碘造影剂过敏反应综述
2017-11-02陈宏王秋林
陈宏,王秋林
(成都医学院第一附属医院心内科,四川 成都 610500)
碘造影剂过敏反应综述
陈宏,王秋林
(成都医学院第一附属医院心内科,四川 成都 610500)
碘造影剂(ICM)广泛应用于血管造影、影像诊断等领域,注射ICM通常是安全的,但也可发生严重的不良反应。本文将从流行病学、分类、临床表现、危险因素、发病机制、预防等方面综述碘造影剂过敏反应进展情况。临床上发生所谓的ICM过敏反应实际上绝大多数属于类过敏反应,真正的过敏反应很少见。过敏反应可以分为4型,以IgE介导的I型过敏反应最常见,IV型过敏反应即延迟反应通常被认为是T细胞介导的,但其机制尚不十分确切。防治措施:(1)尽量应用非离子型ICM;(2)对中、重度过敏反应者需行对症支持治疗。
碘造影剂;过敏反应;发病机制;预防
碘造影剂(iodinated contrast media,ICM)目前广泛应用于血管造影、影像诊断等领域,据统计每年全世界有超过7 500万人次使用ICM[1-2]。注射ICM通常是安全的,但不良事件时有发生,多见的重要不良反应包括造影剂过敏反应、造影剂肾病、甲状腺毒症[3]。而造影剂过敏反应近年来成为学术研究的热点。
1 ICM的发展史、类别及安全性
20世纪50年代第一个血管造影剂-泛影酸(amidotrezoic acid)被发明[4],几十年来血管造影剂不断发展,现广泛应用的碘造影剂都在其分子结构三碘苯环上发展而来。ICM按渗透压[5]可以分为高渗ICM(≥1 400 mOsm/kg.H2O),低渗ICM(500~900 mOsm/kg·H2O)和等渗ICM(290 mOsm/kg·H2O),高渗性是造成不良反应的重要因素。ICM按照电离能力、碘苯环数又可以分成4类[5]:(1)离子型单体:高渗,以泛影葡胺为代表;(2)离子型二聚体:低渗,以碘克酸为代表;(3)非离子型单体:低渗,以碘海醇、碘佛醇为代表;(4)非离子型二聚体:等渗,以碘克沙醇为代表。日本[6]的大型前瞻性对照研究显示:离子型ICM组中不良反应发生率为12.66%,非离子型ICM组为3.13%;在离子型ICM中严重不良反应发生率为3.13%,而非离子型ICM为0.04%。我国徐亚伟教授[7]主持的全国95个中心20 185患者的大型前瞻性研究显示:碘克沙醇不良反应发生率为1.52%,严重不良反应发生率为0.01%,没有患者致命性死亡。上诉数据显示注射ICM是安全的,低渗透压的非离子型ICM比高渗透压的离子型ICM安全性更高[6-7]。现离子型ICM已逐渐被非离子型ICM所取代。
2 ICM不良反应的分类、临床表现
ICM不良反应可以分为3类:(1)过敏样反应(hypersensitivity reactions):包括过敏反应(allergy reactions)和类过敏反应(allergy-like reactions);(2)毒性反应(chemotoxic reactions);(3)与碘造影剂暴露不相关反应[8]。按时间又可分为急性反应和迟发型反应,急性反应是发生在1 h内的不良反应,迟发型反应是1 h~1周发生的不良反应[9-10]。大多数不良反应是非生命危险的,约70%发生在注射ICM前5 min内[11]。急性反应发生率通常是低的,一般认为儿童较成人发生率更低,成人0.2%~0.7%[12-14],儿童0.18%~0.46%[15-16]。急性反应按严重程度分为轻度、中度、重度3个等级,其临床表现[9-10](表1)。有报道,迟发型过敏样反应的发生率为0.5%~14%[17-19],大多数迟发型反应是皮肤反应,表现为轻到中度的,常见的皮肤反应为斑丘疹、迟发型荨麻疹、瘙痒[5,9-10,17-19],接触性皮炎、固定型药疹、史蒂文斯-约翰逊综合征、中毒性表皮坏死松解症、急性泛发性发疹性脓疱病也有报告[8,20]。
