肝素结合表皮生长因子对肝移植模型大鼠肝脏炎症因子及细胞再生的影响
2016-06-27周立新苏继钦王茂林严辉弟林培艺
周立新,苏继钦,王茂林,严辉弟,林培艺
厦门市第二医院肝胆外科,福建厦门361021
肝素结合表皮生长因子对肝移植模型大鼠肝脏炎症因子及细胞再生的影响
周立新,苏继钦,王茂林,严辉弟,林培艺
厦门市第二医院肝胆外科,福建厦门361021
目的 研究肝素结合表皮生长因子(heparin⁃binding epidermal growth factor⁃like growth factor,HB⁃EGF)对肝移植模型大鼠肝脏炎症因子及细胞再生的影响。方法 选择60只SD雄性大鼠并建立肝移植动物模型,随机分为A、B、C三组,B组皮下注入0.1 mg/kg肝细胞生长因子,C组皮下注射0.1 mg/kg HB⁃EGF,A组给予相等剂量生理盐水进行干预。干预后第1、3、5、7天时,比较三组肝脏湿重、肝功能、炎性因子含量。结果 干预后第1、3、5、7天时,B组、C组大鼠移植肝脏的湿重均明显高于A组(P<0.05),血清丙氨酸氨基转氨酶(ALT)、总胆红素(TBIL)含量均明显低于A组(P<0.05);干预后第3、5、7天时,B组、C组血清白蛋白(ALB)含量明显高于A组(P<0.05);干预后第1、3、5、7天时,B组、C组大鼠肝脏组织中肿瘤坏死因子⁃α(TNF⁃α)、白细胞介素⁃6(IL⁃6)含量均明显低于A组(P<0.05);C组大鼠肝脏组织中TNF⁃α、IL⁃6含量明显低于B组(P<0.05)。结论 HB⁃EGF能促进肝移植模型大鼠肝细胞再生,其作用机制可能与保护肝功能、减轻炎症反应有关。
肝移植;肝细胞生长因子;肝素结合表皮生长因子;细胞再生;炎症因子
活体肝移植是目前临床上治疗终末期肝脏疾病的主要方式,但受到移植后免疫排异反应、炎症反应、缺血再灌注损伤等因素的影响,移植后肝脏的存活率并不理想,肝脏损伤的发生风险也较高[1]。近年来关于肝移植的研究中,供体肝脏与受体间比例不匹配是造成肝移植术后肝功能损伤的关键环节,供体肝脏的体积越小、移植后的损伤程度越重[2]。因此,移植后早期需要促进肝脏迅速再生以降低供体肝脏与受体间不匹配的程度[3]。肝素结合表皮生长因子(heparin binding epidermal growth factor⁃like growth factor,HB⁃EGF)是EGF家族的重要成员,对成熟肝细胞的分裂及增殖具有促进作用。本研究中,我们分析了HB⁃
EGF对肝移植模型大鼠肝脏炎症因子及细胞再生的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试剂与仪器 肝细胞生长因子(hepatocyte growth factor,HGF):肝乐宁注射液,长春普华制药股份有限公司,批准文号:国药准字H20054108;规格2 ml。HB⁃EGF:美国Barnstead公司;全自动生化分析仪:日本O⁃lympus Au型;多功能酶标仪:美国Bio⁃rad公司El312e Microplate;低温高速离心机:美国贝克曼库尔特有限公司Allegra 64R型;及配套试剂购买于Roche公司,Ki⁃67、TNF⁃α、IL⁃6酶联免疫吸附试剂盒购买于Ebio⁃science公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 实验动物:供体动物和受体动物均为雄性清洁级SPF大鼠,体质量200~250 g,共60只,随机分为A组(生理盐水组)、B组(HGF组)、C组(HB⁃EGF组)各20只。三组大鼠均建立肝移植动物模型,B组给予0.1 mg/kg皮下注入肝细胞生长因子(1次/d),C组皮下注射0.1 mg/kg HB⁃EGF(1次/d),A组给予相等剂量生理盐水进行干预。
1.2.2 保留肝脏30%动物模型建立:三组大鼠均按照改良的二袖套法建立原位部分肝移植模型,在供体大鼠上切取供体肝脏,切除肝左叶、右叶、两片尾叶及肝中叶镰状韧带左侧的部分,保留肝脏占全肝重量的约30%;切除受体大鼠的肝脏,并将供体肝脏移植进入受体大鼠体内,缝合血管。
