滴滴涕对人大肠癌DLD1细胞上皮间充质转化的影响
2017-04-10董宁宁李卓玉
董宁宁,宋 莉,李卓玉,肖 虹
(1.山西大学生物技术研究所化学生物学与分子工程教育部重点实验室,山西太原 030006;2.山西医科大学第一医院,山西太原 030006)
滴滴涕对人大肠癌DLD1细胞上皮间充质转化的影响
董宁宁1,宋 莉1,李卓玉1,肖 虹2
(1.山西大学生物技术研究所化学生物学与分子工程教育部重点实验室,山西太原 030006;2.山西医科大学第一医院,山西太原 030006)
目的探究滴滴涕(DDT)对人结直肠腺癌上皮细胞(DLD1)上皮间充质转化的影响及机制。方法DLD1细胞用DDT 0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0和100.0 nmol·L-1处理48 h后,倒置显微镜下观察细胞形态;实时荧光定量PCR法检测E-钙黏着蛋白、N-钙黏着蛋白、波形蛋白和锌指转录因子Snail1的mRNA表达。Western蛋白质印迹法检测信号转导和转录激活因子3(STAT3)信号通路主要蛋白STAT3和p-STAT3的蛋白水平。用STAT3抑制剂WP1066(5 μmol·L-1)处理,通过Western印迹法和实时荧光定量PCR法检测其对DDT诱导的STAT3/Snail1信号通路中p-STAT3、STAT3的蛋白水平和上皮间充质转化关键因子E-钙黏着蛋白、N-钙黏着蛋白、波形蛋白和锌指转录因子Snail1的mRNA水平的影响。结果 与正常对照组相比,DLD1细胞在DDT处理48 h后,细胞形态由卵圆形逐渐变为长梭形,E-钙黏着蛋白mRNA相对表达显著降低(P<0.01),为正常对照组的(42.4±2.8)%。N-钙黏着蛋白和波形蛋白mRNA相对表达显著提高(P<0.01),为正常对照组的1.91±0.1倍和(1.5±0.2)倍。STAT3信号通路蛋白STAT3和p-STAT3蛋白表达均升高(P<0.01),为正常对照组的2.1和1.8倍。锌指转录因子Snail1的mRNA相对表达显著升高(P<0.01),是正常对照组的(1.5±0.1)倍。STAT3抑制剂WP1066 5 μmol·L-1处理后,锌指转录因子Snail1 mRNA的表达明显下调(P<0.01),为DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1处理组的(56.3±0.9)%,同时抑制DDT诱导的E-钙黏着蛋白mRNA表达升高(P<0.01),为DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1处理组的2.5±0.1倍,N-钙黏着蛋白和波形蛋白mRNA表达降低(P<0.01),分别为DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1处理组的(50.2±2.9)%和(61.6±6.1)%。结论 DDT可能通过STAT3/Snail1信号通路改变上皮间充质转化子E-钙黏着蛋白、N-钙黏着蛋白和波形蛋白的表达,进而促进大肠癌细胞上皮间充质转化。
滴滴涕;大肠癌;上皮间充质转化;信号转导和转录激活因子3
滴滴涕(clofenotane,p,p′dichlorodiphenyltri⁃chloroethane,DDT)是首个被广泛应用于生产及卫生领域的合成有机氯农药(organochlorine pesti⁃cide,OCP)。DDT曾经在20世纪为防治农业病虫害而被大量广泛使用。随着人们逐渐深入认识到DDT的危害后,2001年,瑞典最先禁止在农业上使用DDT,随后世界各国陆续禁止了DDT的生产和使用。DDT具有难降解性、亲脂性和半挥发性,是一种持久性有机污染物(persistent organic pollutant,POP)[1]。由于DDT曾大规模使用,且又很难在自然环境中降解,残留时间较长,DDT可通过土壤和食物给人类带来极大的安全性问题[2]。