养殖半滑舌鳎肝胰、中肾、鳃、头肾、脾和心中酸性磷酸酶、碱性磷酸酶和过氧化物酶的组织化学定位
2017-07-31王一泽孙敬锋刘军锋郭永军邢克智吕爱军YeongYiksung
王一泽,孙敬锋*,刘军锋,郭永军,邢克智,吕爱军,Yeong Yiksung
(1天津农学院水产学院,天津市水产生态及养殖重点实验室,天津 300384;2天津市渔生堂生物技术有限公司,天津 300404)
养殖半滑舌鳎肝胰、中肾、鳃、头肾、脾和心中酸性磷酸酶、碱性磷酸酶和过氧化物酶的组织化学定位
王一泽1,孙敬锋1*,刘军锋2,郭永军1,邢克智1,吕爱军1,Yeong Yiksung1
(1天津农学院水产学院,天津市水产生态及养殖重点实验室,天津 300384;2天津市渔生堂生物技术有限公司,天津 300404)
目的研究半滑舌鳎肝胰、中肾、鳃、头肾、脾和心中酸性磷酸酶(ACP)、碱性磷酸酶(ALP)和过氧化物酶(POX)的分布及组织定位。方法取健康半滑舌鳎肝胰、中肾、鳃、头肾、脾和心组织进行固定,冰冻切片后进行酶组织化学染色和光密度定量统计分析。结果ACP活性部位为棕色,主要分布于肝胰小叶间胆管和静脉,中肾肾小体中的肾小球和肾间质的肾小管,头肾和脾中的巨噬细胞以及心肌层中,在鳃中未见有分布;ALP活性部位被染为蓝紫色,主要分布于肝胰的胰腺腺泡内,中肾肾间质的肾小管,鳃的鳃丝血管和上皮细胞,脾静脉的管壁处和椭圆体,心外膜和肌膜上以及头肾的血窦腔内皮;POX活性部位被染为茶褐色,主要分布于肝胰小静脉和肝血窦内的血细胞,中肾肾间质的血细胞,鳃的鳃丝血管、鳃小片血窦和上皮细胞,头肾、脾内的血细胞以及心的心肌层和血细胞中。ACP活性由大到小依次为心、肝胰、脾、中肾、头肾;ALP活性由大到小依次为中肾、鳃、头肾、脾、心、肝胰;POX活性由大到小依次为脾、头肾、肝胰、中肾、鳃、心。结论ACP、ALP和POX在半滑舌鳎6种组织中分布特点不同,其活性大小在不同组织中有显著差异。
半滑舌鳎;酶组织化学;酸性磷酸酶;碱性磷酸酶;过氧化物酶
半滑舌鳎(Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther)是一种广泛分布于我国沿海地区的底栖鱼类,尤其在黄海和渤海分布较多[1]。半滑舌鳎出肉率高,营养丰富,味道鲜美,具有较高的经济价值。随着半滑舌鳎人工繁殖及养殖技术的日渐成熟,近年来逐渐成为我国最具吸引力的海水养殖鱼类之一。目前,对半滑舌鳎的组织形态学[2]、摄食习惯[3]、营养饲料[1]和疾病控制[4]等方面已有一些研究。在硬骨鱼类中,头肾、脾是重要的免疫造血器官,肝胰是鱼类的主要消化腺,中肾和鳃承担泌尿机能和渗透压调节功能,心是血液循环的中枢,它们共同维持着鱼类机体正常代谢及生理活动。
