天津市和平区成年人内脏型肥胖与高尿酸血症的关系
2017-01-09郑莉张美琳李萍朱玉凤常红黄国伟
郑莉,张美琳,李萍,朱玉凤,常红,2,黄国伟△
天津市和平区成年人内脏型肥胖与高尿酸血症的关系
郑莉1,张美琳1,李萍1,朱玉凤1,常红1,2,黄国伟1△
目的 分析内脏型肥胖与高尿酸血症(HUA)的关系,为进一步研究肥胖和HUA的关系提供依据。方法选取2014年在天津市和平区健康教育指导中心进行健康体检的1 824例体检人员作为研究对象,对所有研究对象进行体格检查和生化指标检查,并测量内脏脂肪面积(VFA)。采用Logistic回归分析内脏型肥胖与HUA之间的关系。结果随着VFA的增大,男、女性HUA的患病率呈上升趋势(P<0.05);且VFA、腰围(WC)和腰臀比(WHR)与血尿酸(SUA)水平均呈正相关(P<0.05)。Logistic多因素回归分析显示,男性VFA(OR=1.805,95%CI=1.166~2.794)和WHR(OR=2.108,95%CI=1.061~4.189)是HUA发生的影响因素;女性VFA(OR=1.775,95%CI=1.154~2.732),WC(OR=2.015,95%CI=1.137~3.570)和WHR(OR=2.489,95%CI=1.400~4.426)均是HUA发生的影响因素。结论内脏脂肪的蓄积会增加HUA的发生风险。加强人群内脏型肥胖的检测对于预防HUA的发生具有重要意义。
高尿酸血症;内脏型肥胖;内脏脂肪面积;腰围;腰臀比
高尿酸血症(hyperuricemia,HUA)是指由于人体内嘌呤代谢异常,尿酸合成过多或排泄障碍,使尿酸水平升高[1]。研究表明,肥胖与HUA之间关系密切[2-3],随着内脏型肥胖(中心性肥胖)研究的深入,发现内脏型脂肪蓄积、胰岛素抵抗等多种危险因子参与了HUA的形成[4]。腰围(waist circumference,WC)和腰臀比(waist-to-hip ratio,WHR)都是通过测量人体腹部和腰部的外径来预测腹部脂肪蓄积的指标,评估方法方便、可靠,是临床上较常用的指标。内脏脂肪面积(visceral fat area,VFA)作为评价内脏型肥胖的特异性指标,经常用于相关研究中。内脏型肥胖作为一切生活习惯病的温床,现被认为是一种高危性肥胖。本文就内脏型肥胖与HUA关系的分析如下。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象选取2014年在天津市和平区健康教育指导中心参加体检的人群为研究对象,排除体格检查信息不完整者(n=775)和生化指标缺失者(n=287)。最终确定研究对象为1 824人,年龄21~74岁,平均(46.97±12.76)岁,其中男356例,女1 468例。所有入选对象均签署知情同意书。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 体格检查采集研究对象清晨空腹静脉血进行血尿酸(serum uric acid,SUA)、总胆固醇(TC)、三酰甘油(TG)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)及空腹血糖(FPG)的测量。统一测量血压、身高、体质量、WC和臀围(hip circumference,HC),并计算体质指数(BMI)和WHR,BMI=体质量(kg)/身高(m)2,WHR=WC(cm)/HC(cm)。
1.2.2 VFA的测量采用InBody720人体成分分析仪进行VFA的测量。该仪器共有4个电极,受检者空腹赤足站立于足部电极上,手握2个电极,用1~2 min的时间完成全部测量。
1.3 诊断标准HUA诊断标准[5]:SUA水平男性>420μmol/L,女性>360 μmol/L。中国成人内脏型肥胖的诊断标准:男性WC≥85 cm或WHR≥0.90;女性WC≥80 cm或WHR≥0.85[6-7]。