1.2.3 肝脏湿重:干预后第1、3、5、7天时,每组大鼠各取5只处死,称重后用生理盐水清洗肝脏,经液氮冷冻后放置在-80℃冰箱保存。
1.2.4 肝功能:干预后第1、3、5、7天时,每组大鼠各取5只处死,自肝下腔静脉取血5 ml,3 000 r/min离心10 min(离心半径r=3 cm),采用全自动生化分析仪测定丙氨酸氨基转氨酶(alanine aminotransferase,ALT)、白蛋白(albumin,ALB)、总胆红素(total bilirubin,TBIL)含量。
1.2.5 炎性因子:干预后第1、3、5、7天时,每组大鼠各取5只处死,取出肝脏组织,称量适量组织并加入PBS研磨,将研磨液放置在4℃离心机中离心,弃去残渣、保留上清并采用酶联免疫吸附试剂盒测定肿瘤坏死因子⁃α(tumor necrosis factor⁃α,TNF⁃α)、白细胞介素⁃6(interleukin⁃6,IL⁃6)的含量。
1.3 统计学方法 采用SPSS 20.0软件进行统计学分析,计量资料用x ±s表示,不同时间、多组间比较采用方差分析,两两比较采用配对t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 肝脏湿重 干预后第1、3、5、7天时,B组、C组大鼠移植肝脏的湿重均显著高于A组(P<0.05),B、C两组间移植肝脏的湿重比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表1)。
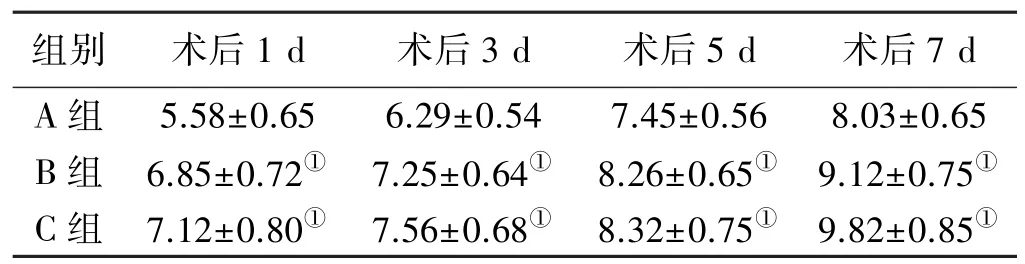
表1 三组大鼠移植肝脏湿重的比较(x ±s,g)Tab 1 Comparison of wet weight of liver transplantation in rats among three groups(x ±s,g)
2.2 肝功能 干预后第1、3、5、7天时,B组与C组大鼠的血清ALT、TBIL含量均明显低于A组(P<0.05),移植后3 d、5 d、7 d时,B组、C组血清ALB含量明显高于A组(P<0.05);B、C两组不同时点ALT、ALB、TBIL含量比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表2)。
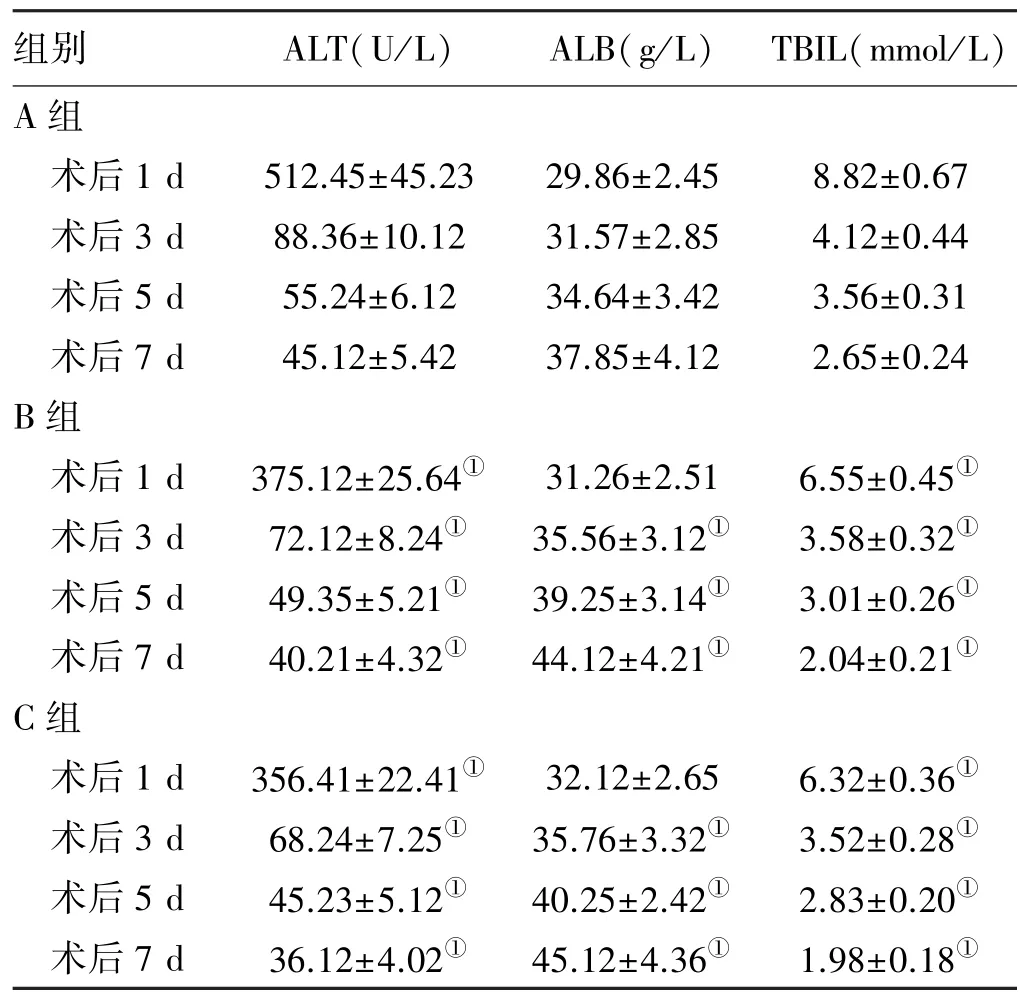
表2 三组大鼠不同时点ALT、ALB、TBIL含量比较(x±s)Tab 2 Comparison of ALT,ALB and TBIL in rats among three groups in different time(x±s)
2.3 肝脏组织中炎症因子含量 干预后第1、3、5、7天时,B组、C组大鼠肝脏组织中TNF⁃α、IL⁃6含量均明显低于A组(P<0.05),C组大鼠肝脏组织中TNF⁃α、IL⁃6含量明显低于B组(P<0.05,见表3)。

表3 三组大鼠不同时点肝脏组织中TNF⁃α、IL⁃6含量比较(x ±s,ng/ml)Tab 3 Comparison of TNF⁃α and IL⁃6 in rats among three groups in different time(x ±s,ng/ml)
3 讨论
供体肝脏与受体比例不匹配是造成肝移植后肝功能损伤、移植物不存活的重要原因。有研究[4]证实,肝移植物损伤的程度与自身体积及重量具有负相关关系,即移植肝脏的重量越大、移植后损伤程度越轻。此外,肝脏移植后受到免疫排异反应、炎症反应、缺血再灌注损伤等因素的影响会出现再生能力受损,细胞再生不足也会造成移植物功能损伤。因此,促进肝移植后肝脏的快速再生能够减轻肝功能损伤[5]。肝细胞生长因子HGF在肝再生过程中发挥着重要的作用,肝切除后输入外源性HGF,可加速肝修复[6]。HB⁃EGF是EGF家族中的新成员,对成熟肝细胞的分裂过程具有促进作用,在肝细胞的再生过程中发挥关键作用[7]。本研究中,干预后第1、3、5、7天时,B、C两组大鼠移植肝脏的湿重显著高于A组,说明HGF、HB⁃EGF能够促进移植肝脏组织的生长、增加移植肝脏组织的重量。