酸性磷酸酶(acid phosphatase, ACP)、碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase, ALP)、过氧化物酶(peroxidase, POX)是重要的水解酶或氧化酶,在机体组织器官执行正常生理功能过程中发挥重要作用。在水生动物中,目前对于ACP、ALP和POX的研究多集中于酶的生化性质以及消化道的分布定位研究[5-9],而对半滑舌鳎各组织器官的酶组织化学分布研究尚缺乏。本研究对ACP、ALP和POX在半滑舌鳎头肾、脾、肝胰、中肾、鳃和心中的分布进行组织化学定位,并进行光密度定量分析。旨在为深入研究半滑舌鳎免疫相关水解酶和氧化酶在不同组织器官中作用机制提供参考资料。
材料与方法
1 材料
健康的半滑舌鳎购自天津市海发珍品实业发展有限公司,体重100~150g,体长20~30cm,解剖后分别取其肝胰、中肾、鳃、头肾、脾、心6种组织,0.85%生理盐水快速洗净,切成5mm×3mm小块。用于ALP和POX染色的组织,分别先经4%甲醛钙和25%戊二醛固定,再利用OCT(Optimal Cutting Temperature Compound)包埋后,进行冷冻切片。用于ACP染色的组织直接利用OCT包埋后,进行冷冻切片。切片厚度7μm。
2 ACP酶组织化学
参照贲长恩和李叔庚[10]报道的方法进行。孵育液配制:10m l醋酸缓冲液(0.05mol/L, pH 5.0)、10mg硝酸铅、0.8g蔗糖和1m l 3% β-甘油磷酸钠混匀后过滤待用。冰冻切片入孵育液37℃孵育1h,蒸馏水浸洗,入1%硫化铵液复染1m in,再次蒸馏水浸洗,最后封片拍照。
3 ALP酶组织化学
参照吕大成等[11]报道的方法进行。孵育液配制:碱性磷酸酶缓冲液(100mmol/L NaCl, 5mmol/L MgCl2, 100mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 9.2~9.4)、5%硝基蓝四唑(NBT)和5% 5-嗅-4-氯-3-吲哚-磷酸盐(BCIP)混匀即可。冰冻切片室温下孵育20min,蒸馏水浸洗,封片观察拍照。
4 POX酶组织化学
