手术治疗喙突骨折合并肩锁关节脱位
2015-05-14陈杭胡晓川杨国勇向明
陈杭 胡晓川 杨国勇 向明
手术治疗喙突骨折合并肩锁关节脱位
陈杭 胡晓川 杨国勇 向明
【摘要】目的 探讨喙突骨折合并肩锁关节脱位的诊断及手术治疗效果。方法 2007 年 5 月至 2014 年5 月,我科采用肩部锁骨远端沿 Langer 线纵形切口显露、复位并固定肩锁关节脱位及喙突骨折,修复肩锁韧带治疗 12 例肩锁关节脱位合并喙突骨折患者。其中男 9 例,女 3 例;年龄 20~56 岁,平均 33 岁。肩锁关节脱位均为 Rockwood III 型,喙突骨折 Eyres 分型:III B 型 8 例,IV B 型 3 例,V B 型 1 例。所有患者均有外伤史,术前经 X 线片及 CT 证实喙突骨折移位。结果 12 例中 10 例获得随访,时间 9~15 个月,平均 12 个月。患者伤口均 I 期愈合,喙突骨折均达骨性愈合,肩锁关节复位良好,肩关节功能良好。本组 10 例终末随访时,Constant 评分 83~95 分,平均 90.8 分;前屈上举平均 156°,外旋平均 45°。Herscovici 疗效评定优8 例,良 2 例。结论 肩锁关节脱位合并喙突骨折中,喙突骨折容易漏诊,所以诊断中应予重视。沿 Langer线纵形切口显露及复位固定治疗,显露充分,操作方便。术中对肩锁关节脱位及喙突骨折双重固定,可恢复肩锁关节及喙突正常的生理解剖位置,有利于患肢功能恢复,且术后切口美观,是一种有效的治疗方法。
【关键词】肩锁关节;脱位;喙突;骨折;骨折固定术,内
肩胛骨喙突位置深在,周围有肌肉及胸壁保护,发生骨折的概率较低,约占肩胛骨骨折的 2%~ 13%[1-3]。喙突骨折伴有肩锁关节脱位的病例则更少见。喙突骨折合并肩锁关节脱位的治疗在临床中报道比较少,且有一定的争议。2007 年 5 月至 2014 年5 月,我科采用切开复位锁骨钩钢板固定肩锁关节、空心螺钉固定喙突骨折治疗 12 例 Rockwood III型肩锁关节脱位合并喙突骨折患者,疗效满意,报道如下。
资料与方法
一、一般资料
本组 12 例,男 9 例,女 3 例;年龄 20~56岁,平均 33 岁。车祸伤 5 例,高处坠落伤 6 例,重物砸伤 1 例;左侧 7 例,右侧 5 例;12 例均为新鲜损伤。受伤至手术时间 2~8 天,平均 5 天。临床表现均为肩部肿痛,肩锁关节压痛、琴键征,肩关节活动受限。本组病例均常规行 X 线及肩部 CT检查,肩锁关节脱位均为 Rockwood III 型,喙突骨折 Eyres[4]分型:III B 型 8 例,IV B 型 3 例,V B 型1 例。
二、手术方法
全麻监护下进行手术。患者取沙滩椅位,患肩部垫高,头转向健侧。沿皮肤 Langer 线位于喙突与肩锁关节之间作长 5~6 cm 切口,深至三角肌及斜方肌筋膜,切开筋膜显露肩锁关节,顺近侧三角肌胸大肌间隙进入,暴露喙突上方。探查喙锁韧带完整性,按压锁骨远端试行复位,复位困难的须清除嵌于肩锁关节内血肿、破碎的关节盘、关节囊等。选择合适的锁骨钩钢板将钩端插入肩峰后下方,按下锁骨使肩锁关节复位,将钢板贴于锁骨上方,复位钳临时固定, 使用螺钉固定。检查肩锁关节复位满意、锁骨钩钢板复位有效后,将喙突周围稍作钝性分离,显露喙突。术者以示、中指探查喙突上缘及内缘作引导,顺喙突轴线向喙突穿入克氏针临时固定。透视位置满意后,采用 1 枚 3 mm 或 4 mm 直径的 AO 空心螺钉沿导针固定喙突,被动活动肩关节无异常后,用可吸收线修复肩锁关节囊、筋膜、肩锁韧带及三角肌、斜方肌的腱性附着部分。术后常规处理,并指导患者逐步进行肩关节功能锻炼。
三、术后处理
术后使用抗生素 24 h,术后 14 天拆线,三角巾悬吊 6 周。术后 4 周内以逐步被动前屈上举、被动外旋锻炼为主,术后 4 周逐步开始主动不负重功能锻炼,术后 3 个月逐步负重活动。复查 X 线片示喙突骨性愈合后取出锁骨钩钢板,时间为术后 3~6 个月,平均 3.8 个月。
