钛合金搅拌摩擦焊接最新研究进展
2017-06-05王快社
袁 洁,王快社,赵 凯,王 文
(西安建筑科技大学冶金工程学院,陕西西安710055)
钛合金搅拌摩擦焊接最新研究进展
袁 洁,王快社,赵 凯,王 文
(西安建筑科技大学冶金工程学院,陕西西安710055)
钛合金具有密度低、比强度高,耐蚀性好,加工性能优异等优点,主要应用于航空航天、交通运输和石油化工等领域。当钛合金作为结构材料应用在不同领域时,传统的熔融焊接方法会产生较大残余应力,组织粗化,变形大,裂纹和孔隙等缺陷;而采用搅拌摩擦焊接技术可以避免传统熔融焊接方法产生的缺陷,从而大幅度提高钛合金焊接接头质量。目前,钛合金的搅拌摩擦焊接技术已成为国内外研究热点。主要介绍搅拌摩擦焊接的原理、工艺特点,国内外关于钛合金FSW焊接接头的宏观形貌、微观组织(晶粒大小、织构)和力学性能等方面的最新研究进展,最后展望了钛合金FSW未来的研究方向。
钛合金;搅拌摩擦焊;微观组织;力学性能
0 前言
钛合金具有密度小、比强度高、耐热、耐蚀等优异性能,在航空、航天、石油化工等领域得到了广泛应用[1-4]。钛合金传统焊接方法有钨极氩弧焊、等离子弧焊、电子束焊、激光焊、电阻焊、钎焊等[5-8],但这些方法的焊接条件苛刻且工艺复杂,焊后存在较大残余应力,变形大,组织粗化,易产生裂纹、气孔及脆性化合物等缺陷,严重影响接头质量,大大降低焊接接头的力学性能[9]。搅拌摩擦焊接(Friction stirwelding,FSW)技术作为一种固相焊接技术,已经在镁合金、铝合金等低熔点合金上得到了广泛的应用[10-15]。随着搅拌头工具的发展,近几年开始对高熔点合金如铜、钢、镍及钛合金的FSW展开研究[16-19]。本研究主要对国内外钛合金FSW接头宏观组织、微观组织及力学性能等进行综述,并展望了钛合金FSW未来的研究方向。
1 钛合金FSW接头组织
钛合金FSW接头表面形貌和横截面的宏观组织如图1所示。表面光滑发亮,横截面宏观组织分为焊核区(Stir Zone,SZ),热影响区(Heat Affected Zone,HAZ)和母材(Base Material,BM),而热机械影响区(Thermo-Mechanically Affected Zone,TMAZ)的存在则存在较大的争议[18-24]。钛合金FSW宏观组织的特点:一方面,钛合金强度较高,难以发生塑性变形,塑性变形过程较复杂;另一方面,钛合金在FSW过程中发生了相变,相变掩盖了TMAZ或HAZ[25]。交界区较窄,通常只有几十到几百微米,这是因为钛合金热导率较低,仅为17 W/(m·K),而铝合金的热导率高达210 W/(m·K)。SZ呈“碗状”形状,且整个接头形貌基本上沿焊缝中心对称,焊缝两侧形貌差别较小。

图1 Ti6Al4V FSW接头宏观形貌[29]Fig.1 Macro-appearance of Ti6Al4V FSW welds
