日本北海道地区泡型包虫病的防控措施
2017-03-08八木欣平孝口裕一郭志宏野中成晃
八木欣平,孝口裕一,郭志宏,野中成晃
(1.日本北海道公共卫生学院传染病科医学动物研究室,日本,北海道 札幌,060-0819;2.青海大学畜牧兽医学院人畜共患病研究室,青海 西宁 810016;3.日本宫崎大学兽医科学部家畜寄生虫病学研究室,日本 宫崎 889-2192)
1 Sanitary education
Sanitary education to residents is performed by distribution on a brochure and notification of a poster through a health center and towns and villages in Hokkaido.When the epidemic area expanded in 1980′s,the presence of echinococcosis was reported by mass communication extensively,and therefore almost all residents in Hokkaido know existence of alveolar echinococcosis.Because correct information about the biological property of the parasite is necessary for sanitary education,Hokkaido local government built a facility of experimental infection for the definitive hosts of the parasite in the Hokkaido Institute of Public Health.The biological characteristics of the parasite isolated from Hokkaido have been clarified by a series of experimental infection studies.
2 Physical check-up and development of early detection technology(serum examination)
As the disease advances,the recovery rate falls.Therefore early detection and treatment are requisite for the control of this disease[4].ELISA(Enzyme-Linked Immuno-Solbent Assay)using crude antigen was developed[5]and used as a mass-screening test since 1983.This serum check has been developed to screen a resident for potential infection.The test is cheap and easy and shows little number of false negatives.Recently 30,000 people a year have been checked by this test in Hokkaido.The residents who become positive by this test got further serum check(Western blotting)and a diagnostic imaging as a confirmation diagnosis.From 1984 to 1993,715,841 people were examined by the screen ELISA,5,653 people became positive in the screening,and 60 people were confirmed for the infection by an ultrasonic check in Hokkaido[6].Before 1984,in order to grasp the number of patients occurred in Hokkaido,the local government had an independent system for patient authorization that was conducted by the council of Hokkaido local government,but the system was changed to that all patients diagnosed by individual physicians should be reported to national government of Japan according to the national law settled in 1984.
3 Water supply improvement
Common wells and river water were used as household water in the Rebun Island.Therefore,the water was thought to be a source of the infection.To prevent the infection through water supply,the diffusion rate of water supply facilities reached to approximately 100% in 1971 in this island.A similar campaign was promoted for improving the maintenance of waterworks in Hokkaido whole field in 1990′s too.
4 Surveillance and control of vector animals
Echinococcusmultilocularis maintains its life cycle using foxes and field rodents in Hokkaido.Prevalence of E.multilocularis in foxes is thought to be a good indicator for monitoring a situation of endemicity.An intense surveillance has been performed by necropsy of foxes since 1966(Figure 1).Every year,100 to 1,000 foxes captured as harmful animals for agricultural field were examined.On the other hand,natural infection of alveolar echinococcosis in pigs has been frequently reported since the first case was found in 1983 in Hokkaido[7].Since all pigs provided to a market are checked by usual examination,a check of a pig was useful for discovery of a new endemic area at the time of expansion in Hokkaido.
