双氢青蒿素通过阻断Wnt/β-catenin信号抑制骨肉瘤细胞系体外增殖和侵袭
2014-11-28王文娟王玉凤冯巧灵何娟文何通川罗进勇
王文娟,赵 丹,徐 静,李 丽,董 谦,王玉凤,冯巧灵,王 锦,何娟文,何通川,罗进勇
(重庆医科大学 检验医学院 检验医学教育部重点实验室 重庆市重点实验室, 重庆 400016)
研究论文
双氢青蒿素通过阻断Wnt/β-catenin信号抑制骨肉瘤细胞系体外增殖和侵袭
王文娟,赵 丹,徐 静,李 丽,董 谦,王玉凤,冯巧灵,王 锦,何娟文,何通川,罗进勇*
(重庆医科大学 检验医学院 检验医学教育部重点实验室 重庆市重点实验室, 重庆 400016)
目的研究双氢青蒿素(DHA)在体外对骨肉瘤细胞增殖和侵袭的抑制作用及其可能的分子机制。方法不同浓度的DHA处理骨肉瘤细胞,结晶紫染色检测细胞增殖。Western blot和荧光素酶报告基因实验检测Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的活化情况。结果DHA在体外能明显浓度依赖性地抑制人骨肉瘤细胞的增殖和侵袭(P<0.05);DHA可降低骨肉瘤细胞β-catenin的蛋白水平和转录调控活性(P<0.01),过表达β-catenin可逆转DHA对骨肉瘤细胞增殖和侵袭的抑制作用(P<0.05),而β-catenin基因沉默则可进一步加强其抑制效果(P<0.01)。结论DHA可明显抑制人骨肉瘤细胞增殖和侵袭,这种作用可能与其阻断Wnt/β-catenin信号通路相关。
双氢青蒿素;骨肉瘤;Wnt/β-catenin;信号通路
骨肉瘤(osteosarcoma,OS)是最常见的恶性成骨性肿瘤之一,尤其好发于儿童和青少年[1]。骨肉瘤恶性程度较高。有80%的患者在确诊时就已经出现肺部转移[2]。目前骨肉瘤的临床治疗面临诸多挑战,如化疗药物的不良反应、肿瘤细胞耐药、肿瘤复发和肺部转移等。即使采取以手术为主,辅以化疗和放疗的综合治疗,其预后仍然不佳[3]。因此,临床需要更为低毒有效的药物用于骨肉瘤的治疗。开发新的治疗药物或新的治疗药物与传统治疗方式相结合是骨肉瘤治疗的重要研究方向,
青蒿素是菊科植物黄花蒿中的有效成分,而双氢青蒿素(dihydroartemisinin,DHA)是由青蒿素经四氢硼钠还原而成的一个重要衍生物。目前DHA作为治疗疟疾的一线药物在临床广为使用[4]。近来研究发现,DHA对于多种恶性肿瘤均具有明显的抑制作用,且不良反应较小[5- 7]。本实验对DHA在体外抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖和侵袭的作用进行了研究,并进一步探讨了其分子机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
