基于机器视觉的鱼类模式生物在线监测技术方法研究
2016-12-06周振宇,邵振洲,施智平等
基于机器视觉的鱼类模式生物在线监测技术方法研究

水质的生物式监测方法灵敏度强,适应性广,能够适应于多种场合的水质监测工作并广泛地应用在水环境的质量检测和水质安全预警中,它能够弥补理化监测方法实时性和综合性较差的缺点,能够产生巨大的社会和经济效益[1]。其基本原理是利用水生生物个体、种群的健康状态、生理特征、运动特征等的变化来指示水体环境质量的变化,表征环境污染状况,从生物学角度为水体环境质量监测和评价提供依据[2-3]。
鱼类是最早运用的模式生物。随着机器视觉技术的不断成熟和广泛应用,视觉辅助的水质自动监测成为一种可能。这种非接触式的监测手段的优势是无需破坏鱼类的正常生活环境,在自然状态下观测鱼类的生理特征和运动特性。鱼所表现出来的“逃避”、“呼吸加快”等异常行为显然要远远提前于生物的病理损伤或死亡,为水环境的在线生物监测技术的有效性提供有力的理论支持。通过利用机器视觉方法,目前国内研究大部分仅将鱼类的一部分运动特征(鱼类的游动速度、游动加速度、游动高度、转弯次数)为指标应用在水质监测中[4-21],缺少对胸鳍、尾鳍运动等信息的统计,也缺少生理特征方面(呼吸频率、呼吸深度等)的重要信息。这使得在一定程度上的局限了观测数据的完整性,也势必会降低水质监测的准确性。
本文以青鳉鱼为模式生物,在机器视觉的基础上,实时监控鱼的胸鳍、尾鳍摆动频率,鱼的呼吸频率、呼吸深度,达到获得更有鲁棒性、健硕性的观测数据。
1 青鳉鱼生理特征检测方法(The detection method of medaka physiological characteristics)
鱼鳃的呼吸对污染物质十分敏感,对于半致死浓度的污染物在30 min内便可被检测到,亚致死的污染物也可在24 h内被检测出。在有污染物存在的情况下,鱼鳃的呼吸会极速加快,并且变得无规律。Gerhardt等[21]将监测电极直接安装在鱼鳃上,监视当前呼吸频率,分析数据并与正常的呼吸频率相比较,以判断水是否被污染。Cairns等[22]在水箱中插入网电极,通过注入电极的信号来记录鱼的呼吸运动。这2种方法虽然能一定程度地反映鱼的真实生理状况,然而无法排除装置本身对鱼类反应的影响且得到的信号往往十分微弱,不直观,容易形成较大的识别误差。
基于视觉的方法是以非接触式的监测手段,通过电荷耦合器件(charge coupled device,CCD)相机在自然状态下观测鱼类的生理特征和行为特性。本文通过分析青鳉鱼鱼鳃部位像素信息统计得到结果“颜色分布规律表(CDT)”,如表1所示。再结合机器学习算法中的线性分类器SVM(支持向量机),可准确定位得到青鳉鱼鱼鳃区域,实验结果如图1和2所示。其中SVM分类器是由颜色空间转换后分别得到的S(HSV)通道、a(Lab)通道组合成的特征向量训练得来。
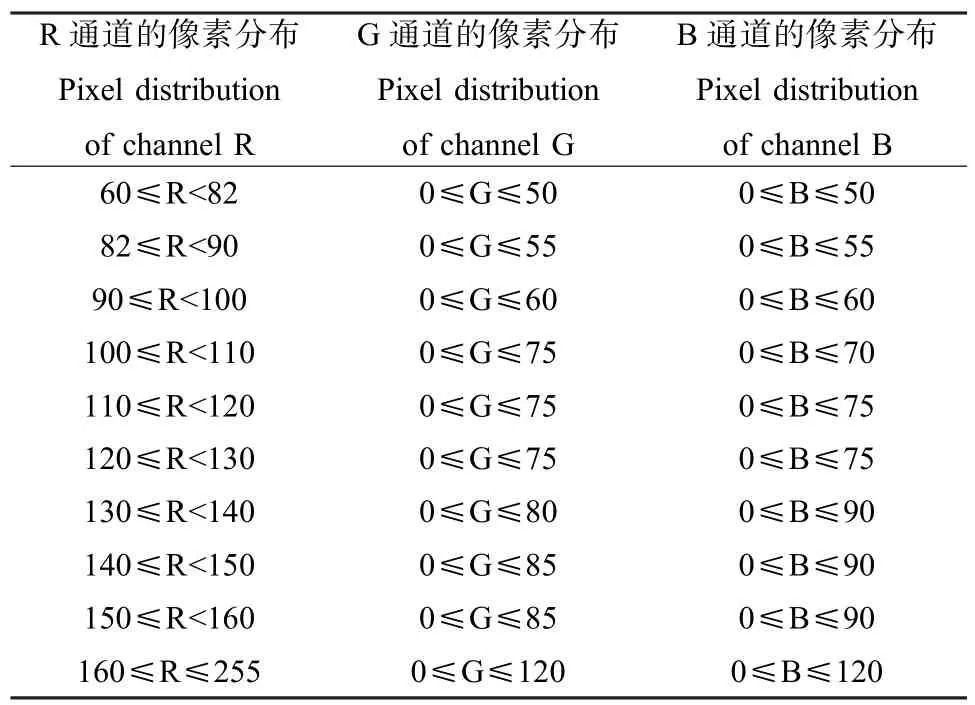
表1 颜色分布规律表Table 1 The color distribution table
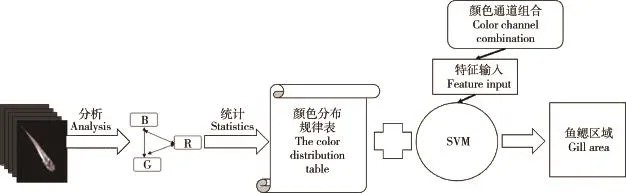
