Comparison of Different Finite Element Modeling M ethods for the Soil-Pile Interaction of Jack-up Platform
2016-05-15XUGengYANRenjun
XU Geng,YAN Ren-jun
(Key Laboratory of High Performance Ship Technology of Ministry of Education,Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430063,China)
Comparison of Different Finite Element Modeling M ethods for the Soil-Pile Interaction of Jack-up Platform
XU Geng,YAN Ren-jun
(Key Laboratory of High Performance Ship Technology of Ministry of Education,Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430063,China)
The main purpose of this study is to develop a correct way to simulate the pile-soil system of the jack-up platform.The characteristics of the interaction between the platform pile legs and pile soil are illustrated.A complete finite element model of jack-up platform is numerically simulated by general finite element software ANSYS,and adopting three modeling methods to simulate the pile-soil system of jack-up platform.The accuracy and feasibility of these three modeling methods are discussed by the comparison between the obtained results and the sample data.
finite element;soil-pile interaction;contact element;spring element;p-y curve
0 Introduction
In the process of installation and operation of jack-up platform,the pile legs may also be subject to transient or cyclic lateral loads arising from earthquake,wind,wave,current,impact,or machine loading and so on,therefore,the mechanical properties of pile legs straightly influence the stability and the security of the jack-up platform[1].The strength analysis about the pile leg has realistic engineering significance.
Kinematic and inertial interaction constitutes a complex and unique phenomenon referred to as soil-pile-structure interaction,and due to the discontinuity of the pile-soil contact surface and the nonlinear property of soil,analysis of pile-soil interaction is a rather complex subject that is still being researched in engineering.
Over the past 20 years,various approaches have been used for the dynamic response analysis of pile-supported structures.In the early stage,geotechnical model test was the only tool in this study.The soil-pile interaction problem has also been investigated by using the shaking table test[2-3]and the centrifuge test[4-5].With the development of computer technology,FE (finite element)method was introduced into this study.Different models of soil-pile system are proposed,and they are usually characterized by the different ways of treating the soil medium in analyses[6-8].However,most of the former researches are in bridges and other civil engineeringworks,in the field of offshore jack-up platform,the related researches are very few.In this context,we use traditional simplified modeling method,contact element modeling method and spring element modeling method to simulate the pile-soil system of a jack-up platform respectively,the result analysis and comparisons are given.
1 M odeling methods of soil-pile system s
1.1 Mechanism of soil-pile interaction problem
The loads are transmitted from main body to the pile soil by the embedded pile foundation and cause the compression and deformation to the soil around[9].The deformation between the pile leg and the soil is inconsistent,so the deformation difference could lead up to a large contact stress and relative displacement.On the other hand,the displacement of pile leg is restricted by the friction between the pile leg and the soil.According to the deformation compatibility,the pile and soil can work together to transient the loads from main body.
This problem includes a number of parameters,such as the soil stratigraphy and properties,the non-linear stress-strain behavior of the soil and pile(material nonlinearity)and the geometrical nonlinearities(separation and slippage).
1.2 Traditional simplified method
In traditional simplified method,the soil-pile-structure interaction is simplified into a kind of boundary condition:the top ends of piles are fixed to a rigid cap in FE analysis(see Fig.1 and Fig.3).
For example,in CCS specification:the pile leg under 3m depth from the soil surface should be fixed constraint[10].Since the loaded piles are designed to resist stresses induced only by the environment and superstructure while neglecting the effects of kinematic interaction. However,this method does not involve the complicate interaction problem.
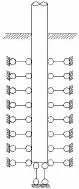
Fig.1 The boundary condition of traditional method