荧光素酶报告质粒Top-luc、过表达β-catenin腺病毒和β-catenin的RNA干扰腺病毒(芝加哥大学医学中心何通川教授惠赠);人骨肉瘤细胞系143B、MG63、SaoS2和U2OS(美国菌种保藏中心ATCC);DHA(四川三奇制药厂),DMSO溶解为浓度为70 mmol/L的原液,-20 ℃保存备用;DMEM高糖培养基和优质胎牛血清(Hyclone公司)。抗体:MMP9(sc-6840)、VEGF(sc-7269)、COX2(sc-65239)、p-P53(sc-18078)、P53(sc-126)、MDM2(sc-965)、c-Myc(sc-41)、Cyclin D1(sc-8396)、β-catenin(sc-7963)、DVL(sc-7400)、p-GSK3β(Ser9)(sc-373800)、GSK3(sc-81402)和β-actin(sc-47778)一抗(Santa Cruz公司)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 结晶紫染色:将143B、MG63、SaoS2和U2OS细胞制备为5×104个/mL的细胞悬液。在24孔板中,每孔加入500 μL细胞悬液,贴壁后按预定分组处理。处理结束后,弃去上清,PBS洗涤两次,醋酸/甲醇固定液(1∶3)固定15 min,结晶紫染色30 min,流水冲洗多余染液,自然干燥后成像。随后,加入20%醋酸溶液1 mL,在室温下振荡处理20 min,吸取其中100 μL液体加至1 mL蒸馏水中,570 nm下测定吸光度。计算肿瘤细胞的相对生长速率(DHA处理组吸光度/DMSO处理组吸光度×100%)。
1.2.2 Transwell实验:按1∶7比例将基质胶(extracellular matrix,ECM)与预冷的无血清培养基充分混合,吸取32 μL混合液均匀铺在Transwell小室内侧面。无血清培养基制备2.5×105个/mL细胞悬液,吸取400 μL细胞悬液加入小室内。24孔板内加入含20%胎牛血清的杜氏改良伊格尔培养基(DMEM)600 μL,培养24 h。湿棉签檫去小室未穿过膜的细胞,无水乙醇室温固定20 min,自然晾干后,苏木精染色20 min,清水漂洗,自然晾干。伊红复染20 min,自然干燥后成像。
1.2.3 Western blot:细胞接种在直径100 mm的培养皿中,待细胞贴壁后加入不同处理因素处理,到相应时间后提取细胞蛋白,按照Western blot步骤测定相应蛋白的变化。
