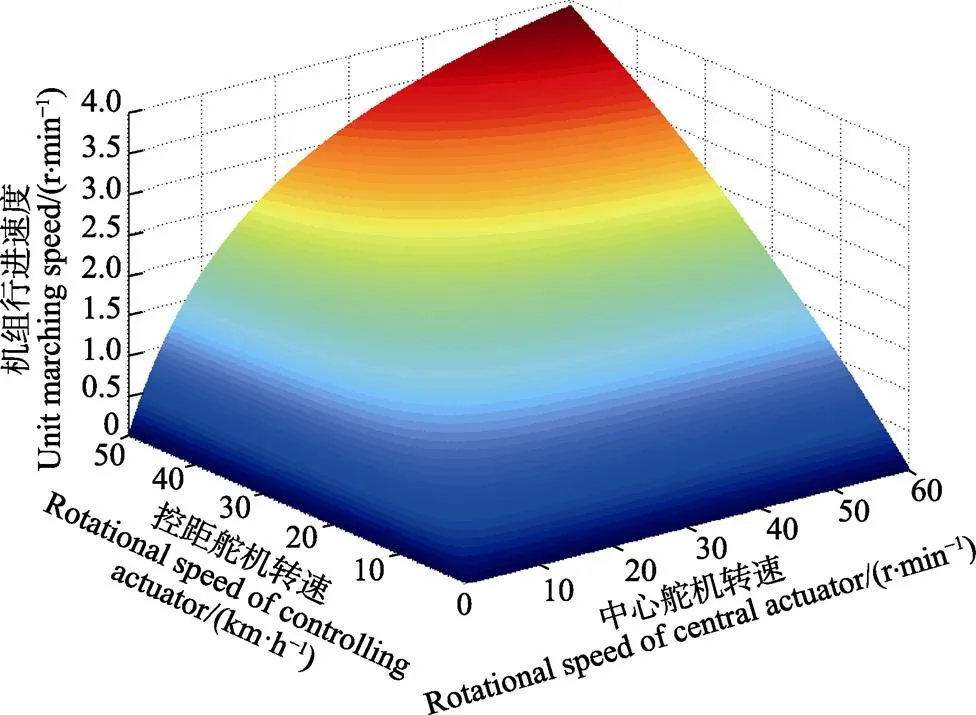
图9 机组行进速度对各舵机转速影响
3 蒜种盒投放试验
蒜种盒投放试验目的是测试机组行进速度对蒜种盒投放效果的影响。试验在山东农业大学机电学院实验室进行。以蒜种盒投放后衔接间隙作为试验指标,试验用蒜种盒长度为 600 mm,设定机械臂与机械手工作时间比=4。行进速度选取6个水平:0.36、0.54、0.72、0.90、1.08和1.26 km/h,由式(7)~(10)计算得相应水平下中心舵机及辅助舵机转速理论值分别为:10.42、15.63、20.83、26.04、31.25、36.46 r/min,控距舵机转速分别为:5.56、8.33、11.11、13.89、16.67、19.44 r/min。每个水平投放15个蒜种盒,每组试验重复3次,使用钢尺测量投放间隙,最终取平均值进行统计,蒜种盒投放结果如图11所示。试验结果显示随着机组行进速度增大,蒜种盒投放后衔接间隙逐渐增大;综合考虑播种机工作效率和蒜种盒投放效果,机组行进速度为0.90 km/h时,衔接间隙为5.6 mm,投放效果较优,满足大蒜播种要求。
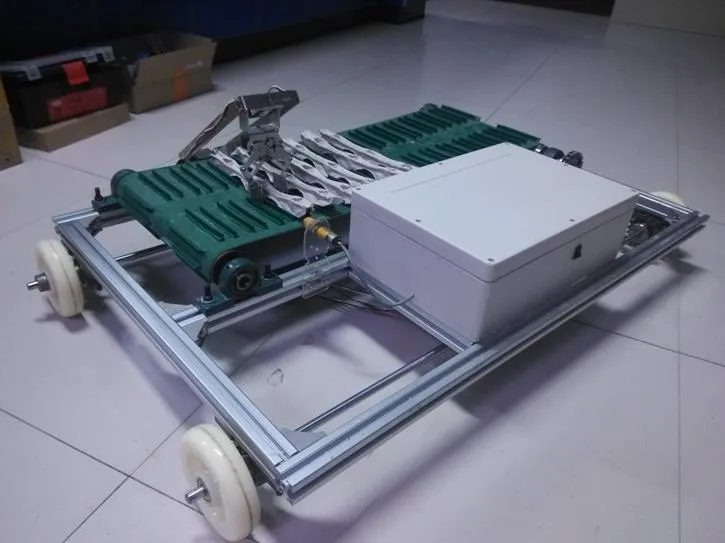

图10 全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置
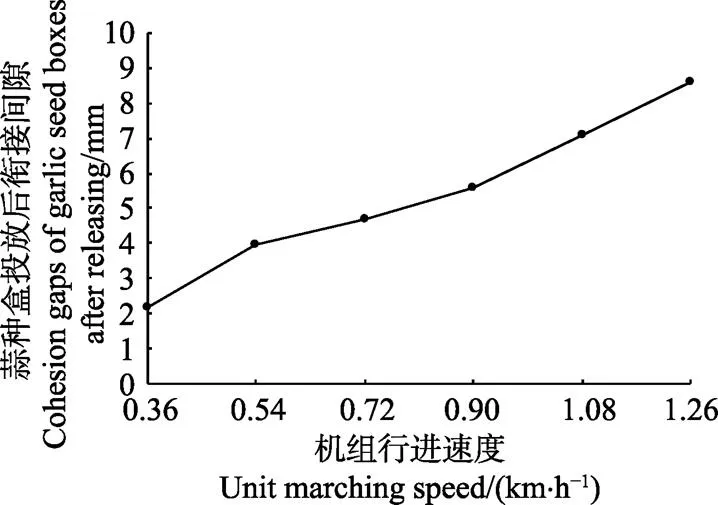
图11 蒜种盒投放后衔接间隙试验结果
4 结 论
1)设计了一种全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置,能够实现蒜种盒自动给进、准确抓取、平稳输送、精确投放的功能,设计了输送装置、提取投放装置以及自动控制系统等关键部件。
2)建立了各关键部件参数数学模型,确定了机械手和机械臂结构和工作参数,探明了机组行进速度与各舵机转速间变化规律。
3)进行了蒜种盒投放试验,结果表明机组行进速度为0.90 km/h,中心舵机、控距舵机转速分别为26.04、26.04、13.89 r/min时投放后衔接间隙为5.6 mm,投放效果较优,能够满足大蒜播种要求。
针对不能彻底消除蒜种盒投放后衔接间隙的问题,后续工作为研究舵机转速控制算法的精确性、舵机转速自动控制方式等。
[1] 马招弟,丁天娇. 中国大蒜出口贸易现状研究[J]. 农村经济与科技,2017,28(2):64,266.
[2] 王盛威,熊露,韩书庆,等. 2016年中国大蒜市场形势分析及后市展望[J]. 农业展望,2016,12(11):4-6.
[3] Benjaphragairat J, Sakurai H, Ito N. Study of the mechanics of a 5 hp power tiller attached to a 10-row garlic planter[J]. Agricultural Mechanization in Asia, 2010, 41(1): 40—44.
[4] Bakhtiari M R, Loghavi M. Development and evaluation of an innovative garlic clove precision planter[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2010, 11(2): 125—136.
[5] Brajesh N, Atul K S, Rajesh K N, et al. Design, Development and Evaluation of Self Propelled Garlic (L.) Clove Planter[D]. Jabalpur: College of Agricultural Engineering Jabalpur, 2010.
[6] Труфляк Е В, Скоробогаченко И С, Сапрыкин В Ю. Ручная сеялка точно-ориентированного посева зубков чеснокаи луковиц[J]. Политематический сетевой электронный научный журнал Кубанского государственного аграрного университета, 2014, 104(10): 1—17.
[7] Bakhtiari M R. Determining physical and aerodynamic properties of garlic to design and develop of a pneumatic garlic clove metering system[J]. Agricultural Engineering International: CIGR Journal, 2015, 17(1): 59—67.
[8] Gajakos A V ,Saraf V V ,Sinha S,et al. Performance evaluation of manually operated garlic planter[J]. International Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 8(1): 31—38.
[9] Zhang Dengquan, Wu, Yanjuan, Zhang Chuangkai. Vertical planting structure design for planter[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 654: 87—90.
