蜂胶醇提物通过抑制C/EBP同源蛋白表达减轻氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导的血管内皮细胞凋亡*
2017-09-22徐晓燕邵夏炎刘映雪李东轩姚树桐
徐晓燕, 邵夏炎, 刘映雪, 李东轩, 焦 鹏, 郝 奇, 田 华, 姚树桐△
(泰山医学院 1药学院, 2人口与计划生育学院, 3基础医学院, 4动脉粥样硬化研究所, 山东 泰安 271000)
蜂胶醇提物通过抑制C/EBP同源蛋白表达减轻氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导的血管内皮细胞凋亡*
徐晓燕1, 邵夏炎2▲, 刘映雪2, 李东轩3, 焦 鹏4, 郝 奇3, 田 华4, 姚树桐3△
(泰山医学院1药学院,2人口与计划生育学院,3基础医学院,4动脉粥样硬化研究所, 山东 泰安 271000)
目的: 研究蜂胶醇提物(ethanol extract of propolis,EEP)对氧化低密度脂蛋白(oxidized low-density lipoprotein,ox-LDL)诱导的血管内皮细胞凋亡的抑制作用,并探讨可能的分子机制。方法: 体外培养人脐静脉内皮细胞(human umbilical vein endothelial cells,HUVECs),给予EEP(7.5、15和30 mg/L)、4-苯丁酸(4-phenylbutyric acid,PBA; 4 mmol/L)预处理1 h,再加入ox-LDL(100 mg/L)或衣霉素(tunicamycin,TM; 4 mg/L)继续培养24 h。分别采用MTT法和Annexin V-FITC/PI双染法检测细胞活力和凋亡情况;试剂盒测定培养液乳酸脱氢酶(lactic dehydrogenase,LDH)和细胞内caspase-3活性。分别采用Western blot和real-time PCR技术检测内质网应激(endoplasmic reticulum stress,ERS)凋亡途径关键蛋白C/EBP同源蛋白(C/EBP homologous protein,CHOP)和Bcl-2的表达变化。结果: 与ERS抑制剂PBA相似,EEP呈剂量依赖性地减轻ox-LDL所诱导的HUVECs损伤,表现为细胞活力增加(P<0.01或P<0.05),LDH漏出、凋亡率和caspase-3活性降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),且可抑制ERS诱导剂TM所致的HUVECs活力下降(P<0.05),以及LDH漏出、细胞凋亡率和caspase-3活性增加(P<0.05或P<0.01);与PBA相似,EEP可抑制ox-LDL所诱导的CHOP上调和Bcl-2下调(P<0.05或P<0.01);另外,与TM组比较,EEP预处理组CHOP蛋白和mRNA表达上调也受到明显抑制(P<0.05或P<0.01)。结论: EEP可减轻 ox-LDL 所诱导的HUVECs凋亡,其机制可能与抑制CHOP介导的ERS凋亡途径有关。
蜂胶醇提物; C/EBP同源蛋白; 氧化低密度脂蛋白; 血管内皮细胞; 细胞凋亡
动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,AS)是心脑血管疾病的主要病理基础之一,而低密度脂蛋白(low-density lipoprotein,LDL)增高是AS的重要危险因子,LDL经过氧化修饰成为氧化低密度脂蛋白(oxidized low-density lipoprotein,ox-LDL)则致AS作用更强[1]。血管内皮细胞凋亡和功能障碍是早期AS过程中的重要病理变化,血管内皮细胞结构受损、功能改变,使血液中脂质和单核细胞更易沉积在内皮下间隙进一步成为泡沫细胞,从而启动粥样斑块的形成与发展,促进AS进程。大量研究表明,ox-LDL可通过多种途径损伤血管内皮细胞,诱导其过度凋亡[2-4]。因此,干预ox-LDL对血管内皮细胞的促凋亡作用对阻止AS发展、降低心血管不良事件的发生率具有重要意义。蜂胶是蜜蜂采集植物树脂等与其上颚腺分泌物混合形成的胶状物质,其中黄酮类、酚酸类等是其重要活性成分,具有抗氧化、抗病毒、抗肿瘤、免疫调节、抗AS等广泛的生物学活性[5]。本实验室的前期研究发现,蜂胶醇提物(ethanol extract of propolis,EEP)能够促进胆固醇逆向转运,阻止AS发展,并可以通过抑制凝集素样氧化低密度脂蛋白受体介导的氧化应激,减轻ox-LDL诱导的血管内皮细胞损伤[6-8],但EEP是否可以通过抑制C/EBP同源蛋白(C/EBP homologous protein,CHOP)介导的内质网应激(endoplasmic reticulum stress,ERS)凋亡途径减轻 ox-LDL 所诱导的血管内皮细胞凋亡,目前国内外尚未见报道。本工作通过研究EEP对 ox-LDL 所诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞(human umbilical vein endothelial cells,HUVECs)CHOP表达和凋亡的影响,探讨了EEP对ox-LDL所诱导的HUVECs凋亡的抑制作用及机制。