1.2.4 荧光素酶报告基因的检测:将143B细胞接种于T-25细胞培养瓶中,浓度为30%,脂质体2000转染Top-luc 质粒3 μg,随后加入DHA处理至不同时间点后测定荧光素酶活性(按照试剂盒说明书进行)。
1.3 统计学分析
2 结果
2.1 DHA抑制人骨肉瘤细胞的增殖
即使低剂量的DHA(2.5 μmol/L)也可抑制143B细胞增殖(P<0.05),而且随着DHA浓度的增加,对143B细胞的增殖抑制作用越强(P<0.05,P<0.01)(图1)。在骨肉瘤细胞系MG63、SaoS2和U2OS中,DHA也表现出相似的抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖的作用(P<0.05,P<0.01)(图2)。
2.2 DHA抑制人骨肉瘤细胞的侵袭
DHA组穿过小室的细胞明显减少(P<0.01)(图3A, B)。DHA可以下调肿瘤侵袭相关蛋白如基质金属蛋白酶9(matrix metallopeptidase 9,MMP9)、血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)和环氧合酶2(cyclooxygenase 2,COX2)的蛋白水平(图3C)。
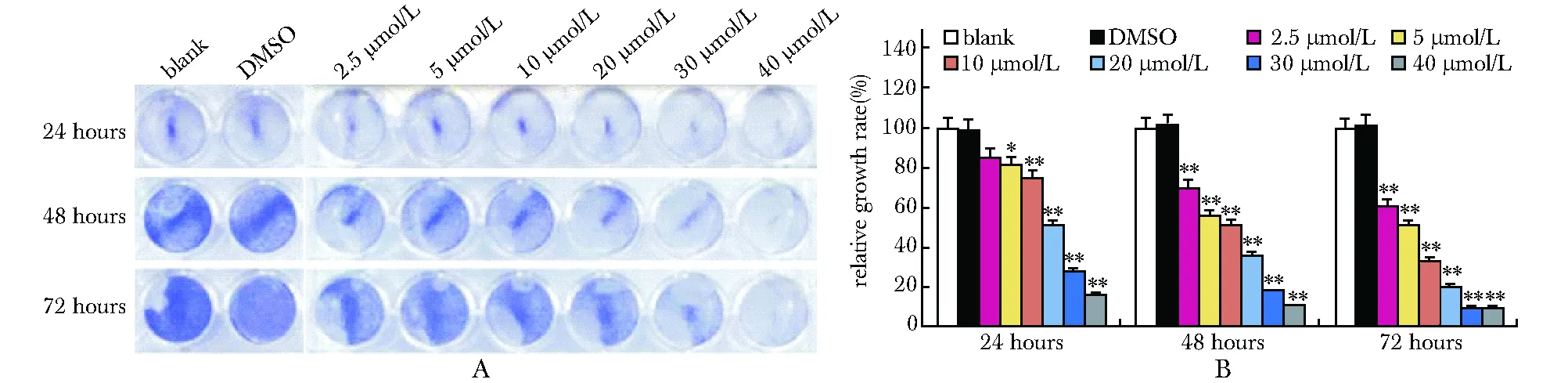
A.cell proliferation (crystal violet staining) result of 143B OS cells treated with DHA as the indicated concentrations; B.the quantitative result of crystal violet staining of 143B cells;*P<0.05,**P<0.01 compared with blank and DMSO
图1DHA抑制骨肉瘤细胞143B的增殖
Fig1DHAinhibitstheproliferationof143BOScells

A.cell proliferation (crystal violet staining) result of MG63,SaoS2 and U2OS cells treated with DHA as the indicated concentrations; B.the quantitative result of crystal violet staining MG63,SaoS2 and U2OS cells;*P<0.05,**P<0.01 compared with blank and DMSO
图2DHA抑制骨肉瘤细胞MG63、SaoS2和U2OS的增殖
Fig2DHAinhibitstheproliferationofMG63,SaoS2andU2OScells
