血清microRNA在多形性胶质母细胞瘤术预后评估中的研究
2016-08-04高秀娟陈熹彦伟尹婧婧巴一
高秀娟 陈熹 彦伟 尹婧婧 巴一
血清microRNA在多形性胶质母细胞瘤术预后评估中的研究
高秀娟①陈熹②彦伟③④尹婧婧⑤巴一①
目的:筛选多形性胶质母细胞瘤(glioblastoma multiform,GBM)患者术前、术后血清中差异表达的microRNAs(miRNAs),并探讨差异表达的miRNAs与患者术后预后的相关性。方法:收集2006年1月至2009年6月48例北京天坛医院经临床病理诊断为GBM患者的术前术后血清样本。采用Solexa测序的方法初步筛选出术前术后表达量有差异的miRNA,用实时荧光定量PCR (quantitative real-time PCR,RT-qPCR)的方法对每个样本进行逐一验证,应用t检验的方法筛选出满足条件的miRNA(两组之间的平均值差异在2倍以上,且P<0.05),对48例患者进行随访,统计生存时间,根据48例患者中位生存时间494 d,将所有标本分为长生存期组和短生存期组,应用Kaplan-Meier法和Log-rank检验,研究患者术后血清miRNAs的表达量与患者生存时间之间是否存在统计学意义的相关性。结果:Solexa结果显示,有63个miRNA表达量存在差异,基于本研究先前的研究成果和其他文献的报道,从中选出4个miRNA(miR-26b,miR-30e,miR-129-3p,miR-206)进行逐一验证并进行统计学分析,结果只有1个miRNAs (miR-30e)在术后患者血清中的表达水平有明显上调现象(术前与术后表达水平平均值差异≥2倍且P<0.05),随访结果显示,生存时间>494 d,患者术后血清miR-30e的表达水平有降低的趋势(P<0.05),但生存分析显示,患者术后血清中miR-30e的表达量与患者总生存时间之间差异无统计学意义(P=0.101)。结论:GBM患者术前术后血清中差异表达的miRNA只有miR-30e,且术后患者血清中的miR-30e水平与肿瘤负荷成负相关关系。生存分析结果显示,术后患者血清miR-30e的表达水平与患者的预后没有明显的相关性。
血清microRNA多形性胶质母细胞瘤生物标志物术后评估miR-30e
多形性胶质母细胞瘤(glioblastoma multiform,GBM)是最常见的中枢神经系统原发性肿瘤,每年有3/10万的新发病例,大约占所有胶质瘤的51%。世界卫生组织(WHO)根据组织病理类型将胶质瘤分为1~4级,GBM属于4级,为高度恶性。尽管目前GBM的标准治疗方案为联合手术、放疗、化疗的综合治疗,但其总生存率(overall survival,OS)仍然不容乐观,中位生存时间约为14个月[1]。目前已有大量研究应用血清microRNA (miRNA)作为肿瘤的生物学标志物用于诊断与预后评估,这使得应用血清miRNA判断GBM患者肿瘤负荷及术后预后情况成为可能[2]。
1 材料与方法
1.1实验材料
1.1.1血清标本的收集及处理本研究收集的2006年1月至2009年6月48例患者血清样本均来自北京天坛医院,所有患者均经术后病理确诊,且所有标本采集前均已签署知情同意书,术前和术后静脉血标本均于术前未接受任何治疗时及术后7~10 d采集。
1.1.2主要试剂10×PCR buffer(TaKaRa Bio Group),25 mM MgCl2(TaKaRa Bio Group),10 mM dNTP(TaKaRa Bio Group),Taq酶(TaKaRa Bio Group),Probe(ABI),5× AMV buffer(TaKaRa Bio Group),RT-prime(ABI),AMV酶(TaKaRa Bio Group),水饱和酚(Gibco),DEPC水(Gibco),miR-16(ABI),氯仿(购自上海化学试剂有限公司),异丙醇(购自上海化学试剂有限公司),无水乙酸钠(购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司),无水乙醇(购自上海化学试剂有限公司)。