参照贲长恩和李叔庚[10]报道的方法进行。将10mg DAB·4HCl溶于5m l蒸馏水和5m l磷酸缓冲液(0.2mol/L, pH 7.0)中配制成POX预孵育液,然后在预孵育液中加入0.1m l H2O2配制成POX孵育液。室温条件下切片先在POX预孵育液孵育20min,然后在POX孵育液中孵育30m in,蒸馏水漂洗,亚甲蓝染核5m in,封片镜检。
5 酶组织化学染色光密度定量与统计学分析
使用Leica DM 4000B显微镜在40倍物镜视野下进行镜检拍照。每种组织检测5张切片,每张切片取3个视野拍照用于数据分析。用Image J图像分析软件对阳性染色部位测定和计算平均光密度(mean optical density, MOD)。使用SPSS 16.0软件对3种酶在不同组织内染色光密度值进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),数据以平均数±标准差来表示,P<0.05表示具有显著性差异。
结 果
ACP染色结果显示ACP阳性部位染为棕色,其在半滑舌鳎的肝胰、中肾、头肾、脾和心中都有分布,而鳃中未见阳性分布。ACP活性主要分布在肝胰小叶间胆管和静脉(图1A),中肾肾小体中的肾小球和肾间质的肾小管(图1B),头肾和脾中的巨噬细胞(图1C、1D)以及心心肌层中(图1E)。
ALP染色结果显示ALP阳性部位染为蓝紫色,其在半滑舌鳎的肝胰、中肾、头肾、鳃、脾和心中都有分布。ALP活性主要分布在肝胰胰腺的腺泡内(图2A),中肾肾间质的肾小管(图2B),鳃的鳃丝血管和上皮细胞(图2C),脾内静脉的管壁和椭圆体内(图2D),心外膜和肌膜上(图2E)以及头肾的血窦腔内皮(图2F)。

图1 半滑舌鳎肝胰、中肾、头肾、脾、心ACP酶组织化学染色。A, ACP在肝胰小叶间胆管(箭头)和静脉(箭)中有分布;B, ACP在中肾肾小体中的肾小球(箭头)和肾间质的肾小管(箭)中有分布;C, ACP在头肾巨噬细胞(箭)中有分布;D, ACP在脾巨噬细胞(箭)中有分布;E, ACP在心心肌层中有分布;CM, 心肌层;HM, 被膜;RCo, 肾小体;RI, 肾间质;比例尺, 100μmFig. 1 Histochemical staining of ACP in the hepatopancreas, m id-kidney, head kidney, spleen and heart of Cynoglossus semilaevis. A, ACP activity detected in the interlobular bile duct (arrowhead) and vein (arrow) of the hepatopancreas; B, ACP activity