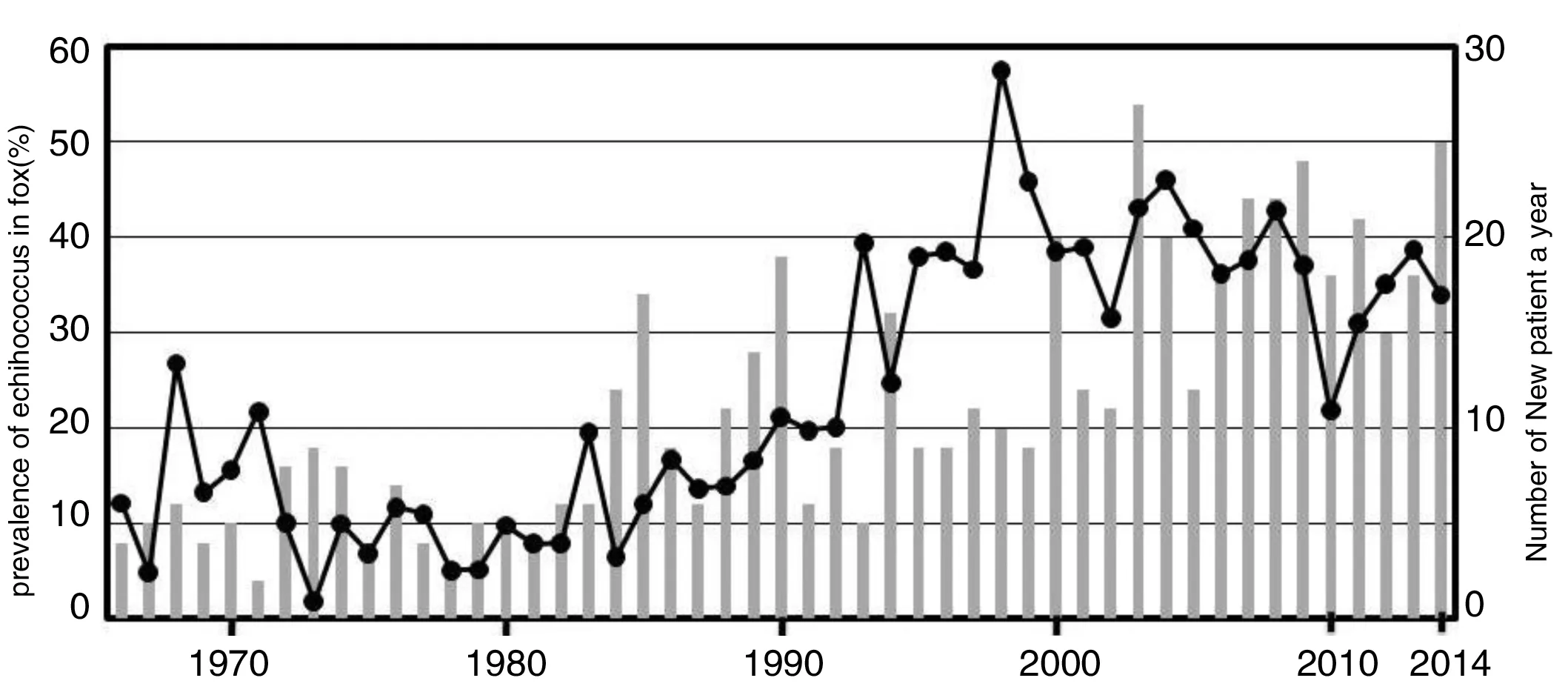
Figure1ChangesintheprevalenceofEchinococcusmultilocularisinfectioninFoxes(line)andnewhumanpatientoccurredayear(bar)
For a countermeasure against vector animals,it was reported that infection risk could be reduced by distributing anthelmintics(praziquantel baits)to foxes[8-9].Following the finding,a guideline of praziquantel baits for foxes was formulated by a council in 2006.
On the other hand,it was reported that 0.4% of pet dogs in Hokkaido was infected with the tapeworm[10].Following the report,Hokkaido Small Animal Veterinary Association issued a booklet that described how to keep dogs safely fromEhinococcusinfection. It also recommends the preventing deworming with praziquantel to dogs that potentially have chance to get field rodents.Because infection of dogs not only directly relates to a risk of human infection but also leads to expansion of an endemic area,preventive periodical deworming in a hyper endemic area is important.
5 Research works
Research is indispensable to take effective measures correctly.Hokkaido Institute of Public Health established by Hokkaido local government is collecting information on domestic and abroad studies as well as is executing researches.Development of a serum examination and surveillance of echinococcosis in the wildlife have been playing the big role in reduction of the risk of this disease.In the special infection facility built by the government,the parasite isolated in Hokkaido was experimentally performed and the biological characteristics of the parasite were clarified[11].The biological characteristics such as patent period of definitive hosts and conditions for deactivating the parasite eggs were useful information for education for prevention of infection(Figure 2).Molecular biological studies are also done in these facilities.Especially in the fields of development of diagnostic technics for the definitive hosts,vaccine development for both definitive and intermediate hosts and drug development for humans,we have been getting promising results[12].