材料和方法
1试剂
HUVECs由中国科学院上海生物化学与细胞生物学研究所细胞库提供;ox-LDL购自北京协生生物科技有限公司;DMEM高糖培养基和RIPA裂解液分别购自HyClone和Solarbio;衣霉素(tunicamycin,TM)、4-苯丁酸(4-phenylbutyric acid,PBA)和抗β-actin抗体购自Sigma;四甲基偶氮唑蓝[3-(4,5-dime-thylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide,MTT]和 Annexin V-FITC/碘化丙啶(propidium iodide,PI)凋亡检测试剂盒分别购自Genview和南京凯基生物科技公司;兔抗CHOP多克隆抗体和辣根过氧化物酶标记山羊抗兔IgG分别为Cell Signaling Technology和北京中杉金桥公司产品;兔抗Bcl-2多克隆抗体购自Santa Cruz;增强化学发光(enhanced chemiluminescence,ECL)试剂盒和二氟化树脂(polyvinylidene difluoride,PVDF)膜分别为Pierce和Millipore产品;Trizol 试剂为 Invitrogen产品;cDNA 合成试剂盒和 RealMaster Mix (SYBR Green)试剂盒购自北京天根公司 ;Caspase-3和乳酸脱氢酶(lactate dehydrogenase,LDH)活性测定试剂盒分别购自碧云天生物和南京建成生物技术公司;其余试剂均为分析纯产品。
2方法
2.1EEP制备和总黄酮测定 采集新鲜泰山松柏蜂胶,烘干、粉碎,按本室既往报道的方法[6]制备EEP。取100克蜂胶溶于1L 95%乙醇中,40 ℃超声提取,共3次,每次3 h,合并3次上清液,50 ℃条件下经旋转蒸发器减压浓缩,烘箱中干燥得EEP。按照国家标准分光光度比色法(GB/T 20574-2006)测定EEP总黄酮含量,结果为(213.46±2.93) mg芦丁当量(RE)/g。 以二甲基亚砜(dimethyl sulfoxide,DMSO)配制EEP母液,实验时用细胞培养基稀释成适当浓度。
2.2细胞培养与实验分组 HUVECs用DMEM高糖培养基(含10%胎牛血清、1×105U/L青霉素和100 mg/L链霉素)于5% CO2培养箱中37 ℃培养。随机分为:(1)正常对照(control)组:培养液中常规培养;(2)ox-LDL组:培养液中加入100 mg/L ox-LDL;(3)EEP+ox-LDL组:培养液中先加入EEP(7.5、15和30 mg/L)预处理1 h,再加入100 mg/L ox-LDL;(4)PBA(ERS抑制剂)+ox-LDL组:培养液中先加入4 mmol/L PBA预处理1 h,再加入100 mg/L ox-LDL;(5)TM(ERS诱导剂)组:培养液中加入4 mg/L TM;(6)EEP+TM组:先给予30 mg/L EEP预处理1 h,再加入4 mg/L TM。除EEP预处理组和TM组外,其它各组均加入0.1%的DMSO,培养 24 h 收集细胞。
2.3细胞活力和LDH测定 接种于96孔板的细胞经处理后,按既往报道的MTT分析方法[9]检测细胞活力。以正常对照组细胞活力为100%,其余各组细胞活力以其吸光度(A)值占对照组A值的百分比表示。同时按照LDH活性检测试剂盒说明书测定各组培养基中LDH活性。
2.4流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡 用Annexin V-FITC/PI双染色法分析细胞凋亡情况。细胞经处理后,收集并重悬于500 μL上样缓冲液,按照凋亡检测试剂盒说明书操作并上机检测。细胞凋亡率由流式细胞仪分析测定。总细胞凋亡率(%)=早期凋亡率+晚期凋亡率。
2.5细胞内caspase-3活性的测定 按照试剂盒说明书操作,即细胞经处理后,收集并用PBS洗涤1次,以裂解液冰浴裂解15 min, 4 ℃条件下16 000 ×g离心15 min,采用Bradford法检测上清液中蛋白浓度。在96孔板中将10 μL裂解上清液、80 μL反应缓冲液和10 μL caspase-3底物混合并在37 ℃条件下孵育2 h。利用多功能酶标仪于405 nm处读取吸光度(A),通过相同条件下获得的标准曲线计算出样品中caspase-3活性,并以正常对照组细胞caspase-3活性为100%,其余各组细胞caspase-3活性以其占正常对照组的百分比表示。