detected in the glomerulus in the renal corpuscle (arrowhead) and tubule in the interstitium (arrow) of the mid-kidney; C, ACP activity detected in the macrophages (arrow) of the head kidney; D, ACP activity detected in the macrophages (arrow) of the spleen; E, ACP activity detected in the cardiac muscle of the heart; CM, cardiac muscle; HM, hepatic membrane; RCo, renal corpuscle; RI, renal interstitium; scale bar, 100μm
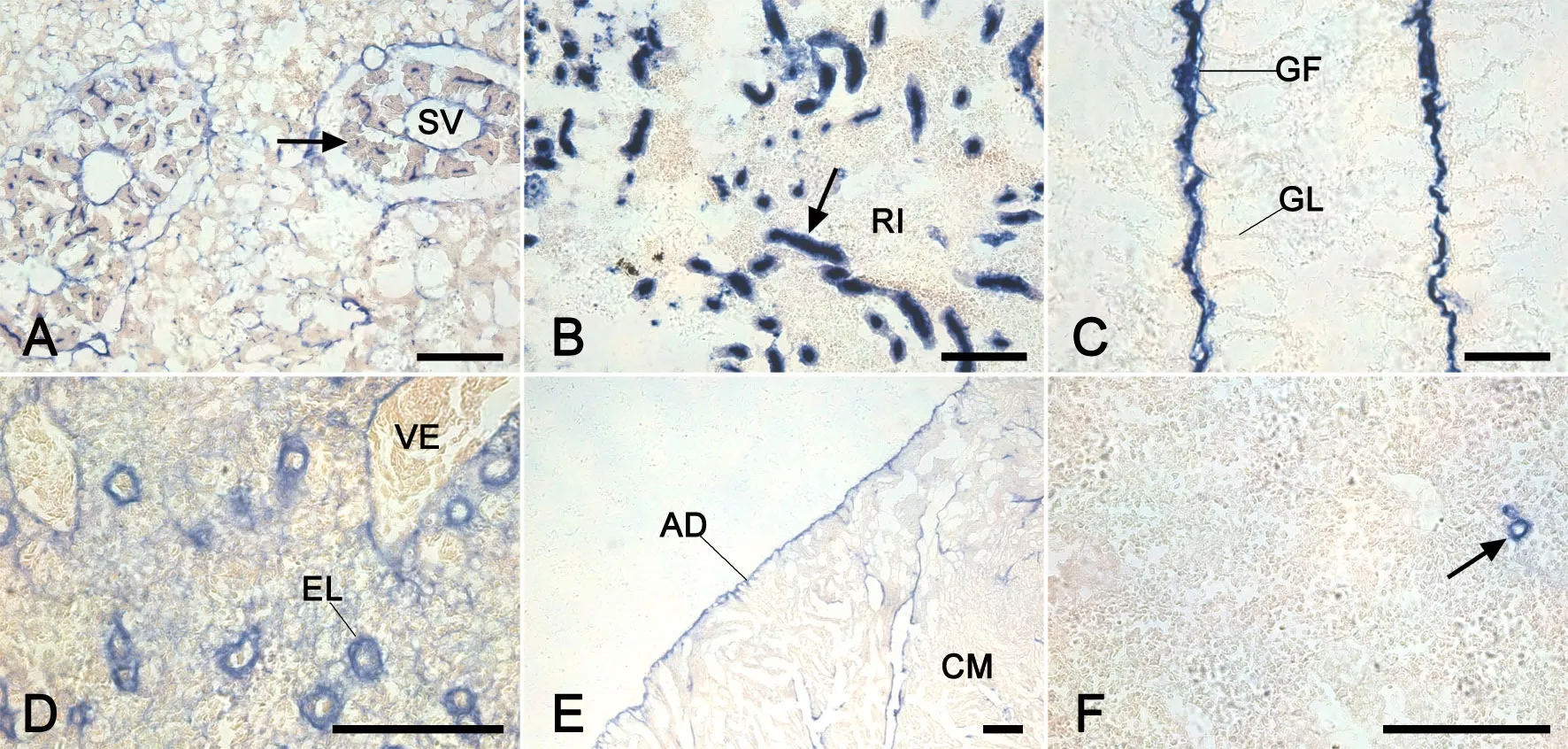
图2 半滑舌鳎肝胰、中肾、鳃、脾、心、头肾ALP酶组织化学染色。A, 肝胰胰腺腺泡(箭);B, 中肾肾间质的肾小管(箭);C, 鳃的鳃丝的血管和上皮细胞;D, 脾静脉的管壁处和椭圆体;E, 心外膜和心肌层肌膜;F, 头肾血窦内皮(箭);AD, 外膜;CM, 心肌层;EL, 椭圆体;GF, 鳃丝;GL, 鳃小片;RI, 肾间质;SV, 小静脉;VE, 静脉;比例尺, 100μmFig. 2 Histochemical staining of ALP in the hepatopancreas, m id-kidney, gill, spleen, heart and head kidney of Cynoglossus semilaevis. A, the pancreatic acinus (arrow) of the hepatopancreas; B, the interstitium tubule (arrow) of the mid-kidney; C, the blood vessel and epithelial cells of gill f laments; D, the venous wall and ellipsoid of the spleen; E, the adventitia and sarolemma of the heart; F, the blood sinus (arrow) of the head kidney; AD, adventitia; CM, cardiac muscle; EL, ellipsoid; GF, gill f lament; GL, gill lamella; RI, renal interstitium; SV, small vein; VE, vein; scale bar, 100μm