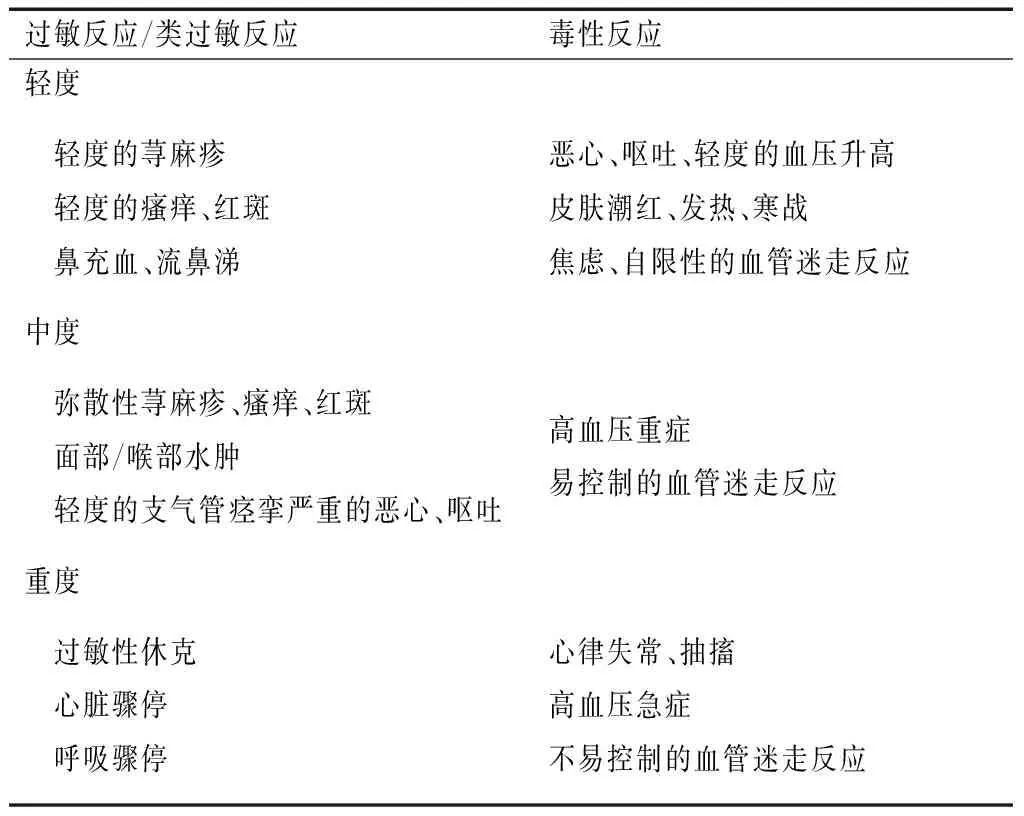
表1 ICM急性反应分类及临床表现[9-10]
3 ICM引起过敏反应的危险因素
速发型过敏反应的危险因素:既往ICM过敏史[6,12,15-16],对食物或其他药物过敏史[21],哮喘病史[6],女性[12-13]。延迟型过敏反应的危险因素:以前的延迟型过敏反应[17],使用白细胞介素-2治疗[22],使用非离子型二聚体ICM[23],有日本血统[17]。
4 ICM过敏样反应的机制
4.1急性过敏样反应的机制
碘造影剂急性过敏样反应的机制还不十分明确,以前认为是非特异性的组胺释放[5]。越来越多的证据表明,急性过敏样反应中存在真正的过敏反应[11,24]。
4.1.1 类过敏反应发生的机制 类过敏反应,又称非变应性过敏反应(non-allergy reactions)首次接触即可通过非免疫途径发生与过敏反应相似的症状[5,24]。临床上发生所谓的过敏反应实际上绝大多数属于类过敏反应[11,24]。类过敏反应的机制包括:(1)直接膜效应机制,可能与ICM的渗透压有关[25];(2)补体系统的激活[26];(3)促进缓激肽释放机制[27]。高渗透压可致细胞脱水、功能障碍,刺激嗜碱性粒细胞和肥大细胞,产生膜反应,诱导肥大细胞脱颗粒释放组胺、白三烯、前列腺素、类胰蛋白酶和细胞因子等介质,这些物质引发的炎症级联反应导致毛细血管扩张、渗透性增加、水肿和支气管平滑肌收缩、粘液分泌增加致支气管痉挛[28]。细胞因子和趋化因子的释放激活了补体系统,会产生过敏毒素(C3a,C4a 和C5a),导致嗜碱性粒细胞和肥大细胞释放更多的组胺和炎性介质[28]。ICM可以刺激XII因子导致缓激肽系统激活,一方面缓激肽释放可引起毛细血管扩张、通透性增加、支气管痉挛,另一方面缓激肽可激活花生四烯酸途径,产生前列腺素、白三烯,可能是参与严重过敏样反应的机制[28-29]。
4.1.2 过敏反应发生的机制 有几项研究证实急性反应,特别是严重的急性反应是由IgE介导的[30-31]。过敏反应的典型特征是初次接触过敏原诱导致敏,再次接触时才会引起症状,是一种病理的免疫应答[24,32]。药物分子及其代谢产物太小不能引发自身免疫反应,被称为半抗原,本身不具备免疫原性,但一旦共价结合到大分子蛋白质、多肽后便具备免疫原性,诱导免疫应答,这种引发的反应可以是抗体介导或细胞介导的[32]。以前认为甲壳类动物、ICM过敏是由碘元素引起的,现在认为碘元素并不是过敏的真正原因,甲壳类动物过敏原主要是原肌球蛋白,但是ICM分子具体哪部分导致了过敏,并不十分明确[24,33]。ICM引起的过敏反应可以分为4型:即I型、II型、III型、IV型,临床上ICM过敏反应最常见的是I型,由IgE介导,其次是IV型即延迟型反应[24,34]。II型反应如碘美普尔引起的血管内溶血[35]和非离子型ICM引起的急性严重的血小板减少症[36]也有报告,III型反应是及其罕见的[24]。有研究发现在ICM过敏反应期间,血浆组胺和类胰蛋白酶水平增高与反应的严重程度呈正相关[37]。通过对血清类胰蛋白酶的连续测量有助于确定急性反应的类型[38]。皮肤点刺试验和皮内试验通常用于检测IgE介导的过敏反应,阳性结果被认为是I型过敏反应,一般推荐用未稀释的ICM做皮肤点刺试验,按1:10稀释的ICM做皮内试验[5]。欧洲的一项多中心前瞻性研究[31]显示:ICM速发型过敏反应患者在2~6个月皮内试验阳性率达50%,皮内试验特异性达96.3%,皮内试验特异性高,可作为ICM过敏反应的初筛手段。