2.6Western blot分析 按本室既往报道的方法[10]提取细胞总蛋白,等量的各组总蛋白经SDS-PAGE分离后电转移至PVDF膜,经封闭、洗脱后与抗CHOP(1∶800)、Bcl-2(1∶400)抗体和抗β-actin(1∶6 000)单克隆抗体室温孵育4 h,洗膜后与辣根过氧化物酶标记的相应II抗室温孵育1 h。抗原-抗体复合物用ECL法显示,应用化学发光成像仪进行图像采集。采用Image-Pro Plus 6.0图像分析软件分析蛋白条带积分吸光度(integrated absorbance,IA)值,以CHOPIA值/β-actinIA值的比值反映CHOP蛋白相对水平。
2.7Real-time PCR技术检测CHOP的mRNA表达 收集细胞后,用Trizol一步法提取RNA。按试剂盒说明配制20 μL的反应体系, 37 ℃反应60 min,将mRNA逆转录为cDNA。按实时荧光定量 PCR 试剂盒说明书配制PCR反应体系为:2.5×RealMaster Mix/20×SYBR solution 4.5 μL、上下游引物各1 μL、cDNA 2 μL及三蒸水1.5 μL,共10 μL。引物由上海生工生物技术公司合成,CHOP的上游引物序列为5’-CCACCACACCTGAAAGCAGAA-3’,下游引物序列为5’-GGTGCCCCCAATTTCATCT-3’;GAPDH的上游引物序列为5’-CCTCCCGCTTCGCTCTCT-3’,下游引物序列为5’-GCTGGCGACGCAAAAGA-3’。在 Rotor-Gene Q荧光定量 PCR 仪上反应,条件为 94 ℃预变性15 min,然后进行40个循环:94 ℃变性20 s,56 ℃退火30 s,68 ℃延伸30 s。GAPDH作为内参照,根据2-ΔΔCt法分析CHOP mRNA的相对表达量,ΔΔCt=实验组(Ct目的基因-Ct内参照基因)-对照组(Ct目的基因-Ct内参基因)。
3统计学处理
采用SPSS 13.0统计学软件分析数据,结果用均数±标准差(mean±SD) 来表示。多组数据比较用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较采用SNK法。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结 果
1EEP抑制ox-LDL诱导的HUVECs活力降低和LDH漏出
MTT 结果显示,ox-LDL 可使HUVECs活力显著降低(P<0.01);而以15 mg/L和30 mg/L EEP预处理HUVECs 1 h,细胞活力则明显增加(P<0.05),表明EEP 可以减轻ox-LDL 诱导的HUVECs活力降低;ERS抑制剂PBA也可减轻ox-LDL 诱导的HUVECs活力降低(P<0.05),与EEP预处理组结果相似,见图1A。
对培养液中LDH活性检测结果显示,与PBA相似, EEP可显著抑制ox-LDL所致的LDH漏出(P<0.05),见图1B。
2EEP抑制TM诱导的HUVECs活力降低和LDH漏出
ERS诱导剂TM 可显著诱导HUVECs损伤,表现为细胞活力降低(P<0.01),LDH漏出增加(P<0.01);而以EEP(30 mg/L)预处理HUVECs 1 h,可以明显减轻TM 诱导的HUVECs活力降低和LDH漏出(P<0.05),见图2。
3EEP抑制ox-LDL诱导的HUVECs凋亡和caspase-3活化
Annexin V-FITC/PI双染流式细胞术检测结果显示,ox-LDL 可使HUVECs总细胞凋亡率明显增加(P<0.01);与PBA预处理组相似,以7.5、15和30 mg/L EEP预处理HUVECs 1 h,可以减轻ox-LDL 诱导的细胞凋亡,尤其以30 mg/L EEP预处理组更为显著(P<0.01),见图3A。
细胞内caspase-3活性测定结果显示,ox-LDL可使caspase-3活性明显增加,而EEP可以显著降低ox-LDL 诱导的caspase-3活性增高(P<0.01),与PBA预处理组相似,见图3B。
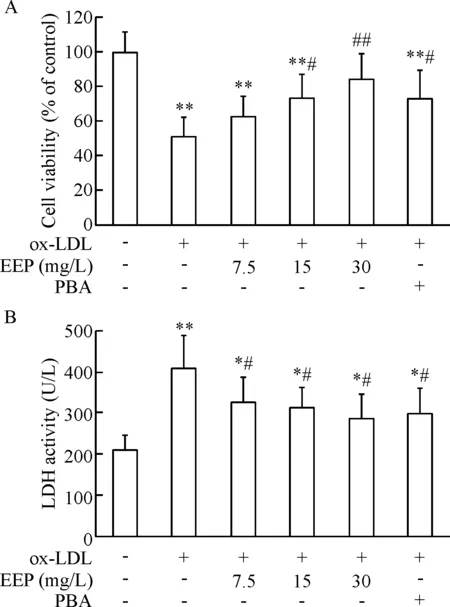
Figure 1. EEP inhibited ox-LDL-induced decrease in the viability of HUVECs and LDH release. HUVECs were pretreated with EEP (7.5, 15 and 30 mg/L) or PBA (4 mmol/L) for 1 h and then incubated with ox-LDL (100 mg/L) for 24 h. A: cell viability determined by MTT assay; B: LDH activity in the media. Mean±SD.n=6.*P<0.05,**P<0.01vscontrol group;#P<0.05,##P<0.01vsox-LDL group.