1.4 统计学方法采用SPSS 19.0统计软件进行数据分析,计量资料以均数±标准差表示,2组间比较采用t检验;多组间比较采用方差分析,组间多重比较用LSD-t检验;计数资料组间比较用卡方(χ2)检验;相关分析采用Pearson相关,内脏型肥胖与HUA的关系采用Logistic回归分析,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 男、女性正常组与HUA组一般资料比较男性HUA组BMI、收缩压(SBP)、舒张压(DBP)、WC、WHR、TC、TG、LDL-C、SUA和VFA均高于正常组;HDL-C低于正常组(均P<0.05);但2组年龄和FPG差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。女性HUA组年龄、BMI、SBP、DBP、WC、WHR、TC、TG、LDL-C、SUA、FPG和VFA水平均高于正常组;而HDL-C水平低于正常组(均P>0.05),见表1。
2.2 VFA、WC和WHR与SUA水平的相关性分析Pearson相关分析显示男性VFA、WC和WHR与SUA水平呈正相关(r分别为0.266、0.276、0.242,均P<0.01),女性VFA、WC和WHR与SUA水平呈正相关(r分别为0.299、0.366、0.325,均P<0.01)。
2.3 男、女性VFA三分组间SUA水平及HUA患病率比较将VFA按三分位分组,结果显示,随着VFA的增大,男、女性的SUA水平和HUA患病率都呈上升趋势,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),见表2。
Tab.1 Comparison of general data between normal group and HUA group in men and women表1 男、女性正常组与HUA组间一般资料比较

Tab.1 Comparison of general data between normal group and HUA group in men and women表1 男、女性正常组与HUA组间一般资料比较
*P<0.05,**P<0.01;1 mmHg=0.133 kPa
男性女性指标t t年龄(岁)BMI(kg/m2)SBP(mmHg)DBP(mmHg)WC(cm)WHR TC(mmol/L)TG(mmol/L)HDL-C(mmol/L)LDL-C(mmol/L)SUA(μmol/L)FPG(mmol/L)VFA(cm2)正常组(n=308)48.06±12.84 25.96±4.30 123.27±15.32 81.26±9.93 85.17±8.16 0.89±0.05 4.99±0.86 1.64±1.24 1.19±022 3.06±0.76 322.13±53.59 6.08±1.48 115.40±34.59 HUA组(n=48)46.04±13.30 28.15±3.72 130.25±19.44 85.29±10.17 91.46±9.95 0.92±0.06 5.34±0.87 2.38±1.86 1.09±0.18 3.37±0.78 464.41±38.82 6.03±0.69 138.51±40.94 1.01 3.34**2.82**2.61**4.81**4.31**2.63**2.66**2.95**2.58*22.30**0.41 4.20**正常组(n=1 402)46.27±12.53 23.77±4.71 116.14±18.34 75.49±10.28 71.98±8.73 0.78±0.05 5.08±1.01 1.19±0.69 1.37±0.27 2.98±0.84 245.26±50.64 5.66±0.86 84.86±36.73 HUA组(n=66)57.50±11.99 27.06±5.37 134.77±21.73 82.03±11.40 79.85±7.63 0.82±0.05 5.52±1.11 1.90±1.00 1.28±0.26 3.25±0.87 393.93±38.05 6.54±2.07 111.09±31.15 7.13**5.51**6.85**5.02**7.19**6.44**3.46**5.77**2.78**2.51*30.50**3.43**5.71**