除皮肤试验外,嗜碱性粒细胞活化试验、药物激发试验也用于ICM过敏反应的诊断与机制的研究。药物激发试验阳性被认为是诊断ICM过敏反应的金标准[5]。Salas等[39]进行了一项为期5年的研究,该研究纳入了90名受试者,采用了皮肤试验、药物激发试验、嗜碱性粒细胞活化试验,所有受试者先采用皮肤试验,再进行药物激发试验,通过皮肤试验与药物激发试验确定过敏反应8人,皮肤试验检出率为62.5%,通过药物激发试验补充检出率为37.5%,在确定过敏反应的8人中做体外血清嗜碱性粒细胞活化试验,检出阳性者5人,阳性率为62.5%,该试验证明嗜碱性粒细胞活化试验也不失为一种检测过敏反应的好方法。
4.2迟发型反应发生的机制
Panto等[19]于1986年最早报告了ICM迟发型反应,在这次研究中有13%的患者发生迟发型发应,5%的患者出现了皮疹,但关于迟发型过敏反应的机制并未阐明。迟发型反应发生的机制尚有争论,过去认为ICM分子及其代谢产物太小,不具抗原性,不能与T细胞结合引起细胞免疫。淋巴细胞激活试验常被用来检测T细胞介导的过敏反应机制。Keller等[40]研究发现ICM刺激T细胞的两种途径:第一种途径为经典的T细胞介导免疫途径,ICM分子与蛋白质结合后形成抗原-半抗原复合物,具有免疫原性,通过抗原提呈细胞处理后,与组织相容性复合体(major histocompatibility complex,MHC)结合形成抗原肽-MHC复合物,被T细胞识别,诱导细胞免疫;第二种称为“p-i途径”,不依赖于抗原提呈细胞,ICM分子就像一个超级抗原,不需加工、处理就能与MHC、T细胞受体结合,ICM分子可通过结合的T细胞识别不同的MHC分子,诱导细胞免疫[41]。在ICM迟发型反应中,另外一些研究[42-43]在皮肤活检处发现了大量T淋巴细胞聚集,以CD4+、CD8+细胞为主,外周血清中发现了CD69、CD25、HLA-DR含量上升,这些都支持有些迟发型反应是由T细胞介导的。
4.3交叉过敏反应
近年来的研究显示先前接触致敏药物并不是免疫介导的过敏发生的先决条件,药物首次接触也可发生免疫介导的过敏反应,这是因为该药物与之前的致敏原具有相似的化学结构导致交叉过敏反应[32]。最近的几个研究显示ICM之间也存在着交叉过敏反应[31,34],其发生与相似的化学结构有关,可能存在着相同的抗原决定簇。ICM交叉过敏反应之间强关联的有碘克沙醇、碘海醇,中度关联的有碘克沙醇、碘海醇、碘佛醇、碘美普尔和碘喷托,弱关联的有碘帕醇、碘比醇、碘普罗胺和碘克沙酸[5]。虽然ICM之间的交叉过敏反应是不常见的[20],但是可能引起严重的后果,也需引起重视。
5 ICM过敏反应的预防
日本大型前瞻性研究示,术前进行ICM过敏皮试并没有减少严重过敏反应的发生率[6],反而本身可能是危险的,美国放射学会并不主张术前ICM过敏皮试来预测哪些患者会发生过敏反应[9]。关于术前预防用药尚有争议,有学者认为[10,24]术前预防用药的价值是有限的,没有随机对照实验表明术前预防用药可以减少严重的不良反应[8,29,44],且术前用药如糖皮质激素、抗组胺药本身可引起药疹、过敏反应,由于有相同的免疫学机制,其产生的过敏反应与ICM引起的过敏反应临床表现是相似的,不易区分[24]。有研究[45]表明术前应用糖皮质激素减少了总体ICM不良反应事件,美国放射学会[9]认为注射ICM至少6 h前应用糖皮质激素效果更好,推荐两种术前预防用药的方法:注射ICM前13 h、7 h、1 h口服50 mg泼尼松龙,并在注射ICM 1 h前静脉注射、肌注或口服50 mg苯海拉明;在注射ICM 12 h、2 h前口服32 mg甲泼尼龙和(或)在注射ICM 1 h前静脉注射、肌注或口服50 mg苯海拉明,紧急情况下可只给予50 mg苯海拉明静脉推注。对于糖尿病、不受控制的高血压病、骨质疏松症、全身性真菌感染、消化性溃疡、憩室炎应用糖皮质激素是谨慎的[9]。推荐所有的患者使用非离子ICM[10]。既往ICM过敏史患者,可改用不同的ICM[9]。延迟型反应一般不建议进行药物预防[10]。