图1EEP抑制ox-LDL所诱导的HUVECs活力降低和LDH漏出
4EEP抑制TM诱导的HUVECs凋亡和caspase-3活化
TM可使HUVECs总细胞凋亡率明显增加(P<0.01),caspase-3活性显著上调(P<0.01);而以30 mg/L EEP预处理可以减轻TM所诱导的细胞凋亡和caspase-3活化(P<0.01),见图4。
5EEP抑制ox-LDL诱导的CHOP上调和Bcl-2下调
Western blot分析结果显示,与对照组比较,ox-LDL可使CHOP蛋白水平显著上调(P<0.01),而降低Bcl-2蛋白水平(P<0.05);与PBA预处理相似,EEP预处理可明显抑制ox-LDL所致的CHOP蛋白上调和Bcl-2下调(P<0.05),见图5A。
采用real-time PCR技术检测细胞内CHOP的mRNA表达,结果与Western blot结果一致,EEP明显抑制ox-LDL所诱导的CHOP的mRNA上调,以 30 mg/L EEP预处理组尤为显著(P<0.01),见图5B。
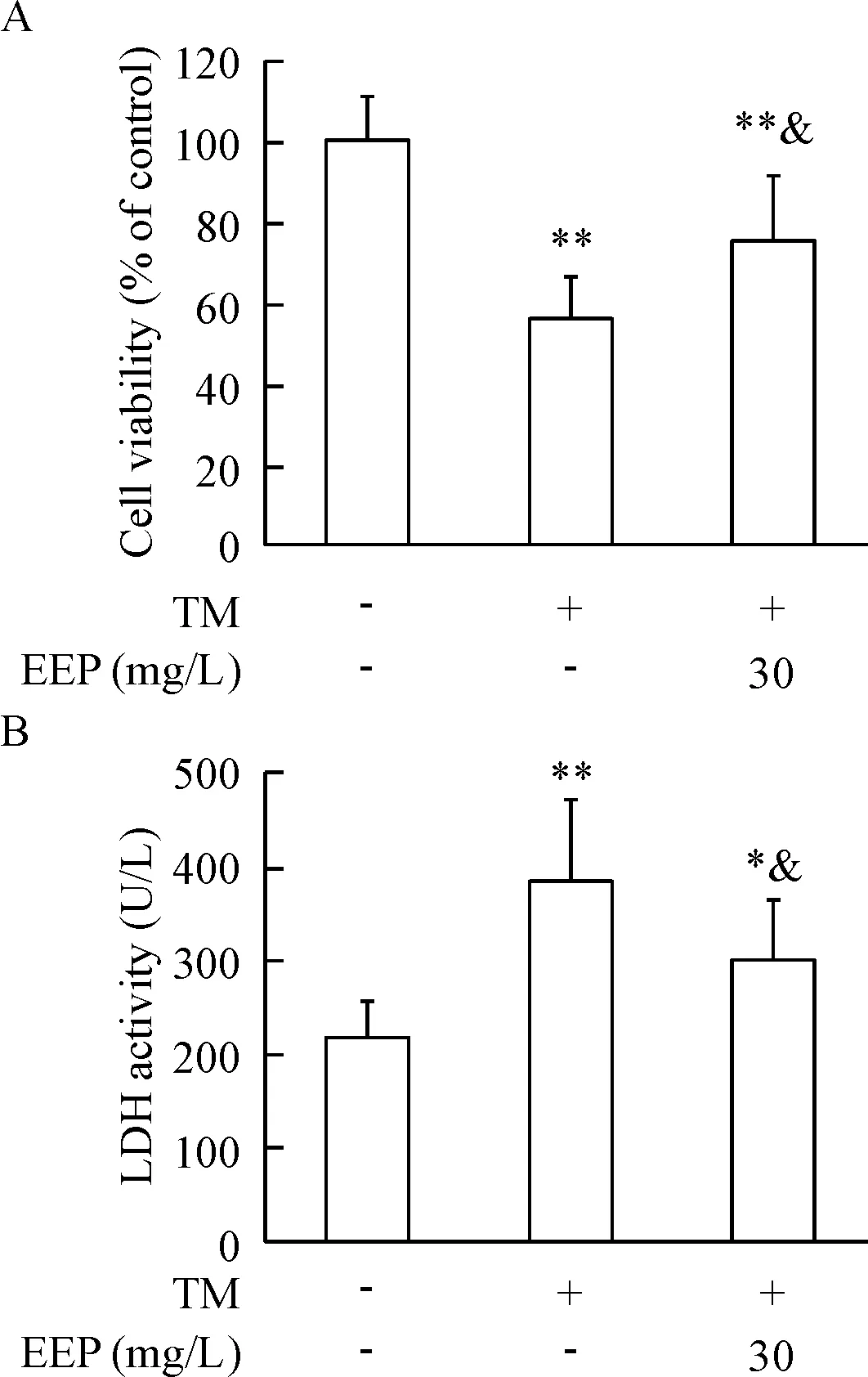
Figure 2. EEP inhibited TM-induced decrease in the viability of HUVECs and LDH release. HUVECs were pretreated with EEP (30 mg/L) for 1 h and then treated with TM (4 mg/L) for 24 h. A: the cell viability determined by MTT assay; B: LDH activity in the media. Mean±SD.n=6.*P<0.05,**P<0.01vscontrol group;&P<0.05vsTM group.