肝脏移植后,肝细胞的再生能够保护移植物、减轻组织损伤[8]。ALT是位于肝细胞内的转氨酶,肝细胞的损伤和破裂会造成ALT大量释放进入血液循环;ALB水平反映肝脏合成功能,当肝脏病变达到一定程度时,ALB会呈一定程度的下降;TBIL大部分来自衰老红细胞裂解释放的血红蛋白,其水平异常升高多提示肝功能受损[9⁃10]。本研究中,B、C两组血清ALT、TBIL含量均明显低于A组,ALB含量明显高于A组,国内学者高银杰等[11]也有类似的文献报道,提示外源性细胞生长因子、HB⁃EGF均能减轻移植组织肝细胞的损伤。
肝移植后造成供体肝脏损伤、影响细胞再生的主要途径包括缺血再灌注损伤、免疫排斥反应、炎症反应等[12],而局部组织中炎症因子的大量合成和释放是多种途径的共同作用方式,TNF⁃α、IL⁃6是两类重要的炎症因子[13]。TNF⁃α来自激活的单核巨噬细胞、中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞,通过与靶细胞表面的受体结合来促进炎症反应的级联放大[14];IL⁃6由单核巨噬细胞、T细胞、成纤维细胞分泌,具有多种生物学功能,是急性反应过程中最敏感的介质。本研究中,C组大鼠肝脏组织中TNF⁃α、IL⁃6含量均明显高于A组、B组,说明HB⁃EGF能够抑制移植肝脏中炎症因子的生成,有助于减轻局部组织中的炎症反应。
本研究结果表明,HB⁃EGF能够促进肝移植模型大鼠肝脏组织再生,其作用机制可能与保护肝功能、减轻炎症反应等有关。需要指出的是,本文观察指标相对较少,未对肝再生率进行比较研究,且缺乏对可能作用机制的深入分析,有待于今后展开更多的基础研究与临床研究去证实。
[1]Tanaka S,Iimuro Y,Hirano T,et al.Prediction of postoperative he⁃patic failure after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma:signifi⁃cance of the aspartate aminotransferase⁃to⁃platelet ratio index[J].Hepatogastroenterology,2014,61(131):755⁃761.
[2]Kobayashi K,Hattori N,Manabe O,et al.Postoperative assessment of hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptor function with Tc⁃99m GSA:the safety margin of resection size in living donor liver transplantation[J].Ann Transplant,2015,20:51⁃58.
[3]刘剑绒,杨扬,张英才,等.HGF与CTLA⁃4Ig双基因修饰增强脐带间充质干细胞的免疫抑制和促增殖作用[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2012,33(6):709⁃715,722.Liu JR,Yang Y,Zhang YC,et al.Enhanced immunomodulatory and pro⁃proliferation properties of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells modified by HGF⁃gene and CTLA⁃4Ig⁃gene[J].Journal of Sun Yat⁃sen University(Medical Sciences),2012,33(6):709⁃715,722.[4]Fang H,Liu A,Dirsch O,et al.Liver transplantation and inflamma⁃tion:is lipopolysaccharide binding protein the link?[J].Cytokine,2013,64(1):71⁃78.
