组氨酸激酶基因barA在水生拉恩菌中的生防调控功能
2015-06-05肖凤虎张蕾谢镇郭岩彬陈敏文王勇军
肖凤虎,张蕾,谢镇,郭岩彬,陈敏文,王勇军,4*
(1.浙江农林大学林业与生物技术学院,浙江临安311300;2.浙江科技学院,杭州310023;3.中国农业大学资源与环境学院,北京100094;4.浙江农林大学生物农药高效制备技术国家地方联合工程实验室,浙江临安311300)
组氨酸激酶基因barA在水生拉恩菌中的生防调控功能
肖凤虎1,张蕾2,谢镇1,郭岩彬3,陈敏文1,王勇军1,4*
(1.浙江农林大学林业与生物技术学院,浙江临安311300;2.浙江科技学院,杭州310023;3.中国农业大学资源与环境学院,北京100094;4.浙江农林大学生物农药高效制备技术国家地方联合工程实验室,浙江临安311300)
为探究水生拉恩菌(Rahnella aquatilis)HX2的生防性状表现机制,利用转座子mini-Tn5对HX2菌株进行随机突变,筛选获得1个对葡萄根癌菌K308(Agrobacterium vitis K308)拮抗活性减弱的突变体,并确定该插入位点的基因为双组分调控系统中的组氨酸激酶基因bar A.该基因编码的蛋白含有组氨酸激酶结构域HAMP(histidine kinases,adenylyl cyclases,methyl binding proteins,phosphatases)、组氨酸磷酸传递结构域His KA(histidine kinase acceptor)、C-端催化ATP结合结构域HATPase_C(histidine associated ATPase C terminal)、磷酸接受结构域REC(receiver domain)和含组氨酸的磷酸转移结构域HPT(histidine phosphotransferase domain),是一种跨膜的杂合组氨酸激酶蛋白.通过双交换突变,获得了bar A缺失突变体并构建了互补菌株.通过比较分析发现,barA基因缺失后,细菌HX2生物膜形成能力显著提高,但细菌游动和涌动能力降低,以及对葡萄根癌病的生防效果从野生型的86.2%降低至26.7%,构建的互补菌株能够恢复突变菌株在该研究中的所有测定性状.由此推测,组氨酸激酶基因bar A是细菌HX2表现生防性状的一个重要调控基因,为生防细菌HX2在植物病害防治上提供理论基础.
水生拉恩菌;组氨酸激酶基因barA;双组分调控系统;生物防治
SummaryRahnella aquatilis HX2,which was isolated from the vineyard soil,is a gram-negative,plant growthpromoting rhizobacteria.Previous results showed that R.aquatilis HX2 has significant antagonistic effect on certain pathogenic bacteria and fungi including Agrobacterium tumefaciens,Xanthomonas oryzae,Fusarium oxysporum,Botrytis cinerea,Altemaria solani,etc,and exhibited the potential biocontrol value against rice sheath blight and crown gall ofgrapevine and sunflower.The completed genomic DNA sequence of R.aquatilis HX2 has been finished.
For further discovery of the regulatory systems which regulate its biocontrol and physiological traits,random mutagenesis based on mini-Tn5 transposon was used to investigate the regulatory genes.The candidated genes were focused on the regulatory function in biocontrol-related physiological traits and biocontrol effects.Consequently,a mutant TR57 which had less antagonitic effect against the plant pathogen Agrobacterium vitis K308 was obtained after the random mutagenesis based on mini-Tn5 transposon and antagonitic assay.The DNA sequence flanking the inserted mini-Tn5 transposon was verified as a Bar A-liked histidine kinase gene.The putative Bar A protein in R.aquatilis HX2 contains HAMP domain,HisKA domain,HATPase_C domain,REC domain and HPT domain.Bar A has been reported as the sensor protein of a two-component regulatory system Bar A/Uvr Y in many bacteria,such as Escherichia coli,Pseudomonas spp.and the Bar A/Uvr Y was known as a global regulatory functioning in bacterial survival under the circumstance of p H value and nutrition change.For further investigation of Bar A in R.aquatilis HX2,null barA mutant was constructed based on homologous recombination.A vector pSRΔbarA was constructed after inserting the flanking region of barA loci into the suicide vector pSR47S,and transformed into E.coli DH5α(λ-pir).The triparental mating strategy was used to transfer the vector pSRΔbarA into R.aquatilis HX2.After the two-step homologous recombination,the null barA mutant MR57 was obtained consequently.Meanwhile,the complemented vector pRK barA was constructed after inserting the barA operon into the shuttle vector pRK415G,and then was transformed into MR57.