图2EEP抑制TM所诱导的HUVECs活力降低和LDH漏出
6EEP抑制TM诱导的CHOP上调
TM可在蛋白和mRNA水平均明显上调CHOP表达(P<0.01);而与TM组比较, EEP预处理组CHOP蛋白和mRNA的表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),见图6 。
讨 论
AS是一种慢性进行性血管炎症性疾病,作为心脑血管疾病的重要病理基础严重危害人类健康。血管内皮细胞损伤及功能紊乱是AS发生发展的始动环节,而ox-LDL是导致内皮损伤的独立危险因素,可降低细胞活力、诱导细胞凋亡并促进炎症因子的表达,进而导致炎症细胞浸润、泡沫细胞形成及粥样斑块的形成和破裂[11]。因此减轻血管内皮细胞损伤被认为是AS防治的重要措施。本工作在ox-LDL诱导的HUVECs损伤模型上观察到,EEP可明显抑制细胞活力降低和LDH漏出,并显著抑制ox-LDL 诱导的细胞凋亡及caspase-3活化,其作用与ERS抑制剂PBA相似。另外,在ERS诱导剂TM诱导的HUVECs损伤模型上也观察到EEP类似的保护作用,提示EEP能够抑制ox-LDL诱导的内皮细胞损伤,其机制可能与抑制ERS介导的凋亡途径有关。
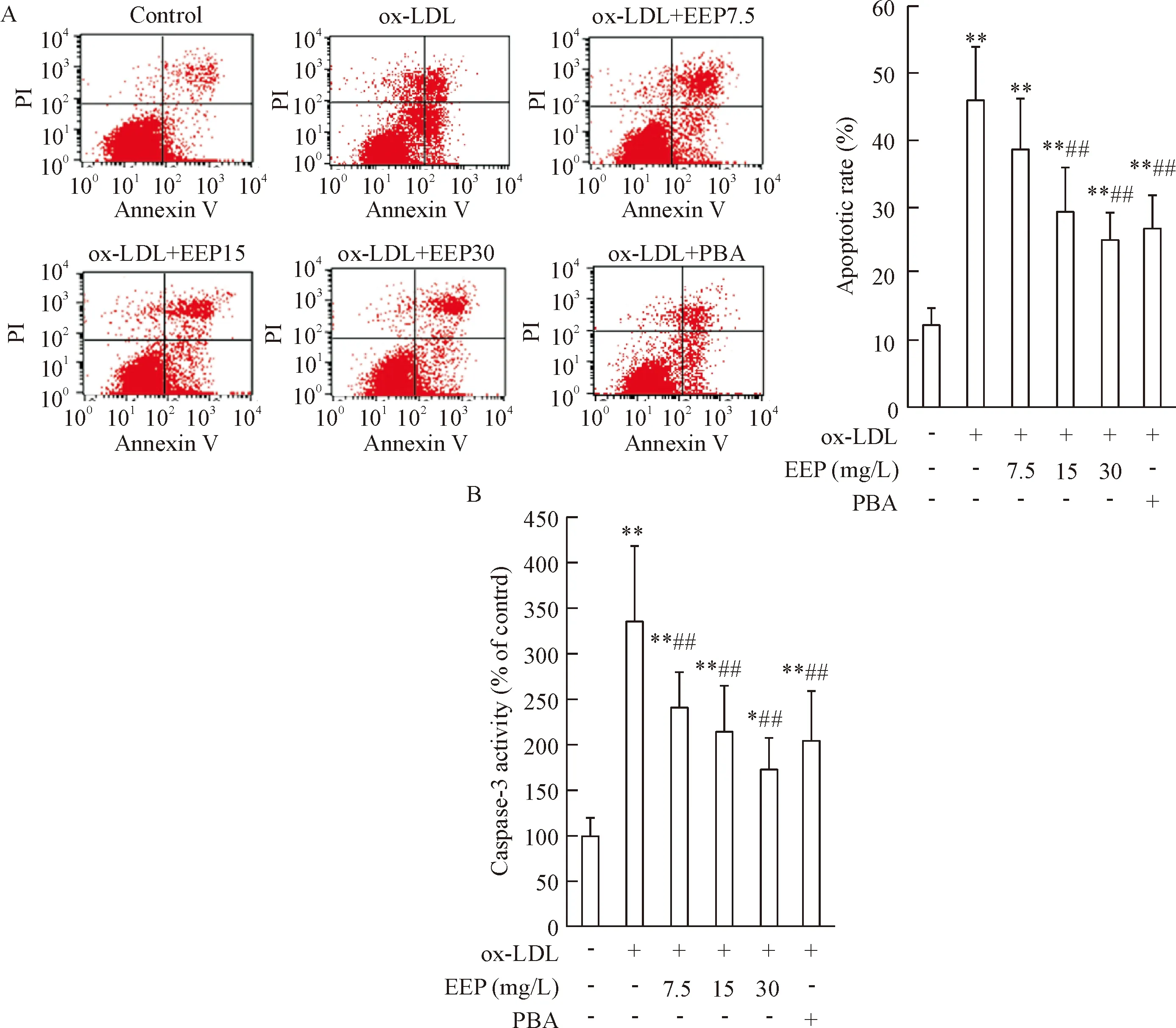
Figure 3. EEP inhibited ox-LDL-induced apoptosis of HUVECs. HUVECs were treated as described in Figure 1. A: the cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry and the total (early- and late-stage) apoptotic cells were represented by the right side of the panel (Annexin V staining alone or together with PI); B: caspase-3 activity was determined by colorimetric assay.Mean±SD.n=6.*P<0.05,**P<0.01vscontrol group;##P<0.01vsox-LDL group.