国内外研究表明DDT污染形势严重。如加拿大St Lawrence河表层水中DDT含量为9~22 ng·L-1[3]。2002年发现,中国江苏省水稻田总DDT残留量最高为1.15 mg·kg-1,超出土壤环境质量三级标准(1.0 mg·kg-1)[4]。环境中残留的DDT可在生物体脂肪组织内富集,并通过食物链逐级放大到较高浓度,对人类生命健康造成严重威胁。DDT及其代谢物具有生殖发育毒性、神经毒性、内分泌干扰功能和免疫毒性等[5]。此外,DDT暴露和多种癌症的发生密切相关,如大肠癌(colorectal cancer,CRC)、乳腺癌和肝癌等[6-9]。
CRC是一种十分常见的恶性肿瘤,而且死亡率在逐年上升。遗传因素、日常饮食习惯如高比例摄入肉类和脂肪等都是CRC发病的诱因。此外,食品和饮料中的化学污染也是一个重要的因素[10]。流行病学调查表明,DDT暴露与CRC发病有关[11-12]。我们前期的研究结果表明,DDT暴露能促进大肠癌细胞增殖并抑制其凋亡[13-15]。上皮间充质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)在肿瘤侵袭和转移中发挥重要作用[16-17]。在EMT过程中,细胞极性消失,细胞间黏附降低,上皮标志蛋白N-钙黏着蛋白表达降低,间质蛋白N-钙黏着蛋白和波形蛋白的表达升高。研究发现,信号转导和转录激活因子3(singnal transducers and activators of transcription 3,STAT3)和锌指转录因子Snail1是EMT的重要调节蛋白[18-19]。Zucchini-Pascal等[20]发现,DDT暴露能诱导人肝细胞发生EMT。此外,DDT处理肝癌细胞后,明显抑制E-钙黏着蛋白表达,并上调N-钙黏着蛋白的表达[8]。因此,DDT可能影响CRC细胞EMT化。目前,关于DDT暴露对CRC癌细胞EMT的影响及分子机制未见报道。本研究旨在探究DDT暴露对人结直肠腺癌上皮细胞(DL Dexter-1,DLD1)EMT的影响及可能机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 细胞、试剂和仪器
DLD1细胞(中国科学院上海分院细胞研究所),于37°C,5%的CO2细胞培养箱中,用含10%胎牛血清和1%青链霉素的RPMI1640培养基培养。DDT和二甲亚砜(DMSO)(美国Sigma公司),用DMSO溶解DDT,配置成100 mmol·L-1的储备液。使用时用RPMI 1640培养基稀释至DDT 0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0和100.0 nmol·L-1;RPMI 1640培养基和胎牛血清(美国Gibco公司);100×青、链霉素和胰蛋白酶(北京Solarbio公司);总RNA抽提试剂Trizol和反转录试剂盒(日本TaKaRa公司);荧光定量PCR试剂盒SGExcel FastSYBR Mixture(带ROX)、荧光定量PCR引物、兔抗人STAT3和p-STAT3单克隆抗体(上海生工公司);HRP标记羊抗大鼠IgG二抗(H+L)和羊抗兔IgG二抗(H+L)(美国Invitrogen公司);STAT3抑制剂WP1066(美国Cayman公司),用DMSO溶解WP1066,配置成 100 mmol·L-1的储备液,WP1066使用终浓度为5 μmol·L-1。CO2细胞培养箱(美国Thermo Forma公司);蛋白质电泳仪和电转仪(美国Bio-Rad公司);倒置显微镜(日本Olympus公司)。
1.2 细胞处理及分组
将DLD1细胞按照实验要求铺板,分为正常对照组(加0.1%DMSO)、DDT 0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0和100.0 nmol·L-1组,抑制剂WP1066 5 μmol·L-1组以及DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1+WP1066 5 μmol·L-1组,作用48 h。