钛合金FSW接头微观组织的研究主要集中在相变和晶粒取向方面。李继忠等人[26]研究了转速对FSW TC4接头组织的影响。当焊速为30 mm/min、转速为150 r/min时,SZ主要为α相等轴超细晶;转速增至200 r/min时,SZ为α相等轴超细晶和片层状α+β的双态组织;转速继续增至250 r/min,SZ全部由片层状α+β组织组成,α等轴晶消失。王快社等人[27]研究表明,SZ组织为细密的等轴晶组织,焊缝最大温度未超过相变温度。王文[18]和Liu等人[24]研究结果表明,SZ组织为片层状α+β结构,组织转变主要为β相向片层α+β相转变,TMAZ为等轴晶α和α+β片层的双态组织,分析认为组织转变受动态再结晶和相变共同作用。TC4 FSW接头未超过相变温度的两种组织形态如图2所示。
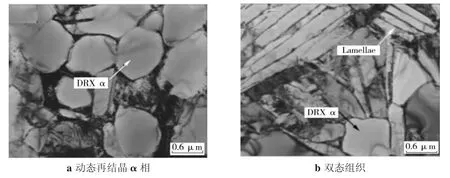
图2 TC4焊核区TEM微观组织[29]Fig.2 Microstructures of SZ in TC4 by FSW
由于钛合金低的导热系数,在厚度方向上也呈现出不同的组织特征。Yoon[28]和姬书得等人[29]研究了Ti6Al4V板材FSW接头厚度方向上的组织,结果表明:在焊速50 mm/min、转速300 r/min下,近焊缝表面组织由完全的片层状β相组成,表明在该区域峰值温度已经超过了β相变温度;中间部分的组织由等轴的α相及片层状的α+β晶粒组成,这个区域的峰值温度未超过β相变温度[18,22,24,30]。最底层的组织主要由完全等轴α相组成。当转速逐渐下降时,近焊缝表面的完全片层状组织范围减小;当转速降为225 r/min时,SZ组织全部为α等轴晶。
焊接参数直接影响焊接温度。当焊接峰值温度低于β相变温度时,钛合金FSW后的组织分为两种,一种为等轴细晶α相,另一种为等轴细晶α相和片层状α+β的双态组织;当峰值温度超过β相变温度时,组织为完全的层状β相。
钛是密排六方(hcp)晶体结构,晶格对称性较低,滑移系相对较少,在FSW过程中易形成变形织构。Zhou等人[31]研究了FSW Ti6Al4V织构演变过程,结果表明:Ti6Al4V钛合金母材为明显轧制织构,FSW后的SZ发生明显的动态再结晶过程,形成{φ1=30°,φ=62°,φ2=30°}织构,且高角度晶界比例明显提升。
Fonda等人[32]研究了近α态钛合金FSW接头的织构演变规律。结果表明,在低焊速下焊接接头主要为hcp p1型剪切织构,在高焊速下主要为bcc D1型剪切织构,hcp p1型织构强度高于bcc D1型。究其原因是在高焊速下,热量在焊缝处停留时间短,搅拌头到焊缝剪切变形传输过程比较慢,所以产生了织构强度稍低的bcc D1型织构。
Liu等人[33]对于工业纯钛FSW接头的微观织构,如图3所示。

图3 EBSD测试结果[38]Fig.3 The results of EBSD[38]
结果表明,BM为明显的轧制织构,SZ区为P1{10}<10>型剪切织构。从前进侧(Advancing Side,AS)到后退侧(Retreating Side,RS),P1型织构发生了转动,AS侧的[0001]α织构与焊接方向垂直,而RS侧的α织构与焊接方向平行,这与Zhou[30]和Yoon等人[34]的研究结果一致。而在镁合金中,从AS到RS的[0001]α织构并没有发生转动[35-36],这表明织构不仅与晶体结构有关,还与FSW过程中材料的塑性变形有重要关联。再者,FSW接头高角度晶界比例明显提升,在焊接过程中伴随着亚晶的转动,晶粒发生了动态再结晶,晶粒显著细化。组织演变一方面与应变和不连续动态再结晶有关,另一方面与织构诱导的晶粒汇聚有关[37-38]。