图3EEP抑制ox-LDL所诱导的HUVECs凋亡
内质网是真核细胞内蛋白合成和钙稳态调控的重要细胞器,并参与脂质合成和氧化还原平衡的维持。在缺氧、氧化应激、胆固醇超负荷等致病因素的作用下,内质网功能紊乱,出现以未折叠和/或错误折叠蛋白积聚和钙稳态失衡为主要特征的ERS反应。一定程度的ERS反应通过暂时性抑制蛋白合成,促进分子伴侣表达有利于维持内质网功能和细胞生存,但是过强或过久的应激则通过激活ERS相关凋亡途径诱发细胞凋亡,导致不可逆损伤[12]。CHOP 又称生长停滞和DNA损害诱导基因153(growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible gene 153,GADD153),是介导ERS 相关凋亡途径的关键分子之一[12]。大量研究表明,CHOP介导AS粥样斑块中巨噬细胞凋亡,并在AS易损斑块的形成中具有重要作用,而CHOP缺陷可抑制巨噬细胞凋亡,缩小粥样斑块坏死面积[13-15]。本课题组前期工作[16-18]和文献报道[19]表明,ox-LDL通过激活CHOP信号途径诱导巨噬细胞凋亡,其机制与下调抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2有关,而EEP和槲皮素通过抑制该信号途径抑制巨噬细胞凋亡,表明CHOP介导的ERS相关凋亡途径参加AS的发生发展,并有可能成为AS防治的重要靶点。来自内皮细胞的研究表明,CHOP介导ox-LDL所诱导的细胞凋亡[20-21],而本实验结果显示,与ERS抑制剂PBA相似,EEP在mRNA和蛋白水平均明显减轻ox-LDL所致的HUVECs中CHOP上调,并抑制 ox-LDL对下游 Bcl-2 的下调作用;另外,对于ERS诱导剂TM诱导的CHOP上调,EEP也有类似的抑制作用。
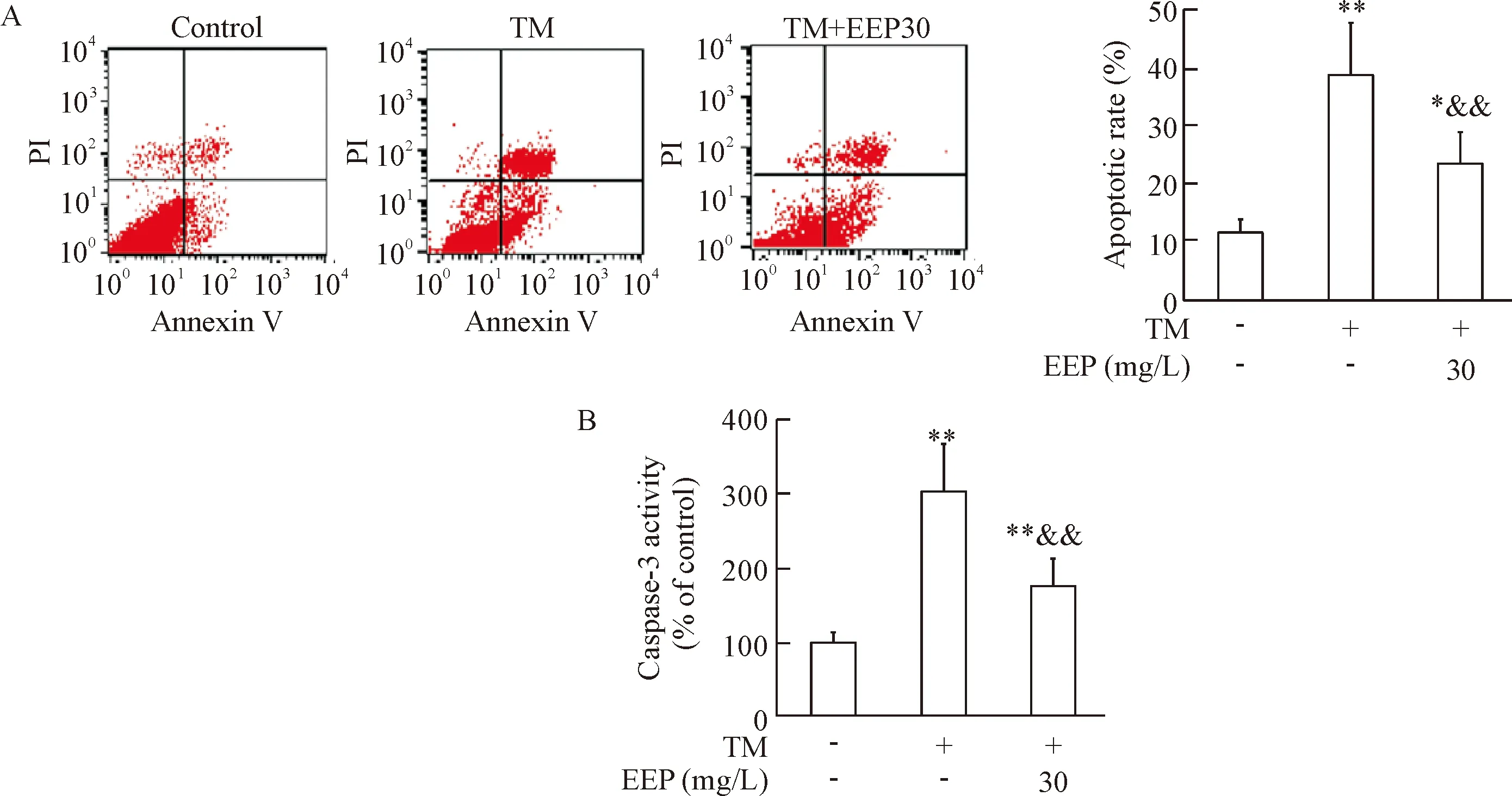
Figure 4. EEP inhibited TM-induced apoptosis of HUVECs. HUVECs were treated as described in Figure 2. A: the cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry and the total (early- and late-stage) apoptotic cells were represented by the right side of the panel (Annexin V staining alone or together with PI); B: caspase-3 activity was determined by colorimetric assay. Mean±SD.n=6.*P<0.05,**P<0.01vscontrol group;&&P<0.01vsTM group.
