超声造影后细针穿刺活检术在颈部淋巴结结核诊断中的应用
2015-08-07张文智杨高怡于天琢蒋慧青王彩芬
张文智,杨高怡,于天琢,蒋慧青,孟 君,王彩芬
·全科医生技能发展·
超声造影后细针穿刺活检术在颈部淋巴结结核诊断中的应用
张文智,杨高怡,于天琢,蒋慧青,孟 君,王彩芬
目的 探讨超声造影后细针穿刺活检术在颈部淋巴结结核诊断中的应用价值。方法 选取2012年1月—2014年3月在杭州市红十字会医院住院因颈部淋巴结肿大、临床疑似淋巴结结核的患者105例,采用掷硬币法将患者分为A组(47例)和B组(58例)。A组进行超声引导下细针穿刺活检术;B组先行超声造影后再行超声引导下细针穿刺活检术。结果 A组患者47枚淋巴结超声表现:18枚(38.3%)为低回声,29枚(61.7%)为低回声伴液化。病理诊断结果:33枚为颈部淋巴结结核,2枚为反应性增生,1枚为转移癌,病理诊断阳性率为76.6%(36/47)。B组患者65枚淋巴结行超声造影:全淋巴结增强型和淋巴结部分增强型58枚(89.2%),7枚(10.8%)为淋巴结边缘增强型和淋巴结无增强型。58枚适合穿刺的淋巴结行超声引导下细针穿刺活检术,病理诊断结果:47枚为颈部淋巴结结核,5枚为反应性增生,3枚为转移癌,病理诊断阳性率为94.8%(55/58)。B组细针穿刺活检术病理诊断阳性率高于A组(χ2=7.47,P<0.05)。结论 超声造影后细针穿刺活检术应用于颈部淋巴结结核,可明显提高病理诊断阳性率。
超声造影;穿刺术;淋巴结;结核
张文智,杨高怡,于天琢,等.超声造影后细针穿刺活检术在颈部淋巴结结核诊断中的应用[J].中国全科医学,2015,18(15):1845-1848.[www.chinagp.net]
Zhang WZ,Yang GY,Yu TZ,et al.Application value of the contrast-enhanced ultrasonography before the fine needle aspiration biopsy in the diagnosis of cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis [J].Chinese General Practice,2015,18(15):1845-1848.
淋巴结结核占肺外结核的首位,以颈部淋巴结结核最常见,占肺外结核的14.3%~57.3%[1-2],其诊断常需病理确诊。有研究报道,颈部淋巴结结核的穿刺活检取材满意度为96.7%,而病理诊断阳性率约73.2%,颈部淋巴结结核治疗原则为早诊断早治疗[3],故提高穿刺活检术中取材准确率以及病理结果的阳性率非常重要[4]。本研究观察超声造影后细针穿刺活检术在颈部淋巴结结核诊断中的应用价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取2012年1月—2014年3月在杭州市红十字会医院住院因颈部淋巴结肿大、临床疑似淋巴结结核的患者105例,其中男33例,女72例;年龄17~61岁,平均31.4岁;70例为单侧多发,21例为双侧多发,14例为单侧单发;活检病变淋巴结数105枚。上述患者均经细针穿刺活检术证实(78例)或手术证实(27例)。排除凝血功能异常、严重心肺功能异常及大面积颈部皮肤破损患者。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 仪器 iU22彩色超声诊断仪(Philips公司)。
1.2.2 研究方法 采用掷硬币法将患者分为A组(47例)和B组(58例)。两组患者签署知情同意书后,A组患者47枚淋巴结进行超声引导下细针穿刺活检术;B组患者65枚淋巴结先行超声造影后选取适合穿刺的58枚再行超声引导下细针穿刺活检术,应用0.9%氯化钠溶液5 ml稀释超声造影剂SonoVue(规格59 mg)后,取4.8 ml经肘静脉弹簧式注射,观察目标淋巴结内造影剂增强模式(全淋巴结增强型、淋巴结部分增强型、淋巴结边缘增强型和淋巴结无增强型),选择全淋巴结增强型和淋巴结部分增强型的目标淋巴结,并确定穿刺活检点(取材目标区:取造影剂增强区)及进针方向。常规消毒、铺巾及局部麻醉后,于超声引导下在目标区多点多方向穿刺,拔出活检针后迅速涂片,并用95%乙醇固定后迅速送病理检查。