[10] 赵丽清,杨然兵,殷元元,等. 智能机械臂在大蒜播种机中的应用[J]. 农机化研究,2014,36(8):104—106. Zhao Liqing, Yang Ranbing, Yin Yuanyuan, et al. The application of the intelligent mechanical arm in the planting of garlic[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2014, 36(8): 104—106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 王丹阳,钱彬彬,胡旭,等. 半自动大蒜栽植机关键部件的设计与试验研究[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报,2014,45(5):566—572.Wang Danyang, Qian Binbin, Hu Xu, et al. Key components design and experimental research of a semi-automatic garlic transplanter[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2014, 45(5): 566—572. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 谢学虎,张永,刘召,等. 大蒜播种机种植机构的设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(1):34—39. Xie Xuehu, Zhang Yong, Liu Zhao, et al. Design of planting mechanism for garlic planter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(1): 34—39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 谢学虎. 大蒜播种机播种机构设计[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2015. Xie Xuehu. Design of Seeding Mechanism for Garlic Sowing Machine[D]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 耿爱军,张兆磊,宋占华,等. 蒜种盒机械投放过程运动学分析与参数优化试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(5):29—35. Geng Aijun, Zhang Zhaolei, Song Zhanhua, et al. Kinematic analysis and parameter optimized experiment of garlic box release process[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(5): 29—35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 张兆磊,耿爱军,李汝莘,等. 蒜种振动排序装置设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2015,37(08):138—147. Zhang Zhaolei, Geng Aijun, Li Rushen, et al. Design and test of the garlic seed sequencing vibration machine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015, 37(08): 138—147. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 魏玉珍,邹栋林,刘勇兰,等. 大蒜芽端筛选及直立种植方案探究[J]. 农机化研究,2017,39(10):113—118.
[17] 魏玉珍,邹栋林,刘勇兰,等. 大蒜直立筛选方法探究及其装置设计[J]. 农机化研究,2017,39(5):122—125.
[18] 杜颖财,王希军,王树洁,等. 增量式编码器自动检测系统[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报,2012,26(11):993—998.Du Yingcai, Wang Xijun, Wang Shujie, et al. Auto detection system of incremental encoder[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2012, 26(11): 993—998. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 王群京,陈丽霞,李争,等. 基于光电传感器编码的永磁球形步进电机运动控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2005,25(13):113—117. Wang Qunjing, Chen Lixia, Li Zheng, et al. The control of a permentmagnet spherical stepper motor based on the coder of optoelectronic sensors[J]. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2005, 25(13): 113—117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 李建勋. 数字电路与逻辑设计[M]. 北京:北京科学出版社,1981.
[21] 乔治·埃利斯. 控制系统设计指南[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2016.
[22] 江晓军. 光电传感与检测技术[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2011.
[23] 余愿. 传感器原理与检测技术[M]. 湖北:华中科技大学出版社,2017.
[24] 赵丽清,马志勇. 大蒜播种机装盘系统蒜瓣定向识别算法的研究[J]. 农机化研究,2013,35(06):163—166.
[25] 杨清明. 基于图像处理的大蒜播种机排序机构设计[D]. 南京:南京农业大学,2010.
[26] 陈忠平. 基于Proteus的51系列单片机设计与仿真[M]. 北京:电子工业出版社,2015.
[27] 郝向泽,何旭鹏,邹翌,等. 基于光电传感器的精密播种机排种性能监测系统的研究[J]. 华南农业大学学报,2017,38(01):120—124.
[28] 张志良. 80C51单片机实用教程:基于Keil C和Proteus[M].北京: 高等教育出版社,2016.
[29] 陈生潭. 信号与系统[M]. 西安: 电子科技大学出版社,2014.
[30] 王鸿钰. 步进电机控制技术入门[M]. 上海: 同济大学出版社,2009.
[31] 刘沛尧,彭舒岗,李建民,等. 数字舵机精确控制法研究与实现[J]. 计算机测量与控制,2014,22(7):2097—2099.Liu Peiyao, Peng Shugang, Li Jianmin, et al. Research and implementation for method of precise digital control of steering gear[J]. Computer measurement and control, 2014, 22(7):2097-2099.
[32] 郭天祥. 新概念51单片机C语言教程[M]. 北京:电子工业出版社,2009.