[5]Hernandez⁃Alejandro R,Zhang X,Croome KP,et al.Reduction of liver ischemia reperfusion injury by silencing of TNF⁃α gene with shRNA[J].J Surg Res,2012,176(2):614⁃620.
[6]应佳丽,王雪玲,范丽娇,等.aFGF、HGF体外诱导小鼠ESC向肝细胞定向分化及标志物研究[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2014,23(11):1305⁃130.Ying JL,Wang XL,Fan LJ,et al.Study of hepatic differentiation in vitro from mouse ESC induced with aFGF and HGF and the expression of hepatic biomakers[J].Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2014,23(11):1305⁃130.
[7]杨焱,李相成,王学浩.肝素结合的类表皮生长因子促进大鼠减体积肝移植术后移植肝细胞的再生[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2008,15(3):155⁃158.Yang Y,Li XC,Wang XH.Promoting Regeneration effect of heparin binding epidermal growth factor⁃like growth factor on rat hepatocytes af⁃ter partial orthotopic liver transplantation[J].Chin J Bases Clin General Surg,2008,15(3):155⁃158.
[8]史艳敏,曲红岩,魏洁.肠内外营养支持对肝衰竭病人肝移植术后营养状况、肝功能及炎性反应的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(2):375⁃377.Shi YM,Qu HY,Wei J.Effect of enteral and parenteral nutrition sup⁃port on nutritional status,liver function and inflammatory response after liver transplantation in patients with liver failure[J].Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2016,36(2):375⁃377.
[8]罗桂金,雷平光.人脐带间充质干细胞辅助治疗对乙肝肝硬化患者肝功能、纤维化指标及炎症程度的影响[J].海南医学院学报,2016,22(11):1069⁃1072.Luo GJ,Lei PG.Effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell adjuvant therapy on liver function and fibrosis indicators as well as the degree of inflammation in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis[J].Journal of Hainan Medical University,2016,22(11):1069⁃1072.
[9]Vondran FW,Schumacher C,Johanning K,et al.Application of the liver maximum function capacity test in acute liver failure:a helpful tool for decision⁃making in liver transplantation?[J].Case Rep Trans⁃plant,2016,2016:7074636.