6 ICM过敏反应的治疗
完善抢救措施、药品准备:在急救室内常规准备氧气、简易呼吸装置、血压计、生理盐水或林格氏溶液、肾上腺素、阿托品、抗组胺药、抗惊厥药(地西泮)等。一旦发生碘过敏样反应,立即停止ICM注射,严密监测生命体征及对症处理。轻度过敏反应如瘙痒、荨麻疹一般观察病情变化,不需特殊处理,也可给予抗组胺药,伴随恶心、呕吐的可给予止吐;中度的过敏反应如支气管痉挛可给予吸氧、β2受体激动剂吸入,伴随血管迷走反应的(低血压和心动过缓),可腿抬高、面罩吸氧、生理盐水或林格氏溶液快速滴入、阿托品静脉推注;对于严重的过敏样反应如过敏性休克给予快速扩容、肾上腺素注射等,心脏、呼吸骤停者立即启动心肺复苏治疗[5,10]。
7 ICM在特殊人群中的应用
对于甲状腺功能亢进或其他甲状腺疾病患者注射ICM可能会出现碘元素触发的延迟性甲状腺功能亢进症状,这些症状通常是自限性的,一般推迟4~6周出现。合并甲状腺癌使用ICM应是谨慎的,特别是甲状腺癌患者正在进行碘131治疗,注射ICM可能是禁忌。对于无尿或少尿的终末期肾衰患者推荐使用低渗透压的ICM,虽然理论上有引起肺水肿、全身性水肿的风险,但大多数低渗透浓度的碘化造影剂不与蛋白质结合的,具有相对低的分子量,并且通过透析容易地清除,所以是ICM在透析患者中是安全的,注射ICM后不需要进行紧急透析[9]。
美国食品与药品管理局,将ICM归为B类药物,在孕妇中,虽然注射ICM可以通过胎盘、进入胎儿体内,但是动物实验没有证据显示其有致突变、致畸作用,且新生儿发生甲状腺功能减退症的是罕见的,不限制ICM在孕妇中的使用[9,46]。Somashekar等[47]回顾性研究了267例重症肌无力患者,发现注射ICM组比没注射ICM组不良反应发生率显著升高,重症肌无力是注射ICM的相对禁忌。
8 结语
现今对ICM过敏反应的危险因素、发生机制尚不十分明确。虽然ICM不良反应是少见的,但中国人口基数大,ICM在临床诊疗的应用日益增多,其发生的过敏反应不容忽视。为了减少ICM过敏反应的发生应严格掌握适应症、禁忌症,仔细询问病史、对危险因素常规筛查,术前术后应严密监测病情,对随时可能出现的过敏反应采取积极的应对措施,同时在介入室常规配备相关抢救措施、药品及训练有素的抢救人员。
[1] Bottinor W,Polkampally P,Jovin I.Adverse reactions to iodinated contrast media[J].International Journal of Angiology,2013,22(3):149-154.
[2] Brockow K,Sánchez-Borges M.Hypersensitivity to contrast media and dyes[J].Immunology and allergy clinics of North America,2014,34(3):547-564.
[3] Thomson KR,Varma DK.Safe use of radiographic contrast media[J].Australian Prescriber,2010,33(1):19-22.
[4] Gavant ML,Ellis JV,Klesges LM.Diagnostic efficacy of excretory urography with low-dose,nonionic contrast media[J].Radiology,1992,182(3):657-660.