四、评价指标
X 线检查评估肩锁关节的复位、喙突骨折的愈合情况。Constant 评分满分 100 分,分别由疼痛( 15 分 )、肌力 ( 25 分 )、功能活动 ( 20 分 ) 及肩关节活动度 ( 40 分 ) 4 个子量表组成。分数越高表示功能越好。按照 Herscovici 等[5]肩关节功能评定标准:优,肩部不痛,恢复正常工作,活动不受限,外展肌力 5 级;良,肩部轻度疼痛,正常工作略受影响,活动稍受限,外展肌力 4 级;可,肩部中度疼痛,正常工作较多影响,外展 45°~90°,外展肌力 3 级;差,严重疼痛,活动少于 45°,外展肌力2 级。
结 果
本组病例术中探查喙锁韧带,未见完全断裂,仅有 2 例喙锁韧带纤维有损伤,但保持连续性。所有患者术后 X 线片示肩锁关节脱位完全复位,喙突骨折对位良好。10 例获随访,时间 9~15 个月,平均 12 个月。1 例 X 线片示喙锁韧带走行方向少许钙化物形成,2 例术后 3 个月内存在疼痛,取出锁骨钩钢板后,疼痛明显缓解,经过康复,肩关节活动功能基本恢复满意。终末随访时,无肩锁关节再脱位病例,喙突骨折均骨性愈合。Constant 评分 83~95 分,平均 90.2 分;前屈上举平均 156°,外旋平均45°。按照 Herscovici 等肩关节评分,本组优 8 例,良 2 例。典型病例见图 1。
讨 论
一、如何避免喙突骨折的漏诊
肩部损伤引起的肩锁关节脱位,诊断相对容易,但对于合并的喙突骨折,特别是移位不大的骨折,临床医师容易忽视而引起漏诊。对于喙突骨折,采用球管向头端倾斜 45° 位投照或摄健侧X 线片对比有助于其诊断;通过 CT 扫描结合三维重建,不仅能明确诊断,且能清晰地显示骨折部位及移位情况,为明确骨折类型和制订手术方案提供有力指导。
二、手术体会
术中沿皮肤 Langer 线位于喙突与肩锁关节之间作手术切口,切口可以充分显露锁骨远端、肩锁关节及喙突,操作简便,术后切口愈合良好,瘢痕小且隐蔽,较美观。
术中先复位肩锁关节,固定钩钢板,喙锁韧带相对松弛,利于喙突骨折复位固定,否则,喙突骨折因喙锁韧带牵拉不易复位固定。手术难点是喙突螺钉的植入,术中将喙突复位后沿喙突轴线[1]偏外侧先钻入 1 枚克氏针临时固定,同时也可以防止在拧入空心螺钉时喙突骨折块产生旋转移位,喙突基底骨折一般不易直视下复位,术中须使用示、中指触摸的方法间接复位及判断复位情况,并可定位喙突轴线的方向,以利导针钻入,术中反复透视确认导针固定的位置及长度合适后拧入空心螺钉固定。
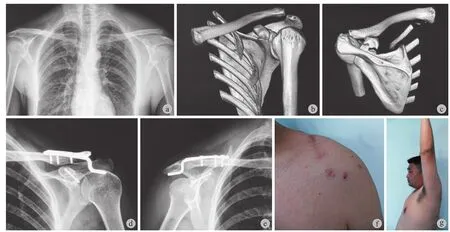

图 1 患者,男,31 岁,左肩部因骑电瓶车摔伤 a:术前双肩关节正位对比片;b~c:术前 CT;d~e:空心螺钉固定喙突、钩钢板固定肩锁关节脱位;f~i:术后 6 个月肩关节功能像Fig.1 Male, 31 years old, left shoulder injury by falling down a: Preoperative anteroposterior contrast of the shoulder; b-c: pre-operation CT, d-e: Coracoid was fixed by cannulated screw. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation was fixed by hook plate; f-j: Shoulder joint functions 6 months post-operation
三、喙突固定的意义