[10]Zhou B,Fan Y,Rao J,et al.Matrix metalloproteinases⁃9 deficiency impairs liver regeneration through epidermal growth factor receptor sig⁃naling in partial hepatectomy mice[J].J Surg Res,2015,197(1):201⁃209.
[11]高银杰,张敏,苏海滨,等.肝移植后乙肝复发患者肝内CD3+、CD4+、CD8+、CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞(Treg)的表达和研究[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2012,21(10):923⁃926.Gao YJ,Zhang M,Su HB,et al.Expression and research of intrahe⁃patic CD3+,CD4+,CD8+,CD4+CD25+regulatory T cell(Treg)in patients with HBV recurrence after liver transplantation[J].Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2012,21(10):923⁃926.
[12]贾莉莉,喻文立,翁亦齐,等.肝移植患者新肝期血清炎症因子的变化及其对心肌损伤的机制研究[J].实用器官移植电子杂志,2015,3(6):354⁃356.Jia LL,Yu WL,Weng YQ,et al.The study of the changes of the in⁃flammatory mediators and myocardial injury during the neohepatic stage in patients undergoing liver transplantation[J].Pract J Organ Transplant(Electronic Version),2015,3(6):354⁃356.
[13]赵德芳,陈立坤.单纯冷藏与低温机械灌注保存肝移植前后炎症因子和凋亡因子的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(33):5322⁃5326.Zhao DF,Chen LK.Static cold storage versus hypothermic machine perfusion:changes in inflammatory cytokines and apoptotic factors in isolated liver before and after liver transplantation[J].Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2015,19(33):5322⁃5326.
[14]罗刚健,池信锦,张瑷兰,等.大鼠自体原位肝移植肺组织TNF⁃α、IL⁃1β和IL⁃6的表达[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2012,33(4):444⁃448.Luo GJ,Chi XJ,Zhang AL,et al.TNF⁃α,IL⁃1β and IL⁃6 genes transplantation and expression level of lung tissue in rats experienced orthotopic autologus liver transplantation[J].Journal of Sun Yat⁃sen University(Medical Sciences),2012,33(7):444⁃448.
(责任编辑:王全楚)
Effect of heparin binding epidermal growth factor⁃like growth factor on hepatic in⁃flammatory cytokines and cell regeneration in rat liver transplantation model
ZHOU Lixin,SU Jiqin,WANG Maolin,YAN Huidi,LIN Peiyi
Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery,the Second Hospital of Xiamen,Xiamen 361021,China
Objective To study the effect of heparin binding epidermal growth factor⁃like growth factor(HB⁃EGF)on hepatic inflammatory cytokines and cell regeneration in rat liver transplantation model.Methods Sixty male SD rats were established animal model of liver transplantation,and randomly divided into group A,group B,group C.Group B subcutaneous injection 0.1 mg/kg hepatocyte growth factor,group C subcutaneous injection 0.1 mg/kg HB⁃EGF,group A was given equal dose of normal saline to intervene.On the 1st,3rd,5th,7th day after intervention,liver wet weight,liver function,liver inflammatory cytokines levels were compared among three groups.Results On the 1st,3rd,5th,7th day after intervention,rats liver wet weight in group B,group C were significantly higher than those in group A(P<0.05).Serum ALT,TBIL were significantly lower than those in group A(P<0.05);on the 3rd,5th,7th day after inter⁃vention,serum ALB in group B,group C was significantly higher than that in group A(P<0.05);on the 1st,3rd,5th,7th day after intervention,liver tissue TNF⁃α,IL⁃6 in group B,group C were signficantly lower than those in group A(P<0.05);liver tissue TNF⁃α,IL⁃6 in group C were signficantly lower than those in group B(P<0.05).Conclusion HB⁃EGF can promote liver transplantation model of rat liver cell regeneration,the mechanism may be related to the pro⁃tection of liver function,and the reduction inflammation reactions.
Liver transplantation;Hepatocyte growth factor;Heparin binding epidermal growth factor⁃like growth factor;Cell regeneration;Inflammatory factors
R575
A
1006-5709(2016)12-1463-04
2016⁃02⁃21
10.3969/j.issn.1006⁃5709.2016.12.047
厦门市科技计划指导性项目(3502Z20139012)
周立新,博士,主任医师,硕士导师,研究方向:肝胆外科临床及基础研究。E⁃mail:zhoulix318@163.com