[5] Rosado IA,Do a DI,Caba as MR,etal.Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Hypersensitivity Reactions to Contrast Media[J].Journal of investigational allergology & clinical immunology:official organ of the International Association of Asthmology (INTERASMA) and Sociedad Latinoamericana de Alergia e Inmunología,2016,26(3):144-155.
[6] Katayama H,Yamaguchi K,Kozuka T,etal.Adverse reactions to ionic and nonionic contrast media.A report from the Japanese Committee on the Safety of Contrast Media[J].Radiology,1990,175(3):621-628.
[7] Zhang BC,Hou L,Lv B,etal.Post-marketing surveillance study with iodixanol in 20 185 Chinese patients from routine clinical practices[J].British Journal of Radiology,2014,87(1034):20130325.
[8] Brockow K,Christiansen C,Kanny G,etal.Management of hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media[J].Allergy,2005,60(2):150-158.
[9] American College of Radiology Committee on Drugs and Contrast Media.ACRManual on Contrast Media Version 10.2.Available:www.acr.org.
[10] European Society of Urogenital Radiology.ESUR Guidelines on contrast media Version 9.0.Available:http://www.esur.org.
[11] Rose TA,Choi JW.Intravenous imaging contrast media complications:the basics that every clinician needs to know[J].The American journal of medicine,2015,128(9):943-949.
[12] Mortelé KJ,Oliva MR,Ondategui S,etal.Universal use of nonionic iodinated contrast medium for CT:evaluation of safety in a large urban teaching hospital[J].American Journal of Roentgenology,2005,184(1):31-34.