Fig.2 Contact element of pile-soil interaction
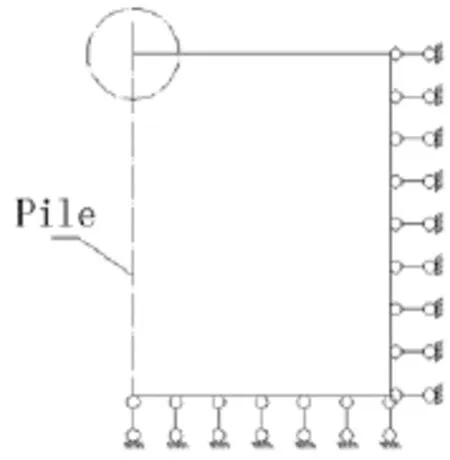
Fig.3 The boundary condition of traditional method
1.3 Contact element method
In this model the calculations of the site response and the soil-pile-structure interaction are performed in a fully coupled manner.The key point of the method is to set contact elements (rigid target surface element and flexible contact surface element)in the pile-soil contact sur-face(see Fig.2).In this modeling method,the soil should be modeled in entity,and constrained the boundary of soil entity.
ANSYS software use Coulomb friction model to simulate the contact surface.There is no slippage if the equivalent shear stress τeqis less than critical shear stress τcrit,on the contrary there is slippage.

where τ1,τ2and τ3are shear stress in 3 coordinate planes,μfis friction coefficient of contact surface,μf=tanφ,φ is friction angle(°),τmaxis the limiting friction,can be obtained by test and material empirical value.
Then the normal stiffness knand shear stiffness ksshould be defined when set the contact parameters.ANSYS suggest knand ksequal to 10 times stiffness of adjacent elements:

where ΔZminis the normal minimum width of adjacent elements,K is bulk modulus,G is shear modulus.
1.4 Spring element modeling method
In this method,the beam of nonlinear Winkler foundation model(see Fig.4)was employed, a methodology of the‘spring’and‘dashpot’coefficients of the spring-damping system is proposed[11].The pile is embedded in a layered soil and supported by distinct side-soil springs,the interaction between the pile and the soil is simulated by the stretching and compression of spring element.Both inertial and kinematic interaction can be studied through a dynamic Winkler model and soil nonlinearity is taken under consideration by means of nonlinear spring element.
In spring element modeling method,the lateral resistance coefficient in pile’s lateral soil should be obtained,the main stream approaches to calculate the lateral resistance of soil is p-y curve method.The curves can show the nonlinearity and plastic deformation of the soil.There are several different p-y curves,in this paper,we adopted the p-y curve which proposed by API Specification[12].The curve formula of soft clay:
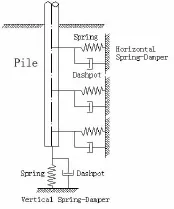
Fig.4 The Winkler foundation model

where p is soil lateral resistance per unit area(kPa);puis ultimate soil lateral resistance per u-nit area(kPa);y is horizontal lateral displacement of pile at depth;y50is horizontal lateral displacement of pile when lateral soil reach 50%pu,y50=2.5ε50D.ε50is the strain at 50% maximum principal stress difference of Δσ-ε curve;D is pile diameter(m).
When

where γ is effective unit weight of soil(N/m3),Cuis undrained shear strength of undisturbed soil.In this context,Cuand ε50are determined by empirical value as following Tab.1.
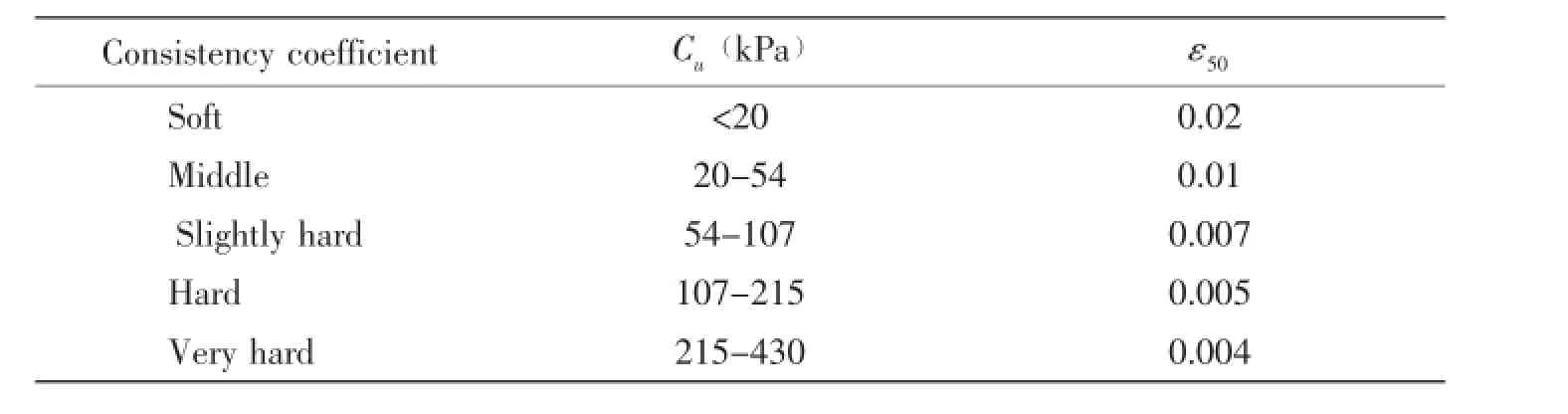
Tab.1 Empirical value of undrained shear strength of clay C50and ε50