图1 颜色分布规律表(CDT)和支持向量机(SVM)Fig.1 The color distribution table(CDT)&support vector machine(SVM)

图2 青鳉鱼鱼鳃提取实验结果Fig.2 Experiment result of extracting gill of medaka fish
根据鱼鳃轮廓,我们可以计算其轮廓面积。在时间T内鱼的呼吸次数n可根据鱼鳃轮廓面积在时间T内的极大(小)值的个数来统计。青鱂鱼的呼吸频率f可由式(1)得出。

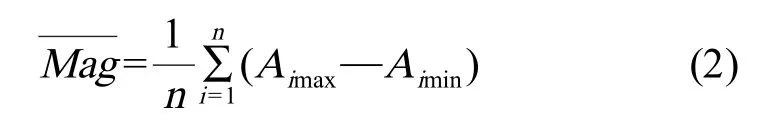
式中,n表示时间T内鱼的呼吸次数,A表示鱼鳃的轮廓面积。
2 青鳉鱼运动特征检测方法(The detection method of medaka motion features)
本文通过对运动鱼进行骨架提取,进而通过提出青鳉鱼骨架模型,可实时计算得到青鳉鱼胸鳍尾鳍摆动频率。
2.1 骨架提取
中轴变换(MAT)是一种用来确定物体、估计物体骨架的细化技术。理论上说,每个骨架点保持了与边界点距离最小的性质,所以如果用以每个骨架点为中心的圆的集合,就可以恢复出原始的区域。具体就是以每个骨架点为圆心,以前述最小距离为半径做圆。它们的包络就构成了区域的边界,填充圆就得到这些区域。由上述可知,骨架就是用1个点与1个点集的最小距离来定义的,可写成式(3):
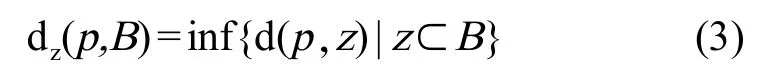
式中,B为边界,z为边界点,p为区域上任意一点。
在去噪后进行骨架提取,最终得到单一的较为完整的鱼体骨架结构。图3为经过骨骼细化后,以及链接了断裂连通域后得到的青锵鱼鱼骨架。该骨架与青锵鱼的整体状态保持一致,对之后采集相应的数据起着关键的作用。

图3 青鳉鱼骨架提取结果Fig.3 Experiment result of skeleton extraction of medaka fish
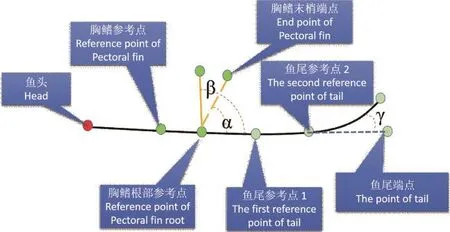
图4 青鳉鱼骨架模型Fig.4 The skeleton model of medaka fish
2.2 青鳉鱼骨架模型
本文提出了青鳉鱼骨架模型如图4,并标定了6个关键点分别为:胸鳍参考点、胸鳍根部参考点、胸鳍末梢端点、鱼尾参考点1、鱼尾参考点2和鱼尾端点,以便于计算得到青锵鱼的胸鳍、尾鳍摆动频率和幅值。胸鳍参考点以青锵鱼鱼鳃与骨架的1个交点为参考点,该点具有较好的稳定性,可以适合作为参考点。得到参考点的同时,还能去除头部无用的并可能会产生干扰的信息。其余各点以胸鳍参考点为初始点,遍历整个鱼骨架,从而先后得胸鳍根部端点、胸鳍末梢端点、鱼尾端点。结果显示如图5所示。
2.3 青鳉鱼运动特征计算
对于胸鳍摆动角度的计算,通过胸鳍参考点、胸鳍根部端点、胸鳍末点3点利用公式(4):
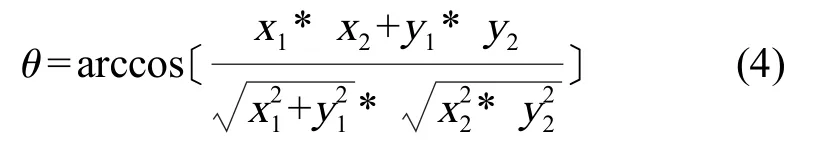
可以得到摆动角度θ,式中x为横坐标,y为纵坐标,进而利用公式(5):
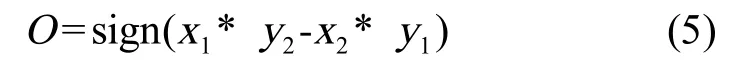
可以判断出是左胸鳍还是右胸鳍的摆动角度。同理,对于青锵鱼鱼尾摆动角度,也可以据此方法得出。进而通过统计一段时间T内,摆动角度的的峰值数量,可统计出摆动次数n。青鳉鱼胸鳍和尾鳍摆动频率计算方程如式(6):
