药物后处理对离体大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤影响的对比研究
2016-12-12张云盛滕天明康毅崔健夏钊张文娟
张云盛 滕天明 康毅 崔健 夏钊 张文娟
·基础研究·
药物后处理对离体大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤影响的对比研究
张云盛 滕天明 康毅 崔健 夏钊 张文娟


急性心肌梗死(acute myocardial infarction)是严重影响人类健康和生活质量的常见病、多发病。及早恢复冠状动脉血流是治疗的关键。但心肌在恢复血供后,可出现一系列再灌注损伤。因此,探讨如何减轻缺血再灌注损伤是目前研究的热点。预处理虽然可显著减轻再灌注损伤,但因心肌缺血难以预测,从而限制了预处理的应用。2005年,Staat等[1]首次将缺血后处理应用到临床,指出缺血后处理组与对照组相比肌酸激酶的释放曲线下面积明显减少,即心肌梗死面积减少36%。本实验室已经验证缺血后处理可有效减轻缺血再灌注心肌组织的坏死、改善心脏泵功能以及降低再灌注心律失常(reperfusion arrhythmia,RA)的发生率[2]。

1 材料与方法
1.1 材料与试剂

1.2.1 离体大鼠心肌缺血/再灌注模型制作 Wistar大鼠(雄性),水合氯醛(40 mg/kg)、肝素5000 U/kg腹腔注射,麻醉完全后开胸迅速取出心脏置于4℃ K-H液中,快速挤出心腔内残留血液,然后将其迅速套扎于离体心脏灌流系统,保持灌注压力为90 cmH2O(1 cmH2O=0.098 kPa), 37℃ K-H液持续灌流。迅速连接BL-420S系统,用容积导体法记录心电图。在靠近肺动脉圆锥处用3/0号医用缝线的3/8弯针勾绕前降支,待心脏稳定片刻后将压力球囊从左心耳插入左心室内,向球囊内注入80~100 μl水调节压力前负荷为5~10 mmHg(1 mmHg=0.133 kPa)。记录心电图、左心室压力变化等指标。待心脏稳定灌流30 min后,实验组结扎前降支,球囊内加压至6 kPa。心电图可见ST 段抬高,造成心肌梗死模型,结扎30 min后迅速松开球囊,打开结扎线。对照组穿线但不进行结扎。待灌流结束后,部分进行1%Evans blue-1% TTC双染色,测定心肌梗死面积。
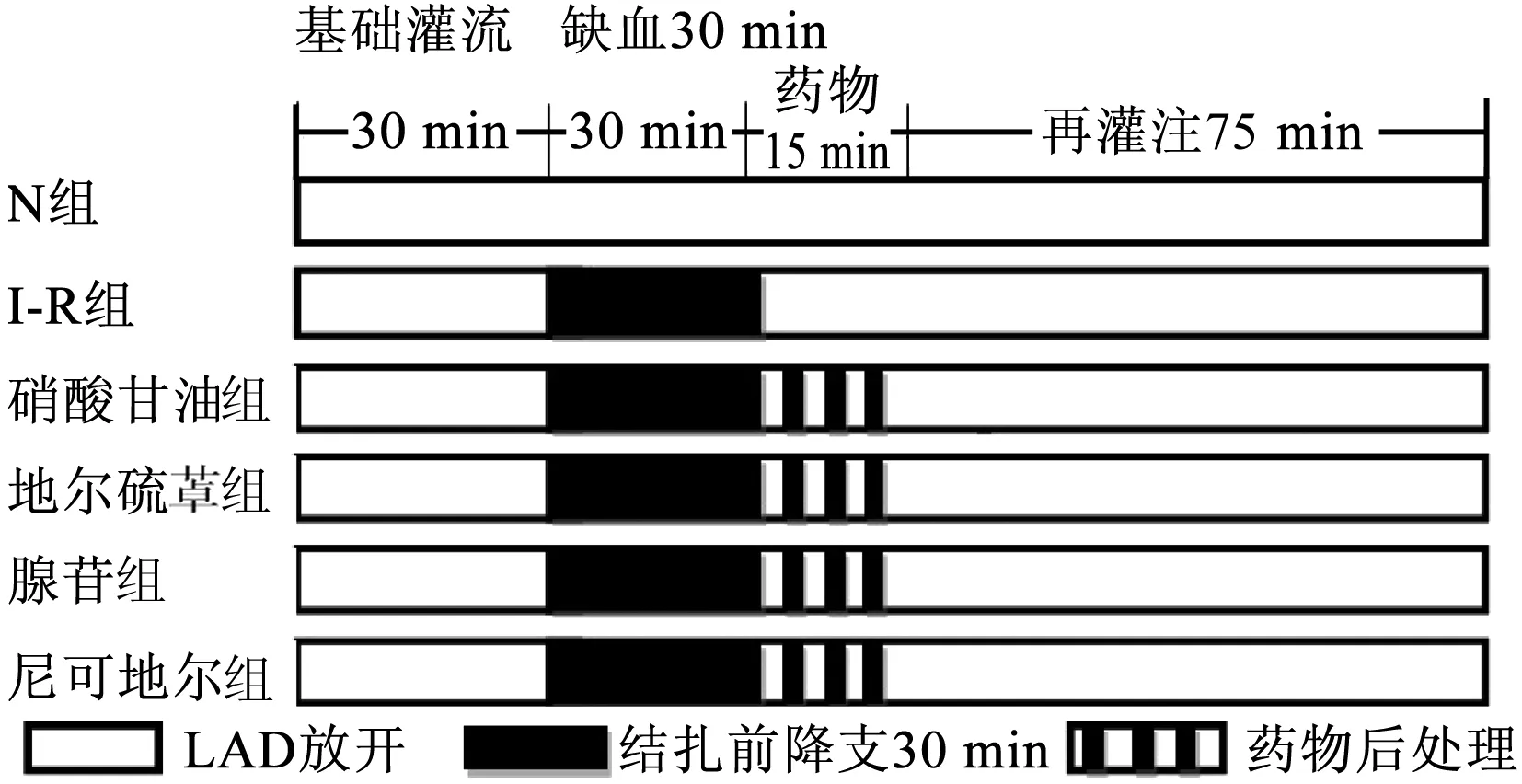
N组,正常对照组;I-R组,缺血再灌注组;LAD,前降支图1 实验流程示意图