The curve formula of sandy soil:

where A is coefficient determined by load condition,under cyclic load A=0.96;under static load A=(3.0-0.8X/D);K is initial modulus of soil resistance,related to frictional angle φ(°):
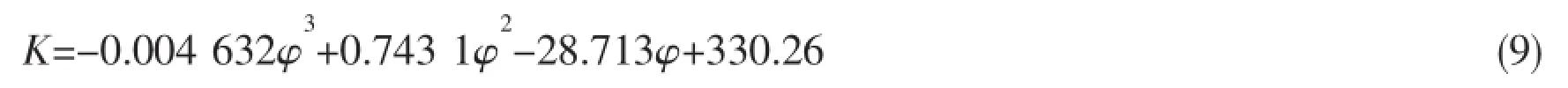
t-z curve shows the relationship between friction force and displacement at axial direction,and q-z curve shows the relationship between reacting force and axial displacement of pile bottom.This paper adopts the regulation of API[12],t-z curve and q-z curve can be chosen as shown in Fig.5.

Fig.5 q-z curve and t-z curve from API
In the figures,q is ultimate bearing capacity of pile,it constitutes by side friction qfand reacting force qp,q=qp+qf;t is dynamic cohesive force;tmaxis maximum cohesive force;z ispile axial displacement.
2 Calculation exam p le
2.1 Platform characteristics
The platform is an experimental test-mining jack-up platform and installing real-timing monitoring system for collecting structural response data for study.Fig.6 shows the overview of jack-up platform.
The main dimension of the platform:
Superstructure length:82 m
Molded breadth:37 m
Molded depth:6.2 m
Pile length:82 m
Pile diameter:3.5 m
Pile shoe height:1.65 m
Embedded depth of pile:10 m

Fig.6 Overview of jack-up platform

Fig.7 Calculation coordinate
2.2 Environmental parameters
The environmental loads in the simulation include wind load,wave load and current load. The coordinate system is shown in Fig.7.Environmental parameters of working conditions is shown in Tab.2.In the simulation,we chose the most dangerous situation:wind load,wave load and current load are in the same direction,and the load direction angle is 90°.
2.3 FE model of pileleg
As the main goal of the analysis is the pile leg,the superstructure is simplified into the boxstructure.Elements of several types are used for different parts of the platform to simulate the actual structure.The pile leg structure and its internal components such as ring ribs and longitudinal bars are constructed out of Shell 63 and Beam 188 elements.Pipe 59 elements without density and elasticity modulus are set in thecenter of pile legs,the wave-current forces are transmitted by the coupling nods of pipe 59 and shell 63 at the direction of wave approach.The FE models of platform and pile leg are shown in Fig.8.
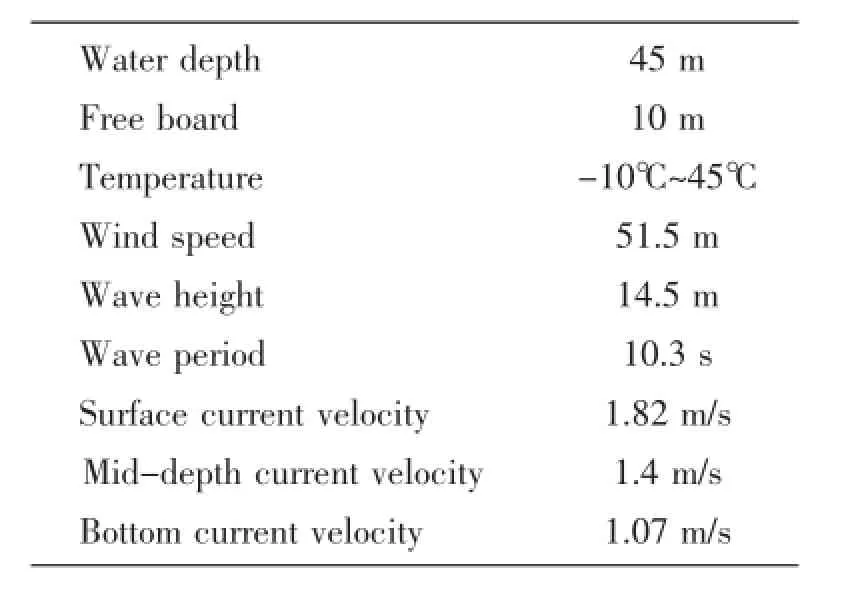
Tab.2 Environmental parameters