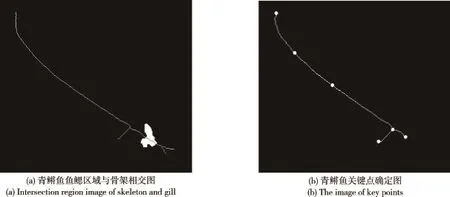
图5 青鳉鱼骨架参考点Fig.5 The skeleton reference point of medaka fish

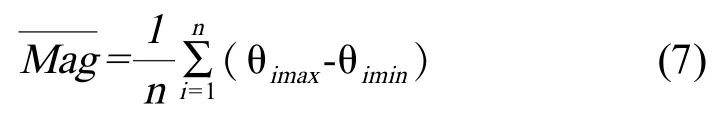
其中θimax和θimin为某个周期i内,青鳉鱼胸鳍、尾鳍的最大摆动角度和最小摆动角度。
3 实验结果与分析(Experimental results and analysis)
为验证本文方法的有效性与可行性,做了如下实验。实验过程采用数码摄像头获取正常水质下的鱼体运动视频图像,每帧图像大小为480×640,帧率为30 fps。
通过实验结果可得,CDT&SVM方法检测得到的青鳉鱼呼吸次数与实际青鳉鱼呼吸次数误差较小,并且对于帧率为30 fps的CCD相机的实时采集,算法能满足实时性。实验在连续1 000帧图像中得到的青鳉鱼呼吸深度谱图结果如图6所示:
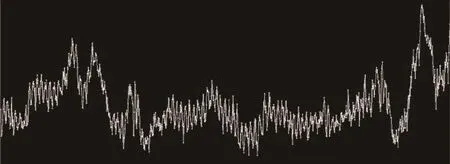
图6 青鳉鱼呼吸深度谱图Fig.6 Spectrum of respiratory depth of medaka fish
青鳉鱼胸鳍尾鳍摆动频率实验结果如表3所示,其中通过算法检测得到的尾鳍摆动数据准确性较高。相较而言,由于青鳉鱼胸鳍很难被准确识别,从而导致胸鳍摆动数据的准确性仍不够准确。算法具有较好的实时性,单帧耗时约23 ms,能满足在线采集、分析的需求。
实验在连续1 000帧图像中得到的青鳉鱼胸鳍、尾鳍摆幅如图7~9所示。
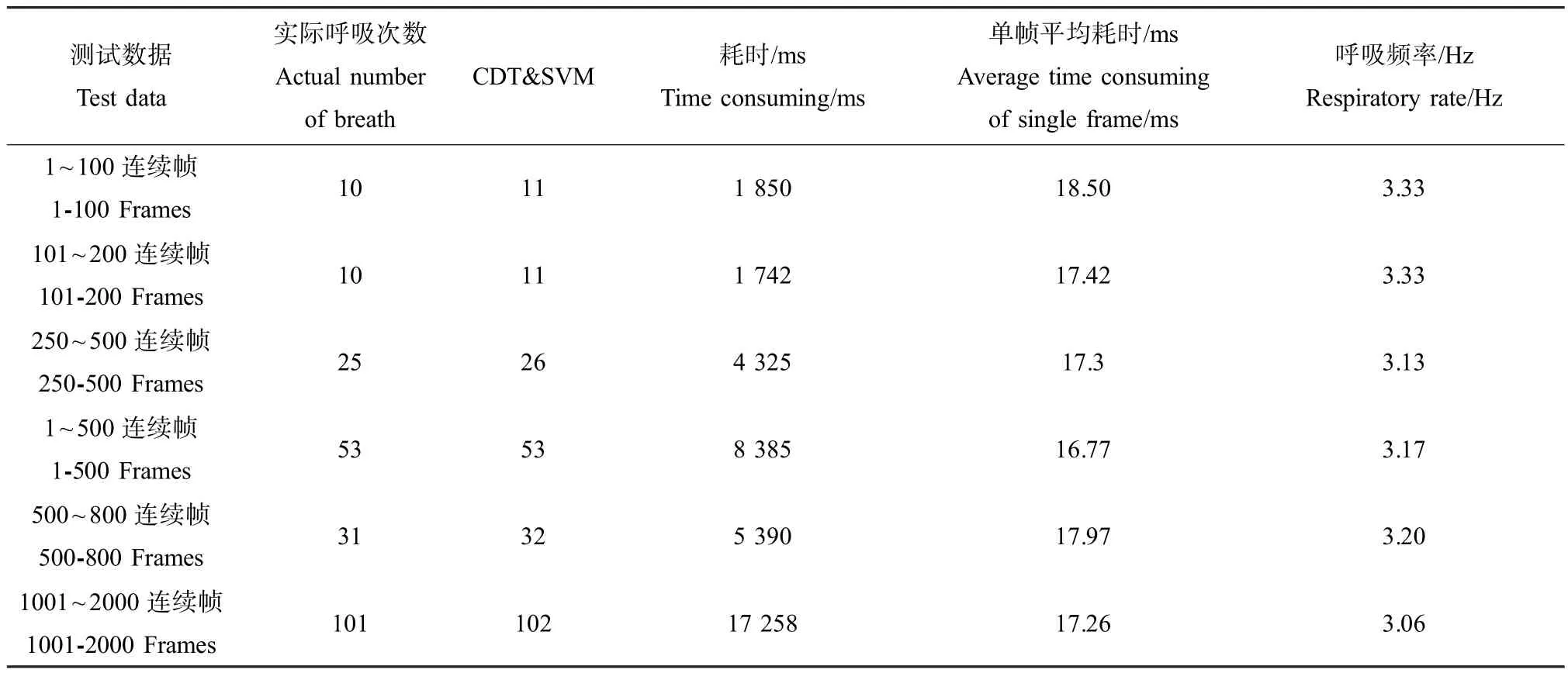
表2 青鳉鱼呼吸频率实测结果Table 2 Experiment result of medaka respiratory rate
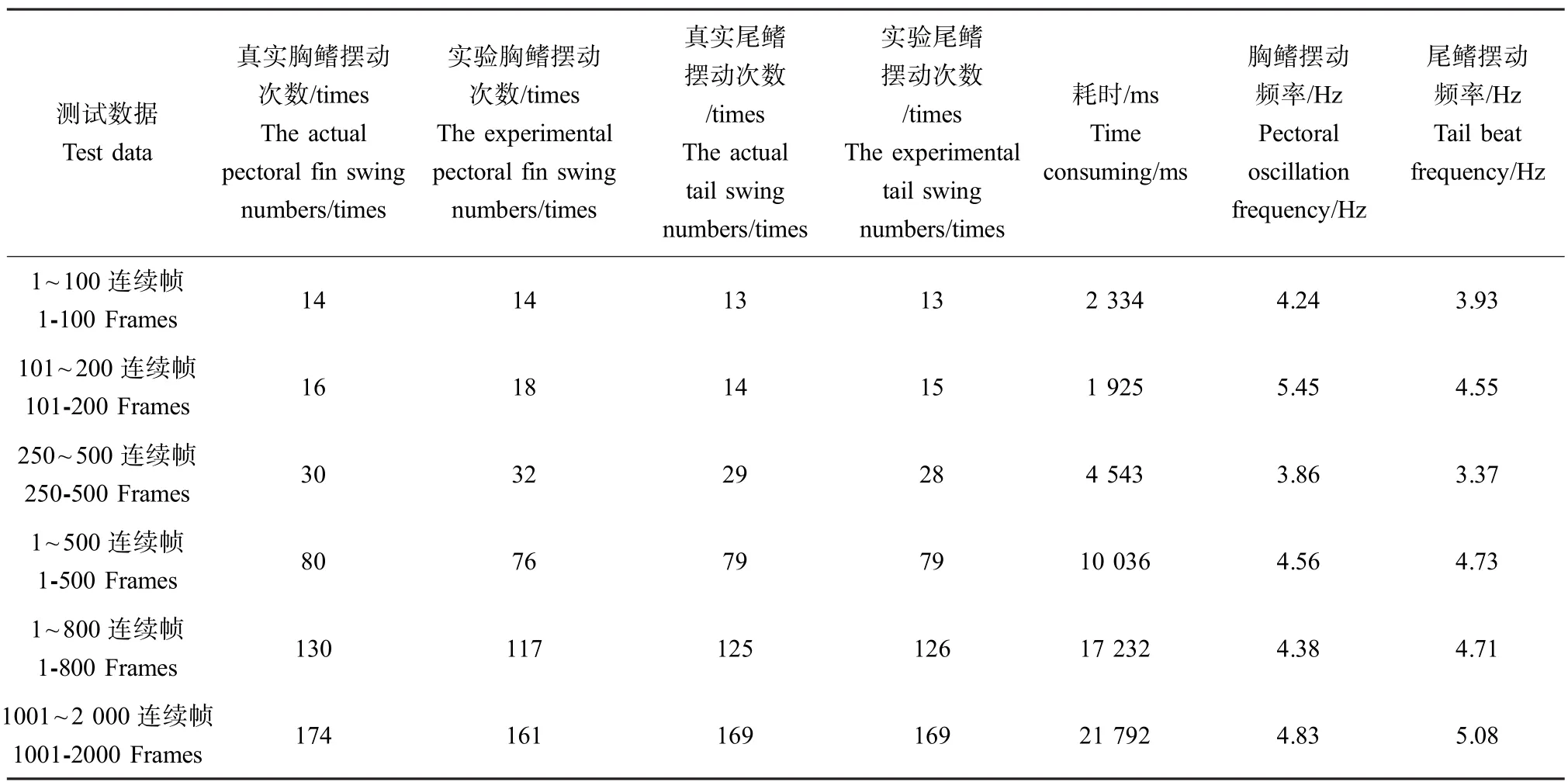
表3 青鳉鱼胸鳍尾鳍摆动频率实测结果Table 3 Experiment result of medaka pectoral fins and tail beat frequency
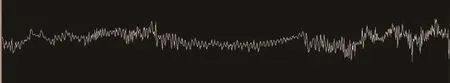
图7 青鳉鱼尾鳍摆幅谱图Fig.7 Spectrum of tail swinging amplitude of medaka fish

图8 青鳉鱼胸鳍(左侧)摆幅谱图Fig.8 Spectrum of left pectoral fin swinging amplitude of medaka fish

图9 青鳉鱼胸鳍(右侧)摆幅谱图Fig.9 Spectrum of right pectoral fin swinging amplitude of medaka fish
综上所述,本文所提出的对青鳉鱼的实时在线监测方法,充分的利用了机器视觉的优点,在准确监测青鳉鱼的运动、生理特征的基础上,仍能保持实时性,满足了在线监测的需求,也能为生物水质监测和预警的发展提供一定支持与参考。