The biocontrol-related physiological traits and biocontrol effect of R.aquatilis HX2 and its derivative strains were compared to valuate the barA regulation function.The experimental results indicated that the mutagenesis of barA caused higher bacterial biofilm formation ability,less swimming and swarming ability.The biocontrol efficiency of barA mutant against A.vitis K308 on grape plants decreased to 26.7%,comparing to 86.2%of the wild type strain.Moreover,the complemented strain could recover all the measured biological characters and biocontrol efficiency.Therefore,it was supposed that the histidine kinase gene barA plays the key role in biocontrol function of R.aquatilis HX2.
In summary,barA is firstly found as a regulation gene functioning in bacterial biocontrol effect in this study. The results also give us the indication that the modification of bacterial two-component regulation systems would be helpful to facilitate the application of biocontrol bacteria.
利用微生物进行病害防治及促进植物生长已经被人们认为是一种降低农业化学品使用的有效方法,如用与植物相关的细菌控制病害发生、刺激宿主植物生长、改善作物的土壤结构等[1].细菌在农业上的应用受到诸多因素的影响,特别是细菌对新环境的适应能力.当前已有报道证实了细菌的很多生物学性状,如生物膜的形成、细菌的游动性、细菌的涌动性、拮抗物质产生能力、定殖能力、抗氧化能力等都直接影响了细菌的生防效果或促生效果[2].这些性状在细菌细胞内都是由很多调控系统来调控表达,如双组分调控系统(two-component regulatory system)、群体感应系统(quorum-sensing system)、c-di-GMP(cyclic diguanylate)调控系统、σ因子调控系统等,使细菌能敏感地感受外界条件,调控细胞体内功能基因的表达[2].
双组分调控系统是当前细菌功能基因调控研究的一个热点.该系统由一个受体组氨酸激酶和一个反应调控因子组成.受体组氨酸激酶大多是一些跨膜蛋白,膜外结构域感应外界信号,如营养物质、p H值、渗透压等,然后通过构型变化,激活胞内激酶进行自身磷酸化,通过磷酸转移激活反应调节因子.反应调节因子通过直接作用于DNA或者调控其他转录因子作用于下游基因,最终达到细菌感应环境而调控自身功能基因表达的目的.当前已经确定的调控因子有GacS-Gac A调控荧光假单胞菌(Pseudomonas f luorescens)的定殖、2,4-DAPG的产量[3-5],CusR-CusS调控大肠埃希菌(Escherichia coli)K-12对铜离子的适应[6],SenX3-RegX3调控耻垢分枝杆菌(Mycobacterium smegmatis)对磷的吸收,从而调控细菌在寄主体内的定殖[7].ComD-ComE感受外界刺激蛋白的浓度,从而调控肺炎链球菌(Streptococcus pneumoniae)的感受态形成[8];RoxS-RoxR调控恶臭假单胞菌(Pseudomonas putida)对细菌群体浓度的感应,从而调控细菌在植物叶表的定殖[9];PhoP-PhoQ调控细菌荧光假单胞菌的群体感应以及生物膜的形成,从而调控细菌2P24的生防功能[10].