POX染色结果显示POX阳性部位染为茶褐色,其在半滑舌鳎的肝胰、中肾、头肾、鳃、脾和心中都有分布。POX活性主要分布在肝胰小静脉和肝血窦内的血细胞(图3A),中肾肾间质的血细胞(图3B),鳃的鳃丝血管、血窦和鳃小片上皮细胞(图3C、3D),头肾、脾内的血细胞(图3E、3F)以及心心肌层和血细胞中(图3G)。
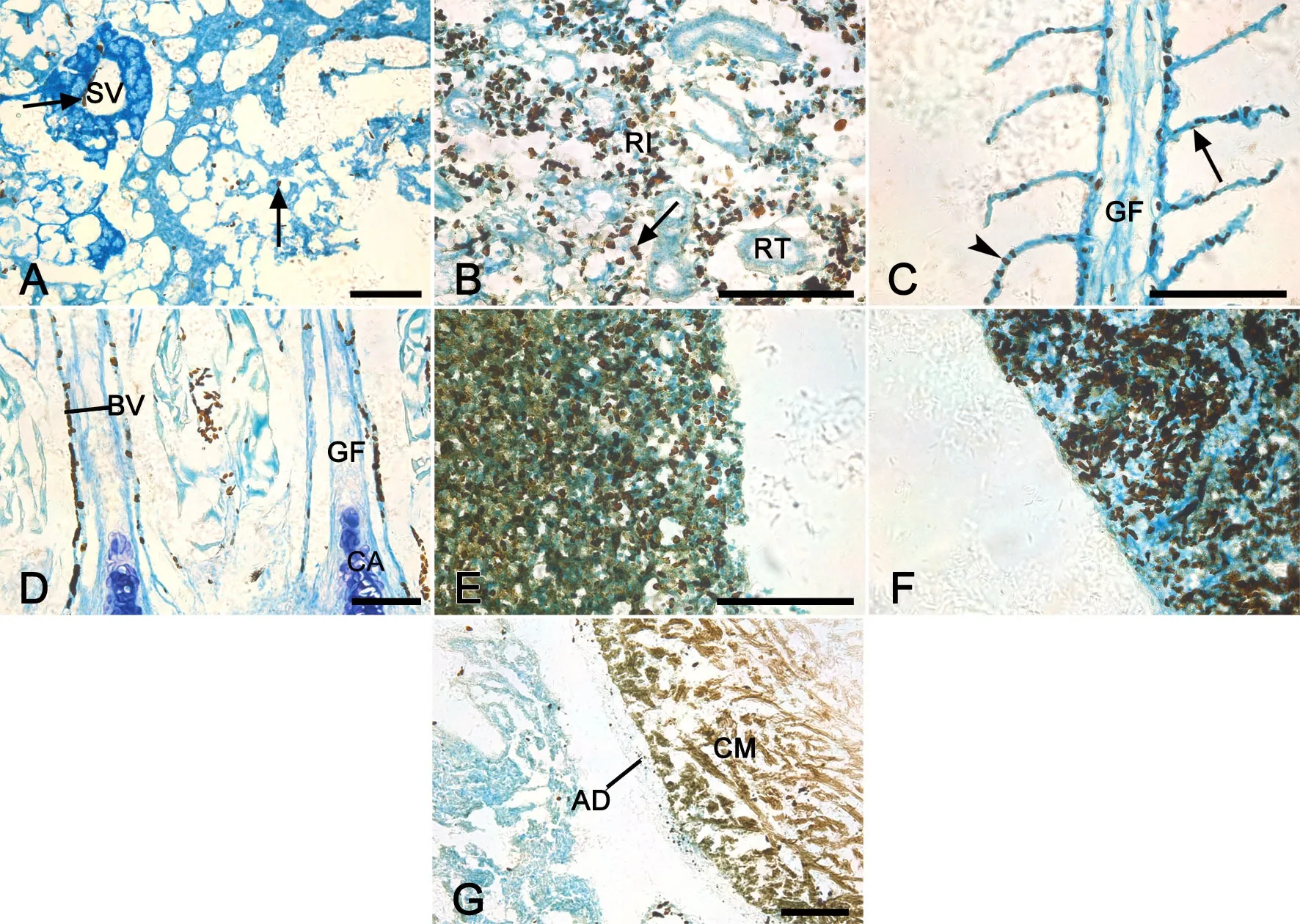
图3 半滑舌鳎肝胰、中肾、鳃、头肾、心、脾POX酶组织化学染色。A, 肝胰小静脉和肝血窦内的血细胞(箭);B,中肾肾间质的血细胞(箭);C, 鳃的鳃丝血窦(箭头)和鳃小片上皮细胞(箭);D, 鳃的鳃丝血管的血细胞;E, POX遍布在整个头肾组织的血细胞中;F, POX遍布在整个脾组织的血细胞中;G, 心肌层以及血细胞;AD, 外膜;BV, 血管;CA, 鳃丝软骨;CM, 心肌层;GF, 鳃丝;RI, 肾间质;RT, 肾小管;SV, 小静脉;比例尺, 100μmFig. 3 Histochemical staining of POX in the hepatopancreas, m id-kidney, gill, head kidney, heart and spleen of Cynoglossus semilaevis. A, the blood cells in the vein and hepatic sinusoid (arrow) of the hepatopancreas; B, the blood cells in the interstitium (arrow) of the mid-kidney; C, the sinusoid of gill f laments (arrowhead) and epithelial cells of gill lamellae (arrow); D, the blood cells in gill blood vessels; E, the blood cells all over the head kidney; F, the cardiac muscle and blood cells of the