2 力学性能
力学性能是衡量FSW接头质量的关键指标,目前针对FSW钛合金力学性能的研究主要包括显微硬度、拉伸性能,针对疲劳性能的研究相对较少。
Fujii等人[39]研究了工业纯钛FSW后SZ区晶粒尺寸、显微硬度和拉伸性能的关系,如表1所示。随着焊速的提升,SZ区晶粒尺寸呈减小趋势,显微硬度值呈增大趋势。同时,随着焊速的增大,抗拉强度(Ultimate Tensile Strength,UTS)先增大后减小(见图4),当焊速为300 mm/min时,虽然晶粒得到细化,但热输入量的降低使塑性变形不充分,导致UTS减小。
Zhang等人[22]对Ti6Al4V FSW接头的力学性能进行了评价,如图5所示。拉伸试验分为两部分,一种拉伸试样平行段包含整个焊缝,另一种拉伸试样平行段只包含SZ区。结果表明:第一种拉伸试样的UTS、YS(屈服强度)都达到BM的95%以上,伸长率可达55%。随着转速的增大,α相和β相尺寸增大,完全片层状组织使得强度和伸长率略有降低。第二种拉伸试样由于SZ为细小的α相,相比BM, UTS与屈服强度增约15%,伸长率增约42%。Liu等人[24,40-41]对TC4 FSW接头力学性能分析表明,FSW接头UTS均能达到BM的92%以上,断裂位置位于SZ区,这是因为在FSW过程中经历了回复与再结晶,材料发生软化。

图4 不同参数条件下焊接接头的抗拉强度[39]Fig.4 Tensile strength of the samples at different welding speeds

表1 不同焊接条件Ti6Al4V焊接接头的晶粒尺寸与硬度关系表[44]Table 1 Summary of the grain size and hardness of the samples welded under different conditions
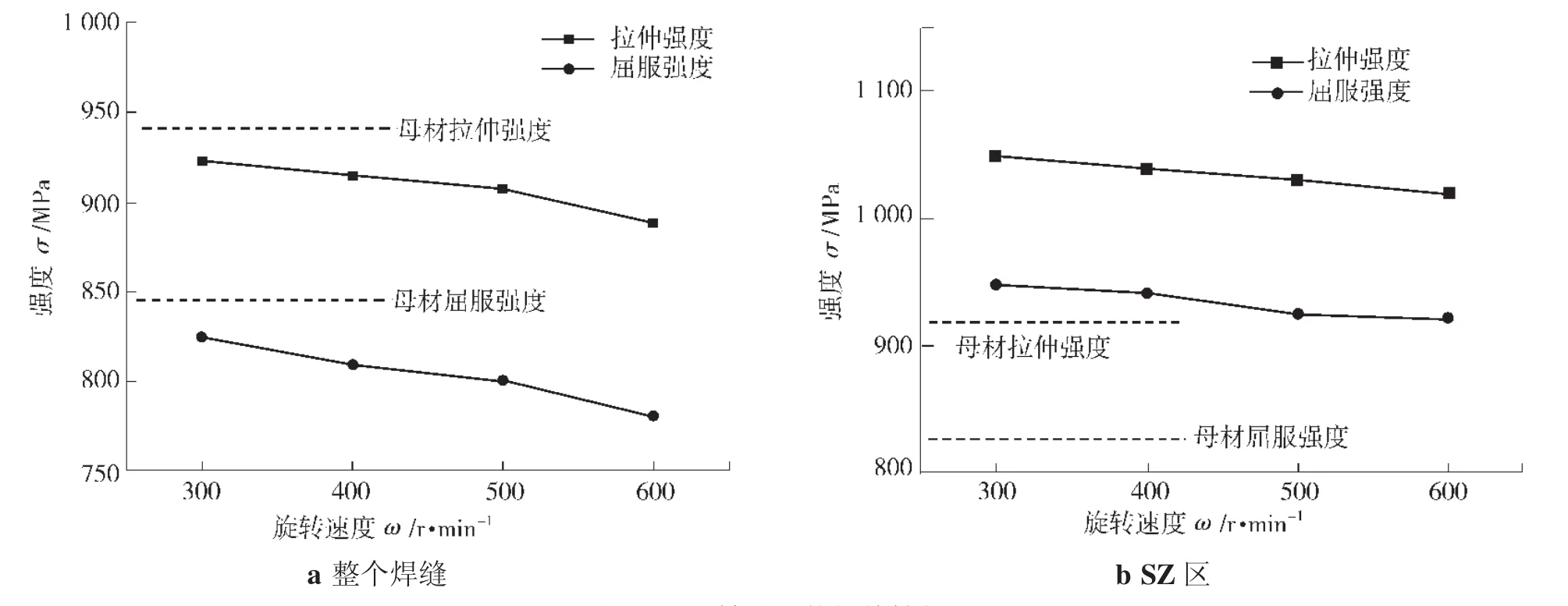
图5 不同转速下的拉伸性能[27]Fig.5 Effect of rotational speed on tensile properties[27]
Edwards等人[23,42-43]对Ti6Al4V FSW的研究结果表明,FSW后接头疲劳性能相比BM降低了50%,对焊缝进行热处理后相比BM提升了约20%,同时UTS、YS均得到提升,故对于钛合金FSW接头,选择合理的焊后热处理能够提升接头的疲劳寿命。
分析总结目前关于钛合金FSW力学性能的相关文献,钛合金FSW力学性能呈现以下特点:(1)钛合金FSW后力学性能指标良好,UTS最高能达到BM的99%以上;(2)在焊缝无缺陷状态下,通过合理的热处理制度,UTS、YS可进一步提高;(3)FSW后晶粒得到细化,高角度晶界比例增加,有利于材料强塑性的结合。总之,钛合金FSW后的力学性能与多种因素有关,包括晶粒大小,α与β相含量、尺寸及分布,晶粒取向的变化。