水生拉恩菌(Rahnella aquatilis)HX2是1株从葡萄根围分离出的细菌,能产生抗生素[11],其对水稻黄单胞菌(Xanthomonas oryzae)、葡萄土壤杆菌(Agrobacterium vitis)、黄瓜枯萎病菌(Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cucumerinum)、西瓜枯萎病菌(F. oxysporum f.sp.niveum)、番茄灰霉(Botrytis cinerea)等多种植物病原细菌和真菌具有明显的拮抗作用,对葡萄根癌病具有显著的防治效果[12].为进一步探明该细菌的生防机制,本研究利用转座子随机突变,获得1株突变体,发现了组氨酸激酶基因bar A对细菌生防相关性状以及生防效果的调控特征.
1 材料与方法
1.1 菌株、质粒与培养条件
本研究所用菌株、质粒见表1.水生拉恩菌(R. aquatilis)HX2及其衍生菌株在PDA培养基中28℃培养,大肠埃希菌在LB(Luria-Bertani)培养基中37℃培养.三亲杂交在ABM基本培养基上进行[13].使用抗生素的终质量浓度分别为氨苄西林(ampicilin,AP)50μg/m L,卡那霉素(kanamycin,Km)50μg/m L,四环素(tetracycline,Tc)20μg/m L.
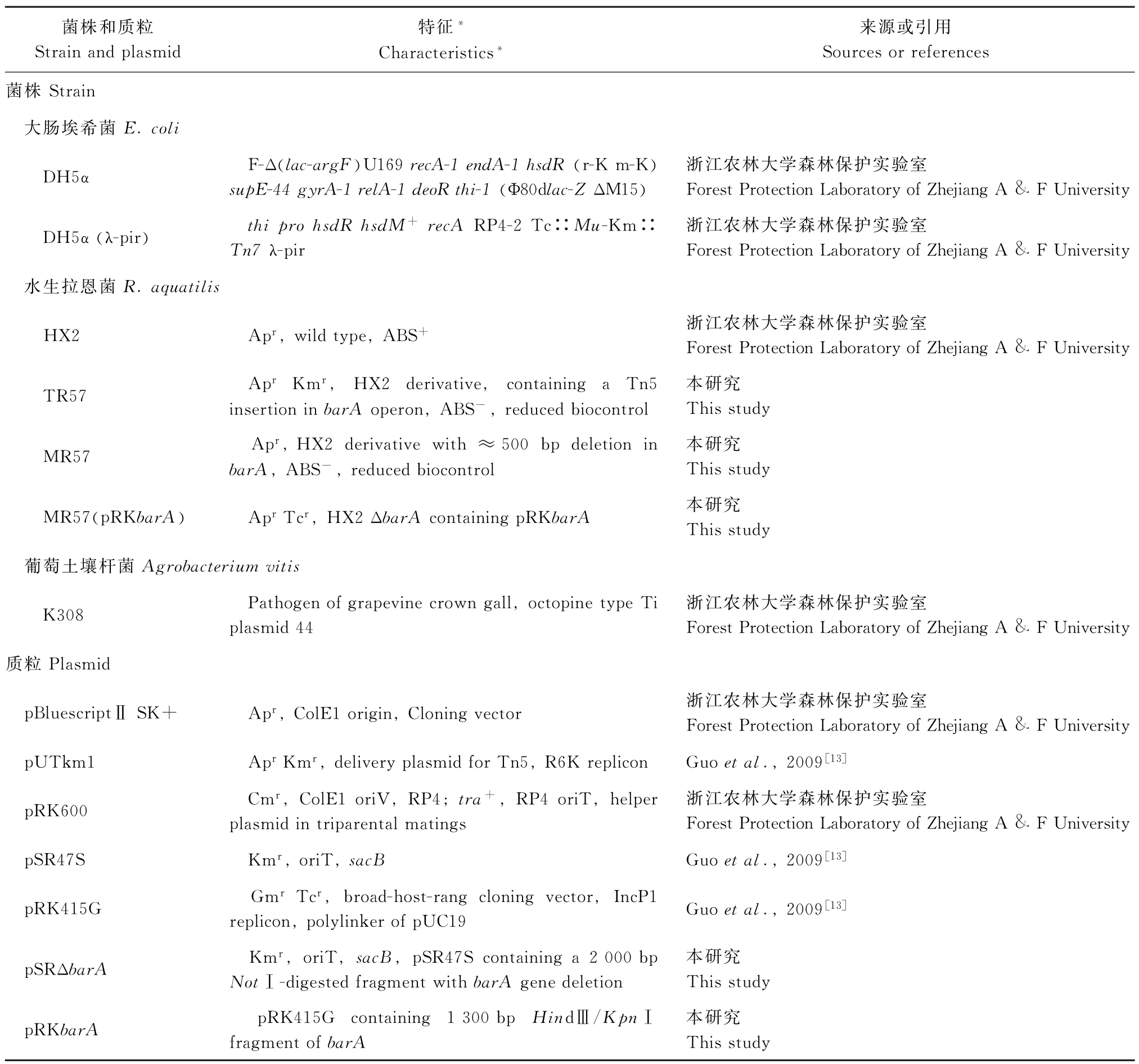
表1 本研究所用菌株和质粒Table 1 Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study
1.2 barA基因缺失突变体及其互补菌株构建
根据bar A基因在细菌HX2染色体中的定位及其侧翼序列,用设计好的引物P1/P2、P3/P4以基因组DNA为模板进行PCR扩增,得到bar A基因的上、下游片段,其长度大约1 000 bp,经相应限制性酶切后连接到载体pBluescriptⅡSK+上.以连接barA上、下游片段的p BluescriptⅡSK+质粒为模板,用引物P7/P8扩增连接片段,长度约为2 000 bp.经限制性内切酶NotⅠ酶切后连接到自杀性载体pSR47s上,得到缺失载体pSRΔbar A.将缺失载体通过三亲(pSRΔbar A、p RK600、HX2)杂交转入HX2菌株中,再进行2次筛选获得缺失突变菌株MR57.