1.1.3实验仪器Centrifuge 5417R型台式离心机(Eppendorf),纯水仪(Millipore),PTC-1148 PCR仪(Bio-Rad),ABI Prism 7300荧光定量PCR仪(ABI),各量程移液器(Gilson)。
1.2方法
1.2.1血清制备取5 mL促凝生化管1只,标记住院号/ID、姓名、采血时间,采集患者血5 mL,颠倒混匀,室温放置20 min;室温22~25℃,3 000 r/min,10 min。放入-80℃冰箱保存。
1.2.2用于Solexa测序的血清总RNA的提取将混合血清分别装于已标记的除酶的50 mL离心管中,加入TRIzol(体积为血清体积的2倍),用力震荡混匀,室温静置15 min,离心,收集上清,加入与上清等体积的异丙醇沉淀,-20℃,沉淀2 h,离心,弃上清,取沉淀,用2 mL 75% 的DEPC乙醇,逐个清洗离心管,分装到除酶的1.5 mL EP管中,离心,然后用2 mL的TRIzol逐个清洗乙醇洗涤后的离心管,将乙醇清洗液离心,去上清,取沉淀。用TRIzol清洗液再次清洗至沉淀完全溶解。加入TRIzol 1/5体积的氯仿,混匀静止10 min,离心,取上清(400~600 μL)加入等体积的异丙醇,沉淀,-20℃,2 h,离心,弃上清,取沉淀,加入1 mL 75%乙醇洗涤,涡旋后离心,弃上清,取沉淀,待沉淀干燥后,加20 μL DEPC水溶解,待沉淀溶解后,放入-80℃冰箱保存,待测序。
1.2.3Solexa测序服务由深圳华大基因科技服务有限公司提供。
1.2.4用于实时荧光定量PCR(quantitative real-time PCR,qRT-PCR)的血清RNA的提取取100 μL血清加入300 μL DEPC水中,充分震荡混匀后加入200 μL酸性酚(pH=4.7~5.5),剧烈震荡混匀后加入200 μL氯仿,再次充分震荡后,静置15 min,离心。吸取上清液(约400 μL),加入800 μL异内醇并加入醋酸钠(pH=5.2,3 M)40 μL,充分混匀,-20℃静置>2 h,离心。充分弃上淸后,加入75%乙醇1 mL,轻柔颠倒数次,离心,弃上清,室温晾干后,加入20 μL DEPC水,溶解后放入-80℃冰箱保存。
1.2.5逆转录逆转录反应体系为10 μL,在0.2 mL薄壁管中依次加入DEPC水4μL,5×AMVbuffer 2μL,dNTP mixture 1 μL,AMV酶0.5 μL,RT-Primer 0.5 μL,和RNA 2 μL充分混匀离心后置于PCR仪,设置逆转录程序为16℃30 min、42℃30 min、85℃5 min、4℃forever。
1.2.6RT-qPCRRT-qPCR反应体系为20 μL,向EP管中分别加入dd H2O 14.77 μL,10×buffer 2 μL,MgCl21.2 μL,dNTPs mixture 0.4 μL,Taq酶0.3 μL,TaqMan probe+primer 0.33 μL,和cDNA 1 μL,每个标本每种miRNA做3次重复,每块96孔板中均用已知浓度的miR-16成熟体经逆转录生成的cDNA等浓度梯度(10倍为1个阶梯)稀释后做标准曲线,设置反应程序为95℃5 min、95℃15 s、60℃l min。
1.3统计学分析
采用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计学分析。术前与术后miR-30e的表达水平采用t检验分析,以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。用miR-30e浓度的均值做为分界点,将术后所有患者的miR-30e的浓度分为两组,采用Kaplan-Meier法和Log-rank检验,并绘制生存曲线,以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1Solexa测序结果