1.3 统计学方法 采用SPSS 13.0统计软件包进行数据分析,计数资料比较采用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
A组患者47枚淋巴结超声表现:18枚(38.3%)为低回声,29枚(61.7%)为低回声伴液化。病理诊断结果:33枚为颈部淋巴结结核,2枚为反应性增生,1枚为转移癌,病理诊断阳性率为76.6%(36/47);其余11枚(23.4%)病理不能明确诊断,经超声造影后细针穿刺活检术病理诊断为颈部淋巴结结核6枚,经手术证实为淋巴瘤5枚。
B组患者65枚淋巴结行超声造影:全淋巴结增强型(见图1、2)和淋巴结部分增强型(见图3、4)58枚(89.2%),7枚(10.8%)为淋巴结边缘增强型(见图5)和淋巴结无增强型(见图6)。选取58枚适合穿刺的淋巴结行超声引导下细针穿刺活检术,病理诊断结果:47枚为颈部淋巴结结核,5枚为反应性增生,3枚为转移癌,病理诊断阳性率为94.8%(55/58);其余3枚(5.2%,3/58)病理不能明确诊断,经手术证实为淋巴瘤。B组细针穿刺活检术病理诊断阳性率高于A组,差异有统计学意义(χ2=7.47,P<0.05)。
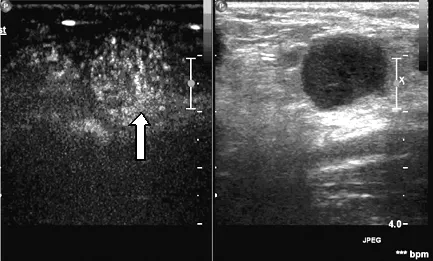
注:箭头示为淋巴门区
图1 左半图示患者1颈部转移癌超声造影后全淋巴结增强图,右半图为二维对照图
Figure 1 Intensification of whole lymphaden after contrast-enhanced ultrasonography on cervical metastatic cancer in patient 1 on the left;2-dimensional contrast figure on the right
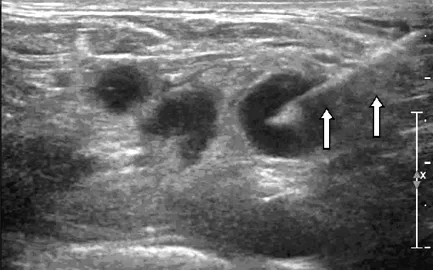
注:箭头示穿刺活检针
图2 患者1穿刺取材过程图
Figure 2 Process of sampling for fine aspiration needle biopsy in patient 1
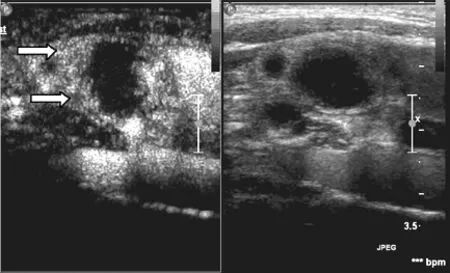
注:箭头示为淋巴结部分增强区
图3 左半图示患者2颈部淋巴结结核超声造影后淋巴结部分增强图,右半图为二维对照图
Figure 3 Intensification of partial lymphaden after contrast-enhanced ultrasonography on cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis in patient 2 on the left;2-dimensional contrast figure on the right
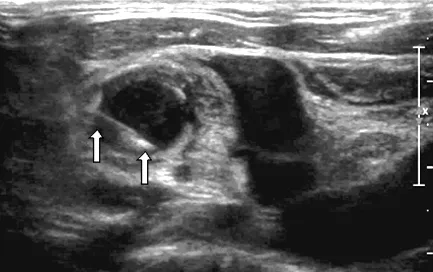
注:箭头示穿刺活检针
图4 患者2穿刺取材过程图
Figure 4 Process of sampling for fine aspiration needle biopsy in patient 2
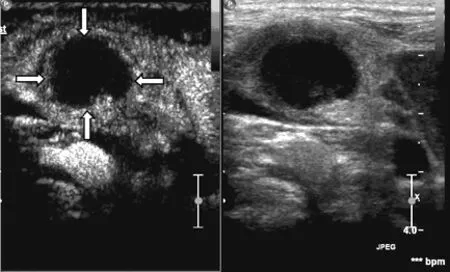
注:箭头示为边缘增强型淋巴结
图5 左半图示患者3颈部淋巴结结核超声造影后淋巴结边缘增强图,右半图为二维对照图
Figure 5 Contrast-enhanced Ultrasonography on cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis in patient 3 on the left;2-dimensional contrast figure on the right