2.3DHA可阻断骨肉瘤细胞中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路
经典的肿瘤相关分子p-P53、P53和MDM2均未发生明显变化。但DHA处理使β-catenin蛋白在骨肉瘤细胞内明显减少,β-catenin靶蛋白c-Myc和cycling D1的蛋白水平也相应下降;Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中调节β-catenin蛋白水平的重要分子DVL的蛋白水平以及GSK3β的磷酸化水平均明显下调(图4 A)。而且β-catenin的转录调控活性也明显被DHA所抑制(P<0.01)(图4 B)。
2.4Wnt/β-catenin信号通路与DHA抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖和侵袭相关
在143B细胞中成功过表达β-catenin(图5A)或对β-catenin进行基因沉默(图5B)。结果发现单独过表达β-catenin,143B的增殖和侵袭均无明显变化,但过表达β-catenin可以逆转DHA对于骨肉瘤细胞的抑制作用(P<0.05),使得细胞的增殖和侵袭能力得到一定程度恢复(图6);而仅有β-catenin基因沉默时,143B的增殖和侵袭就有所下降(P<0.05),不仅如此,β-catenin基因沉默可以进一步加强DHA对于143B的增殖和侵袭的抑制作用(P<0.01)(图6)。
3 讨论
骨肉瘤原发于骨组织,其致死率和致残率较高。
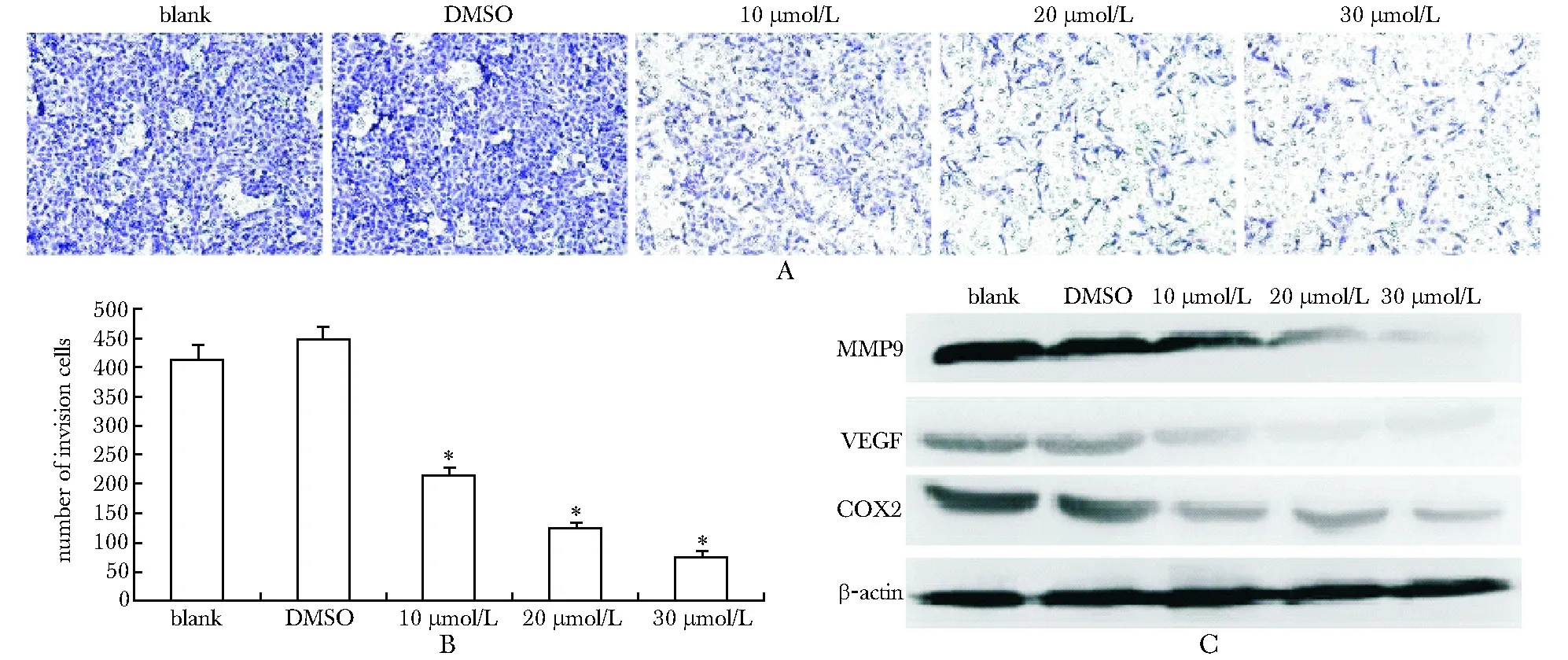
A.the transwell migration assay in 143B cells treated with DHA as the indicated concentrations (×100); B.the quantitative result of transwell migration assay in 143B cells;*P<0.01 compared with blank and DMSO; C.Western blot assay for the MMP9, VEGF and COX2 protein level in 143B cells
图3DHA抑制骨肉瘤细胞143B的侵袭
Fig3DHAinhibitsmigrationandinvasionof143BOScells
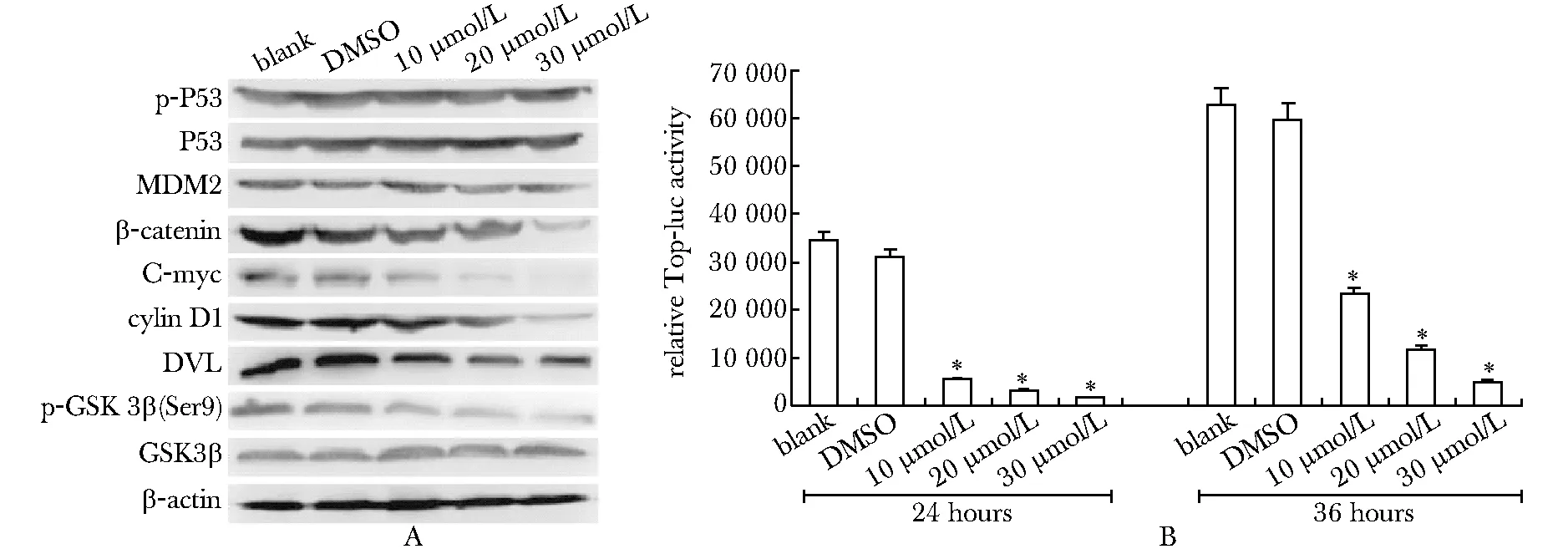