Fig.8 The FE model of platform
2.4 Simplification assumptions
Due to the complicated and uncertain characteristics of soil,in the case of without affecting the solution,the following assumptions were adopted to simplify the FE model.
(1)Pile subsoil provides support reaction force for the end of pile,while soil around pile provides frictional resistance to prevent pile sinking.
(2)Frictional effects which caused by bending of piles are ignored.
(3)Elastic material is adopted to simulate the pile,but,because of the complicated mechanical properties of soil and lacking of specialized soil module in ANSYS,thus the finite element model of soil can be treated approximately as elastic-plastic and Druck-Prager constitutive model is applied[13].
(4)According to the soil depth,the approximate characteristics of soil can be equivalent to a layer.In the calculation,the soil is divided into five layers and the soil parameters of each layer are shown in the following Tab.3.

Tab.3 Soil properties of 5 layers
3 Sim ulation results
Taking advantage of proposed 3 modeling methods,the numerical analysis of platform at operating condition and self-existence were conducted.The results are then compared withavailable monitoring data.
Comparison of pile response was investigated using the displacement distribution.Tab.4, Figs.9 and 10 compare the lateral displacement of embedded part of pile from traditional simplified method,contact element method,spring element method and monitoring.It can be generally seen that computed results by contact element method and spring element method are in good agreement,and the spring element method predictions,in general,match the deformation obtained by monitoring sensors better.

Tab.4 Lateral displacement of pile at soil surface(unit:m)

