CT、MRI在眼眶海绵状血管瘤与眼眶神经鞘瘤影像学鉴别诊断中的研究
2017-11-28李金星郭庆环张林昌
李金星,郭庆环,张林昌
(天津市第五中心医院 放射科,天津300451)
CT、MRI在眼眶海绵状血管瘤与眼眶神经鞘瘤影像学鉴别诊断中的研究
李金星,郭庆环,张林昌*
(天津市第五中心医院 放射科,天津300451)
目的对CT、MRI在眼眶海绵状血管瘤与眼眶神经鞘瘤的影像学鉴别诊断中的应用价值进行研究。方法选取我院2015年3月至2016年3月收治的经CT诊断为眼眶海绵状血管瘤患者38例和眼眶神经鞘瘤患者45例,经MRI诊断为眼眶海绵状血管瘤患者41例和眼眶神经鞘瘤患者39例。对所有患者进行肿瘤鉴别诊断,主要分为定性诊断符合和定位诊断符合,定性诊断符合是影像学诊断与病理诊断结果一致;定位诊断符合是影像学诊断与手术定位结果一致。分别计算CT、MRI的定性、定位诊断符合率。结果CT诊断的38例眼眶海绵状血管瘤患者定性诊断正确的31例,定性诊断符合率为81.58%;定位诊断正确33例,定位诊断符合率为86.84%。CT诊断的45例眼眶神经鞘瘤患者定性诊断正确的39例,定性诊断符合率为86.67%;定位诊断正确37例,定位诊断符合率82.22%。MRI诊断的41例眼眶海绵状血管瘤患者定性诊断正确的38例,定性诊断符合率为92.68%;定位诊断正确39例,定位诊断符合率为95.12%。MRI诊断的39例眼眶神经鞘瘤患者定性诊断正确的36例,定性诊断符合率为92.31%;定位诊断正确的37例,定位诊断符合率为94.87%。CT、MRI诊断眼眶海绵状血管瘤的定性符合率和定位符合率差异均无统计学意义(Pgt;0.05),CT、MRI诊断眼眶神经鞘瘤的定性符合率和定位符合率差异也均无统计学意义(Pgt;0.05)。结论CT、MRI在眼眶海绵状血管瘤和眼眶神经鞘瘤的影像学鉴别诊断中均具有非常重要的作用,二者的定性、定位诊断符合率均很高,具有很高的应用价值。
CT;MRI;眼眶海绵状血管瘤;眼眶神经鞘瘤;影像学鉴别诊断
(ChinJLabDiagn,2017,21:1890)
眼眶海绵状血管瘤与眼眶神经鞘瘤都是临床上常见的一种眼眶肿瘤,其中眼眶海绵状血管瘤的临床表现多为引起缓慢地、渐进性单侧眼球突出,眼眶海绵状血管瘤患者的早期症状很难被发现,患者也难以察觉,因此对患者的健康造成较大的威胁[1,2]。本文主要探讨CT和MRI在眼眶海绵状血管瘤和眼眶神经鞘瘤的影像学鉴别诊断中的应用价值和效果,具体报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料
选取我院2015年3月至2016年3月收治的经CT诊断为眼眶海绵状血管瘤患者38例(男20例,女18例)和眼眶神经鞘瘤患者45例(男24例,女21例),经MRI诊断为眼眶海绵状血管瘤患者41例(男21例,女20例)和眼眶神经鞘瘤患者39例(男19例,女20例)。CT诊断的患者中最低年龄18岁,最高年龄72岁,平均年龄(39.1±2.5)岁;MRI诊断的患者中最低年龄21岁,最高年龄73岁,平均年龄(41.2±2.3)岁。所有患者影像学诊断后均行手术并做病理学诊断。CT和MRI诊断的两组患者在年龄、性别等一般资料方面无显著性差异,具有可比性。