图4EEP抑制TM所诱导的HUVECs凋亡
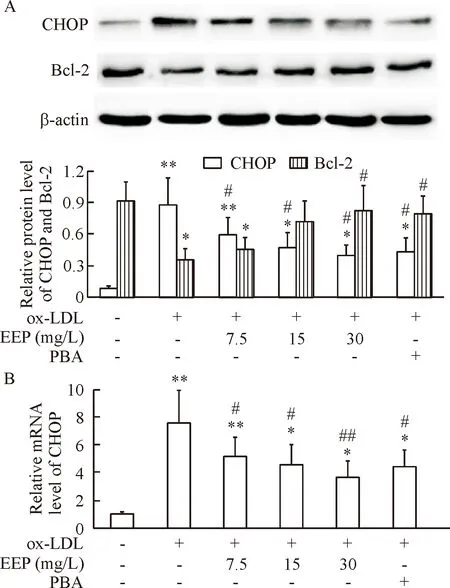
Figure 5. EEP inhibited ox-LDL-induced CHOP upregulation and Bcl-2 downregulation. HUVECs were treated as described in Figure 1. The protein levels of CHOP and Bcl-2, and the mRNA levels of CHOP were detected using Western blot (A) and real-time PCR (B), respectively. Mean±SD.n=4.*P<0.05,**P<0.01vscontrol group;#P<0.05,##P<0.01vsox-LDL group.
图5EEP抑制ox-LDL所诱导的CHOP上调和Bcl-2下调
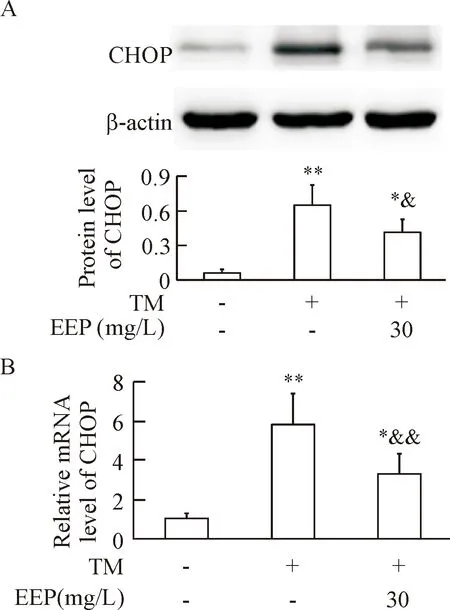
Figure 6. EEP inhibited TM-induced CHOP upregulation. HUVECs were treated as described in Figure 2. The protein and mRNA levels of CHOP were detected using Western blot (A) and real-time PCR (B), respectively. Mean±SD.n=4.*P<0.05,**P<0.01vscontrol group;&P<0.05,&&P<0.01vsTM group.
图6EEP抑制TM所诱导的CHOP上调
综上所述,本研究结果提示EEP可减轻 ox-LDL 所诱导的HUVECs凋亡,其机制可能与抑制CHOP介导的ERS凋亡途径有关。
[1] Trpkovic A, Resanovic I, Stanimirovic J, et al. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein as a biomarker of cardiovascular diseases[J]. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci, 2015, 52(2):70-85.
[2] Zhang L, Jia YH, Zhao XS, et al. Trichosanatine alle-viates oxidized low-density lipoprotein induced endothelial cells injury via inhibiting the LOX-1/p38 MAPK pathway[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2016, 8(12):5455-5464.
[3] Ma S, Yao S, Tian H, et al. Pigment epithelium-derived factor alleviates endothelial injury by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2017, 16:31.
[4] Zhang M, Jiang L. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein decreases VEGFR2 expression in HUVECs and impairs angiogenesis[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2016, 12(6):3742-3748.
[5] Sforcin JM. Biological properties and therapeutic applications of propolis[J]. Phytother Res, 2016, 30(6):894-905.
[6] Fang Y, Li J, Ding M, et al. Ethanol extract of propolis protects endothelial cells from oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced injury by inhibiting lectin-like oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor-1-mediated oxidative stress[J]. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 2014, 239(12):1678-1687.
[7] Fang Y, Sang H, Yuan N, et al. Ethanolic extract of propolis propolis inhibits atherosclerosis in ApoE-knockout mice[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2013, 12:123.
[8] Yu Y, Si Y, Song G, et al. Ethanolic extract of propolis promotes reverse cholesterol transport and the expression of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 and G1 in mice[J]. Lipids, 2011, 46(9):805-811.
[9] 李严严, 徐晓燕, 张家君, 等. 蜂胶醇提物通过抑制caspase-12减轻氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导的巨噬细胞凋亡[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2015, 31(12): 2202-2208.