1.2.3 血流动力学参数统计 根据左心室压力曲线,分析记录稳定灌流30 min时(结扎前基础状态值)、缺血15 min、缺血30 min、再灌注30 min及再灌注45 min左心室发展压(left ventricular developed pressure,LVDP),LVDP=左心室压力曲线最高值-左心室压力曲线最低值。记录再灌注30 min及45 min时左心室内压力最大上升/下降速率(±dp/dtmax),各取10个连续心动周期的平均值为基准。
1.2.4 心电指标统计 观察各组离体大鼠心脏再灌注期间室性心律失常(VA)出现的时间和持续时间,记录室性早搏的个数,统计室性心动过速(室速)及心室颤动(室颤)发生率和总持续时间。以在室速或室颤后出现3个及以上的正常窦性心律作为室速或室颤终止的指标。心律失常的评分依据CURTIS评分方案[7],记录各组大鼠RA评分(表1,图2)。

表1 心律失常CURTIS评分方案

图2 再灌注心律失常示意图 A.正常心电图;B.频发室性早搏;C.室性心动过速;D.心室颤动
1.2.5 心肌Evans-blue和TTC双染色 灌流结束后将进行再灌注组大鼠的前降支重新结扎,将1% Evans-blue 2 ml经主动脉根部逆行注入心脏,洗去浮色后,冻存于-20℃冰箱1 h后取出,沿心脏长轴方向由心尖部向心底部均匀切割成2 mm薄片共7片,置于1% TTC溶液,水浴(37℃)加热10 min,取出后以10%甲醛溶液浸泡2 h固定染色,区分正常区域(深蓝色)、缺血未梗死区域(红色,TTC染色阳性)及梗死区域(灰白色,TTC染色阴性)。用高清数码相机抓拍图像后,利用Image Proplus 7.0图像分析软件计算心肌梗死区(infarcted region,IR)及缺血区域(area at risk,AAR),以IR/AAR(%)表示心肌梗死面积百分比。
1.3 统计学分析
所有数据均采用SPSS 22.0统计软件进行处理。正态分布的计量资料以均数±标准差表示,LVDP、±dp/dtmax采用重复测量方差分析,心肌梗死面积比较采用单因素方差分析,组间比较采用LSD法检验。非正态分布的计量资料用中位数和四分位数[M(Q1,Q3)]表示,组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis-H秩和检验,不校正α水准[8]。计数资料比较采用卡方检验或者Fisher确切概率法。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 各组大鼠左心室压力变化比较(表2)
几个硬性条件一定要满足,如月嫂年龄要在45岁以下、普通话标准、形象较好、持有高级育婴员职业资格证书等。培训课程方面,她打算直接聘请北京的培训师,培训月子餐制作、催乳、小儿推拿、母婴护理、早教课程等。后期计划与北京的用人单位一起开发培训课程,目的是解决两地培训技能标准不统一的问题。

2.2 各组大鼠左心室心功能变化比较(表3)

2.3 各组大鼠再灌注心律失常比较(表4)

2.4 各组大鼠心肌梗死面积比较
3 讨论
缺血的组织、器官经恢复血液灌注后不但不能使其功能和结构恢复,反而加重其功能障碍和结构损伤的现象称为心肌缺血再灌注损伤(myocardial ischemia-reprefusioninjury,MIRI)。研究表明,MIRI的发生可能与活性氧的作用、钙超载、白细胞的炎症反应作用、心肌细胞高能磷酸化合物生成障碍以及细胞内酸中毒等相关[9]。药物后处理对预防MIRI的发生及减轻MIRI带来的损伤,具有临床价值。

表2 各组大鼠不同状态下LVDP的比较


表3 各组大鼠不同状态下左心室±dp/dtmax比较

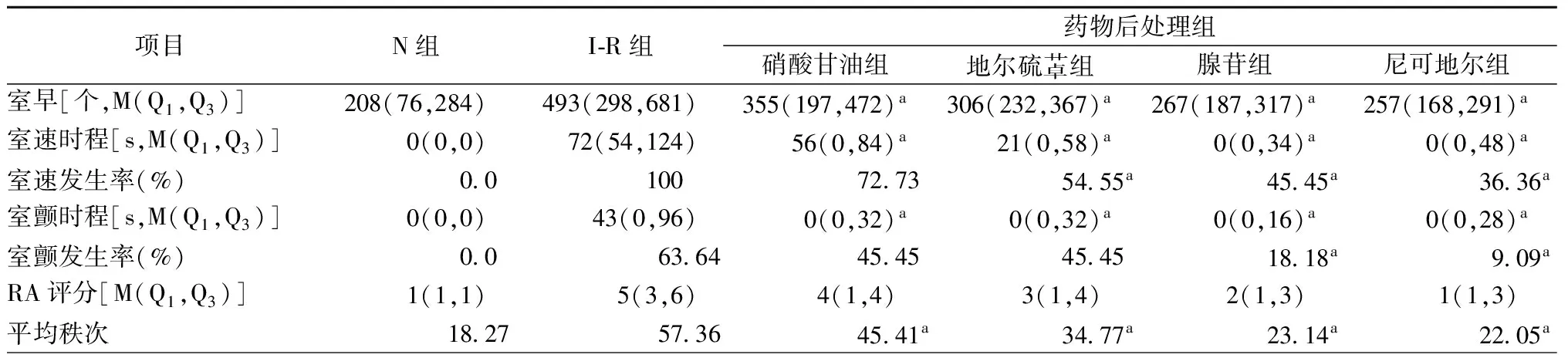
表4 各组大鼠再灌注室性心律失常发生率、时程及RA评分(n=11)
注:RA,再灌注心律失常;N组,正常对照组; I-R组,缺血再灌注组; a,与I-R组比较,P<0.05