喙突尖部有喙锁韧带、喙肩韧带附着,喙突基底部有联合肌腱、胸小肌附着。一些学者认为,肩锁关节复位后,喙突会自动复位。因此,单纯复位固定肩锁关节脱位即可[1-3]。喙突骨折的内固定仅仅适用于肩锁关节复位后,喙突不稳定的情况[6-7]。随着肩关节运动医学的发展,喙突在维持肩胛带稳定中的作用越来越受到重视。喙突骨折移位必然改变喙锁韧带、喙肩韧带、喙肱韧带的生理位置及力线,进而影响肩锁关节及盂肱关节的稳定。因此,目前大多数学者更倾向于手术内固定治疗移位的喙突骨折[8-9]。本组病例同期固定喙突骨折的目的是恢复喙突的解剖位置,使喙突骨折端加压,以利更好地愈合,避免去除锁骨钩钢板后遗留肩锁关节的半脱位、肩关节疼痛及活动受限。
四、锁骨钩钢板去除时机
锁骨钩钢板通过穿过肩峰的钩以及锁骨端的钉板结构形成杠杆作用,使锁骨远端获得稳定而持续的压力。保证肩锁、喙锁韧带及周围软组织在稳定的无张力环境愈合。锁骨钩钢板内固定具有使用方便、操作简单、固定可靠和术后可早期进行功能锻炼等优点,是治疗喙突骨折合并肩锁关节脱位的常用选择。但存在术后肩痛及肩关节僵硬[10]、肩关节活动受限以及不同程度的肩峰撞击,另外有锁骨骨吸收[11-12]、内植物周围骨折[13]。锁骨钩钢板一般应在肩关节运动恢复至前臂可完全举过头前,即术后8~12 周时取出。笔者建议喙突骨折愈合后尽早去除钩钢板。本组病例中 2 例术后 3 个月内存在轻度疼痛、外展受限明显,取出锁骨钩钢板后,疼痛明显缓解,肩关节活动功能基本恢复正常。本组病例去除钩钢板时间 3~6 个月,平均 3.8 个月。
综上所述,合并喙突骨折的肩锁关节脱位临床发生率低,需要仔细体检及完善必要的影像学资料,避免漏诊。锁骨钩钢板固定肩锁关节的同时空心螺钉固定喙突骨折,是一种有效的治疗方法,合适时机取出钩钢板[14-16],合理的康复可以达到较好的临床治疗效果。
参 考 文 献
[1] Imatani RJ. Fractures of the scapula: a review of 53 fractures. J Trauma, 1975, 15(6):473-478.
[2] Ada JR, Miller ME. Scapular fractures. Analysis of 113 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1991, (269):174-180.
[3] Wilber MC, Evans EB. Fractures of the scapula. An analysis of forty cases and a review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1977, 59(3):358-362.
[4] Eyres KS, Brooks A, Stanley D. Fractures of the coracoid process. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1995, 77(3):425-428.
[5] Herscovici D Jr, Fiennes AG, Allgöwer M, et al. The floating shoulder: ipsilateral clavicle and scapular neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1992, 74(3):362-364.
[6] 冯沃君, 杨会营, 王军. 喙突的解剖学测量及其临床意义. 中医外治杂志, 2011, 20(5):7-8.
[7] Montgomery SP, Loyd RD. Avulsion fracture of the coracoid epiphysis with acromioclavicular separation. Report of two cases in adolescents and review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1977, 59(7):963-965.