[1]徐建瑜,崔绍荣,苗香雯,等.计算机视觉技术在水产养殖中的应用与展望[J].农业工程学报,2005,21(8): 174-178 Xu J Y,Cui S R,Miao X W,et al.Application and prospect of computer vision technology in aquaculture[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2005,21(8):174-178(in Chinese)
[2]Heinz G H,Haseltine S D.Avoidance behaviour of young black ducks treated with chromium[J].Toxicology Letters,1981(8):307-310
[3]Steiner U K.Linking antipredator behaviour,ingestion, gut evacuation and costs of predator induced responses in tadpoles[J].Animal Behaviour,2007,74(5):1473-1479
[4]Nimkerdphol K,Nakagawa M.Effect of sodium hypochlorite on zebrafish swimming behavior estimated by fractal dimension analysis[J].Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering,2008,105(5):486-492
[5]Hughes N F,Kelly L H.New techniques for 3D video tracking of fish swimming movements in still or flowing water[J].Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences,1996,53:2476-2483
[6]耿彩英.用于水质监测的活体鱼视频图像理解[D].杭州:杭州电子科技大学,2009:12 Geng C Y.The video image understanding of live fish used for water quality monitoring[D].Hangzhou:Hangzhou Dianzi University,2009:12(in Chinese)
[7]Zhu L Q,Weng W.Catadioptric stereo-vision system for the real-time monitoring of 3D behavior in aquatic animals[J].Physiology&Behavior,2007,91:106-119
[8]Wu G H,Yang Y,Zeng L J.Novel method based on video tracking system for simultaneous measurement of kinematics and flow in the wake of a freely swimming fish [J].Review of Scientific Instruments,2006,77:114302