以引物对P5/P6扩增bar A基因,构建bar A基因互补菌株,经Hin dⅢ和KpnⅠ双酶切后连接到穿梭质粒p RK415G中,得到互补载体p RK bar A.将该载体通过三亲杂交导入缺失突变体MR57中,得到互补菌株MR57(p RK bar A).
1.3 生物膜的定量测定
生物膜的形成及定量依据O’Toole等[14]的方法:将待测各菌株分别在LB培养基上活化24 h,制备成1×109CFU/m L的菌悬液,取100μL菌悬液加入到装有1 m L胞外多糖(extracellular polysaccharide,EPS)培养液的1.5 m L离心管中,28℃静置培养48 h,用无菌水冲洗1遍,加入1.5 m L 1%结晶紫染液,染色15 min,用无菌水将染液冲洗干净.每管用95%乙醇洗涤,以不加菌悬液的EPS作为对照,用紫外分光光度计测定D(590 nm).吸光值D(590 nm)的大小与生物膜形成能力成正比.每个处理5个重复.
1.4 细菌游动和涌动能力检测
参考Chow等[15]的方法进行调整,分别在含有质量分数为0.3%和0.5%琼脂粉的PDA培养基上检测细菌游动和涌动能力,每隔3 h观测细菌菌落直径.每个处理5个重复.
1.2 葡萄根癌菌A.vitis K308平板抑菌检测
采用Stonier双层培养法[16],将待测各菌株配制成菌悬液,各吸取5μL点于PDA培养基上,28℃培养48 h,用三氯甲烷熏蒸杀死细菌.10~12 h后,吸取50μL K308菌悬液加入10 m L融化后冷却到50℃的半固体YEB培养基中,迅速混匀,立即倒入培养基,铺成均匀的薄层,28℃培养24 h,观察抑菌圈的出现并定时测量抑菌圈的直径.每个处理5个重复.
1.6 室温防治葡萄根癌病
将HX2、突变体以及互补菌株制成菌悬液,重悬于无菌的0.9%氯化钠溶液中,分别与等量的病原菌K308悬浮液混匀,以K308单独接种作为对照.用灭菌接种针在3年生葡萄苗上呈纵向划伤,吸取5μL待测菌液接种于伤口,并用封口膜包裹伤口,3 d后去掉封口膜,25℃培养箱培养60 d后观察结瘤情况并称质量,每个处理设5个重复,按分级标准调查发病情况并计算防治效果.