[8] Taga I, Yoneda M, Ono K. Epiphyseal separation of the coracoid process associated with acromioclavicular sprain. A case report and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1986, (207):138-141.
[9] Wang KC, Hsu KY, Shih CH. Coracoid process fracture combined with acromioclavicular dislocation and coracoclavicular ligament rupture. A case report and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1994, (300):120-122.
[10] Martín-Herrero T, Rodríguez-Merchán C, Munuera-Martínez L. Fractures of the coracoid process: presentation of seven cases and review of the literature. J Trauma, 1990, 30(12):1597-1599.
[11] 黄柏辉. 肩锁关节脱位合并喙突骨折的治疗. 实用骨科杂志, 2007, 13(11):662.
[12] 荆兆峰, 赵以瑜, 王瑞国. 微创治疗重度肩锁关节脱位合并喙突骨折. 中国骨伤, 2010, 23(1):46-48.
[13] De Baets T, Truijen J, Driesen R, et al. The treatment of acromioclavicular joint dislocation Tossy grade III with a clavicle hook plate. Acta Orthop Belg, 2004, 70(6):515-519.
[14] Gstettner C, Tauber M, Hitzl W, et al. Rockwood type III acromioclavicular dislocation: surgical versus conservative treatment. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 2008, 17(2):220-225.
[15] Meda PV, Machani B, Sinopidis C, et al. Clavicular hook plate for lateral end fractures: a prospective study. Injury, 2006, 37(3):277-283.
[16] Flinkkilä T, Ristiniemi J, Lakovaara M, et al. Hook-plate fixation of unstable lateral clavicle fractures: a report on 63 patients. Acta Orthop, 2006, 77(4):644-649.
( 本文编辑:王萌 )
. 肩关节外科 Shoulder surgery .
Operative treatment of coronoid process fractures associated with acromioclavicular dislocation
CHEN Hang,
HU Xiao-chuan, YANG Guo-yong, XIANG Ming.
Department of Upper Extremity Trauma, Sichuan Orthopaedic
Hospital, Chengdu, Sichuan, 610041, PRC
Corresponding author: XIANG Ming, Email: josceph_xm@sina.com
【Abstract】Objective To investigate the diagnosis and effectiveness of operative treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation associated with coronoid process fractures. Methods From May 2007 to May 2014, 12 cases ( 9 males, 3 females ) of acromioclavicular dislocation associated with coronoid process fractures underwent longitudinal exposure of the distal clavicle of the shoulder along Langer line, reduction, fixation of the acromioclavicular dislocation and coronoid process fractures, and acromioclavicular ligament repair. The average age was 33 years old ( range: 20-56 years ). All acromioclavicular dislocations were of Rockwood type III. Eyres type of coronoid process fractures: III B in 8 cases, IV B in 3 cases, V B in 1 case. All patients had injury history, coronoid process dislocation and fracture were confirmed by preoperative X-ray films and CT scan. Results Ten out of 12 patients were followed up with the mean period of 12 months ( range: 9-15 months ). All incisions healed by the first intention. Coronoid process fracture healing was achieved in all patients with good acromioclavicular joint reduction and shoulder joint functions. In the latest follow-up, the mean Constant score was 90.8 points ( range: 83-95 points ). The mean forward flexion was 156°, while mean external rotation 45°. According to Herscovici evaluation criteria: excellent in 8 cases, good in 2 cases. Conclusions Missed diagnosis of coronoid process fractures may occur in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation associated with coronoid process fractures, which should be paid close attention. Longitudinal exposure of the distal clavicle of the shoulder along Langer line and reduction provide sufficient view and convenience. By the double fixation for acromioclavicular dislocation and coronoid process fractures, normal anatomical position can be restored, which is beneficial for the recovery of affected limb functions and post-operative oppearance of the incision. It is an effective treatment method.
【Key words】Acromioclavicular joint; Dislocations; Coracoid; Fractures, bone; Fracture fixation, internal
( 收稿日期:2015-04-28 )
通信作者:向明,Email: josceph_xm@sina.com
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-252X.2015.07.004
作者单位:610041 成都,四川省骨科医院上肢科
中图分类号:R683.4