3 结论
钛合金FSW的开发和应用刚刚起步,具有广阔的应用前景。对钛合金FSW的研究应从以下方面深入研究:(1)钛合金FSW组织演变机制及控制;(2)钛合金FSW目前主要集中于薄板的研究,应实现不同板厚的连接,满足实际工业化应用;(3)对于钛合金FSW的力学性能,除考虑到晶粒尺寸与相变外,还要深入研究织构对接头力学性能的影响,同时开展超塑性变形机制的研究,以扩大钛合金作为结构件的应用范围;(4)开展FSW接头腐蚀性能研究,满足在腐蚀工况条件下的应用。
[1] 钱九红.航空航天用新型钛合金的研究发展及应用[J].稀有金属,2000,24(3):218-223.
[2]李梁,孙健科,孟祥军,等.钛合金的应用现状及发展前景[J].钛工业进展,2004,21(5):19-24.
[3] 朱知寿.我国航空用钛合金技术研究现状及发展[J].航空材料学报,2014,34(4):44-50.
[4] 金和喜,魏克湘,李建明,等.航空用钛合金研究进展[J].中国有色金属报,2015,25(2):280-292.
[5]程东海,黄继华,林海凡,等.TC4钛合金激光拼焊接头显微组织及力学性能分析[J].焊接学报,2009,30(2):103-106.
[6]BALASUBRAMANIAN T S,BALASUBRAMANIAN V,MUTHUMANIKKAM M A,等.焊接方法对Ti-6Al-4V合金接头微观组织及拉伸和冲击性能的影响[J].中国有色金属学报(英文版),2011(6):1253-1262.
[7]WU B,LI J W,TANG Z Y.Study on the Electron Beam Welding Process of TC4 Titanium Alloy[J].Rare Metal Materials and Engineering,2014,43(4):786-790.
[8]MA X Y,GONG S L,ZHANG J X,et al.Formation microstructure and mechanical properties of double-sided laser beam welded Ti-6Al-4V T-joint[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2016,26(3):729-735.
[9] 高飞.钛及钛合金材料的焊接技术[J].石油化工建设,2006,28(4):38-42.
[10]KARTSONAKIS I A,RAGATOGIANNIS D A,KOUMOULOS E P,et al.Corrosion behavior of dissimilar friction stir welded aluminum alloys reinforced with nanoadditives[J]. Materials&Design,2016,102(15):56-57.