防治效果/%=(对照的病情指数-处理的病情指数)/对照的病情指数×100.
1.7 统计分析
运用SPSS 17.0软件中的单因素分析方差(one-way ANOVA)比较各处理数据的差异性.所有数据以平均值±标准差表示.
2 结果与分析
2.1 R.aquatilis HX2产细菌素突变体的筛选及barA基因鉴定
利用mini-Tn5对HX2菌株进行随机突变,获得约3 000个突变体,将突变体菌株对葡萄根癌病菌A.vitis K308进行拮抗检测,发现突变体TR57的拮抗圈明显降低(图1A).提取突变体基因组DNA,根据mini-Tn5的序列,测定转座子插入位点的序列,比对细菌基因组序列[13](NCBI登录号:CP003403)发现,转座子插入推定的barA基因中间(图1B).分析该基因编码的氨基酸序列,发现该基因从N端开始,依次含有HAMP结构域、His KA结构域、HATPase_C结构域、REC结构域和HPT结构域(图1C),与报道的大肠埃希菌Bar A蛋白相似.
2.2 R.aquatilis HX2中barA缺失突变体的构建
按图2A设计bar A基因两端序列引物P1和P2扩增bar A下游片段,P3和P4扩增bar A上游片段(表2),缺失bar A基因中His KA结构域和HATPase_C结构域,长度为464 bp.将扩增获得的DNA片段连接到自杀载体pSR47S上,获得载体pSRΔbar A,将载体通过三亲杂交,转入到HX2菌株中,2次遗传重组获得克隆,利用两端引物P1和P4进行PCR扩增(表2),以基因组为对照发现,获得了1株阳性克隆为缺失突变体菌株MR57(图2B);该菌株与野生型菌株相比,在bar A基因内部缺少了464 bp(图2B),与设计结果一致.

图1 R.aquatilis HX2中barA突变体的筛选及Bar A蛋白结构分析Fig.1 Screening of bar A mutant of R.aquatilis HX2 and putative secondary structure of Bar A

表2 本试验所用PCR引物Table 2 Primers used in this study
2.3 R.aquatilis HX2中barA基因生物学功能及生防调控功能分析
按图2A设计bar A的互补载体引物,将扩增的片段连接到载体p RK415G上,获得bar A互补载体p RK bar A.利用电击转化至突变体菌株MR57中,获得互补菌株MR57(p RK bar A).将野生型菌株HX2、突变体菌株MR57和互补菌株MR57(p RK bar A)进行拮抗根癌病菌A.vitis K308,并检测生物膜形成能力、细菌游动和涌动能力.结果(图3)表明,MR57较野生菌株HX2的拮抗能力明显下降,互补菌株能恢复细菌对根癌菌的拮抗能力.同时发现,bar A突变后,生物膜形成能力明显上升,而细菌的游动和涌动都呈现下降趋势,说明bar A突变后,细菌处于一种相对不活跃的状态,对环境的敏感性下降.互补菌株能恢复细菌的生物膜形成,以及细菌游动和涌动的能力.
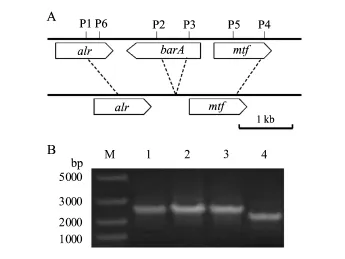
图2 R.aquatilis HX2的barA缺失突变体的构建Fig.2 Construction of bar A null mutant of R.aquatilis HX2
为进一步确定bar A对细菌生防能力的影响,将突变体菌株MR57和HX2分别与K 308菌株混合,在葡萄植株上进行防治效果检测,发现HX2可以很好控制K308引起的根癌病,防效可以达到86.2%,bar A突变体处理组与对照组的瘤质量差别不明显,对根癌病防效下降至26.7%,说明bar A对R.aquatilis HX2的生防功能具有重要调控作用(表3).