A.Western blot assay for p-P53, P53, MDM2, β-catenin, C-myc, Cyclin D1, DVL, p-GSK3β (Ser 9) and GSK3β protein level in 143B cells; B.β-catenin-controlled TOP-luc reporter result in 143B cells;*P<0.01 compared with blank and DMSO
图4DHA抑制骨肉瘤细胞143B的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路
Fig4DHAsuppressesWnt/β-cateninsignalinginhuman143BOScells

A.Western blot assay for exogenous β-catenin in 143B cells; B.Western blot assay for knockdown of β-catenin in 143B cells
图5在143B细胞中有效过表达β-catenin及沉默β-catenin
Fig5Theeffectiveexpressionofexogenousβ-cateninandgenesilenceofβ-cateninin143BcellsconfirmedbyWesternblotassay
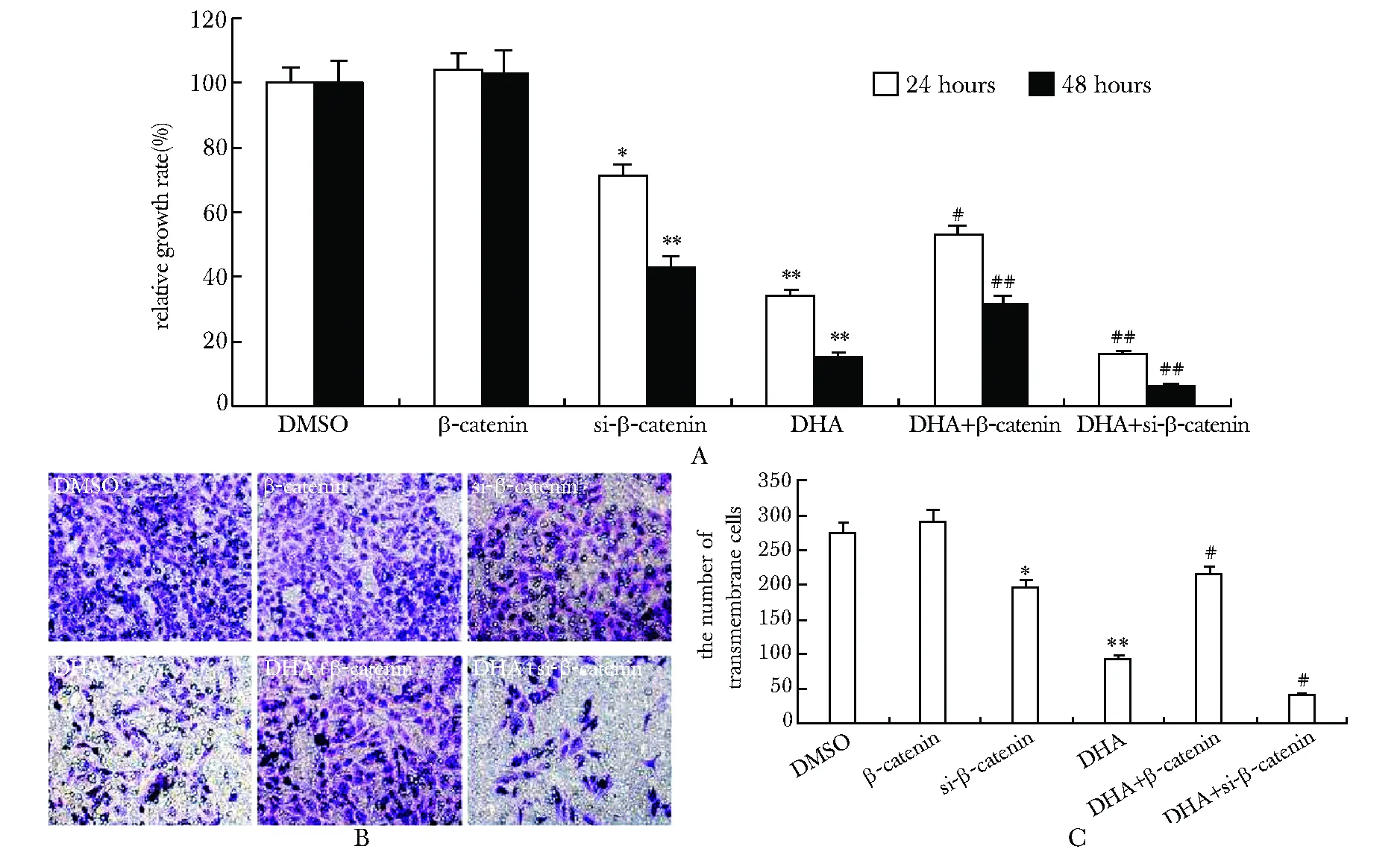
A.the quantitative result of 143B growth rate (crystal violet staining) treated by DHA with/without exogenous expressed β-catenin or knockdown of β-catenin;*P<0.05,**P<0.01 compared with DMSO;#P<0.05,##P<0.01 compared with DHA; B.the transwell invasion result (with EMC) in 143B cells treated by DHA with/without exogenous expressed β-catenin or knockdown ofβ-catenin(×100); C.the quantitative transwell invasion result in 143B cells treated by DHA with/without exogenous expressed β-catenin or knockdown ofβ-catenin;*P<0.05,**P<0.01 compared with DMSO;#P<0.01 compared with DHA