[9]Wu G H,Zeng L J.Video tracking method for three-dimensional measurement of a free-swimming fish[J].Science in China Series G-Physics and Astronomy,2007,50: 779-786
[10]王丽娜.基于动态图像理解的水质生物监测系统研究与应用[D].杭州:杭州电子科技大学,2011:1 Wang L N.Research and application on water quality biomonitoring system based on dynamic image understand-ing[D].Hangzhou:Hangzhou Dianzi University,2011:1 (in Chinese)
[11]胡江龙.多目标跟踪算法在水质监测中的应用[D].杭州:杭州电子科技大学,2012:5 Hu J L.Water quality monitoring using multi-object tracking algorithm[D].Hangzhou:Hangzhou Dianzi University,2012:5(in Chinese)
[12]马欣.生物式水质监测的报警方法研究[D].杭州:杭州电子科技大学,2012:3 Ma X.Research on alarming method of biological watermonitoring[D].Hangzhou:Hangzhou Dianzi University, 2012:3(in Chinese)
[13]Wu J,Xiao G,Zhang Y L,et al.Fish group tracking based on delaunay triangulation network[C].2011 4th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing (CISP),2011:534-537
[14]吴军.基于视觉感知的鱼群目标检测与跟踪技术研究[D].杭州:浙江工业大学,2011:4 Wu J.Research on detecting and tracking of fish group based on machine vision[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University of Technology,2011:4(in Chinese)
[15]于欣,侯晓娇,卢焕达,等.基于光流法与特征统计的鱼群异常行为检测[J].农业工程学报,2014,30(2):162-168 Yu X,Hou X J,Lu H D,et al.Anomaly detection of fish school behavior based on features statistical and optical flow methods[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2014,30(2):162-168(in Chinese)