术前术后血清中,表达量有差异的miRNA共63个。根据本研究先前的研究和其他文献的研究成果、血清样本量的多少、miRNAs表达量差异的大小,我们选出4个miRNAs做为后续RT-qPCR的验证。
2.2qRT-PCR结果
在Solexa筛选出的miRNA中,选出表达差异较大的4个miRNAs(miR-26b,miR-30e,miR-129-3p,miR-206),见表1。做qRT-PCR,逐一检测浓度,选出与Solexa结果趋势一致、术前术后浓度差异在2倍以上且差异具有统计学意义的miRNA。结果显示只有miR-30e满足条件,术前术后变化倍数为5.91,P= 3.37×10-14(表2,图1)。
2.3随访及生存分析结果
经过术后随访统计患者的生存期,根据48例GBM患者生存时间的中位数为494 d,将患者分为两组,生存时间≥494 d者为长生存期组,反之则为短生存期组。长生存期组术后血清miR-30e的表达水平较短生存期组低(图2)。以miR-30e表达水平的中位数为界点,将48例患者分为两组做生存分析及Log-rank检验。检验结果显示,术后患者血清中miR-30e表达水平与GBM患者的生存时间无明显相关性(P=0.101,图3)。

表1 筛选miRNAs的Solexa测序结果Table 1 Solexa sequencing copies of four selected miRNAs in the sera collected pre-and post-operation
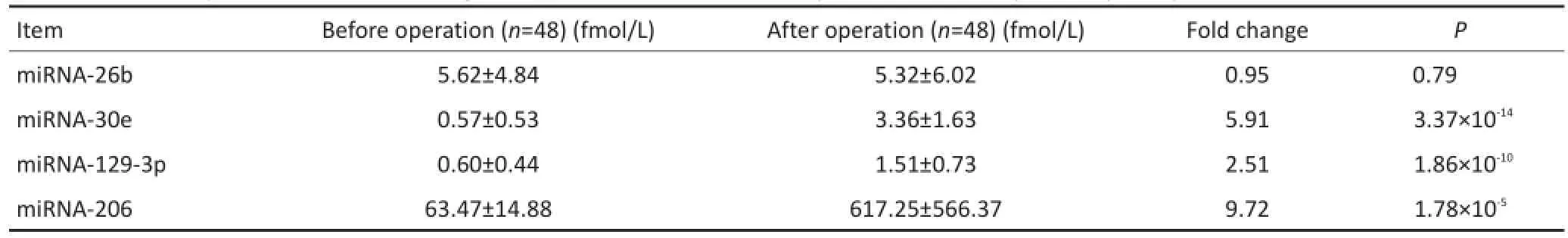
表2 48例GBM患者术前术后血清miRNAs的比较Table 2 miRNA expression levels,fold changes,and P-values of the sera of 48 patients with GBM pre-and post-operation
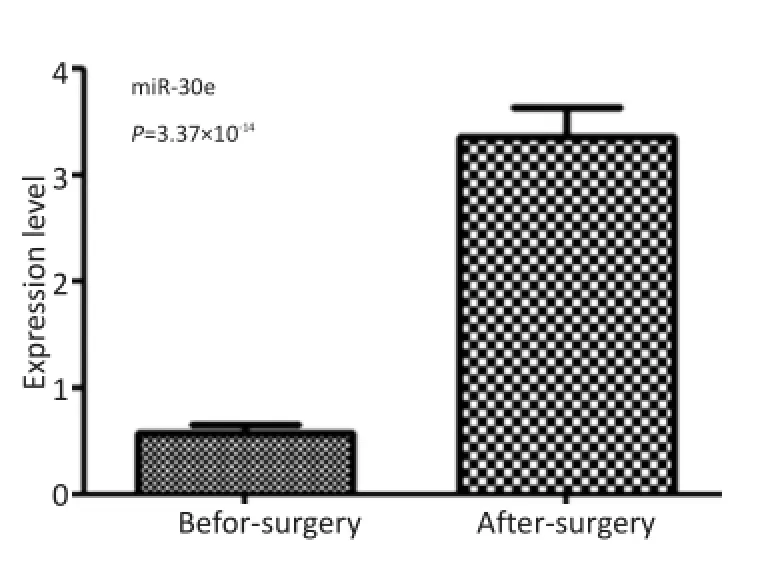
图1 48例GBM患者术前术后血清miR-30e表达水平比较Figure 1 miR-30e expression in the sera of 48 patients with GBM preand post-operation
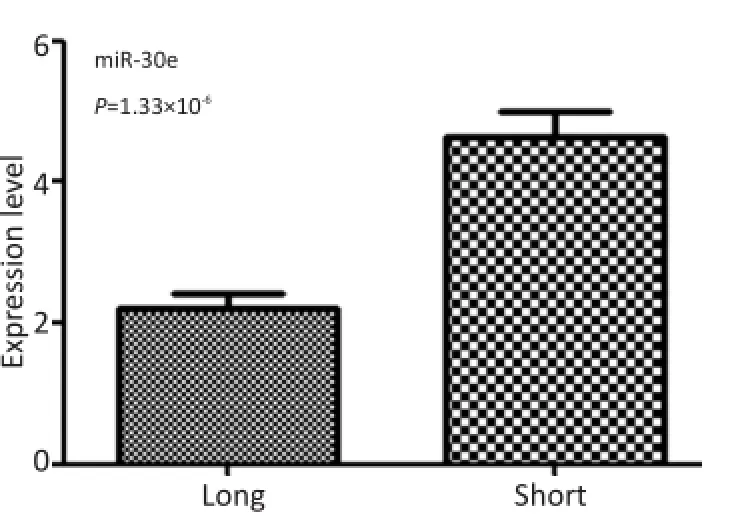
图2 24例长生存期患者和24例短生存期患者术后血清miR-30e表达水平比较Figure 2 miR-30e expression in the sera of long-(n=24)and short-(n= 24)survival patients with GBM post-operation
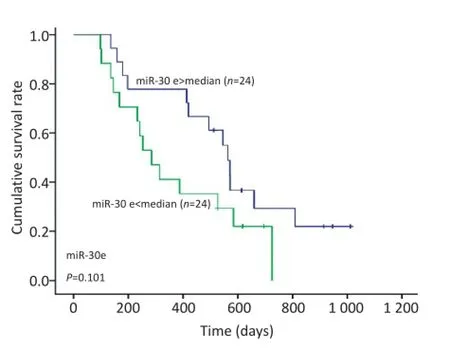
图3 48例患者术后血清中miR-30e不同表达水平生存曲线的比较Figure 3 Comparison of the survival curves of different plasma miR-30e expression levels of patients with GBM post-operation
3 讨论