[11]WOO W,CHOO H,BROWN D W,et al.Texture variation and its influence on the tensile behavior of a friction-stir processed magnesium alloy[J].Scripta Materialia,2006,11(54):1859-1864.
[12]RAO H M,JORDON J B,GHAFFARI B,et al.Fatigue and fracture of friction stir linear welded dissimilar aluminumto-magnesium alloys[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2016,82(3):737-747.
[13]MIRONOV S,ONUMA T,SATO Y S,et al.Microstructure evolution during friction-stir welding of AZ31 magnesium alloy[J].Acta Materialia,2015(100):301-312.
[14]BABU S R,SENTHIL V S,KARUNAMOORTHY L,et al. Investigation on the effect of friction stir processing on the super-plastic forming of AZ31B alloy[J].Material Design,2014,53(1):338-348.
[15]NARESH N,SATISH V K,SATYAM S.A bottom-up approach for optimization of friction stir processing parameters;a study on aluminum 2024-T3 alloy[J].Material Design,2015(65):127-138.
[16]XUE P,KOMIZO Y,UEJI R,et al.Enhanced mechanical properties in friction stir welded low alloy steel joints via structure refining[J].Materials Science&Engineering A,2014(606):322-329.
[17]XUE P,XIAO B L,Ma Z Y.Achieving ultrafine-grained structure in a pure nickel by friction stir processing with additional cooling[J].Materials and Design,2014,56(4):848-851.
[18]王文,李瑶,王庆娟,等.TC4钛合金FSW接头组织转变特征[J].稀有金属材料与程,2014,43(5):1143-1147.
[19]SU J Q,NELSON T W,MCNELLEY T R,et al.Development of nanocrystalline structure in Cu during friction stir processing(FSP)[J].Materials Science and Engineering A,2011,528(16-17):5458-5464.
[20]RAMIREZ A J,JUHAS M C.Microstructural Evolution in Ti-6Al-4V Friction Stir Welds[J].Materials Science Forum,2003(426-432):2999-3004.
[21]LEE W B,LEE C Y,CHANG W S,et al.Microstructural investigation of friction stir welded pure titanium[J].Mat-erials Letters,2005,59(26):3315-3318.
[22]ZHANG Y,SATO Y S,KOKAWA H,et al.Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V friction stir welds[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A,2008,485(1-2):448-455.
[23]EDWARDS P,RAMULU M.Investigation of microstructure surface and subsurface characteristics in titanium alloy friction stir welds of varied thicknesses[J].Science and Technology of Welding and Joining,2009,14(5):476-483,488.
[24]LIU H J,ZHOU L.Microstructural zones and tensile characteristics of friction stir welded joint of TC4 titanium alloy [J].Transaction Nonferrous Metal Society of China,2010,20(10):1873-1878.
[25]赵强,王玉,王建涛.钛合金FSW接头的微观组织分析[J].航天制造技术,2006(5):42-46,56.
[26]李继忠,董春林,栾国红,等.TC4钛合金搅拌摩擦焊焊缝成形及微观组织研究[J].航空制造技术,2013,436(16):160-163.
[27]王快社,马宏刚,王文,等.TA2工业纯钛表面搅拌摩擦加工组织及性能[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2011,40(9):1530-1533.
[28]YOON S,UEJI R,FUJII H.Effect of rotation rate on microstructure and texture evolution during friction stir welding of Ti6Al4V plates[J].Materials Characterization,2015(106):352-358.
[29]姬书得,温泉,马琳,等.TC4钛合金搅拌摩擦焊厚度方向的显微组织[J].金属学报,2015,51(11):1391-1399.
[30]ZHOU L,LIU H J,LIU P,et al.The stir zone microstructure and its formation mechanism in Ti-6Al-4V friction stir welds[J].Scripta Materialia,2009,61(6):596-599.
[31]ZHOU L,LIU H J,WU L Z.Texture of friction stir welded Ti6Al4V alloy[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2014,24(2):368-372.