1.2方法
磁共振成像扫描采用Siemens Magnetom Skyra3.0T超导核磁共振仪,圆形极化相控阵颅脑表面线圈,扫描参数:T1W(TR169ms,TR2.5ms)、T2W(TR3500ms,TE69ms),FOV340 mm×340 mm,层间距0.4 mm,层厚4 mm,激励2次。所有患者均进行增强扫描,造影剂为轧喷酸葡胺(广州康臣药业公司),静脉给药,注射后立即扫描。CT扫描根据患者的具体情况选择合适的层面,部分行增强扫描,采用东芝TCT-80 A CT扫描仪,扫描参数:层厚5 mm,层间距5 mm,矩阵512×512。增强对比剂采用泛影葡胺,静脉给药50-100 ml[3]。
1.3观察指标[4]
在患者的手术过程中观察病灶的位置,将影像学诊断结果与之比较,判断是否正确。对患者的病灶组织进行病理学检验,将影像学诊断结果与病理结果比较,判断是否正确。
1.4统计学方法
对所得数据资料全部采用SPSS18.0统计软件进行统计分析,计数资料采用卡方检验,计量资料采用t检验。当Plt;0.05时,差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1CT、MRI诊断眼眶海绵状血管瘤的定位、定性诊断符合率比较CT诊断的38例眼眶海绵状血管瘤患者定性诊断正确的31例,定性诊断符合率为81.58%;定位诊断正确33例,定位诊断符合率为86.84%。MRI诊断的41例眼眶海绵状血管瘤患者定性诊断正确的38例,定性诊断符合率为92.68%;定位诊断正确39例,定位诊断符合率为95.12%,见表1,图1,图2。差异均无统计学意义(Pgt;0.05)。
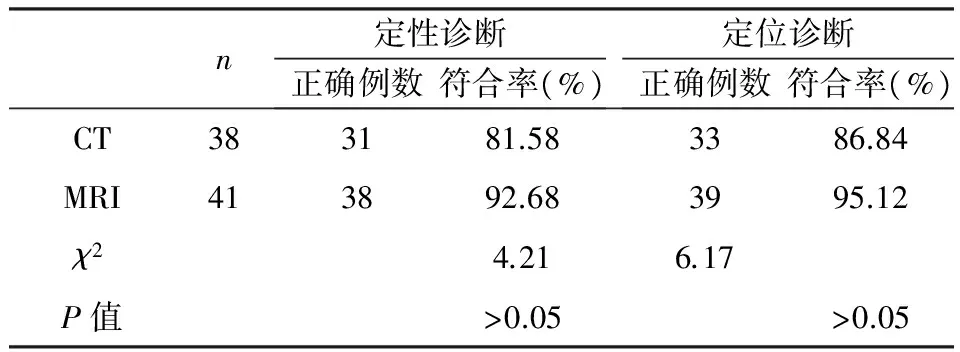
表1 CT、MRI诊断眼眶海绵状血管瘤的定位、定性诊断符合率比较
2.2CT、MRI诊断眼眶神经鞘瘤的定位、定性诊断符合率比较CT诊断的45例眼眶神经鞘瘤患者定性诊断正确的39例,定性诊断符合率为86.67%;定位诊断正确37例,定位诊断符合率82.22%。MRI诊断的39例眼眶神经鞘瘤患者定性诊断正确的36例,定性诊断符合率为92.31%;定位诊断正确的37例,定位诊断符合率为94.87%。见表2。
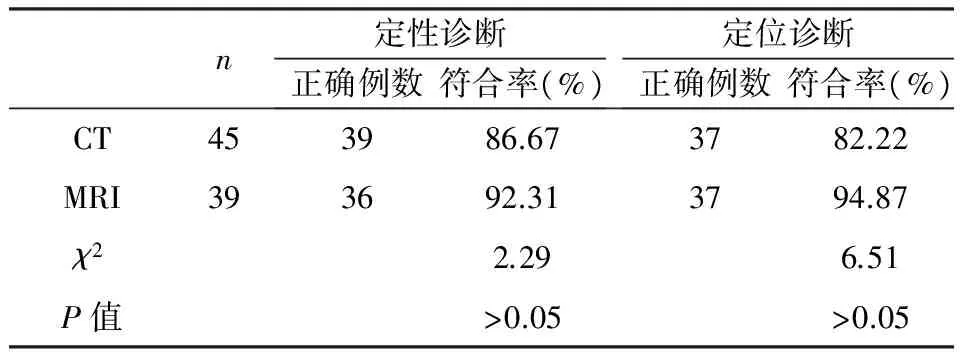
表2 CT、MRI诊断眼眶神经鞘瘤的定位、定性诊断符合率比较
3 讨论
眼眶海绵状血管瘤和眼眶神经鞘瘤都是临床上常见的一种眼眶肿瘤,其中眼眶神经鞘瘤在眼眶肿瘤中的发病率较高,对患者的身体健康带来严重的影响,严重的甚至会威胁到患者的生命[5,6]。眼眶神经鞘瘤在眼眶肿瘤中的发病率高达20%左右,相关报道显示,神经源肿瘤分类中,神经鞘瘤占比位居第一位[7]。CT的扫描平面分为矢状、水平和冠状三个方向,临床扫描时可根据患者的具体情况选择其他位置层面进行扫描[8]。磁共振成像将某些特定的原子核放置在磁场内,由射频脉冲对其激励,让原子核吸收后释放出脉冲信号,从而形成体层像[9,10]。由于两种疾病的早期症状都不是很明显,患者自身难以察觉得到,普通的检查手段误诊率也较高,故而CT和MRI这两种较为先进的影像学检查手段在这两种疾病的鉴别诊断中发挥着巨大的作用[11,12]。