1.3 细胞形态观察
DLD1细胞按每孔1×104细胞接种于24孔板中,次日待细胞贴壁后,分别用DDT 0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0和100.0 nmol·L-1处理48 h,倒置显微镜下观察细胞形态变化并拍照。
1.4 实时荧光定量PCR检测E-钙黏着蛋白、N-钙黏着蛋白、波形蛋白和锌指转录因子Snail1的mRNA表达
将DLD1细胞按每孔1×105个细胞种于12孔板中,次日待细胞贴壁后,分别用DDT 0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0和100.0 nmol·L-1的处理48 h,收集细胞,提取总RNA,然后按照逆转录试剂盒说明书,将RNA逆转录合成DNA。按实时荧光定量PCR试剂盒说明进行PCR。目的基因mRNA表达用GAP⁃DH基因进行均一化处理。基因表达变化的计算采用倍增变化率,基因倍增变化率=2-ΔΔCt(ΔCt为目的基因和内参照基因Ct值的差值)。PCR反应引物如表1。
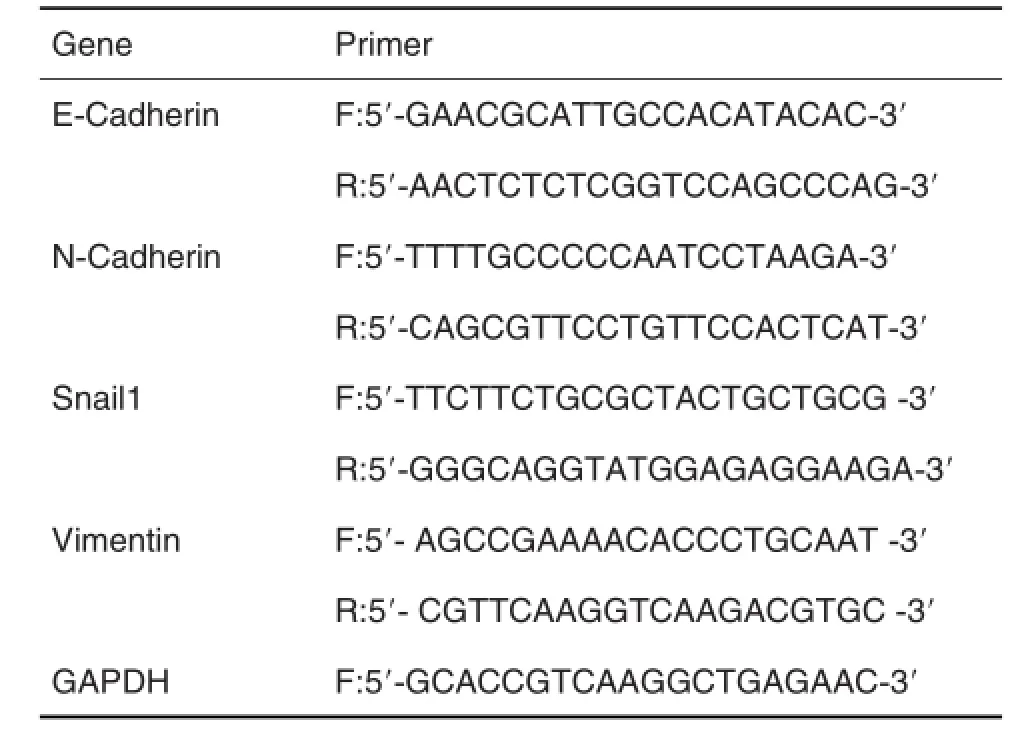
Tab.1 Primer sequences of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,Snail1,vimentin and GAPDH for real-time quantitative PCR
1.5 Western蛋白质印迹检测蛋白表达
在60 mm培养皿中接种1×106DLD1细胞,用DDT 0.1,1.0和10.0 nmol·L-1处理48 h,然后收集细胞,加入裂解液裂解10 min,收集上清。蛋白浓度用BCA法进行定量。40 μg的蛋白质样品于12%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳进行分离。电泳结束后,将分离的蛋白条带转至PVDF膜上,用含5%脱脂奶粉的TBST室温下封闭1 h,1∶500一抗4°C过夜孵育,TBST洗膜3次,每次10 min。然后室温孵育1∶2000二抗1 h,TBST洗膜3次,每次10 min。最后于暗室进行化学发光液显像。使用Image J分析软件对蛋白条带进行积分吸光度分析,以目标蛋白条带的积分吸光度值与对应的α-微管蛋白积分吸光度值的比值表示目标蛋白的相对表达水平。
1.6 统计学分析
用SPSS17.0统计学分析软件进行数据分析,实验结果用表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,P<0.05认为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 不同浓度DDT对大肠癌细胞DLD1细胞形态的影响
细胞形态观察(图1)结果显示,正常对照组细胞大多呈圆形或者卵圆形,DDT 0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0和100.0 nmol·L-1处理组细胞,大多呈长梭形,细胞间隙明显增宽,有的长出多个触角。

Fig.1 Effect of clofenotane(p,p′dichlorodiphenyltrichlo⁃roethane,DDT)on morphological change of colorectal cancer DLD1 cells.DLD1 cells were treated with DDT for 48 h. Arrows show spindle cell and antenna of cells.
2.2 DDT对DLD1细胞上皮间充质转化标志蛋白E-钙黏着蛋白、N-钙粘着蛋白、波形蛋白及锌指转录因子Snail1 mRNA表达的影响