heart; G, the blood cells all over the spleen; AD, adventitia; BV, blood vessel; CA, cartilage; CM, cardiac muscle; GF, gill f lament; RI, renal interstitium; RT, renal tubule; SV, small vein; scale bar, 100μm
用Image J图像分析软件对各种酶反应产物进行光密度定量分析显示,ACP在心和肝胰中活性最强,其次是脾,在中肾和头肾中酶活性最弱;ALP在中肾活性最强,其次是鳃,头肾和脾活性较弱,而心和肝胰酶活力最弱;POX在脾和头肾中活性最强,其次是肝胰,中肾和鳃中的POX活力较弱,心内酶活性最弱(表1)。
讨 论
本研究首次对半滑舌鳎的肝胰、中肾、鳃、头肾、脾和心中ACP、ALP和POX的分布进行了定位分析,并对酶活性大小进行了比较。
ACP是溶酶体的一种标志酶,不仅参与吞噬细胞的胞内消化和胞饮作用[5,6],还参与核酸和蛋白质的代谢、免疫调节、信号传导等重要生命活动[7,12,13],在疾病的发生发展、免疫防御反应和细胞损伤与修复过程中发挥重要的生物学效应[10]。组织化学研究结果表明,ACP在半滑舌鳎肝胰、心、头肾、脾、中肾中都有分布,而在鳃中未见阳性分布。而在文昌鱼(Branchiostoma belcheri tsingtauense)中,则观察到ACP分布于鳃丝上皮细胞[14]。对酶活性强弱进行定量分析表明,ACP在肝胰和心中较强。在泥鳅(Misgurnus Anguillicadatus)和卵形鲳鲹(Trachinotus ovatus)中,ACP在肝中活性较强[8,15],这与本实验结果相似。由于肝胰是鱼类的物质能量代谢中心,心是整个循环系统的动力中心,而ACP广泛参与代谢调节和能量转换等生命活动[16],因此较强的ACP活性可能与相应的器官承担的主要生理功能有关。
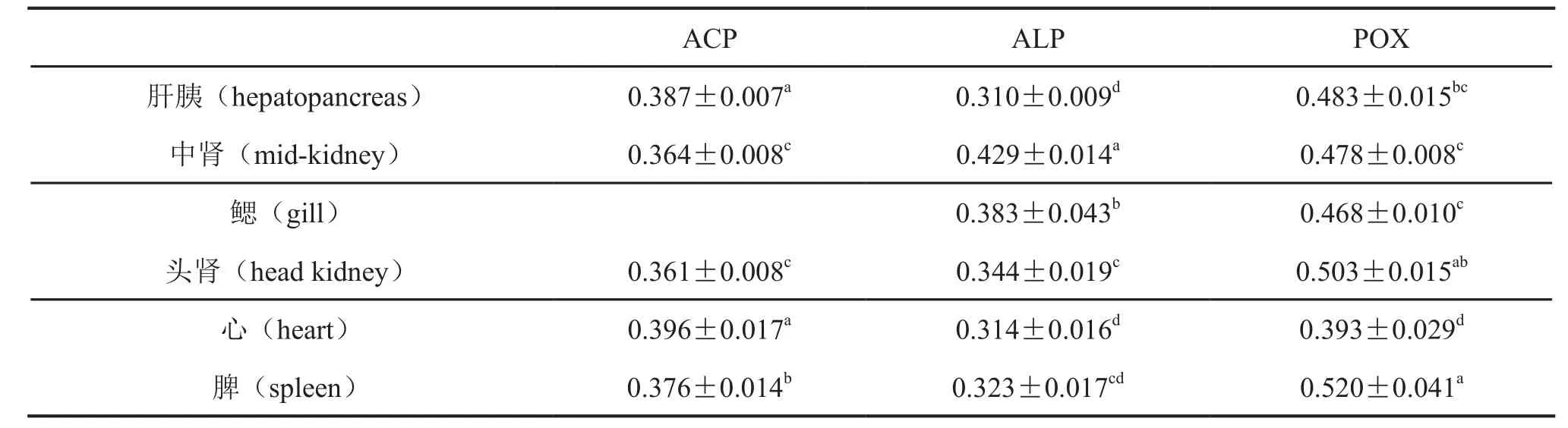
表1 半滑舌鳎肝胰、中肾、鳃、头肾、心、脾中ACP、ALP和POX活性定量分析Tab. 1 Quantitative analysis of the activity of ACP, ALP and POX in the hepatopancreas, m id-kidney, gill, head kidney, heart and sp leen of Cynoglossus sem ilaevis.