[13] Wang CL,Cohan RH,Ellis JH,etal.Frequency,outcome,and appropriateness of treatment of nonionic iodinated contrast media reactions[J].American Journal of Roentgenology,2008,191(2):409-415.
[14] Cochran ST,Bomyea K,Sayre JW.Trends in adverse events after IV administration of contrast media[J].American Journal of Roentgenology,2001,176(6):1385-1388.
[15] Dillman JR,Strouse PJ,Ellis JH,etal.Incidence and severity of acute allergic-like reactions to iv nonionic iodinated contrast material in children[J].American journal of roentgenology,2007,188(6):1643-1647.
[16] Callahan MJ,Poznauskis L,Zurakowski D,etal.Nonionic Iodinated Intravenous Contrast Material-related Reactions:Incidence in Large Urban Children's Hospital-Retrospective Analysis of Data in 12 494 Patients[J].Radiology,2009,250(3):674-681.
[17] Christiansen C,Pichler WJ,Skotland T.Delayed allergy-like reactions to X-ray contrast media:mechanistic considerations[J].European radiology,2000,10(12):1965-1975.
[18] Loh S,Bagheri S,Katzberg RW,etal.Delayed Adverse Reaction to Contrast-enhanced CT:A Prospective Single-Center Study Comparison to Control Group without Enhancement 1[J].Radiology,2010,255(3):764-771.
[19] Panto PN,Davies P.Delayed reactions to urographic contrast media[J].The British journal of radiology,1986,59(697):41-44.
[20] Gómez E,Ariza A,Blanca-López N,etal.Nonimmediate hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media[J].Current opinion in allergy and clinical immunology,2013,13(4):345-353.
[21] Brockow K.Contrast media hypersensitivity-scope of the problem[J].Toxicology,2005,209(2):189-192.
[22] Choyke PL,Miller DL,Lotze MT,etal.Delayed reactions to contrast media after interleukin-2 immunotherapy[J].Radiology,1992,183(1):111-114.
[23] Webb JA,Stacul F,Thomsen HS,etal.Late adverse reactions to intravascular iodinated contrast media[J].European radiology,2003,13(1):181-184.
[24] B hm I,Morelli J,Nairz K,etal.Myths and misconceptions concerning contrast media-induced anaphylaxis:a narrative review[J].Postgraduate medicine,2017,129(2):259-266.
[25] Brockow K,Ring J.Anaphylaxis to radiographic contrast media[J].Current opinion in allergy and clinical immunology,2011,11(4):326-331.
[26] Szebeni J.Hypersensitivity reactions to radiocontrast media:the role of complement activation[J].Current allergy and asthma reports,2004,4(1):25-30.
[27] Johansson SGO,Bieber T,Dahl R,etal.Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use:Report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization,October 2003[J].Journal of allergy and clinical immunology,2004,113(5):832-836.
[28] Schopp JG,Iyer RS,Wang CL,etal.Allergic reactions to iodinated contrast media:premedication considerations for patients at risk[J].Emer gency Radiology,2013,20(4):299-306.
[29] Morcos SK.Review article:Acute serious and fatal reactions to contrast media:our current understanding.[J].British Journal of Radiology,2005,78(932):686-693.
[30] Salas M,Gomez F,Fernandez TD,etal.Diagnosis of immediate hypersensitivity reactions to radiocontrast media[J].Allergy,2013,68(9):1203-1206.
[31] Brockow K,Romano A,Aberer W,etal.Skin testing in patients with hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media-a European multicenter study[J].Allergy,2009,64(2):234-241.
[32] Palmiere C,Comment L,Mangin P.Allergic reactions following contrast material administration:nomenclature,classification,and mechanisms[J].International journal of legal medicine,2014,128(1):95-103.
[33] Baig M,Farag A,Sajid J,etal.Shellfish allergy and relation to iodinated contrast media:United Kingdom survey[J].World journal of cardiology,2014,6(3):107-111.
[34] Torres MJ,Gomez F,Doa I,etal.Diagnostic evaluation of patients with nonimmediate cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media[J].Allergy,2012,67(7):929-935.
[35] Mayer B,Leo A,Herziger A,etal.Intravascular immune hemolysis caused by the contrast medium iomeprol[J].Transfusion,2013,53(10):2141-2144.