表3 R.aquatilis HX2和barA突变体对葡萄根癌病的防治效果Table 3 Control efficiency of R.aquatilis HX2 and its barA nullmutant on grape crown gall disease
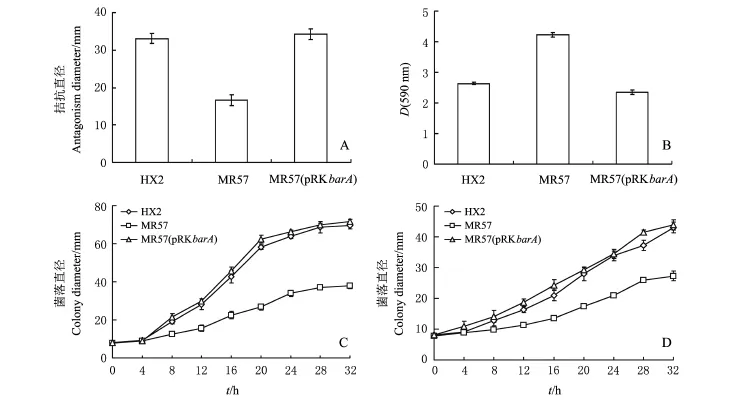
图3 R.aquatilis HX2、barA突变体和互补菌株的生物性状比较Fig.3 Comparison of biological traits among R.aquatilis HX2,bar A mutant MR57 and the bar A complemented strain MR57
3 讨论
本研究利用转座子随机突变细菌R.aquatilis HX2,筛选得到1个能明显降低葡萄根癌病防效的突变体,并鉴定了转座子插入位点为一个组氨酸激酶基因bar A.通过缺失突变,发现bar A基因突变后,细菌拮抗葡萄根癌病菌能力的确明显下降,同时发现细菌更容易形成生物膜,细菌游动和涌动能力都减弱.最后比较了突变体与野生型菌株防治葡萄根癌病的效果,发现bar A基因突变后,细菌的生防能力显著降低,防效从86.2%降低至26.7%.结果表明,组氨酸激酶基因bar A在生防细菌R. aquatilis HX2中发挥着重要的调控作用.该结果与已报道的P.fluorescens中感应蛋白基因gacS的结果相似[3-4].
受体组氨酸激酶Bar A首次在大肠埃希菌中发现可以在env Z缺失突变时调控感应调节因子OmpC和Omp F,从而对环境适应做出相应的调控[17].后续发现Bar A与一个调节因子Uvr Y相互作用,Bar A感应外界环境中的信号发生磷酸化,激活细胞体内的Uvr Y蛋白,组成了一个完整的双组分调控系统[18].R.aquatilis HX2中的Bar A蛋白含有HAMP结构域、His KA结构域、HATPase_C结构域、REC结构域和HPT结构域(图1C).细菌利用Bar A的N端形成跨膜区域嵌入细胞膜内,感应外界信号,通过改变HAMP结构域构型[19],激活His KA结构域以及HATPase_C结构域进行磷酸化或者去磷酸化[20-21],REC结构域提供磷酸化接受位点[22],HPT结构域可以稳定Bar A与Uvr Y磷酸交换的状态[23].最终,Bar A蛋白感应外界信号,如p H变化、甲酸、乙酸等环境改变[24-25],通过磷酸化将信号传递给细胞体内的Uvr Y,实现细菌对环境的适应(图4).