图6DHA对骨肉瘤细胞增殖和侵袭的抑制与β-catenin有关
Fig6β-cateninfunctionsintheinhibitoryeffectofDHAonOScells
在采用传统的手术、化疗和放疗后,骨肉瘤的预后仍不佳。天然药物和中药有效成分已视为是高效低毒的抗肿瘤药物的理想来源。近来发现抗疟疾药物DHA也具有抗肿瘤的效果[5- 7]。已证实DHA抗肿瘤的机制可能涉及体内铁的平衡[6],并与丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen activated protein kinases,MAPKs)中的P38和ERK1/2信号通路相关[7]。本研究则发现,DHA可以明显抑制骨肉瘤细胞的增殖和侵袭, 该抑制作用可能是通过阻断Wnt/β-catenin信号而实现的。
本研究表明经典的肿瘤相关分子p-P53、P53和MDM2可能与DHA的抗骨肉瘤细胞增殖和侵袭无关。Wnt/β-catenin信号在肿瘤的发生中具有重要的作用[8- 10]。而DHA可以抑制经典的Wnt/β-catenin信号,导致β-catenin在细胞内水平下降,并抑制其转录调控活性。DHA可以抑制DVL的蛋白水平,DVL是调控β-catenin水平的重要分子,其受到抑制后,将会影响β-catenin降解复合物的形成,从而抑制复合物对于β-catenin的降解[9]。GSK3β可以直接磷酸化β-catenin,导致其降解。GSK3β在第9位丝氨酸磷酸化,会导致GSK3磷酸化β-catenin的活性减弱[10]。而DHA则可抑制GSK3β的第9位丝氨酸磷酸化,导致GSK3β催化活性增加。由此推断DHA极可能通过下调DVL蛋白水平,并通过抑制GSK3β的第9位丝氨酸磷酸化而促进GSK3β的催化活性,从而促进β-catenin降解,下调β-catenin在细胞内的蛋白水平,并由此抑制骨肉瘤细胞的增殖和侵袭。
本研究主要的意义在于探讨了DHA抑制骨肉瘤细胞的分子机制,发现了DHA抗肿瘤活性与阻断肿瘤细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路有关,在一定程度上为DHA抗肿瘤的应用提供了理论和实验基础。
[1] Tang N, Song WX, Luo J,etal. Osteosarcoma development and stem cell differentiation[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2008, 466:2114- 2130.