[36] Bata P,Tarnoki AD,Tarnoki DL,etal.Acute severe thrombocytopenia following non-ionic low-osmolarity intravenous contrast medium injection[J].Korean journal of radiology,2012,13(4):505-509.
[37] Krause W,Niehues D.Biochemical characterization of X-ray contrast media[J].Investigative radiology,1996,31(1):30-42.
[38] Gomez E,Torres MJ,Mayorga C.Immunologic evaluation of drug allergy[J].Allergy,asthma & immunology research,2012,4(5):251-263.
[39] Salas M,Gomez F,Fernandez TD,etal.Diagnosis of immediate hypersensitivity reactions to radiocontrast media[J].Allergy,2013,68(9):1203-1206.
[40] Keller M,Lerch M,Britschgi M,etal.Processing-dependent and -independent pathways for recognition of iodinated contrast media by specific human T cells[J].Clinical & experimental allergy,2010,40(2):257-268.
[41] Pichler WJ.Pharmacological interaction of drugs with antigen-specific immune receptors:the pi concept[J].Current opinion in allergy and clinical immunology,2002,2(4):301-305.
[42] Kanny G,Pichler W,Morisset M,etal.T cell-mediated reactions to iodinated contrast media:evaluation by skin and lymphocyte activation tests[J].Journal of allergy and clinical immunology,2005,115(1):179-185.
[43] Torres MJ,Mayorga C,Cornejo-Garcia JA,etal.Monitoring non-immediate allergic reactions to iodine contrast media[J].Clinical & Experimental Immunology,2008,152(2):233-238.
[44] Tramèr MR,vonElm E,Loubeyre P,etal.Pharmacological prevention of serious anaphylactic reactions due to iodinated contrast media:systematic review[J].Bmj,2006,333(7570):675-678.
[45] Greenberger PA,Patterson R.The prevention of immediate generalized reactions to radiocontrast media in high-risk patients[J].Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology,1991,87(4):867-872.
[46] Arima S,Taniguchi Y,Sonoda A,etal.How to Manage Allergic Reactions to Contrast Agent in Pregnant Patients[J].American Journal of Roentgenology,2016,206(2):247-252.
[47] Somashekar DK,Davenport MS,Cohan RH,etal.Effect of intravenous low-osmolality iodinated contrast media on patients with myasthenia gravis[J].Radiology,2013,267(3):727-734.
Allergyreactionsinducedbyiodinatedcontrastmediaareview
CHEN Hong,WANG Qiu-lin
(DepartmentofCardiology,TheFirstAffiliatedHospitalofChengduMedicalCollege,Chengdu610500,Sichuan,China)
Iodinated contrast media (ICM) are widely used in angiography,imaging diagnosis and other fields.ICM are generally considered to be relatively safe,but serious adverse reactions may occur.We will summarize the progress on allergy reactions induced by ICM from prevalence,classification,clinical manifestations,risk factors,pathogenesis,prevention and so on.Most hypersensitivity reactions of ICM are allergy-like reactions,the real allergic reactions are few.Allergic reactions can be divided into four kinds,type I allergic reactions are most common and it is IgE-mediated.Type IV allergic reactions or so-called delayed reactions are usually considered T-mediated, but the pathogenesis of type IV allergic reactions is not very precise.The preventive and therapeutic measures are as follows:(1)application of nonionic ICM as far as possible;(2)the patients with moderate or severe allergic reactions to ICM should receive the symptomatic and supportive treatments.
Iodinated contrast media;Allergic reactions;Pathogenesis;Prevention
10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2017.05.043
四川省科技厅科技支撑计划(2016SZ0052)
2017-05-14
陈宏(1990-),男,硕士研究生。E-mail:349855997@qq.com
王秋林,E-mail:wangredox@163.com
时间: 2017-10-10 02∶28
http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1254.R.20171010.0228.088.html
1005-3697(2017)05-0798-05
R593.1
A
(学术编辑吕湛)
本刊网址:http://www.nsmc.edu.cn作者投稿系统http://noth.cbpt.cnki.net邮箱xuebao@nsmc.edu.cn