ALP主要参与物质转运和离子分泌等生命活动过程[8,16,17],与免疫防御和消化吸收功能密切相关[5,18]。我们观察到,在半滑舌鳎肝胰、中肾、鳃、头肾、脾和心组织中均有ALP阳性分布,其活性在中肾中最强,其次是鳃、脾、头肾、肝胰和心,且在肾小管的刷状缘和鳃丝上皮细胞及血管内分布更加密集。这是因为海水鱼主要依靠肾小管和鳃丝上皮细胞承担分泌离子和排泄的功能[19],ALP在这些生理活动中有着更为重要的作用。
POX在动物、植物、微生物中广泛存在,主要催化过氧化氢和有机过氧化物对各种有机物和无机物的氧化作用。本实验检测到,POX普遍分布于各个组织的血细胞中,以及鳃小片上皮细胞和心肌层中,其活性在头肾和脾中最强,其次是鳃、中肾和肝胰,而心中较弱。血细胞是鱼类机体重要的免疫细胞,其中的白细胞直接参与了免疫应答或者相关免疫防御过程,同时承担着鱼类机体非特异性和特异性免疫的主要机能。血细胞在鱼类的抗感染免疫过程中会产生大量的H2O2等具有强氧化性的活性氧中间体来杀伤病原体。所以POX在血细胞中广泛存在,可以利用其催化作用,发挥H2O2和有机过氧化物的杀伤病原微生物的作用,同时降低细胞内H2O2和有机过氧化物的水平,起到保护宿主细胞的作用。头肾、脾作为鱼类重要的免疫器官,是鱼类抗感染免疫过程中适应性免疫应答发生发展的重要场所。鱼类的鳃直接接触养殖水体中大量的致病性或非致病性微生物。所以POX在头肾、脾、鳃中活性较强,有利于发挥其催化H2O2和有机过氧化物氧化反应的作用,最后产生杀伤病原微生物的生物学效应。
[1] Wang QK, Zhang Y, Bai DQ, et al. Estimation of Dietary Copper (Cu) Requirement of Cynoglossus semilaevis, Günther. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, 2015, 32(D4): 245-255.
[2] Ma AJ, Wang XA. Functional morphology of the olfactory organ of the tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. Chin J Oceanol Limn, 2010, 28(2): 209-217.
[3] Dou SZ. Food habits and seasonal variation of stomach contents of tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis (Günther) in the Bohai Sea. Chin J Oceanol Limn, 1993, 11(1): 89-96.
[4] Tang XQ, Zhou L, Zhan WB. Isolation and characterization of pathogenic Listonella anguillarum of diseased halfsmooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther). J Ocean U China, 2008, 7(3): 343-351.
[5] Gajger IT, Nejedli S, Kozarić Z. Histochem ical distribution of digestive enzymes in the intestine of the common two-banded seabream, Diplodus vulgaris, Geoffroy St-Hilaire 1817. Anat Histol Embryol, 2013, 42(3): 161-167.
[6] Kužir S, Gjurčević E, Nejedli S, et al. Morphological and histochemical study of intestine in w ild and reared European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). Fish Physiol Biochem, 2012, 38(3): 625-633.
[7] 魏炜,张洪渊,石安静.育珠蚌酸性磷酸酶活力与免疫反应关系的研究.水生生物学报,2001,25(4):413-415.
[8] 区又君,罗奇,李加儿.卵形鲳鲹碱性磷酸酶和酸性磷酸酶的分布及其低温保存.南方水产科学,2011,7(2):49-54.
[9] 谢毓玲,王锦乙,袁保勤,等.乌鳢消化道黏膜6种重要酶的组织化学定位.中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2016,25(5):416-421.
[10] 贲长恩,李叔庚.组织化学.北京:人民卫生出版社,2001,271-364.
[11] 吕大成,祝小琴,张敏,等.虎纹蛙消化道黏膜6种酶的组织化学定位.中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2015, 24(1):66-71.
[12] 孙虎山,王宜艳,孙修勤,等.栉孔扇贝外套膜酸性和碱性磷酸酶电镜细胞化学研究.高技术通讯,2002,12(5):99-102.