实时荧光定量PCR结果(图2)显示,与正常对照组相比,DDT 0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0和100.0 nmol·L-1处理组E-钙黏着蛋白mRNA相对表达降低(P<0.01),分别为正常对照组的(67.2±8.8)%,(48.6± 3.8)%,(42.4±2.8)%,(71.6±8.3)%和(73.7± 6.4)%;DDT各处理组N-钙黏着蛋白mRNA相对表达升高(P<0.01),分别为正常对照组的1.5±0.1,1.6±0.2,1.9±0.1,1.5±0.2和(1.4±0.1)倍;DDT各处理组波形蛋白mRNA相对表达升高(P<0.01),分别为正常对照组的1.2±0.1,1.3±0.1,1.5±0.2,1.3±0.2和(1.2±0.1)倍。DDT各处理组锌指转录因子Snail1 mRNA相对表达显著升高(P<0.01),分别为正常对照组的1.2±0.1,1.3±0.1,1.5±0.1,1.3±0.1和(1.2±0.1)倍。

Fig.2 Effect of DDT on mRNA expressions of E-cad⁃herin,N-cadherin,vimentin and Snail1 in DLD1 cells by real-time PCR.See Fig.1 for the cell treatment.,n=3.**P<0.01,compared with normal control group.
2.3 DDT对DLD1细胞STAT3和p-STAT3蛋白表达的影响
Western蛋白质印迹检测结果(图3A)显示,与正常对照组相比,DDT 0.1,1.0和10.0 nmol·L-1处理组STAT3和p-STAT3蛋白水平升高(P<0.01),STAT3蛋白水平分别为正常对照组的1.3,2.1和1.3倍,p-STAT3分别为正常对照组的1.4,1.8和1.4倍。
2.4 STAT3抑制剂WP1066对DDT诱导DLD1细胞E-钙黏着蛋白、N-钙黏着蛋白、波形蛋白和锌指转录因子Snail1mRNA表达的影响
实时荧光定量PCR结果(图4)显示,与DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1处理组相比,DDT+WP1066组E-钙黏着蛋白mRNA表达升高(P<0.01),是DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1处理组的2.5±0.1倍;N-钙粘着蛋白和波形蛋白mRNA表达降低(P<0.01),分别是DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1处理组的(50.2±2.9)%和(61.6±6.1)%;锌指转录因子Snail1 mRNA表达降低(P<0.01),为DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1处理组的(56.3±0.9)%。

Fig.4 Effect of WP1066 on mRNA expression of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,vimentin and Snail1 in DDT-induced DLD1 cells.DLD1 cells were pre-incubated with WP1066(5 μmol·L-1)for 0.5 h and then treated withDDT 1.0 nmol·L-1for 48 h.,n=3.**P<0.01,compared with normal control(0)group;##P<0.01,compared with DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1alone treatment group.