近年来,血清miRNA运用于临床诊断的研究已在世界范围内广泛开展,而且在肿瘤的早期诊断上取得较大成果,并且随着检测技术的进步而获得更多的可用于疾病诊断的血清miRNA。通过与疾病相关的血清miRNA最新技术手段的规范化和商业化,使血清miRNA可能成为新的疾病诊断和预后的标志物。Hu等[3]在对非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer,NSCLC)研究中应用Solexa法对长期生存患者与短期生存患者血清miRNA进行初选,并获得11种在两组血清中均有表达,且表达差异至少为5倍的miRNA。随后该研究在使用qRT-PCR法对更多血清样本进行验证,最终发现4种具有显著差异且可用于NSCLC的生存预期的血清miRNA (miR-1、miR-30d、miR-486、miR-499)。GBM是一种最常见的中枢神经系统原发性肿瘤,是恶性程度最高的一种胶质瘤,尽管近年来肿瘤治疗的手段有很大的提高,但是GBM患者的预后仍没有明显的提高与改善。
近年来,与胶质瘤相关的miRNA的研究越来越多,集中在胶质瘤组织miRNA表达谱分析上,并在此基础上对一些特异性变化的miRNA靶标及相关功能进行研究,探讨miRNA在胶质瘤中的作用和机制。胶质瘤组织中的miRNA大体分为两种,一种是保护性的,参与“抗肿瘤”过程,另一种是风险性的,参与“促肿瘤”过程。保护性的miRNA有:miR-21[4-9]、miR-221/222[10-14]、miR-23a[15]、miR-10b[16]、miR-381[17]、miR-372[18]、miR-30e*[19]等。风险性的有:miR-34a[20-22],miR-146a[23],miR-124,miR-128,miR-146b,miR-218[24]、miR-326[25]、miR-885-5p、miR-491-5p[26]、miR-25、miR-32[27]等。
关于GBM患者血清中的miRNAs的研究相对较少。血清中的miR-21、miR-128和miR-342-3p的表达水平与正常对照组相比有很大的差异。通过这3 个miRNAs可以区分出GBM患者与非GBM患者,且具有相当高的灵敏性和特异性。这3个miRNAs在接受手术和放化疗后都恢复到正常水平。miR-128和miR-342-3p与胶质瘤的病理级别关系呈正相关。利用循环miRNAs稳定的特点,通过高通量、涵盖广的miRNAs芯片技术,分析发现19个GBM患者血浆中差异表达在1.5倍以上的miRNAs,其中3个表达上调,16个表达下调。这些差异表达的miRNAs可为早期诊断提供非侵入性的筛选方法。此外,miR-30c-2-3p高表达与GBM患者不良预后相关[28]。目前,细胞外miRNAs的来源尚未完全清楚。部分研究者认为,细胞外的miRNAs是通过微囊泡的形式从细胞中释放出来。有研究也证明出胶质瘤细胞也释放含有miRNAs的微囊泡[29]。这些微囊泡的直径在50~500nm之间。然而,也有研究认为,这些细胞外的miRNAs是以与蛋白结合成复合物的形式存在,而不是存在于微囊泡中。综合以上结论,本研究推测,GBM患者血清中的miRNAs可能是从胶质瘤细胞中分泌出来后,通过某种机制(尚未确定)中部分破坏的血脑屏障,进入血液循环。有趣的是,一些miRNAs在不同体液中的表达水平不同。由于血脑屏障的存在,系统的研究胶质瘤患者血清中miRNAs的来源,及其与组织中miRNAs之间的关系是十分有必要的。
miR-30e定位于1号染色体的1p34.2[29],被认为是放疗诱导的miR-30e,通过促进细胞基质金属蛋白酶MMP-2,来提高胶质瘤细胞的侵袭性。这一过程还伴随着EGFR的上调,和下游一些生物活性物质的激活,EGFR的上调是由于miR-30e增强EGFR蛋白的稳定性[30]。miR-30e还有许多其他功能,包括:促进放疗后神经胶质细胞的增殖,负性调节NK细胞的细胞毒性,调节转录生长因子β诱导的细胞外基质的陈生,互相调节成骨细胞及脂肪细胞的分化[31-32]。在其他肿瘤中,miR-30e的功能是多种多样的。在多种肿瘤中,miR-30e已经被证明是肿瘤抑制因子。