图4 R.aquatilis HX2中的Bar A感应调控模型Fig.4 Putative model of Bar A sensing system in R.aquatilis HX2
水生拉恩菌HX2是1株生防效果优良的菌株.已有研究结果验证了该细菌的细菌素产生是细菌生防的一个重要方面[12].本研究中R.aquatilis HX2的生防效果可能和细菌素产生有关并受到bar A的调控,bar A缺失后,可能导致细菌素的产生下降.生物膜的形成与细菌在环境中的定殖有一定的关系[26],细菌的定殖能力是生防菌发挥其生防功能的前提条件.研究结果同时发现,R.aquatilis中bar A基因缺失突变体产生生物膜的能力显著提高,说明bar A基因有调控生物膜形成的功能.细菌游动和涌动也是细菌适应环境和表现生防功能的重要性状,bar A对R.aquatilis HX2游动和涌动都具有显著的调控功能.从本研究结果表明,组氨酸激酶基因bar A对生防细菌R.aquatilis HX2的生防功能有关键的调控作用.后续研究将针对bar A基因下游调控基因进行筛选,以获得bar A调控生防的信号途径,为生防细菌R.aquatilis HX2在病害防治及应用上提供理论基础.
(References):
[1] Compant S,Duffy B,Nowak J,et al.Use of plant growthpromoting bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases:Principles,mechanisms of action,and future prospects. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2005,71(9):4951-4959.
[2] Gray E J,Smith D L.Intracellular and extracellular PGPR:Commonalities and distinctions in the plant-bacterium signaling processes.Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2005,37(3):395-412.
[3] Duffy B K,Dfago G.Controlling instability in gacS-gac A regulator genes during inoculants production of Pseudomonas fluorescens biocontrol strains.Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2000,66(8):3142-3150.
[4] 魏海雷,张力群.荧光假单胞菌2P24中生防相关调控基因gacS的克隆和功能分析.微生物学报,2005,45(3):368-372. Wei H L,Zhang L Q.Cloning and functional characterization of the gacS gene of the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas fluorescens 2P24.Acta Microbiologica Sinica,2005,45(3):368-372.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 闫小雪,张力群.调控基因gac A在荧光假单胞菌2P24防治土传病害中的作用.植物病理学报,2004,34(3):272-279.
Yan X X.Zhang L Q.The role of regulatory gene gac A in the suppression of soil-borne diseases by Pseudomonas fluorescens 2P24.Acta Phytopathologica Sinica,2004,34(3):272-279.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] Munson G P,Lam D L,Outten F W,et al.Identification of a copper-responsive two-component system on the chromosome of Escherichia coli K-12.Journal of Bacteriology,2000,182(20):5864-5871.
[7] James J N,Hasan Z,Loerger T R,et al.Deletion of Sen X3-RegX3,a key two-component regulatory system of Mycobacterium smegmatis results in growth defects under phosphate-limiting conditions.Microbiology,2012,158(11):2724-2731.
[8] Guiral S,Hénard V,Granadel C,et al.Inhibition of competence development in Streptococcus pneumoniae by increased basal-level expression of the Com DE twocomponent regulatory system.Microbiology,2006,152(2):323-331.
[9] Fernández-Pinar~nar R,Ramos J L,Rodríguez-Herva J J,et al.A two-component regulatory system integrates redox state and population density sensing in Pseudomonas putida. Journal of Bacteriology,2008,190(23):7666-7674.
[10] Yan Q,Gao W,Wu X G,et al.Regulation of the Pcol/PcoR quorum-sensing system in Pseudomonas fluorescens 2P24 by the PhoP/Pho Q two-component system.Microbiology,2009,155(1):124-133.
[11] Chen F,Li J Y,Guo Y B,et al.Biological control of grapevine crown gall:Purification and partial characterisation of an antibacterial substance produced by Rahnella aquatilis strain HX2.European Journal of Plant Pathology,2009,124:427-437.
[12] Chen F,Guo Y B,Wang J H,et al.Biological control of grape crown gall by Rahnella aquatilis HX2.Plant Disease,2007,91(8):957-963.
[13] Guo Y,Li J,Li L,et al.Mutations that disrupt either the pqq or the gdh gene of Rahnella aquatilis abolish the production of an antibacterial substance and result in reduced biological control of grapevine crown gall.Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2009,75(21):6792-6803.