[13] Li JY, Sun XQ, Zheng FR, et al. Histochem ical localization and characterization of AKP, ACP, NSE, and POD from cultured Apostichopus japonicus. Chin J Oceanol Limn, 2009, 27(3): 550-554.
[14] 孙建梅,张士璀,王勇军,等.酸性磷酸酶在文昌鱼体内的分布.海洋水产研究,2006,27(4):17-20.
[15] 杜启艳,王萍,王友利,等.长期饥饿和再投喂对泥鳅不同组织糖原、酸性磷酸酶和碱性磷酸酶的影响.江西师范大学学报(自然科学版),2008,32(4):488-493.
[16] 徐春生,刘仪,包慧君,等.中华鳖肾脏的组织化学特性研究.水生生物学报,2011,35(1):67-74.
[17] Meyran JC, Graf F. Ultrahistochem ical localization of Na+-K+ ATPase, Ca2+-ATPase and alkaline phosphatase activity in a calcium-transporting epithelium of a crustacean during moulting. Histochem, 1986, 85(4): 313-320.
[18] 孙虎山,王晓安.紫彩血蛤鳃的组织化学和扫描电镜研究.动物学杂志,1999,34(4):9-12.
[19] 林浩然.鱼类生理学(第2版).广州:广东高等教育出版社,2007,98-131.
Histochem ical localization of acid phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase and peroxidase in the hepatopancreas, m id-kidney, gill, head kidney, sp leen and heart of cu ltured Cynoglossus sem ilaevis Günther
Wang Yize1, Sun Jingfeng1*, Liu Junfeng2, Guo Yongjun1, Xing Kezhi1, Lv Aijun1, Yeong Yiksung1
(1Tianjin Key Lab of Aqua-Ecology and Aquaculture, Fisheries College, Tianjin Agricultural University, Tianjin 300384, China;2Tianjin Yushengtang Biotechnology Co.,Ltd., Tianjin 300404, China)
ObjeciveTo investigate the distribution and histochem ical localization of acid phosphatase (ACP), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and peroxidase (POD) in the hepatopancreas, mid-kidney, gill, head kidney, spleen and heart of Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther.M ethodsTissue samples were taken from the hepatopancreas, m id-kidney, gill, head kidney, spleen and heart of healthy Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther, fxed and then frozen sectioned. Enzyme histochem ical staining was performed on the sections, and the mean optical density (MOD) was measured for quantitative analysis.ResultsACP stain was brown, mainly located in the interlobular bile duct and vein of hepatopancreas, glomerulus in renal corpuscle and tubule in interstitium of the mid-kidney, macrophages in head kidney, spleen and myocardium, while absent in the gill. The blue-purple-stained ALP was detected in the pancreatic acinus of hepatopancreas, tubule in the interstitium of mid-kidney, blood vessel and epithelial cells of gill f laments, venous wall and the ellipsoid of spleen, the adventitia and sarolemma of heart, and the blood sinus of head kidney. The dark-brown-stained POX was localized in the blood cells in the vein and hepatic sinusoid of hepatopancreas and those in the interstitium of m id-kidney, blood vessel of gill f laments, sinusoid and epithelial cells of gill lamellae, blood cells of head kidney, spleen and heart, and myocardium. ACP activity was in descending order in the heart, hepatopancreas, spleen, m id-kidney and head kidney; ALP activity was in descending order in the m id-kidney, gill, head kidney, spleen, heart and hepatopancreas; POX activity was in descending order in the spleen, head kidney,hepatopancreas, m id-kidney, gill and heart.ConclusionThe distribution of ACP, ALP, and POX vary in the six types of tissues investigated, and there are signif cant dif erences in their expressions and activities.
Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther; enzyme histochem istry; acid phosphatase; alkaline phosphatase; peroxidase
Q174
ADOI:10.16705/ j. cnki. 1004-1850.2017.03.005
2016-12-17
2017-05-02
天津市应用基础与前沿技术研究计划项目(15JCZDJC34000,16JCZDJC33500);国家自然科学基金项目(31272692)
王一泽,男(1993年),汉族,硕士研究生
*通讯作者(To whom correspondence should be addressed):sun_jf@163.com