2.5 STAT3抑制剂WP1066对DDT诱导DLD1细胞STAT3和p-STAT3蛋白表达的影响
Western蛋白质印迹检测结果(图5)显示,与DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1处理组相比,DDT和WP1066(5 μmol·L-1)共处理组中的p-STAT3蛋白水平降低,为正常对照组的47.8%(P<0.01),STAT3蛋白水平无明显变化,表明STAT3/Snail1信号通路被抑制。
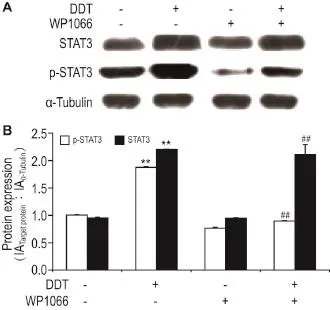
Fig.5 Effect of WP1066 on protein expression of STAT3 and p-STAT3 in DDT-induced DLD1 cells by Western blotting.See Fig.4 for the cell treatment.B was the semi-quantitative result of A.,n=3.**P<0.01,compared with normal control(0)group;##P<0.01,compared with DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1alone treatment group.
3 讨论
本研究表明,DDT暴露能明显改变大肠癌DLD1细胞的细胞形态,显著降低EMT标志蛋白E-钙黏着蛋白表达水平,提高N-钙黏着蛋白和波形蛋白的表达水平,提示,DDT促进大肠癌DLD1细胞的EMT。此外,本研究发现,DDT暴露激活STAT3/ Snail1信号通路,而STAT3抑制剂WP1066处理明显抑制DDT对大肠癌DLD1细胞EMT的影响。以上结果表明,DDT通过激活STAT3/Snail1信号通路改变EMT标志蛋白的表达进而促进大肠癌DLD1细胞EMT的发生。
EMT在肿瘤细胞的侵袭和转移中起着关键作用[16-17]。E-钙黏着蛋白的缺失和间充质蛋白E-钙黏着蛋白和波形蛋白的过表达是肿瘤细胞发生EMT的标志。E-钙黏着蛋白介导细胞-细胞间粘附,并保持完整的基底膜和细胞形态。E-钙黏着蛋白表达缺失会导致细胞丧失上皮表型,降低细胞粘附,易于转移。E-钙黏着蛋白是一种主要的粘附分子并且促进细胞-细胞粘附。波形蛋白是一种保持细胞形态和完整细胞质的中间丝蛋白。E-钙黏着蛋白和波形蛋白的过表达是与肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移能力密切相关[21-22]。本研究结果显示,经DDT处理后,大肠癌细胞DLD1细胞形态发生明显改变,由原有的圆形或卵圆形向长梭形转变,细胞间间隙明显增宽,长出触角。实时荧光定量PCR结果表明,上皮标志蛋白E-钙黏着蛋白的mRNA表达显著降低,而间充质蛋白N-钙黏着蛋白和波形蛋白的mRNA表达显著升高,在DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1作用下,这几种蛋白的变化最为明显,这可能是由于DDT浓度过高会对细胞具有一定的毒性,而浓度过低时,对这些蛋白的影响未达到最显著的效果[13-14]。上述结果表明,DDT暴露促进人大肠癌DLD1细胞EMT与其影响E-钙黏着蛋白、N-黏粘着蛋白和波形蛋白的表达有关。
有研究表明,STAT3在肿瘤细胞EMT发生过程中起着关键作用[23]。当STAT3磷酸化后可与Snail等转录因子的启动子上特异DNA序列结合而调节其表达。本研究结果表明,DDT暴露能上调STAT3和p-STAT3的蛋白表达,表明DDT暴露诱导STAT3的激活。进一步研究发现,DDT暴露明显上调Snail1的表达,揭示DDT可能通过STAT3上调Snail1。为了证明这一假设,本研究利用STAT3抑制剂WP1066抑制DDT诱导的STAT3激活。研究结果表明,与DDT处理组相比,DDT和WP1066共处理组中的p-STAT3蛋白表达明显降低,而Snail1的表达也明显下调。上述结果表明,DDT通过激活STAT3进而上调Snail1的表达。研究报道,Snail1能间接或直接抑制E-钙黏着蛋白的表达,Snail1与Smad相互作用蛋白1竞争结合E-钙黏着蛋白的启动子E-Box系列(5′-CACCTG-3′),从而抑制E-钙黏着蛋白的表达[24-25]。此外,Snail1能够上调N-钙黏着蛋白和波形蛋白的表达[26]。本研究发现,STAT3抑制剂WP1066与DDT共处理大肠癌DLD1细胞后,与DDT处理组相比,Snail1表达明显下调的同时,E-钙黏着蛋白表达升高,E-钙黏着蛋白和波形蛋白表达降低。由此提示,DDT通过激活STAT3/Snail1信号通路进而改变EMT化标志蛋白的表达。