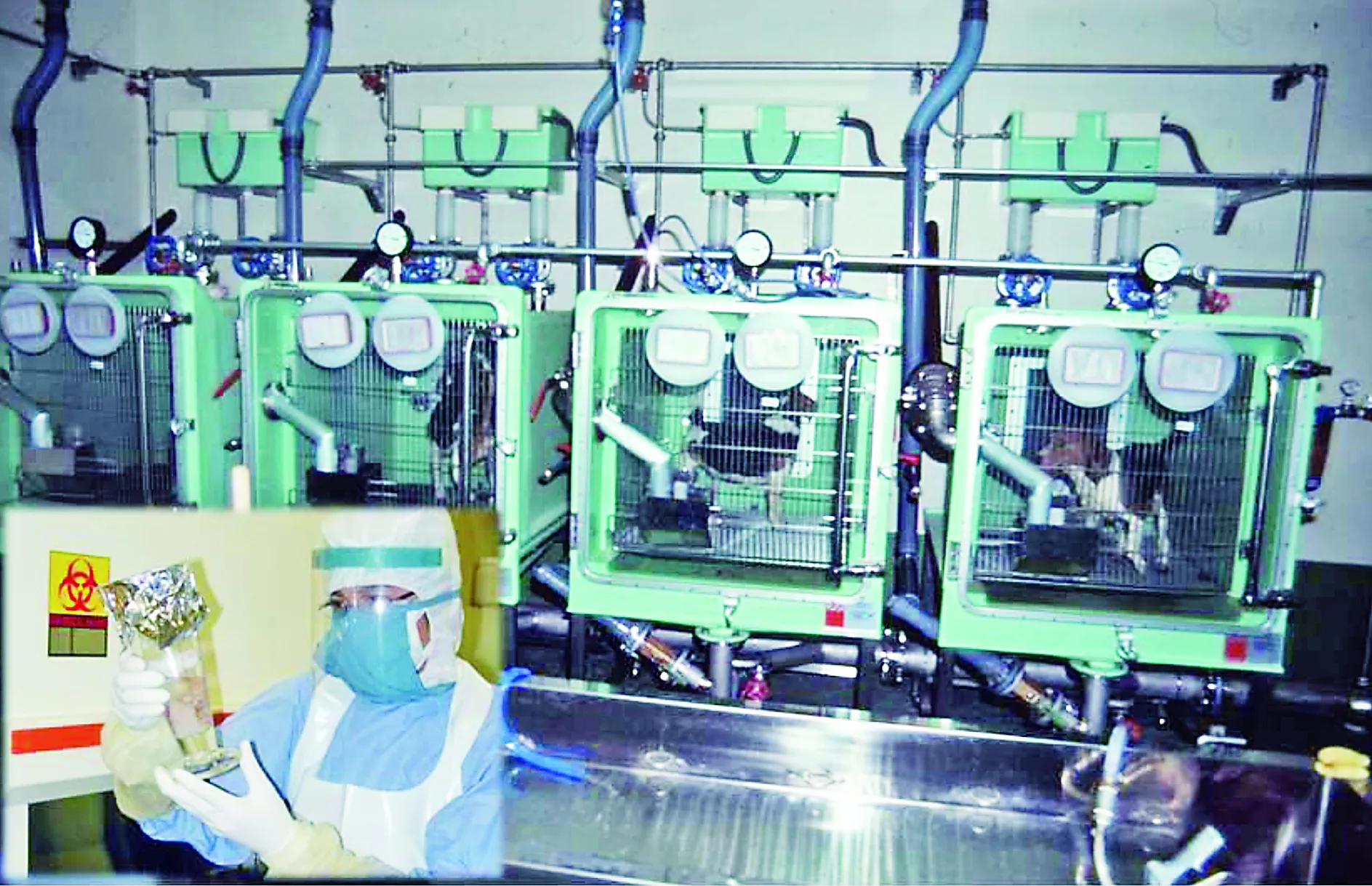

Figure2SpecialfacilityforEchinococcusinfectionbuiltintheHokkaidoInstituteofPublicHealth
Alveolar echinococcosis is expanding in Europe[13].In Hokkaido,a lot of patients occurred at Rebun Island and this pressed a resident for a big burden. Hokkaido local government has been playing a central role in measures by taking the leading part and getting cooperation with universities and medical agencies.The expansion of the parasite to the Hokkaido whole field was confirmed the second half of 1980′s.However,patient′s explosive increase could be restricted.It could be a result of appropriate measure performed by the councils.Measures against alveolar echinococcosis in Hokkaido would act as a model of other zoonosis.