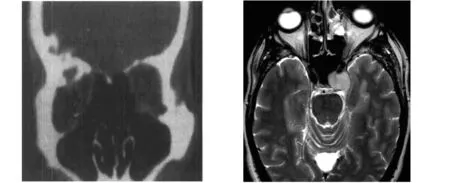
图1眼眶海绵状血管瘤CT诊断图2眼眶海绵状血管瘤MRI诊断
本研究显示T诊断的38例眼眶海绵状血管瘤患者定性诊断正确的31例,定性诊断符合率为81.58%;定位诊断正确33例,定位诊断符合率为86.84%。CT诊断的45例眼眶神经鞘瘤患者定性诊断正确的39例,定性诊断符合率为86.67%;定位诊断正确37例,定位诊断符合率82.22%。MRI诊断的41例眼眶海绵状血管瘤患者定性诊断正确的38例,定性诊断符合率为92.68%;定位诊断正确39例,定位诊断符合率为95.12%。MRI诊断的39例眼眶神经鞘瘤患者定性诊断正确的36例,定性诊断符合率为92.31%;定位诊断正确的37例,定位诊断符合率为94.87%。CT、MRI诊断眼眶海绵状血管瘤的定性符合率和定位符合率差异均无统计学意义(Pgt;0.05),CT、MRI诊断眼眶神经鞘瘤的定性符合率和定位符合率差异也均无统计学意义(Pgt;0.05)。通过本文的研究结果可以看出,CT和MRI在诊断眼眶海绵状血管瘤和眼眶神经鞘瘤中的定性诊断符合率和定位诊断符合率均无显著的差异,且二者的诊断符合率均较高,说明其在眼眶海绵状血管瘤和眼眶神经鞘瘤的鉴别诊断中应用价值高[13]。
相关临床报道认为[14,15],虽然CT和MRI在诊断眼眶海绵状血管瘤和神经鞘瘤的符合率无显著差异,但在扫描特点上来看,MRI和CT的增强扫描特点基本一致,作出的定性诊断结果基本一致,而在神经鞘瘤的诊断上,MRI优于CT,因为MRI可以更加清晰的显示肿瘤的位置、边界以及形状。
[1]倪 卓,马小葵,郭秉宽.1422例眼眶肿瘤的病理分类[J].中华眼科杂志,1991,27:71.
[2]宋国祥.眼眶肿瘤的超声显像[J].中华眼科杂志,1983,19:39.
[3]宋国祥,田文芳.眼眶海绵状血管瘤的临床分析[J].中华眼科杂志,1988,24:132.
[4]陈星荣,沈天真,段承祥,等主编.全身CT和MRI[M].上海:上海医科大学出版社,1994.546.
[5]孙丰源,宋国祥.眼眶神经鞘瘤诊断中现代检查方法的应用[J].中华眼科杂志,1994,30:354.
[6]WSB Lee K F.The agger nasi cell:the key to understanding the anatomy of the frontal recess[J].Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.2014,12(9):497.
[7]Choi Bi,Lee HJ,Han JK,et al.Detection of hypervascular nodular hepatocellur carcinomas:value of triphasic helical CT compared with iodized oil CT[J].AJR,2013,157(2):219.