[16]Pinkiewicz T H,Purser G J,Williams R N.A computer vision system to analyse the swimming behavior of farmed fish in commercial aquaculture facilities:A case study using cage-held Atlantic salmon[J].Aquacultural Engineering,2011,45:20-27
[17]Lee J H,Wu M Y,Guo Z C.A tank fish recognition and tracking system using computer vision techniques[C]. Computer Science and Information Technology,2010,4: 528-532
[18]Serra-Toro C,Montoliu R,Traver V J,et al.Assessing water quality by video monitoring fish swimming behavior[C].20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition(ICPR),2010,8:23-26
[19]Christodoulou L,Kasparis T,Marques O.Advanced statistical and adaptive threshold techniques for moving object detection and segmentation[C].Digital Signal Processing(DSP),17thInternational Conference,2011:1-6
[20]Tan J S,Chang T K,Ooi P L,et al.Fast and robust zebrafish segmentation and detection algorithm under different spectrum conditions[C].Sensors Applications Symposium(SAS),2014:189-194
[21]Gerhardt A,Janssens D B L,Mo Z,et al.Short-term responses ofOryzias latipes(Pisces:Adrianichthyidae)and Macrobrachium nipponense(Crustacea:Palaemonidae)to municipal and pharmaceutical waste water in Beijing,China:Survival,behaviour,biochemical biomarkers[J]. Chemosphere,2002,47(1):35-47