N组,正常对照组;I-R组,缺血再灌注组图3 各组心脏染色切片
硝酸甘油(nitroglycerin)是硝酸酯类药物的基础药物,临床上主要用于治疗心绞痛、急性心肌梗死、重度高血压病和冠状动脉痉挛等疾病[10]。硝酸甘油经过线粒体ALDH2等途径在机体内生物转化生成小分子物质即一氧化氮(NO)[11],NO可以通过G-蛋白偶联受体系统的级联反应舒张血管,发挥对心血管系统的保护作用。低浓度硝酸甘油(10-8mol/L)对心肌具有明显的保护作用,表现为促进心室力学指标恢复、心肌梗死面积减小及乳酸脱氢酶释放减少[3]。RA发生的基本条件是冠状动脉阻断15~45 min后进行再灌注,缺血时间过长及过短,其发生率均降低。本实验采用结扎30 min后进行再灌注。与I-R组相比,硝酸甘油组在再灌注后压力降低减缓,心肌梗死面积明显减少,室颤与室速的发生率与I-R组比较则差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),但可以缩短室颤与室速的发生时间(P<0.05),总体可以降低RA评分(P<0.05)。

尼可地尔(nicorandil)是一种硝酸酯样作用的钾通道开放剂,既可以发挥开放细胞膜与线粒体钾离子通道的作用,也可以发挥类硝酸酯样扩张冠状动脉血管的作用。尼可地尔通过激活胞浆内鸟苷酸环化酶(GA)致使环磷酸鸟苷酸(cGMP)细胞水平增多和胞浆钙减少,从而使血管平滑肌松弛,发挥扩张血管的活性作用[16]。尼可地尔可以增加钾离子从细胞的流出,使静息膜电位负值更大(超极化),由于膜的超级化致使钙离子内流减少,减少了缺血再灌注部位心肌早期和晚期后除极,因此有抗RA的作用。有实验研究发现,尼可地尔在抗心律失常方面效果优异,心脏泵功能得到了改善,心肌梗死面积减少[17]。与I-R组比较,尼可地尔组室速、室颤的发生率均降低(P<0.05)。
腺苷(adenosine)是一种内源性嘌呤核苷,同时也是一种细胞膜ATP-K+通道开放剂,在机体内参与重要的病理生理过程。根据腺苷与腺苷受体结合能力的差异以及对腺苷环化酶的活性调控作用不同,腺苷受体分为4个亚型[18]:A1、A2A、A2B、A3,腺苷可以通过激活腺苷受体参与心肌再灌注损伤的保护作用。此外,腺苷还可以减轻钙超载,减轻中性粒细胞的激活,使超氧阴离子等自由基减少[19]。本实验中,与I-R组相比,腺苷组在再灌注后压力降低减缓,心肌梗死面积减少,同时在减少RA方面效果更佳。
[1] Staat P, Rioufol G, Piot C, et al. Postconditioning the human heart.. Circulation,2005,112(14):2143-2148.
[2] 孙倩,王清,滕天明,等. Apelin-13对离体大鼠心肌缺血再灌注影响的研究. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2015,9(16):3057-3062.
[3] 姜翠荣,高琴,王晓梅,等. 不同浓度硝酸甘油对大鼠离体心脏缺血/再灌注损伤的作用. 蚌埠医学院学报,2011,36(1):7-10.
[4] Tosaki A, Szekeres L, Hearse D J. Diltiazem and the reduction of reperfusion-induced arrhythmias in the rat: protection is secondary to modification of ischemic injury and heart rate. J Mol Cell Cardiol,1987,19(5):441-451.
[5] Mitani A, Kinoshita K, Fukamachi K, et al. Effects of glibenclamide and nicorandil on cardiac function during ischemia and reperfusion in isolated perfused rat hearts. Am J Physiol,1991,261(6 Pt 2):H1864-H1871.
[6] Sun L, Li DL, Zhao M, et al. The role of muscarinic receptors in the beneficial effects of adenosine against myocardial reperfusion injury in rats. PLoS One,2011,6(11):e25618.
[7] Curtis MJ, Walker MJ. Quantification of arrhythmias using scoringsystems: an examination of seven scores in an in vivo model ofregional myocardial ischaemia. Cardiovasc Res,1988,22(9):656-665.
[8] 张文彤,闫洁. SPSS统计分析基础教程.北京:高等教育出版社, 2004:289 -292.
[9] Turer AT, Hill JA. Pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and rationale for therapy. Am J Cardiol,2010,106(3):360-368.
[10] 吴春涛,马士新. 重组人脑利钠肽对急性心肌梗死经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后心力衰竭患者心肌酶、梗死面积的影响.中国介入心脏病学杂志,2016,24(7):394-397.
[11] Chen Z,Stamler JS. Bioactivation of nitroglycerin by the mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase. Trends Cardiovasc Med,2006,16(8):259-265.
[12] Fukuda S, Nakamura Y, Egi K, et al. Comparison of direct effects of clinically available vasodilators; nitroglycerin, nifedipine, cilnidipine and diltiazem, on human skeletonized internal mammary harvested with ultrasonic scalpel. Heart Vessels,2016,31(10):1681-1684.