Fig.9 Lateral displacement of pile at operating condition
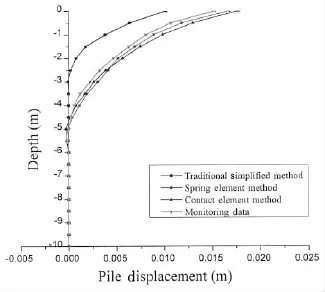
Fig.10 Lateral displacement of pile at self-existence
4 Conclusions
The aim of this paper is to compare the accuracy and practicability of different modeling method to the soil-pile interaction problem.From the results of the study,following conclusions can be drawn:
(1)Though simple and practical,the model is essentially incapable of describing the real features of the side soil.This method is easy to operate in FE software but it usually gets more deviation results.
(2)The advantages of a contact element model include the capability of performing the analysis of a column-pile in a fully coupled manner,without resorting to the independent calculations of site or superstructure response,and a small number of parameters are needed inthe calculation.With the entity model of soil,it is possible to model any arbitrary soil profile and study the 3-D effects.But the results are also highly conservative.
(3)In spring element model,the calculation accuracy of spring element method is more accurate than contact element method,but the spring element method based on p-y curve needs more relevant parameters.These parameters should be obtained by field test or empirical equations.If exact parameters are acquired,the spring element model can obtain accurate results with minimum computational time required.
(4)In the practical engineering analysis,the modeling method should be selected according to the structure characteristics,existing data and accuracy requirement.
[1]Williams M S,Thompson R S G,Houlsby G T.A parametric study of the non-linear dynam ic behavior of an offshore jack-up unit[J].Engineering Structure,1999,21:383-394.
[2]Meymand P J.Shaking table scale model test of nonlinear soil-pile-super-structure interaction in soft clay[D].PhD dissertation,University of California,Berkelev,1998.
[3]Normand P.Shaking table tests on model piles:A literature survey[R].Research Report 95-3.Department of Civil Engineering,University of Canterbury,New Zealand,1995.
[4]Hushmand B,Scott R F,Crouse C B.Centrifuge liquefaction tests in a laminar box[J].Geotechnique,1988,38:253-65.
[5]Dorby R,Abdoun T.Recent studies on seism ic centrifuge modelling of liquefaction and its effect on deep foundations[C]. In:Proceedings of the fourth international conference on recent advances in geotechnical earthquake engineering and soil dynamics,2001,Paper no.SOAP-3.
[6]Kellezi L,Stromann H.FEM analysis of jack-up spudcan penetration for multi-layered critical soil conditions[C]//The BGA(British Geotechnical Association)International Conference on Foundations(ICOF).Dundee,Scotland,2003:411-420.
[7]Boulanger R W,Curras C J,Kutter B L,Wilson D W,Abghari A.Seismic soil-pile-structure interaction experiments and analyses[J].Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,1999,125:750-9.
[8]Hutchinson T C,Chai Y H,Boulanger R W,Idriss I M.Inelastic seismic response of extended pile-shaft-supported bridge structures[J].Earthquake Spectra,2004,20:1057-80.
[9]Bowles J E.Foundation analysis and design[M].McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.,2001.
[10]CCS.Rules for the classification and construction of offshore p latform[S].Beijing,2005.
[11]Kampitsis A E,Sapountzakis E J,Giannakos S K,Gerolymos N A.Seismic soil-pile-structure kinematic and inertial interaction-A new beam approach[J].Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2013,55:211-224.
[12]API.Recommended practice for planning,design and constructing structures and pipelines for arctic conditions[S].APIRP2N, 1995.
[13]Ding Haojiang,He Fubao.The finite element method of elastic and plastic mechanics[M].Beijing:China Machine Press, 1992.
几种自升式平台桩土作用有限元简化方法的比较
徐庚,严仁军
(武汉理工大学高性能船舶技术教育部,武汉430063)
文章以某一自升式海洋平台桩腿结构作为研究对象,在分析环境载荷作用下自升式海洋平台桩腿—土相互作用机理的基础上,结合通用有限元软件ANSYS,对于如何在有限元建模中正确地考虑桩腿—土的相互作用的问题进行了研究,建立了完整的海洋平台桩腿模型,并分别采用了三种不同的有限元建模方法来模拟土层和桩腿之间的相互作用,通过有限元计算结果与实际检测样本数据的比较,分析了三种简化方法的准确性和可行性。
有限元模拟;桩土相互作用;接触模型;弹簧单元;p-y曲线
U661.4
A
徐庚(1988-),男,武汉理工大学博士研究生;严仁军(1961-),男,武汉理工大学教授,博士生导师。
U661.4
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2016.09.009
1007-7294(2016)09-1181-09
Received date:2016-04-21
Foundation item:Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant No.51479513);the Fundamental Research Founds for the Central Universities(Grant No.2016-YB-014)
Biography:XU Geng(1988-),male,doctoral candidate,E-mail:xugeng_1988@163.com; YAN Ren-jun(1961-),male,professor/tutor.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
船舶力学的其它文章
- Recent Progress in Hydrodynam ic M odel Test for Two Floating Bodies at Close Proxim ity in W aves
- Numerical Analysis of Load-noise of a Highly-skewed Propeller behind Subm arine
- Vibration due to Propeller-Shaft-Hull Coupling of a SWATH
- Structural Strength Evaluating M ethod of the Azimuth Thruster Propeller Blade
- Application of Inertia Relief in the Prediction of W elding Deformation for Large Complex Structures
- Dynam ic Pre-ultim ate Strength Evaluation of Containership based on a 2D M odified Hydroelasticity M ethod in Extrem e W aves