miR-30e在慢性髓系白血病(chronic myeloid leukemia,CML)细胞系与患者组织中低表达,通过下调BCR-ABL的表达抑制肿瘤细胞的增值,诱导凋亡,增加治疗敏感性[33]。在乳腺癌的标本中,miR-30e的表达量是下降的,而外源性的在多种肿瘤中,miR-30e已经被证明是肿瘤抑制因子。可抑制乳腺癌细胞的增值。在肺癌组织中,miR-30e的表达量下降,而外源性的miR-30e可抑制细胞的生长,发挥抑癌基因的作用[34]。在鼻咽癌组织中,miR-30e联合其他4个miRNAs,有判断预后的作用,且miR-30e与鼻咽癌的无疾病生存期关系呈正相关[35]。已有研究证明GBM细胞可释放MVs。根据本研究结果假设推论,术后GBM患者血清中miR-30e水平较术前上升的原因可能为GBM细胞可能通过某种未知机制抑制miR-30e的产生或抑制其释放入血,术后这种抑制作用被解除,大量含有miR-30e的微囊泡释放入血。而复发时血清中的miR-30e的水平很可能会相应降低,这使得miR-30e可能成为预测GBM患者复发的潜在生物学标志物。
因此本研究收集48例GBM患者术前和术后血清miRNA,采用Solexa技术和RT-qPCR技术对这些样本进行筛选和逐一检测,并进行统计学分析最后得出结论。可以应用患者术后血清中miR-30e的表达水平检测术后患者的肿瘤负荷情况,从而初步判断患者的预后。目前对于血清miRNA的研究还处于起步阶段,随着对血清miRNA的作用机制研究的深入,也会促进对血清miRNA与相应疾病之间生理生化关系的认识。进而明确血清miRNA在疾病发生发展中的具体作用。
[1]Adamson C,Kanu OO,Mehta AI,et al.Glioblastoma multiforme:a review of where we have been and where we are going[J].Expert Opin Investig Drugs,2009,18(8):1061-1083.
[2]Liu R,Chen X,Du Y,et al.Serum microRNA expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer[J]. Clin Chem,2012,58(3):610-618.
[3]Hu Z,Chen X,Zhao Y,et al.Serum microRNA signatures identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling predict survivalof non-small cell lung cancer[J].Clin Oncol,2010,28(10):1721-1726.
[4]Hermansen SK,Dahlrot RH,Nielsen BS,et al.MiR-21 expression in the tumor cell compartment holds unfavorable prognostic value in gliomas[J].J Neurooncol,2013,111(1):71-81.
[5]Han L,Yue X,Zhou X,et al.MicroRNA-21 expression is regulated by β-catenin/STAT3 pathway and promotes glioma cell invasion by direct targeting RECK[J].CNS Neurosci Ther,2012,18(7):573-583.