综上所述,DDT暴露通过激活STAT3/Snail1信号通路抑制E-钙黏着蛋白表达并上调E-钙黏着蛋白和波形蛋白表达,这些EMT标志蛋白的改变促进大肠癌DLD1细胞EMT的发生,这一过程可能是DDT暴露促进肠癌发展的关键机制之一。
[1]Aamir M,Khan S,Nawab J,Qamar Z,Khan A. Tissue distribution of HCH and DDT congeners and human health risk associated with consump⁃tion of fish collected from Kabul River,Pakistan[J].Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,2016,125:128-134.
[2]Ding H,Li XG,Liu H,Wang J,Shen WR,Sun YC,et al.Persistent organochlorine residues in sediments of Haihe River and Dagu Drainage River in Tianjin,China[J].J Environ Sci(China),2005,17(5):731-735.
[3]Quémerais B.Lemieux C.Lum KR.Concentra⁃tions and sources of PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in the St.Lawrence River(Canada)and its tributaries[J].Chemosphere,1994,29(3):591-610.
[4]An Q,Dong YH,Wang H,Wang X,Wang MN,Guo ZX.Organochlorine pesticide residues in culti⁃vated soils,in the south of Jiangsu,China[J]. Acta Pedol Sin(土壤学报),2004,41(3):414-419.
[5]Beard J,Australian Rural Health Research Collab⁃oration.DDT and human health[J].Sci Total Envi⁃ron,2006,355(1-3):78-89.
[6]Gupta PK. Pesticide exposure-indian scene[J]. Toxicology,2004,198(1-3):83-90.
[7]Song L,Zhao J,Jin X,Li Z,Newton IP,Liu W,et al.The organochlorine p,p'-dichlorodiphenyltri⁃chloroethane inducescolorectalcancergrowth through Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J].Toxicol Lett,2014,229(1):284-291.
[8]Jin X,Chen M,Song L,Li H,Li Z.The evalua⁃tion of p,p'-DDT exposure on cell adhesion of he⁃patocellularcarcinoma[J].Toxicology,2014,322:99-108.
[9]Gerber R,Smit NJ,Van Vuren JH,Nakayama SM,Yohannes YB,Ikenaka Y,et al.Bioaccumulation and human health risk assessment of DDT and other organochlorine pesticides in an apex aquatic predator from a premier conservation area[J].Sci Total Environ,2016,550:522-533.