[10] 苗 成, 李金国, 苗 芳, 等. 槲皮素对ox-LDL 所致的小鼠巨噬细胞脂质蓄积和过氧化的影响[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2013, 29(8):1370-1374.
[11] 邱雅慧. 血管内皮细胞的功能以及损伤修复与动脉粥样硬化[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007, 11(10):1927-1929, 1933.
[12] 姚树桐, 秦树存. 内质网应激在动脉粥样硬化发生、发展和防治中的作用[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2014, 30(2):364-368, 384.
[13] Yu X, Wang Y, Zhao W, et al. Toll-like receptor 7 promotes the apoptosis of THP-1-derived macrophages through the CHOP-dependent pathway[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2014, 34(3):886-893.
[14] Tsukano H, Gotoh T, Endo M, et al. The endoplasmic reticulum stress-C/EBP homologous protein pathway-mediated apoptosis in macrophages contributes to the instability of atherosclerotic plaques[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2010, 30(10):1925-1932.
[15] Thorp E, Li G, Seimon TA, et al. Reduced apoptosis and plaque necrosis in advanced atherosclerotic lesions ofApoe-/- andLdlr-/- mice lacking CHOP[J]. Cell Metab, 2009, 9(5):474-481.
[16] Yao S, Zong C, Zhang Y, et al. Activating transcription factor 6 mediates oxidized LDL-induced cholesterol accumulation and apoptosis in macrophages by up-regulating CHOP expression[J]. J Atheroscler Thromb, 2013, 20(1):94-107.
[17] Tian H, Sun HW, Zhang JJ, et al. Ethanol extract of propolis protects macrophages from oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by inhibiting CD36 expression and endoplasmic reticulum stress-C/EBP homologous protein pathway[J]. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2015, 15:230.
[18] 姚树桐, 苗 成, 刘庆华, 等. 槲皮素预处理对衣霉素所致巨噬细胞凋亡的抑制作用及机制[J]. 生理学报, 2013, 65(1):47-54.
[19] McCullough KD, Martindale JL, Klotz LO, et al. Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl-2 and perturbing the cellular redox state[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2001, 21 (4):1249-1259.
[20] Tao YK, Yu PL, Bai YP, et al. Role of PERK/eIF2α/CHOP endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in oxidized low-density lipoprotein mediated induction of endothelial apoptosis[J]. Biomed Environ Sci, 2016, 29(12):868-876.
[21] Hong D, Bai YP, Gao HC, et al. Ox-LDL induces endothelial cell apoptosis via the LOX-1-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2014, 235(2):310-317.
(责任编辑: 林白霜, 罗 森)
Ethanol extract of propolis protects vascular endothelial cells from oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by inhibiting C/EBP homologous protein expression
XU Xiao-yan1, SHAO Xia-yan2, LIU Ying-xue2, LI Dong-xuan3, JIAO Peng4,HAO Qi3, TIAN Hua4, YAO Shu-tong3
(1College of Pharmacy,2College of Population and Family Planning,3College of Basic Medical Sciences,4Institute of Atherosclerosis, Taishan Medical University, Taian 271000, China. E-mail: yst228@126.com)
AIM: To investigate the inhibitory effect of ethanol extract of propolis (EEP) on oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced vascular endothelial cell apoptosis and the underlying molecular mechanisms.METHODS: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were pretreated with EEP (7.5, 15 and 30 mg/L) or 4-phenylbutyric acid (PBA, 4 mmol/L) for 1 h and then treated with ox-LDL (100 mg/L) or tunicamycin (TM, 4 mg/L) for 24 h. The cell viability and apoptosis were determined by MTT assay and Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining, respectively. The activities of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) in the medium and caspase-3 in the HUVECs were measured. The protein and mRNA levels of C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), a proapoptotic molecule under endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), and its downstream Bcl-2 were examined by Western blot and real-time PCR, respectively.RESULTS: Like PBA (an ERS inhibitor), EEP protected HUVECs from ox-LDL-induced injury in a dose-dependent manner, as assessed by the increased cell viability and the decreased LDH release, apoptotic rate and caspase-3 activation. The decrease in cell viabi-lity and the increases in LDH release, apoptotic rate and caspase-3 activation induced by TM, an ERS inducer, were also attenuated by EEP. Moreover, EEP suppressed ox-LDL-induced CHOP upregulation and Bcl-2 downregulation, and this effect was similar to that of PBA. Similarly, EEP significantly suppressed TM-induced CHOP upregulation both at the protein and mRNA levels.CONCLUSION: EEP may protect HUVECs from ox-LDL-induced apoptosis, and the mechanism is at least partially involved in suppressing CHOP-mediated ERS-associated apoptotic pathway.
Ethanol extract of propolis; C/EBP homologous protein; Oxidized low-density lipoprotein; Vascular endothelial cells; Apoptosis
1000- 4718(2017)09- 1551- 07
2017- 03- 22 [
] 2017- 05- 03
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No. 81570410; No. 81202949);泰山医学院国家级大学生创新训练项目(No. 201510439100; No. 201510439126);山东省高等学校科技计划(No. J14LM52)
R285.5; R363.2
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000- 4718.2017.09.003
△通讯作者 Tel: 0538-6225010; E-mail: yst228@126.com
▲并列第1作者