[6]Gwak HS,Kim TH,Jo GH,et al.Silencing of microRNA-21 confers radio-sensitivity through inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway and enhancing autophagy in malignant glioma cell lines[J].PLoS One,2012,7(10):e47449.
[7]Wang J,Li Y,Wang X,et al.Ursolic acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma cell lines U251 by suppressing TGF-β1/miR-21/PDCD4 pathway[J].Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol,2012,111(2):106-112.
[8]Zhang S,Wan Y,Pan T,et al.MicroRNA-21 inhibitor sensitizes human glioblastoma U251 stem cells to chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide[J].J Mol Neurosci,2012,47(2):346-356.
[9]Qian X,Ren Y,Shi Z,et al.Sequence-dependent synergistic inhibition of human glioma cell lines by combined temozolomide and miR-21 inhibitor gene therapy[J].Mol Pharm,2012,9(9):2636-2645.
[10]Galardi S,Mercatelli N,Farace MG,et al.NF-kB and c-Jun induce the expression of the oncogenic miR-221 and miR-222 in prostate carcinoma and glioblastoma cells[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2011,39(9):3892-3902.
[11]Quintavalle C,Garofalo M,Zanca C,et al.miR-221/222 overexpession in human glioblastoma increases invasiveness by targeting the protein phosphate PTPμ[J].Oncogene,2012,31(7):858-868.
[12]Hao JW,Zhang CZ,Zhang AL,et al.miR-221/222 is the regulator of Cx43 expression in human glioblastoma cells[J].Oncol Rep,2012,27(5):1504-1510.
[13]Zhang C,Zhang J,Hao J,et al.High level of miR-221/222 confers increased cell invasion and poor prognosis in glioma[J].J Transl Med,2012,10(1):1-11.
[14]Chen L,Zhang J,Han L,et al.Downregulation of miR-221/222 sensitizes glioma cells to temozolomide by regulating apoptosis independently of p53 status[J].Oncol Rep,2012,27(3):854-860.