[8]Khan MA,Combsc,Brunt EM,et al.Positron emission tomography scanning in the evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Ann Nucl Med,2012,14(2):121.
[9]Tabit CE,Chung WB,Hamburg NM,et al.Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus:molecular mechanisms and clinical implications[J].Rev Endocr Metab Disord,2014,11(1):61.
[10]Endemann DH,Schiffrin EL.Endothelial dysfunction[J].J Am Soc Nephrol,2015,15(8):1983.
[11]Izzard AS,Rizzoni D,Agabiti-Rosei E,et al.Small artery structure and hypertension:ada ptive changes and target organ damage[J].J Hypertens,2011,23(2):247.
[12]Zhang Y,Li W,Yan T,et al.Early detection of lesions of dorsal artery of foot in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus by high-frequency ultrasonography[J].J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci,2011,29(3):387.
[13]Nicolls MR,Haskins K,Flores SC.OXidant stress,immune dysregulation,and vascular function in typeI diabetes[J].Antio Xid Redo X Signal,2012,9(7):879.
[14]Gokce N,Vita JA,Mc Donnell M,et al.Effect of medical and surgical weight loss on endothelial vasomotor function in obese patients[J].Am J Cardiol,2011,95(2):266.
[15]Lteif AA,Han K,Mather K J.Obesity,insulin resistance,and the metabolic syndrome:determinants of endothelial dysfunction in whites and blacks[J].Circulation,2013,112(1):32.
CTandMRIstudyondifferentialdiagnosisoforbitalcavernoushemangiomaandorbitalschwannomaimage
LIJin-xing,GUOQing-huan,ZHANGLin-chang*.
(TheFifthCentralHospitalofTianjin,Tcanjin300451,China)
ObjectiveTo study the CT and MRI value in the differential diagnosis of orbital cavernous hemangioma and orbital schwannoma image.Methodsin our hospital from March 2015 to March 2016 were diagnosed by CT in 45 cases and 38 cases of orbital schwannoma in patients with orbital cavernous hemangioma,39 cases diagnosed by MRI and 41 cases of orbital schwannoma in patients with orbital cavernous hemangioma.All the patients underwent the differential diagnosis of tumors,mainly divided into qualitative diagnostic and positioning diagnosis and qualitative diagnosis is consistent with the imaging diagnosis and pathological diagnosis; localization diagnosis is the imaging diagnosis and surgical positioning results.Calculation of CT,MRI qualitative,positioning diagnostic compliance rate.ResultsCT diagnosis of 38 cases of orbital cavernous hemangioma in patients with qualitative diagnosis of 31 cases,the rate of qualitative diagnosis was 81.58%;33 cases were diagnosed correctly,the positioning accuracy of the diagnosis was 86.84%.CT diagnosis of 45 cases of orbital schwannoma were qualitatively correct diagnosis in 39 cases,diagnosis coincidence rate was 86.67%; 37 cases were diagnosed correctly positioning,positioning diagnosis rate 82.22%.MRI diagnosis of 41 cases of orbital cavernous hemangioma of the qualitative diagnosis of 38 cases,the rate of qualitative diagnosis was 92.68%; 39 cases were diagnosed correctly,the positioning accuracy of the diagnosis was 95.12%.MRI diagnosis of 39 cases of orbital schwannoma were qualitatively correct diagnosis in 36 cases,diagnosis coincidence rate was 92.31%; 37 cases of correct diagnosis,diagnosis coincidence rate is 94.87%.CT MRI,the qualitative diagnosis of orbital cavernous hemangioma coincidence rate and coincidence rate of localization was no statistically significant difference (Pgt;0.05),CT MRI,the qualitative diagnosis of orbital neurilemoma coincidence rate and localization coincidence rate differences were not statistically significant(Pgt;0.05).ConclusionCT and MRI in orbital cavernous hemangioma and orbital neurilemoma were imaging plays a very important role in the differential diagnosis,the coincidence rate is very high,the two qualitative diagnosis,and has high application value.
CT;MRI;cavernous hemangioma;orbital schwannoma;differential diagnosis imaging
*通讯作者
1007-4287(2017)11-1890-04
R739.8
A
张林昌,男,51岁,主任医师,研究方向,眼科疾病。
2016-11-17)