[1]Minagawa T.The reconsideration of Natural History of Echinococcosis at Rebun Island[in Japanese].Hokkaido J Med Sci,1999,74(2):113-134.
[2]Minagawa T.Survey of echinococcosis in Hokkaido and measures against it[in Japanese].Hokkaido J Med Sci,1997,72(2):569-581.
[3]Kamiya M,Lagopa JTG,Nonaka N,et al.Current control strategyes targeting sources of echinococcosis in Japan.Rev sci tec Off int Epiz,2006,25(3):1055-1066.
[4]Uchino J,Sato N,Une Y,et al.Surgical management of screened and unscreened patients with alveolar echinococcosis of the liver In Alveolar Ehicnococcosis,Strategy for Eradication of Alveolar Echinococcosis of the Liver(eds.Uchino J,Sato N),Fujishoin,Sapporo,1996,313-320.
[5]Sato H,Mitamura H,Arai J,Kumagai M,et al.Serological diagnosis of human hydatid diseases by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent assay(Part 1)Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent assay by multilocularEchinococcusantigen[in Japanese].Rep Hokkaido Inst Publ Health,1983,33,8-15.
[6]Suzuki K,Uchino J,Sato N,et al.Development and efficacy of mass screening of alveolar echinococcosis.In Alveolar echinococcosis strategy for eradication of alveolar echinococcosis of the liver(J.Uchino & N.Sato,eds).Fuji Shoin,Sapporo,1996,213-217.
[7]Sakui M,Ishige M,Fukumoto S,et al.SpontaneousEchinococcusmultilocularis infection in swine in north-eastern Hokkaido,Japan.Jpn J Parasitol,1984,33,291-296.
[8]Takahashi K,Uraguchi K,Hatakeyama H,et al.Efficacy of anthelmintic baiting of foxes againstEchinococcusmultilocularis in northern Japan.Vet Parasitol,2013,198(1-2):122-126.
[9]Tsukada H,Hamazaki K,Ganzorig S,et al.Potential remedy againstEchinococcusmultilocularis in wild red foxes using baits with anthelmintic distributed around fox breeding dens in Hokkaido,Japan.Parasitol,2002,125(2):119-129.
[10]Nonaka N,Kamiya M,Kobayashi F,et al.Echinococcusmultilocularis infection in pet dogs in Japan. Vector borne Zoonotic Dis,2009,9(2):201-206.
[11]Matsumoto J,Yagi K.Experimental studies onEchinococcusmultilocularis in Japan,focusing on biohazardous stages of the parasite.Exp Parsitol,2008,119(4):534-541.
[12]Yagi K.Past and future experiments at the special facility forEchinococcusmultilocularis at Hokkaido Institute of Public Health[in Japanese].Rep Hokkaido Inst Publ Health,2016,66,1-8.
[13]Gottstein B,Stojkovic M,Vuitton DA,et al.Threat of alveolar echinococcosis to public health-a challenge for Europe.Trends Parasitol,2015,31(9):407-412.