[14] O’Toole G A,Kolter R.Flagellar and twitching motility are necessary for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. Molecular Microbiology,1998,30(2):295-304.
[15] Chow S,Gu K,Jiang L,et al.Salicylic acid affects swimming,twitching and swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa,resulting in decreased biofilm formation. Journal of Experimental Microbiology and Immunology,2011,15:22-29.
[16] Stonier T.Agrobacterium tumefaciens ConnⅡ.Production of an antibiotic substance.Journal of Bacteriology,1960, 79(6):889-898.
[17] Nagasawa S,Tokishita S,Aiba H,et al.A novel sensorregulator protein that belongs to the homologous family of signal-transduction proteins involved in adaptive responses in Escherichia coli.Molecular Microbiology,1992,6(6):799-807.
[18] Pernestig A K,Melefors T J,Georgellis D.Identification of Uvr Y as the cognate response regulator for the Bar A sensor kinase in Escherichia coli.Journal of Biological Chemistry,2001,276(1):225-231.
[19] Parkinson J S.Signaling mechanisms of HAMP domains in chemoreceptors and sensor kinases.Annual Review of Microbiology,2010,64:101-122.
[20] Dago A E,Schug A,Procaccini A,et al.Structural basis of histidine kinase autophosphorylation deduced by integrating genomics,molecular dynamics,and mutagenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2012,109(26):1733-1742.
[21] Laub M T,Goulian M.Specificity in two-component signal transduction pathways.Annual Review of Genetics,2007,41:121-145.
[22] Hoch J A,Varughese K I.Keeping signals straight in phosphorelay signal transduction.Journal of Bacteriology,2001,183(17):4941-4949.
[23] Janiak-Spens F,Sparling D P,West A H.Novel role for an HPT domain in stablizing the phosphorylated state of a response regulator domain.Journal of Bacteriology,2000,182(23):6673-6678.
[24] Chavez R G,Alvarez A F,Romeo T,et al.The physiological stimulus for the Bar A sensor kinase.Journal of Bacteriology,2010,192(7):2009-2012.
[25] Mondragón V,Franco B,Jonas K,et al.p H-dependent activation of the Bar A-Uvr Y two-component system in Escherichia coli.Journal of Bacteriology,2006,188(23):8303-8306.
[26] Déziel E,Comeau Y,Xillemur R.Initiation of biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 57RP correlates with emergence of hyperpiliated and highly adherent phenotypic variants deficient in swimming,swarming and twitching motilities.Journal of Bacteriology,2001,183(4):1195-1204.
Regulatory function of histidine kinase sensor encoding gene barA in bio-control effect of Rahnella aquatilis.Journal of Zhejiang University(Agric.&Life Sci.),2015,41(1):56-63
Xiao Fenghu1,Zhang Lei2,Xie Zhen1,Guo Yanbin3,Chen Minwen1,Wang Yongjun1,4*(1.School of Forestry and Bio-technology,Zhejiang Agricultural and Forestry University,Lin’an 311300,Zhejiang,China;2.Zhejiang University of Science and Technology,Hangzhou 310023,China;3.College of Resources and Environmental Sciences, China Agricultural University,Beijing 100094,China;4.National and Provincial Joint Engineering Laboratory of Bio-pesticide Preparation,Zhejiang Agricultural and Forestry University,Lin’an 311300,Zhejiang,China)
Rahnella aquatilis;histidine kinase sensor encoding gene barA;two-component regulatory system;biocontrol
Q 754
A
10.3785/j.issn.1008-9209.2014.03.122
国家自然科学基金资助项目(31200386);浙江省自然科学基金资助项目(LY12C14006);浙江省大学生科技创新活动计划(新苗人才计划)资助项目(2012R412030).
王勇军,Tel:+86 571 63742763;E-mail:wangyj@zafu.edu.cn
联系方式:肖凤虎,E-mail:xiaofh126@126.com
2014 03 12;接受日期(Accepted):2014 06 09;
日期(Published online):2015 01 19
URL:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/33.1247.S.20150119.1654.005.html