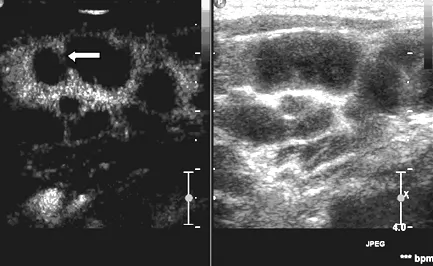
注:箭头示为淋巴结包膜破坏,互相融合
图6 左半图示患者4颈部淋巴结结核超声造影后淋巴结无增强图,包膜破坏,互相融合,右半图为二维对照图
Figure 6 No Intensification in lymphaden which showed damaged envelop and merging after contrast-enhanced ultrasonography on cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis in patient 4 on the left;2-dimensional contrast figure on the right
3 讨论
颈部淋巴结引流丰富,人体800多个淋巴结中约300个位于颈部,其病变以颈部肿块为常见的临床症状,常规影像学检查无法明确诊断而延误治疗,尤其在颈部淋巴结结核患者,不进行早期诊断和早期治疗,将出现破溃及窦道形成而严重影响患者日常生活,临床诊断需依据病理结果。
超声引导下淋巴结穿刺活检已成为诊断淋巴结性质的最直接、最简便的方法[5-6]。但具有相对的盲目性和一定的随意性,尤其在液化坏死范围比较大的结核性病变淋巴结以及病变淋巴结整体坏死的转移性癌中,更体现出此方法的不可取性,本研究A组患者中的11枚行超声引导下细针穿刺活检术的颈部最大(或较大)淋巴结,病理未能明确诊断,而再次行超声造影后细针穿刺活检术,超声造影示其中6例患者已行穿刺颈部淋巴结术,呈造影剂边缘灌注或淋巴结内无造影剂灌注,而重新选择目标淋巴结,进行超声造影后细针穿刺活检术而明确诊断,充分表明超声造影能更敏感地显示坏死区[7],且坏死率与淋巴结大小无相关性[8]。据报导,超声引导下颈部淋巴结一次穿刺成功率93%[9],但本研究未经超声造影选择目标区而进行超声引导下细针穿刺活检术的病理诊断阳性率为76.6%,而超声造影后细针穿刺活检术的病理诊断阳性率为94.8%,故超声引导下细针穿刺活检术有其局限性。
本研究发现,超声造影后选择目标淋巴结及取材区进行细针穿刺活检术,其特异性高,能马上获得病理学结果,引导临床制定有效的治疗方案,造影剂灌注区为淋巴结的活性部分,经此区活检取材准确性好,造影剂无灌注区为坏死区,经此区取材容易取坏死物,导致病理无法明确诊断,增加患者第2次活检的概率。超声造影后细针穿刺活检术也可以有效地避免穿刺路径上的血管损伤,从而能够极大减少并发症的发生。病理明确诊断的患者,可以替代手术切除活检,减少术后切口不愈合或形成窦道的可能,对于颈部淋巴结肿瘤性病变也减少了肿瘤切开后种植性转移的可能[10],并且穿刺过程简洁,穿刺部位不留手术瘢痕,对于年轻女性患者来说超声造影后细针穿刺活检术不失为一种更好的选择。
本研究中8例淋巴瘤患者无一例病理明确诊断为淋巴瘤,因淋巴瘤的病理诊断较其他恶性病变复杂,穿刺活检不易取到被膜区,得不到重要区域的病理信息,对可疑患者仍需手术切除活检,手术切除能更进一步得到淋巴瘤的病理分型[11]。
笔者认为,超声造影提示淋巴结边缘增强型,如进行细针穿刺活检术,因取出坏死组织或脓性物,病理常不能明确诊断,故超声造影表现为此型的淋巴结建议放弃活检,而另选周围全淋巴结增强型或淋巴结部分增强型进行细针穿刺活检术,有利于提高病理诊断阳性率。超声造影应用于颈部淋巴结结核细针穿刺活检术,已为本院临床诊断广泛采用。因本院结核科为全国重点临床基地及浙江省结核病定点诊治医院,故未有超声造影应用于淋巴结转移性癌穿刺活检,此方法应用于淋巴结转移性癌有待于进一步研究。
总之,超声造影后细针穿刺活检术兼有超声造影后选材的可靠性和超声引导下细针穿刺活检术的准确性。超声造影应用于颈部淋巴结结核的细针穿刺活检术中,能为穿刺活检做充分的准备,能极大减少穿刺过程中的出血概率,提高病理诊断阳性率;为临床工作带来更高的确诊率和成功率,能明显减少患者因恐惧及重复穿刺带来的痛苦;为超声和临床相结合奠定基础。