栗晓宇,耿爱军,侯加林,张 姬,张智龙. 全自动蒜种盒提取投放装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(23):32-37. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.23.005 http://www.tcsae.org
Li Xiaoyu, Geng Aijun, Hou Jialin, Zhang Ji, Zhang Zhilong. Design and experiment of full-automatic lifting and releasing device of garlic seed box[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(23): 32-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.23.005 http://www.tcsae.org
Design and experiment of full-automatic lifting and releasing device of garlic seed box
Li Xiaoyu1, Geng Aijun1,2※, Hou Jialin1, Zhang Ji1,Zhang Zhilong1
(1.271000,;2.271000,)
Garlic is one of the major cash crops in China, and it is mainly distributed in Shandong, Henan and Jiangsu Provinces. Single grain sowing is crucial for garlic planting, it needs to follow the agronomic requirements of root down and scaly bud upward, and therefore garlic planting mainly uses artificial means, but this method has shortcomings of strong labor intensity and low efficiency. Correspondingly, some developed countries like America and Korea have realized garlic planting mechanization in 1950-1960s, which have extensive arable land and indefinite requirement of garlic scaly bud direction when planting, and thus foreign garlic planting machinery is not suited to China’s national conditions. In recent years, the garlic planter is developed towards automation and intelligence. However, existing garlic planter is hard to distinguish the direction of garlic scaly bud, and it also has complex structure and low efficiency. The scaly bud direction distinguishing is a core technology of garlic planter, and it is also the most difficult technical operation. Therefore, how to ensure direction of the garlic seed scaly bud in the process of planting has been a key technical problem of garlic planter. According to present condition, a full-automatic extraction and release device of garlic seed box was designed based on garlic seed box method, and it can automatically track driving according to the travel speed of machine. The full-automatic extraction and release device of garlic seed box consists of drive system, conveying device, extraction and release device, speed encoder, photoelectric sensor and MCU (micro-controller unit) system. The drive system consists of stepper motor, sprocket and chain, and it has 2 parts, and one provides transmission power for the whole machine walking, and the other controls conveying device working. The conveying device consists of conveying belt, roll shaft and bearing housing, the conveying belt is transversely mounted on the frame through roll shaft and bearing housing, and its working state is controlled by MCU system. The conveying device mainly carries out transverse transportation of garlic seed boxes. The extraction and release device consists of steering wheel, central actuator, mechanical arm, auxiliary actuator and manipulator, among which the manipulator consists of U shape rotating frame, L shape mounting panel, distance controlling actuator, special shaped gear disk, connecting rod, connecting arm and claws, and it mainly realizes the functions of garlic seed boxes precision capture, smooth traffic and seamless release. The velocity measurement encoder is used for detecting unit movement speed, and provides speed messages to central actuator and distance controlling actuator. The photoelectric sensor is used to detect whether the garlic box is in place. The garlic seed box planting method reduces the damage of garlic seed and improves work efficiency, and solves the problem of the direction of garlic seed. This paper designed mechanical arm and manipulator, the mathematical model of each key component was established through the theory analysis, and thus the structure and working parameters of mechanical arm and manipulator were determined. At the same time, the influence rule of the speed of device marching on operation parameters of mechanical arm and manipulator was proved, and the influencing factors of the clearance of adjacent garlic seed boxes were specified. The test was carried out for testing the influence of the speed of device marching on the clearance of adjacent garlic seed boxes after they were released. The results showed that when the speed of marching is 0.90 km/h, and the speeds of central actuator, auxiliary actuator and distance controlling actuator are 26.04, 26.04, and 13.89 r/min, respectively, the clearance of adjacent garlic seed boxes is less, which is 5.6 mm, and the release effect is better. The machine has better stability and release effect, and work efficiency of device has been improved obviously. The research results can provide reference for realizing automation of garlic planting.
agricultural machinery; design; crops; garlic planting; garlic seed boxes; lifting and releasing; automation
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.23.005
S223.2+5
A
1002-6819(2017)-23-0032-06
2017-06-10
2017-11-22
山东省农机装备研发创新计划项目(2016YF009);山东省重点研发计划项目(2016GNC112004);国家特色蔬菜产业技术体系项目资助(CARS-24-D-01);山东农业大学“双一流”园艺机械装备协同创新团队(SYL2017XTTD07)
栗晓宇,主要从事农业机械研究。Email:lixiaoyu@sdau.edu.cn
耿爱军,副教授,主要从事农业机械设计及理论的研究。Email:gengaj@sdau.edu.cn