[10] Colosio C,Tiramani M,Maroni M.Neurobehavioral effects of pesticides:state of the art[J].Neurotoxi⁃cology,2003,24(4-5):577-591.
[11] Jaga K.Serum organochlorine pesticide levels in patients with colorectal cancer in Egypt[J].Arch Environ Health,1999,54(3):217-218.
[12] Soliman AS,Smith MA,Cooper SP,Ismail K,Khaled H,Ismail S,et al.Serum organochlorine pesticide levels in patients with colorectal cancer in Egypt[J].Arch Environ Health,1997,52(6):409-415.
[13]Liu JX,Zhao JY,Jin XT,Li ZY,Song L.Effect oflow concentrations of p,p'-dichlorodiphenyltrichlo⁃roethane on proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal adenocarcinoma SW620 cells[J].Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol(中国药理学与毒理学杂志),2015,29(2):227-233.
[14]Song L,Zhao J,Jin X,Li Z,Newton IP,Liu W,et al.The organochlorine p,p'-dichlorodiphenyltri⁃chloroethane inducescolorectalcancergrowth through Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J].Toxicol Lett,2014,229(1):284-291.
[15]Song L,Zhao MR,Liu JX,Li ZY,Xiao H,Liu WP. P,p′-Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane inhibits the apoptosisofcolorectaladenocarcinoma DLD1 cells through PI3K/AKT and Hedgehog/Gli1 signaling pathways[J].Toxicol Res,2015,4(5):1214-1224.
[16] Tsuji T,Ibaragi S,Hu GF.Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell cooperativity in metastasis[J]. Cancer Res,2009,69(18):7135-7139.
[17]Thiery JP.Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression[J].Nat Rev Cancer,2002,2(6):442-454.
[18]Zhao S,Venkatasubbarao K,Lazor JW,Sperry J,Jin C,Cao L,et al.Inhibition of STAT3 Tyr705 phosphorylation by Smad4 suppresses transforming growth factor beta-mediated invasion and metastasis in pancreatic cancer cells[J].Cancer Res,2008,68(11):4221-4228.
[19]Huang C,Yang G,Jiang T,Zhu G,Li H,Qiu Z. The effects and mechanisms of blockage of STAT3 signaling pathway on IL-6 inducing EMT in human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro[J].Neoplasma,2011,58(5):396-405.
[20]Zucchini-Pascal N,Peyre L,de Sousa G,Rahmani R. Organochlorine pesticides induce epithelialto mesenchymal transition of human primary cultured hepatocytes[J].Food Chem Toxicol,2012,50(11):3963-3970.
[21]Rivat C,De Wever O,Bruyneel E,Mareel M,Gespach C,Attoub S.Disruption of STAT3 signaling leads to tumor cell invasion through alterations of homotypic cell-cell adhesion complexes[J].Onco⁃gene,2004,23(19):3317-3327.
[22]Iwamaru A,Szymanski S,Iwado E,Aoki H,Yokoyama T,Fokt I,et al.A novel inhibitor of the STAT3 pathway induces apoptosis in malignant glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo[J].Onco⁃gene,2007,26(17):2435-2444.
[23]Masuda M,Wakasaki T,Suzui M,Toh S,Joe AK,Weinstein IB.Stat3 orchestrates tumor develop⁃ment and progression:the Achilles′heel of head and neck cancers?[J].Curr Cancer Drug Targets,2010,10(1):117-126.
[24]Wu Y,Zhou BP.New insights of epithelial-mesen⁃chymal transition in cancer metastasis[J].Acta Bio⁃chim Biophys Sin(Shanghai),2008,40(7):643-650.
[25]Cano A,Pérez-Moreno MA,Rodrigo I,Locascio A,Blanco MJ,del Barrio MG,et al.The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transi⁃tions by repressing E-cadherin expression[J].Nat Cell Biol,2000,2(2):76-83.
[26]Kaufhold S,Bonavida B.Central role of Snail1 in the regulation of EMT and resistance in cancer:a target for therapeutic intervention[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2014,33:62.