[1]Li LJ.Status and control strategy for infectious diseases in China[J].Chinese Journal of Clinical Infectious Diseases,2008,1(1):1-6.(in Chinese) 李兰娟.我国感染病的现状及防治策略[J].中华临床感染病杂志,2008,1(1):1-6.
[2]Zhu LZ.Enhancing collaborative study on extra-pulmonary tuberculosis [J].Chinese Journal of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases,2008,31(2):81-82.(in Chinese) 朱莉贞.加强对肺外结核病的协作研究[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2008,31(2):81-82.
[3]Zhu XL,Cui YC,Hou WJ,et al. Application of pathological diagnosis by using ultrasound-guided percutaneous biopsy for cervical lymph lesions[J]. Journal of International Oncology,2012,39(1):72-75.(in Chinese) 朱晓琳,崔玥婵,侯文静,等.超声引导下经皮穿刺活检对颈部淋巴结病变诊断的应用价值[J].国际肿瘤学杂志,2012,39(1):72-75.
[4]Hu YJ,Zeng MX,Jin X,et al.Clinical application of image-guided percutaneous core-needle biopsy of unusual enlarged lymph nodes[J].Chinese Journal of Surgical Oncology,2011,3(4):247-249. (in Chinese) 胡永军,曾明喜,金恂,等.经皮穿刺淋巴结活检术在情况特殊淋巴结肿大病例中的应用[J].中国肿瘤外科杂志,2011,3(4):247-249.
[5]Hohlweg-Majert B,Metzger MC,Voss PJ,el al.Preoperative cervical lymph node size evaiuation in patients with malignant head/neck tumors:comparison between ultrasound and computer tomography [J].J Cancer Res Clin Oncol,2009,135(6):753-759.
[6]Britton PD,Goud A,Godward S,et al.Use of ultrasound-guided axillary node core biopsy in staging of early brest cancer [J].Eur Radiol,2009,19(3):561-569.
[7]Sun DS,Chen Y,Zhong JY,et al.Application of CEUS-guided needle biopsy for superficial lymphadenopathy[J].Chinese Journal of Interventional Imaging and Therapy,2012,9(4):229-232.(in Chinese) 孙德胜,陈芸,钟洁愉,等.超声造影引导浅表淋巴结穿刺活检的应用[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2012,9(4):229-232.