[13] Mannign AS,Hearse DJ. Reperfusion-induced arrhythmias:Mechanisms and prevention. J Mol Cell Cardial,1984,16(6):497-518.
[14] Carozzi S, Nasini MG. Ca2+concentration in the peritoneal dialysissolution regulates peritoneal fibroblast proliferation and peritonealmacrophage and lymphocyte cytokine release. Perit Dial Int,1993, 13 Suppl 2: S41-S44.
[15] Sheehan FH, Epstein SE. Effects of calcium channel blocking agents on reperfusion arrhythmias. Am Heart J,1982,103(6):973-977.
[16] César IC, Godin AM, Araujo DP,et al. Synthesis,antinociceptive activity and pharmacokinetic profiles of nicorandil and its isomers. Bioorg Med Chem,2014,22(9):2783-2790.
[17] Lathrop DA, Nànàsi PP, Varrò A. In vitro cardiac models of dog Purkinje fibre triggered and spontaneous electrical activity: effects of nicorandil. Br J Pharmacol,1990,99(1):119-123.
[18] 易云,高云. 腺苷A2B受体在心血管系统研究新进展. 中国药理学通报,2014,30(1):21-24.
[19] Singh M, Shah T, Khosla K, et al. Safety and efficacy of intracoronary adenosine administration in patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis,2012,6(3):101-114.
[20] Eltzschig HK, Bonney SK, Eckle T. Attenuating myocardial ischemia by targeting A2B adenosine receptors. Trends Mol Med,2013,19(6):345-354.
Comparative study of the effect of different drugs on post-conditioning of myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury on isolated rat heart models
ZHANG Yun-sheng,TENG Tian-ming,KANG Yi,CUI Jian,XIA Zhao,ZHANG Wen-juan.
Cardiology of Tianjin Medical University General Hospital,Tianjin 300052, China
ZHANG Wen-juan,Email:zwjzyy2013@163.com
Objective To observe and compare the effects of nitroglycerin, diltiazem, nicorandil and adenosin on isolated rat myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury modles, and to investigate the protective effect and related mechanisms of respective agents. Methods Sixty-six Wistar rats were randomly divided into six groups: normal group (N Group), ischemia-reperfusion group (I-R group), nitroglycerin+ischemia-reperfusion group, diltiazem+ischemia-reperfusion group, adenosine+ischemia-reperfusion group, nicorandil+ischemia-reperfusion group. The normal group (N group) was given continued perfusion of normal liquid for 150 min; the I-R group was given stable perfusion for 30 min followed by ligating the LAD for 30 min and subsequent reperfusion for 90 min. For the drug post-conditioning groups, the models were given reperfusion with nitroglycerin (10-8mol/L), diltiazem (5 μmo/L), nicorandil (200 μmo/L) and adenosine (100 μmo/L) for 15 min respectively, and then perfused with K-H liquid for 75 min. Observed and recorded reperfusion arrhythmia (RA), Left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP),±dp/dtmax by Taimeng (Chengdu) BL-420s system and calculated myocardial infarct size.Results (1) LVDP was lowest in the I-R group compared with the other