[2] Kager L, Zoubek A, Potschger U,etal. Primary metastatic osteosarcoma: presentation and outcome of patients treated on neoad-juvant Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study Group protocols[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2003, 21:2011- 2018.
[3] Lamoureux F, Richard P, Wittrant Y,etal. Therapeutic Relevance of Osteoprotegerin Gene Therapy in Osteosarcoma: Blockade of the Vicious Cycle between Tumor Cell Proliferation and Bone Resorption[J]. Cancer Res, 2007, 67:7308- 7318.
[4] O’Neill PM, Posner GH. A medicinal chemistry perspective on artemisinin and related endoperoxides[J]. J Med Chem, 2004, 47: 2945- 2964.
[5] Chen H, Sun B, Wang S,etal. Growth inhibitory effects of dihydroartemisinin on pancreatic cancer cells: involvement of cell cycle arrest and inactivation of nuclear factor-kappaB[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2010, 136:897- 903.
[6] Ba Q, Zhou N, Duan J,etal. Dihydroartemisinin exerts its anticancer activity through depleting cellular iron via transferrin receptor-1[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7:e42703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042703.
[7] Firestone GL, Sundar SN. Anticancer activities of artemisinin and its bioactive derivatives[J]. Expert Rev Mol Med, 2009, 11:e32. doi: 10.1017/S1462399409001239
[8] Berthon A, Martinez A, Bertherat J,etal. Wnt/β-catenin signalling in adrenal physiology and tumour development[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2012, 351:87- 95.
[9] Luo J, Chen J, Deng ZL,etal. Wnt signaling and human diseases: what are the therapeutic implications?[J]. Lab Invest, 2007, 87:97- 103.
[10] Jope RS, Yuskaitis CJ, Beurel E. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): inflammation, diseases, and therapeutics[J]. Neurochem Res, 2007, 32:577- 595.
Dihydroartemisinin (DHA) inhibits proliferation and invasion ofosteosarcoma cell lineinvitroby suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling
WANG Wen-juan, ZHAO Dan, XU Jing, LI Li, DONG Qian, WANG Yu-feng, FENG Qiao-ling,WANG Jin, HE Juan-wen, HE Tong-chuan, LUO Jin-yong*
(Key Laboratory of Laboratory Medical Diagnostics, Ministry of Education, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the proliferation and invasion inhibitory effect of dihydroartemisinin (DHA) on human osteosarcoma (OS) cells and the possible molecular mechanism involved.MethodsOS cells were seeded and treated with different concentrations of DHA. Cells were stained with crystal violet to find cell viability. ECM Transwell assay was used to assess the alteration in cellular invasion induced by DHA in OS cells. Western blot and luciferase assay were used to evaluate activation of Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway.ResultsDHA can inhibit proliferation and reduce invasion in human OS cells. Total protein and transcription activity of β-catenin in OS cells were reduced by DHA treatment. Moreover, the inhibitory effect of DHA on OS cells was reversed by over-expression ofβ-catenin, but was further enhanced by know-down of β-catenin, respectively.ConclusionsOur results showed that DHA can inhibit tumor proliferation and invasion of OS cells by inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
dihydroartemisinin; osteosarcoma; Wnt/β-catenin; signal pathway
2013- 08- 26
2013- 12- 20
国家自然科学基金(31071304,81272006);973子课题(2011CB707906)
*通信作者(correspondingauthor): luojinyong@sina.com
1001-6325(2014)08-1017-06
R 743.2
A