[8]Yang GY,Zhang Y,Zhao D,et al.Contrast-enhanced ultrasonographic features of cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis[J].Chinese Journal of Clinical Infectious Diseases,2010,3(5):277-279.(in Chinese) 杨高怡,张莹,赵丹,等.颈部淋巴结结核超声造影分析[J].中华临床感染病杂志,2010,3(5):277-279.
[9]Ai H,Yin YM,Pan WQ,et al.Clinical value of percutaneons biopsy under the guidance of color doppler ultrasound[J].Chinese Journal of Ultrasound Diagnosis,2004,5(11):843-845.(in Chinese) 艾红,尹益民,潘文倩,等.彩色多普勒超声引导下穿刺活检技术的临床应用价值[J].中国超声诊断杂志,2004,5(11):843-845.
[10]Cui YY,Gu JC,Sun ZD,et al.The clinical applied value of color ultrasound-guided biopsy in the diagnosis of neck lump[J].Journal of Jinzhou Medical College,2006,27(3):4-6.(in Chinese) 崔煜艳,谷京城,孙志丹,等.彩超引导下穿刺活检对颈部包块诊断的临床价值[J].锦州医学院学报,2006,27(3):4-6.
[11]查长松,隋向梅,刘莹,等.超声引导下浅表淋巴结穿刺活检的临床应用[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2002,11(9):571-572.
修回日期:2015-03-13)
(本文编辑:李婷婷)
Application Value of the Contrast-enhanced Ultrasonography Before the Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy in the Diagnosis of Cervical Tuberculous Lymphadenitis
ZHANGWen-zhi,YANGGao-yi,YUTian-zhuo,etal.
DepartmentofUltrasound,RedCrossHospitalofHangzhou,Hangzhou310003,China
Objective To study the application value of the contrast-enhanced ultrasonography before the fine aspiration needle biopsy (FNAB) in the diagnosis of cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis.Methods 105 patients with neck lymph node enlargement and clinical suspected tuberculous lymphadenitis who were admitted to Red Cross Hospital of Hangzhou during January 2012 to March 2014,were divided into group A (47 cases) and group B (58 cases) by coin tossing method.Cases in group A received FNAB under the guidance of ultrasonography;cases in group B received contrast-enhanced ultrasonography firstly,then received FNAB under the guidance of ultrasonography.Results The ultrasonography findings of 47 lymph nodes in group A:18 lymph nodes (38.3%) displayed the character of low echo,29 lymph nodes (61.7%) displayed the character of low echo and liquidation.The pathological diagnosis of 47 lymph nodes in group A:33 lymph nodes were cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis,2 were reactive hyperplasia,1 was metastatic carcinoma,the positive rate of pathological diagnosis was 76.6% (36/47).The contrast-enhanced ultrasonography findings of 65 lymph nodes in group B:58 lymph nodes (89.2%) showed intensified in whole node or in partial node,7 (10.8%) showed not intensified or showed intensified in edge of node.The pathological diagnosis of 58 lymph nodes in group B:47 lymph nodes were cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis,5 were reactive hyperplasia,3 were metastatic carcinoma of 58 patients,the positive rate of pathological diagnosis was 94.8% (55/58).The positive rate of pathological diagnosis in group B was significantly higher than that in group A (χ2=7.47,P<0.05).Conclusion The application of the contrast-enhanced ultrasound before FNAB in the diagnosis of cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis can obviously improve the positive rate of pathological diagnosis.
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound;Punctures;Lymph nodes;Tuberculosis
浙江省医药卫生计划项目(2014KYA183);杭州市医药卫生科技计划项目(2013A39,2010B028);杭州市科技计划发展项目(20120633B01)
310003浙江省杭州市红十字会医院超声科
杨高怡,310003浙江省杭州市红十字会医院超声科;E-mail:yanggaoyi@163.com
R 551.24
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2015.15.024
2014-12-21;