[32]FONDA R W,KNIPLING K E.Texture development in near-α Ti friction stir welds[J].Acta Materialia,2010,58(9):6452-6463.
[33]LIU F C,LIAO J,GAO Y,et al.Influence of texture on strain localization in stir zone of friction stir welded titanium[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2015(626):304-308.
[34]YOON S,UEJI R,FUJII H.Microstructure and texture distribution of Ti-6Al-4V alloy joints friction stir welded below transus temperature[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2016(229):390-397.
[35]YANG Q,FENG A H,XIAO B L,et al.Influence of texture on super plastic behavior of friction stir processed ZK60 magnesium alloy[J].Materials Science and Engineering A,2012,556(9):671-677.
[36]LIU D J,X R L,LI Z Y,et al.The activation of twinning and texture evolution during bending of friction stir welded magnesium alloys[J].Materials Science and Engineering A,2015(646):145-153.
[37]MIRONOV S,SATO Y S,KOKAWA H.Development of grain structure during friction stir welding of pure titanium [J].Acta Materialia,2009,57(15):4519-4528.
[38]WU L H,WANG D,XIAO B L,et al.Microstructural evolution of the thermomechanically affected zone in a Ti6-Al4V friction stir welded joint[J].Scripta Materialia,2014(78-79):17-20.
[39]FUJII H,SUN Y F,KATO H,et al.Investigation of welding parameter dependent microstructure and mechanical properties in friction stir welded pure Ti joints[J].Materials Science and Engineering A,2010,527(15):3386-3391.
[40]ZHOU L,LIU H J,LIU Q W.Effect of rotation speed on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V friction stir welded joints[J].Materials and Design,2010,31(5):2631-2636.
[41]LIU H J,ZHOU L,LIU Q W.Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of friction stir welded joints of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy[J].Materials and Design,2010,31(3):1650-1655.
[42]EDWARDS P,RAMULU M.Fatigue performance of Friction Stir Welded Ti-6Al-4V subjected to various post weld heat treatment temperatures[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2015(75):19-27.
[43]EDWARDS P,RAMULU M.Identification of process parameters for friction stir welding Ti6Al4V[J].Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology,2010,132(3):61-78.
[44]EDWARDS P,RAMULU M.Effect of process conditions on super plastic forming behavior in Ti6Al4V friction stir welds[J].Science and Technology of Welding and Joining,2009,14(7):669-680.
Latest research progress of friction stir welding of titanium alloys
YUAN Jie,WANG Kuaishe,ZHAO Kai,WANG Wen
(College of Metallurgy Engineering,Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology,Xi'an 710055,China)
Titanium alloys with some advantages of low density,high specific strength,good corrosion resistance and excellent processing performance are mainly used in the aerospace,transportation,petrochemical and other fields.When using titanium alloys as structural materials in different fields,the traditional fusion welding method will produce a larger residual stress,microstructure coarsening,large deformation,cracks,pores and other defects,while the friction stir welding(FSW)technology can avoid these defects,thus sharply improves the quality of the welded joints of titanium alloys.In addition,the FSW technology of the titanium alloy has become a research focus.In this paper,the theory and technology characteristics of FSW are introduced,and the latest research progress of the welded joints in FSW for titanium alloys at home and abroad is also introduced from the aspects of the macrostructure,microstructure(grain size,texture)and mechanical properties.And the further trends of FSW of titanium alloys are discussed.
titanium alloys;friction stir welding;microstructure;mechanical properties
TG457.19
C
1001-2303(2017)05-0067-06
10.7512/j.issn.1001-2303.2017.05.14
2017-02-10;
2017-02-23
国家自然科学基金(U1360105);国家自然科学基金(51574192)
袁 洁(1991—),女,在读硕士,主要从事搅拌摩擦焊接的研究工作,E-mail:yuanjxauat@126.com。
本文参考文献引用格式:袁洁,王快社,赵凯,等.钛合金搅拌摩擦焊接最新研究进展[J].电焊机,2017,47(05):67-72.