[15]Tan X,Wang S,Zhu L,et al.cAMP response element-binding protein promotes gliomagenesis by modulating the expression of oncogenic microRNA-23a[J].ProcNatlAcadSciUSA,2012,109(39):15805-15810.
[16]Sun L,Yan W,Wang Y,et al.MicroRNA-10b induces glioma cell invasion by modulating MMP-14 and uPAR expression via HOXD10[J]. Brain Res,2011,1389(7):9-18.
[17]Tang H,Liu X,Wang Z,et al.Interaction of hsa-miR-381 and glioma suppressor LRRC4 is involved in glioma growth[J].Brain Res,2011,1390(20):21-32.
[18]Li G,Zhang Z,TuY,et al.Correlationof microRNA-372upregulationwith poor prognosis in human glioma[J].Diagn Pathol,2013,8(1):e28.
[19]Jiang L,Lin C,Song L,et al.MicroRNA-30e*promotes human glioma cell invasiveness in an orthotopic xenotransplantation model by disrupting the NF-κB/IκBα negative feedback loop[J].J Clin Invest,2012,122(1):33-47.
[20]Sun L,Wu Z,Shao Y,et al.MicroRNA-34a suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in U87 glioma stem cells[J].Technol Cancer Res Treat,2012,11(5):483-490.
[21]Silber J,Jacobsen A,Ozawa T,et al.miR-34a repression in proneural malignant gliomas upregulates expression of its target PDGFRA and promotes tumorigenesis[J].PLoS One,2012,7(3):e33844.
[22]Yu X,Zhang W,Ning Q,et al.MicroRNA-34a inhibits human brain glioma cell growth by down-regulation of Notch1[J].Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology-Medical Sciences,2012,32(3):370-374.
[23]Mei J,Bachoo R,Zhang CL.MicroRNA-146a inhibits glioma development by targeting Notch1[J].Mol Cell Biol,2011,31(17):3584-3592.
[24]Bo Y,Guo G,Yao W.MiRNA-mediated tumor specific delivery of TRAIL reduced glioma growth[J].J Neurooncol,2013,112(1):27-37.
[25]Wang S,Lu S,Geng S,et al.Expression and clinical significance of microRNA-326 in human glioma miR-326 expression in glioma[J]. Med Oncol,2013,30(1):373.
[26]Yan W,Zhang W,Sun L,et al.Identification of MMP-9 specific microRNA expression profile as potential targets of anti-invasion therapy in glioblastoma multiforme[J].Brain Res,2011,1411(1):108-115.
[27]Suh SS,Yoo JY,Nuovo GJ,et al.MicroRNAs/TP53 feedback circuitry in glioblastoma multiforme[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2012,109 (14):5316-5321.
[28]Wang ZQ,Wang HY,Deng ML,et al.Plasma MicroRNA expression profiles in glioblastoma[J].The Practical Journal of Cancer,2015,30 (4):475-478.[汪志强,王辉云,邓美玲,等.胶质母细胞瘤患者血浆miRNA表达谱研究[J].实用癌症杂志,2015,30(4):475-478.]
[29]Zhang R,Wang YQ,Su B.Molecular evolution of a primate-specific microRNA family[J].Mol Biol Evol,2008,25(7):1493-1502.
[30]Kwak SY,Kim BY,Ahn HJ,et al.Ionizing radiation-inducible miR-30e promotes glioma cell invasion through EGFR stabilization by directly targeting CBL-B[J].FEBS J,2015,282(8):1512-1525.
[31]Jiang L,Qiu W,Zhou Y,et al.A microRNA-30e/mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 axis mediates TGF-β1-induced tubular epithelial cell extracellular matrix production and kidney fibrosis[J].Kidney Int,2013,84(2):285-296.
[32]Wang J,Guan X,Guo F,et al.miR-30e reciprocally regulates the differentiation of adipocytes and osteoblasts by directly targeting lowdensity lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6[J].Cell Death Dis,2013,4(10):e845.