Tab.2 Comparison of SUA level and prevalence rate of HUA between VFA groups in men and women表2 男、女性内脏脂肪面积三分组间SUA水平及HUA患病率比较
2.4 HUA危险因素分析以是否为HUA为因变量(否=0,是=1),以年龄、SBP、DBP、WC、WHR、TC、TG、FPG、VFA为自变量进行Logistic多因素回归分析,结果显示男性VFA和WHR是HUA发生的影响因素;女性VFA、WC和WHR均是HUA发生的影响因素;见表3、4。

Tab.3 Logistic regression analysis of the factors assigned table表3 Logistic回归分析各因素赋值表
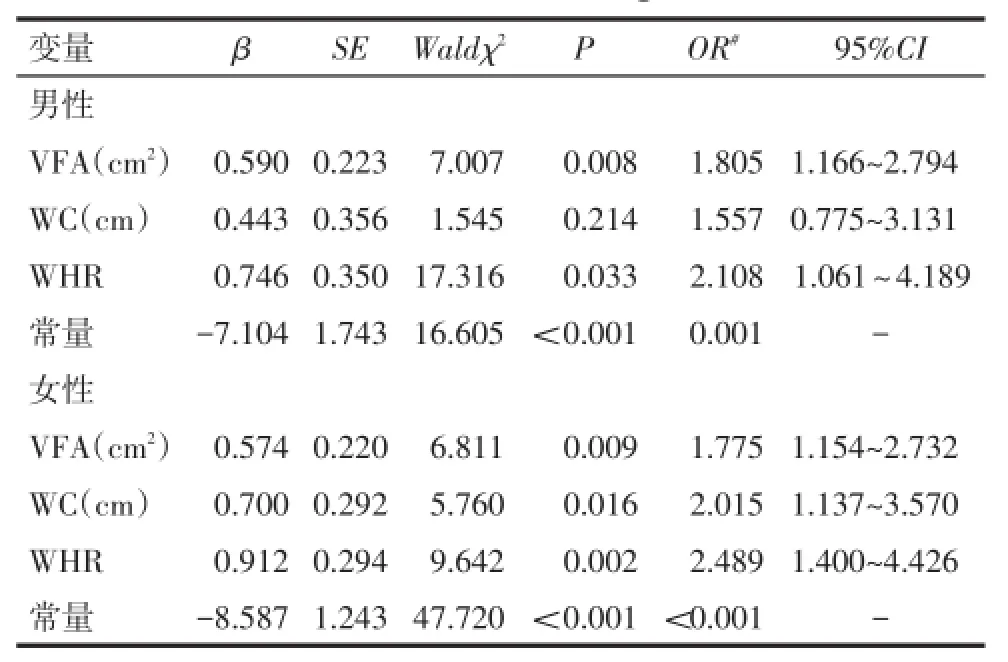
Tab.4 Logistic analysis of risk factors in hyperuricemia patients表4 HUA危险因素的Logistic分析
3 讨论
本次调查结果显示男、女性HUA组的WHR明显高于正常组,WHR与SUA水平呈正相关。WHR是最早应用于临床社区工作中的用于判定腹型肥胖的人体测量学指标;有研究认为WHR能反映中心性肥胖,亦即内脏型肥胖的情况[8]。李晓静等[9]发现男性HUA组的WHR显著高于正常组,且WHR与SUA水平呈正相关。杨楷等[10]则认为WHR高是男性HUA发生的独立危险因素。本研究结果与上述研究的结果一致。且笔者还发现女性WHR也是HUA发生的影响因素。
陆续有研究发现,相较于其他肥胖指标,WC与内脏脂肪含量的相关性更强[11-12]。研究表明,WC越大,SUA水平越高,且这两者的关系与性别密切相关,男性WC与SUA水平的关系更加密切,甚至可能成为预测SUA水平的良好指标[13-14]。但也有不同意见认为女性WC与SUA水平的关系更密切[15]。本研究发现,男、女性HUA组的WC均高于正常组,且WC与SUA水平呈正相关,但是男性WC不是HUA发生的影响因素,女性WC是HUA发生的影响因素。推测可能的原因有:(1)本研究男性样本量相对较小,难以显示其中规律。(2)本研究中诊断男、女性内脏型肥胖的标准是采用中国卫生部颁发的《中国成年人超重与肥胖症预防与控制指南》中推荐的腰围切点,与国外研究中内脏型肥胖的诊断标准有所不同。
VFA能够客观地反映上腹及下腹部脂肪储量,是评价内脏型肥胖的特异性指标。Lee等[16]的研究显示,HUA患者的VFA显著高于健康对照组,进一步分析后表明,内脏型肥胖是HUA发生的独立危险因素。国内的一项研究也显示,SUA水平与VFA呈正相关,SUA水平高的人群VFA明显增大;且相较于BMI等指标,VFA对SUA水平的影响更大[17]。本研究结果显示,VFA与SUA水平具有显著的正相关性,且将VFA三分组比较发现,随着VFA的增大,男、女性SUA水平和HUA的患病率均呈上升趋势,与前述文献报道的结果一致。
综上所述,内脏型肥胖是HUA发生的危险因素,内脏脂肪的蓄积会导致HUA发生风险的增加,加强内脏型肥胖的检测对于预防HUA的发生有重要意义。但是,本研究也存在局限性:首先,本研究是一个横断面研究,且样本量有限。其次,本研究是采用体脂仪进行VFA的测量,精确程度有限。所以,关于内脏型肥胖与HUA之间的关系,还需要更多的研究予以论证。
[1]Wang JY.Study on hyperuricemia and its nursing[J].JiangsuScience&Technology Information,2013,(22):1-3.[王家银.高尿酸血症及其护理研究[J].江苏科技信息,2013,(22):1-3]. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-7530.2013.22.044.