groups after 30 min and 45 min of reperfusion (P<0.05). In the drug post-conditioning groups after 30 min reperfusion, LVDP in the diltiazem group [(92.68±5.09) mmHgvs. (84.26±3.02) mmHgvs. (83.35±2.88) mmHg] and in the nicorandil group [(88.95±1.75) mmHgvs. (84.26±3.02) mmHgvs. (83.35±2.88) mmHg] was higher than the nitroglycerine and the adenosine treated group. LVDP after 45 min reperfusion in the diltiazem group [(90.39±4.29) mmHgvs. (82.09±4.24) mmHgvs. (80.98±3.89) mmHg] and in the nicorandil group [(86.13±2.38) mmHgvs. (82.09±4.24) mmHgvs. (80.98±3.89) mmHg] was higher than the nitroglycerin and adenosine groups respectively. The diltiazem group has higher LVDP than the nicorandil group after reperfusion (P<0.05). The difference between the nitroglycerin group and the adenosine group was not statistically significant (P>0.05). (2)±dp/dtmax was lowest in the I-R group than the other groups after 30 min and 45 min reperfusion (P<0.05). ±dp/dtmax in the diltiazem group and the nicorandil group were significantly higher than those in the nitroglycerin group and the adenosine group at 30 min and 45 min after reperfusion. ±dp/dtmax of the diltiazem group was higher than the nicorandil group, and the difference was significant (P<0.05). There was no difference between the nitroglycerin group and the adenosine group (P>0.05). (3) Comparison of the RA score showed the score of the IR group [5(3,6), 57.36] was significantly higher than all the drug post-conditioning groups as nicorandil group [1(1,3), 22.05], diltiazem group [3(1,4), 34.77], nitroglycerin group [4(1,4), 45.41] and adenosine group [2(1,3), 23.14] (P=0.000,P=0.000,P=0.004,P=0.000). The nicorandil group had the lowest score. There was no significant difference between the nicorandil group and the adenosine group (P=0.771). (4) Myocardial infarct size was (27.04±2.45)% in the nitroglycerin group, (17.01±1.13)% in the diltiazem group, (47.97±1.22)% in the adenosine group and (34.95±1.25) in the nicorandil group. IR group (55.51±1.43)% had the largest infarct size among all the groups statistical difference (allP<0.01). The infarct size in the diltiazem group was the smallest.Conclusions In the treatment of myocardial ischemia and reperfusion, all of the four drugs(nitroglycerin, diltiazem, nicorandil and adenosine) can reduce myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, and play a protective role in ischemic myocardium. Diltiazem showed promising improvement in cardiac pump function and reducing the area of myocardial infarction. In the post-conditioning for RA, nicorandil and adenosine showed better performance.
Drug post-conditioning; Ischemia/reperfusion; Nitroglycerin; Diltiazem; Nicorandi; Adenosine
10.3969/j.issn.1004-8812.2016.10.008
天津市高等学校科技发展基金计划项目(20110151)
300052 天津,天津医科大学总医院心血管内科(张云盛、滕天明、崔健、夏钊、张文娟);天津医科大学药理学实验室(康毅)
张文娟,Email:zwjzyy2013@163.com
R542.2
2016-06-18)