[33]Hershkovitz-Rokah O,Modai S,Pasmanik-Chor M,et al.MiR-30e induces apoptosis and sensitizes K562 cells to imatinib treatment via regulation of the BCR-ABL protein[J].Cancer Lett,2015,356(2):597-605.
[34]Wu F,Zhu S,Ding Y,et al.MicroRNA-mediated regulation of Ubc9 expression in cancer cells[J].Clin Cancer Res,2009,15(5):1550-1557.
[35]Liu N,Chen NY,Cui RX,et al.Prognostic value of a microRNA signature in nasopharyngeal carcinoma:a microRNA expression analysis [J].Lancet Oncol,2012,13(6):633-641.
(2016-04-08收稿)
(2016-06-07修回)
(编辑:孙喜佳校对:郑莉)
Serum microRNA profiles as novel biomarkers for the post-operative evaluation and survival of patients with glioblastoma multiform
Xiujuan GAO1,Xi CHEN2,Wei YAN3,4,Jingjing YIN5,Yi BA1
Correspondence to:Yi BA;E-mail:yiba99@yahoo.com
1Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology,Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital,National Clinical Research Center for Cancer,Tianjin Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy,Tianjin 300060,China;2State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology,Nanjing University,Nanjing 210093,China;3First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University,Nanjing,210000,China;4Beijing Tiantan Hospital,Beijing 100050,China;5Aerospace Central Hospital,Beijing 100049,China
Objective:To investigate the differentially expressed miRNAs in serum collected post operation and compared these miRNAs with those collected pre-surgery among patients suffering from glioblastoma multiform(GBM)and undergoing regular clinical follow-up.These miRNAs may be potential biomarkers for the post-operative evaluation of patients with GBM.Methods:Forty-eight patients with GBM and clinical pathological diagnosis were enrolled in this study.In the initial biomarker screening stage,total RNAs were extracted and subjected to Solexa sequencing to select miRNAs with significantly altered expression pre-and post-operation. Some of these differentially expressed miRNAs were chosen and verified through TaqMan probe-based qRT-PCR assay.A t-test was performed to determine the miRNAs that satisfied the two criteria,namely,fold change>2 and P<0.05.All of the patients were followed-up,and survival data were collected.The patients were then classified into two groups,namely,long-and short-survival groups,on the basis of the median of the miR-30e expression levels in the sera collected post-operation.Kaplan-Meier method and Log-rank test(SPSS version 19.0,IBM)were employed to determine the possible relationships between miR-30e expression levels in the sera collected post-operation and patients'overall survival.Results:Solexa revealed 63 differentially expressed miRNAs.Four miRNAs,namely,miR-26b,miR-30e,miR-129-3p,and miR-206,were selected on the basis of previous and present findings.These miRNAs were then verified in the RT-qPCR phase.Among these miRNAs,only miR-30e was significantly upregulated post-operation.The serum miR-30e expression level post-operation was not significantly associated with the overall survival of the patients.A low miR-30e expression level corresponded to prolonged survival.Conclusion:miR-30e was upregulated in the sera collected post-operation from patients with GBM.This miRNA may be negatively related to the tumor load of these patients.The miR-30e expression level in the serum col-lected post-surgery serum was not significantly associated with overall survival.Therefore,miR-30e may serve as a novel potential noninvasive biomarker for the post-operative evaluation of patients with GBM.
serum miRNA,GBM,biomarker,post-operative evaluation,miR-30e
10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2016.13.395
①天津医科大学肿瘤医院消化肿瘤科,国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心,天津市肿瘤防治重点实验室(天津市300060);②南京大学医药生物技术国家重点实验室;③南京医科大学第一附属医院;④北京天坛医院;⑤北京航天中心医院
巴一yiba99@yahoo.com

高秀娟专业方向为肿瘤的早期诊断与治疗。E-mail:xiujuangaodoctor@163.com