[2]Juraschek SP,Miller ER 3rd,Gelber AC.Body mass index,obesity and prevalent gout in the United States in 1988-1994 and 2007-2010[J].Arthritis Care Res(Hoboken),2013,65(1):127-132. doi:10.1002/acr.21791.
[3]Aune D,Norat T,Vatten LJ.Body mass index and the risk of gout:a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies[J].Eur J Nutr,2014,53(8):1591-1601.doi:10.1007/ s00394-014-0766-0.
[4]Wang JY,Chang BC.Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors of hyperuricemia/gout[J].Int J Endocrinol Metab,2016,36(2):78-81.[王靖宇,常宝成.高尿酸血症/痛风流行病学特点及危险因素[J].国际内分泌代谢杂志,2016,36(2):78-81].doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4157.2016.02.002.
[5]Duan Y,Liu C.Comments on Chinese guideline of hyperuricemia and gout[J].Int J Endocrinol Metab,2013,33(6):376-378.[段宇,刘超.《高尿酸血症和痛风治疗中国专家共识》解读[J].国际内分泌代谢杂志,2013,33(6):376-378].doi:10.3760/cma.j. issn.1673-4157.2013.06.005.
[6]Wen XX,Mai JZ,Gao XM,et al.Cut-off values of waist circumference for central obesity in Chinese adults[J].Chin J Cardiol,2015,43(9):822-826.[温潇潇,麦劲壮,高向民,等.成人中心性肥胖的腰围切点分析[J].中华心血管病杂志,2015,43(9):822-826].doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2015.09.016.
[7]Tian YH,Zhou XL,Wu LH,et al.Association between waist-to-hip ratio and chronic kidney disease[J].Journal of Ningxia Medical University,2015,37(8):913-916.[田延红,周晓玲,吴丽华,等.腰围臀围比与慢性肾脏病间的相关性分析[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2015,37(8):913-916].doi:10.16050/j.cnki.issn1674-6309.2015.08.013.
[8]Taylor RW,Keil D,Gold EJ,et al.Body mass index,waist girth and waist-to-hip ratio as indexes of total and regional adiposity in women:evaluation using receiver operating characteristic curves[J].Am J Clin Nutr,1998,67(1):44-49.
[9]Li XJ,Jia XJ,Ma N,et al.Study on the Correlation between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity in men[J].J Clin Res,2013,30(8):1467-1471.[李晓静,贾晓娇,马宁,等.男性高尿酸血症与腹型肥胖相关性研究[J].医学临床研究,2013,30(8):1467-1471].doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2015.17.041.
[10]Yang K,Ma J,Liu H,et al.Relationship between serum uric acid levelandobesityrelatedindex[J].ChineseJournalof Microcirculation,2008,18(4):66-67.[杨楷,马杰,刘红,等.血尿酸水平与肥胖相关指数的关系[J].微循环学杂志,2008,18(4):66-67].doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-1740.2008.04.028.
[11]Borruel S,Moltó JF,Alpañés M,et al.Surrogate markers of visceral adiposity in young adults:waist circumference and body mass index are more accurate than waist hip ratio,model of adipose distribution and visceral adiposity index[J].PLoS One,2014,9(12):e114112. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0114112.