[22]Cairns Jr J,Thompson K W,Hendricks A C.Effects of fluctuating sublethal applications of heavy metal solutions upon the gill ventilatory response of blue gills(Lepomis macrochirus)[M].Duluth,Minn.,Cincinnati,Ohio:U.S. Environmental Protection Agency,Research and Development,Environmental Research Laboratory,Center for Environmental Research Information,1981
quality monitoring provides a novel solution in this field.The water quality is detected by the biological response to reflect the direct or indirect pollution.However,the observation indexes and quantitative criteria are major problems to estimate in the complex water environment.In this paper,the medaka fish is chosen as the model organism,and the corresponding physiological characteristics and movement characteristics are observation indexes,such as breathing frequency,pectoral oscillation frequency,tail beat frequency,etc.By adopting machine vision based method,the real-time monitoring and analysis are achieved.Experimental results show that the proposed method can provide the support and reference for the development of biological water quality monitoring and early warning.The measured breathing frequency of medaka fish was 3.06 Hz,the pectoral oscillation frequency was 4.83 Hz and the tail beat frequency was 5.08 Hz.The results are consistent with the actual indexes.
biological water quality monitoring;real time;observation index
简介:张融(1971—),女,工程师,主要研究方向为环境工程、工业设计。
饶凯峰(1976—),男,助理研究员,研究方向为水生态毒理与监测预警。