Effect of clofenotane on epithelialmesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer DLD1 cells
DONG Ning-ning1,SONG Li1,LI Zhuo-yu1,XIAO Hong2
(1.Institute of Biotechnology,Key Laboratory of Chemical Biology and Molecular Engineering of National Ministry of Education,Shanxi University,Taiyuan 030006,China;2.The First Affiliated Hospital,Shanxi Medical University,Taiyuan 030006,China)
OBJECTIVE To explore the effect of clofenotane(DDT)on epithelial-mesenchymal transition(EMT)and the relevant molecular mechanism in human colorectal cancer cells.METHODS Human colorectal cancer cells DLD1 were treated with DDT 0.01,0.1,1.0,10.0 and 100.0 nmol·L-1for 48 h.Then,the morphology of DLD1 cells was observed.mRNA levels of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,vimentin and Snail1 were detected by real-time PCR.Protein expression of STAT3 signaling pathway of proteins STAT3 and p-STAT3 was detected by Western blotting.STAT3 inhibitor WP1006(5 μmol·L-1)was addedto determine its impact on DDT-induced alternation of STAT3/Snail1 signaling and EMT-related molecules. Protein expression of STAT3 and p-STAT3 was detected by Western blotting and mRNA levels of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,Vimentin and Snail1 were detected by real-time PCR.RESULTS DLD1 cell morphology was changed after exposure to DDT 0.01-100.0 nmol·L-1.Meanwhile,real-time PCR showed that the mRNA level of E-cadherin was significantly decreased compared with normal cell control (P<0.01),which was 42.4±2.8%of that in the normal control group.The mRNA levels of N-cadherin,Vimentin and Snail1 were significantly increased(P<0.01),which were 1.91±0.1,1.5±0.2 and 1.5±0.1 times that of the normal control group.DDT 0.1,1.0 and 10.0 nmol·L-1exposure induced up-regulation of STAT3 and p-STAT3 protein levels(P<0.01),which were 2.1 and 1.8 times that of the normal control group. The addition of STAT3 inhibitor WP1066(5 μmol·L-1)prevented STAT3 from phosphorylation as well as the up-regulation of Snail1(P<0.01),which was(56.3±0.9)%that of the DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1treat⁃ment group.Compared with DDT treatment alone,the mRNA levels of EMT-related molecules were remarkably reversed by WP1066(5 μmol·L-1)co-treatment,increasing E-cadherin but decreasing N-cadherin and vimentin in DLD1 cells(P<0.01),which were 50.2±2.9%and 61.6±6.1%of those in the DDT 1.0 nmol·L-1treatment group,respectively.CONCLUSION DDT alters the expressions of EMT-related molecules including E-cadherin,N-cadherin and vimentin via STAT3/Snail1 signaling,thus promoting the EMT process in human colorectal cancer cells.This progress may be closely related to DDT-induced colorectal cancer development.
clofenotane;colorectal cancer;epithelial-mesenehymal transition;singnal transducers and activators of transcription 3
SONG Li,E-mail:lsong@sxu.edu.cn,Tel:(0351)7017774
R996
A
1000-3002-(2017)02-0172-07
10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2017.02.08
Foundation item:The project supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(21207084);National Natural Science Foundation of China(31271516);Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province(2014011027-5);University Science and Technology Innovation Project of Shanxi Province(2016122);and Shanxi Scholarship Council of China (2016-115)
2016-09-06 接受日期:2017-01-24)
(本文编辑:贺云霞)
国家自然科学基金(21207084);国家自然科学基金(31271516);山西省自然科学基金(2014011027-5);高等学校科技创新项目(2016122);山西省回国留学人员科研资助项目(2016-115)
董宁宁,女,硕士研究生,主要从事环境毒理学研究。
宋莉,E-mail:lsong@sxu.edu.cn,Tel:(0351)7017774