[12]Ma L,Yu F,Wang L,et al.Analysis on the correlation between three index of obesity and hyperuricemia[J].Journal of Xinjiang Medical University,2013,36(2):204-207.[马玲,于飞,王莉,等.肥胖指标在研究高尿酸血症危险因素中的意义[J].新疆医科大学学报,2013,36(2):204-207].doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-5551.2013.02.012.
[13]Lin KP.The relationship between serum uric acid concentration and metabolic syndrome in university freshmen[J].J Nuts Res,2009,17(4):286-292.doi:10.1097/JNR.0b013e3181c003a7.
[14]Samara A,Herbeth B,Aubert R,et al.Sex-dependent associations of leptin with metabolic syndrome-related variables:the Stanislas study[J].Obesity(Silver Spring),2010,18(1):196-201.doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.156.
[15]Rho YH,Woo JH,Choi SJ,et al.Association between serum uric acid and the Adult Treatment PanelⅢ-defined metabolic syndrome:results from a single hospital database[J].Metabolism,2008,57(1):71-76.doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2007.08.008.
[16]Lee J,Lee JY,Lee JH,et al.Visceral fat obesity is highly associated with primary gout in a metabolically obese but normal weighted population:a case control study[J].Arthritis Res Ther,2015,17:79.doi:10.1186/s13075-015-0593-6.
[17]Mou LP,Jiang JJ,Su JB,et al.Relation between serum uric acid level and body fat distribution.metabolic syndrome in obesity[J]. China&Foreign Medical Treatment,2014,33(29):11-13.[牟伦盼,蒋建家,苏劲波,等.血尿酸与体脂分布及代谢综合征的相关性研究[J].中外医疗,2014,33(29):11-13].doi:10.3969/j. issn.1674-0742.2014.29.006.
(2016-07-10收稿 2016-09-20修回)
(本文编辑 闫娟)
The relationship between visceral obesity and hyperuricemia in adults of Heping District of Tianjin
ZHENG Li1,ZHANG Meilin1,LI Ping1,ZHU Yufeng1,CHANG Hong1,2,HUANG Guowei1△
1 Department of Nutrition and Food Science,School of Public Health,Tianjin Medical University,Tianjin 300070,China;2 Department of Rehabilitation and Sports Medicine,Tianjin Medical University△
ObjectiveTo analyze the relationship between visceral obesity and hyperuricemia(HUA),and to provide the basis for the further study of obesity and HUA.MethodsA total of 1 824 participants came from Tianjin Heping District Health Education Guidance Center in 2014 were selected in this study.The investigation was performed with physical examination and laboratory test for all subjects.Body fat analyzer was used to measure the visceral fat area(VFA). The Logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the relationship between visceral obesity and HUA.ResultsThe prevalence of HUA in men and women increased gradually with VFA increasing(P<0.05).There was a positive correlation between VFA,waist circumference(WC),waist-to-hip ratio(WHR)and serum uric acid(SUA)level(P<0.05).According to the results of Logistic regression analysis,VFA(OR=1.805,95%CI=1.166-2.794)and WHR(OR=2.108,95%CI=1.061-4.189)were the risk factors of HUA in men.And in women,VFA(OR=1.775,95%CI=1.154-2.732),WC(OR=2.015,95% CI=1.137-3.570)and WHR(OR=2.489,95%CI=1.400-4.426)were the risk factors of HUA.ConclusionThe accumulation of visceral fat will increase the risk of HUA.So it is necessary to strengthen the detection of visceral obesity to prevent the development of HUA.
hyperuricemia;visceral obesity;visceral fat area;waist circumference;waist-to-hip ratio
R589.7
A
10.11958/20160626
国家科技支撑计划项目(2012BAI02B00)
1天津医科大学公共卫生学院营养与食品卫生学系(邮编300070);2天津医科大学康复与运动学系
郑莉(1990),女,硕士在读,主要从事营养与慢性病的防治研究
△通讯作者E-mail:huangguowei@tmu.edu.cn
