腹横肌平面阻滞在乳房再造术后镇痛中的临床研究
2014-11-01梁佐迪刘炜炜蔡大升
周 珩, 邓 娜, 梁佐迪, 刘炜炜, 蔡大升
论 著
腹横肌平面阻滞在乳房再造术后镇痛中的临床研究
周 珩, 邓 娜, 梁佐迪, 刘炜炜, 蔡大升
目的探讨腹横肌平面阻滞在腹壁皮瓣乳腺癌患者乳房再造术后镇痛的临床效果。方法回顾性分析腹横肌平面阻滞置管间断注射局部麻醉药术后镇痛和术后患者自控静脉镇痛48 h镇痛效果、阿片类药物的使用量及术后镇痛相关并发症的发生率。结果腹横肌平面阻滞组术后镇痛效果与患者自控静脉镇痛组相当,但阿片类药物使用量和术后镇痛相关并发症发生率却远低于患者自控静脉镇痛组。结论腹壁皮瓣乳腺癌患者乳房再造术后应用腹横肌平面阻滞置管镇痛可提供与传统术后镇痛方法相当的镇痛效果,同时又具有传统术后镇痛方法所不具备的优势,值得临床应用。
术后镇痛; 乳房再造; 腹横肌平面阻滞
腹横肌平面(transversus abdominis plane, TAP)阻滞是一种较新的阻滞技术。这种神经阻滞技术可以提高腹部术后镇痛效果,如肾移植[1]和妇科腹腔镜手术[2],有报道称亦可用于剖宫产术后镇痛[3-4]。TAP阻滞是一种较新的阻滞技术。本研究主要对比腹壁皮瓣乳房再造术后两种不同的镇痛模式。
1 对象与方法
1.1 一般资料 回顾性分析2008年7月至2013年6月中国医科大学附属第一医院行腹壁皮瓣乳房再造术的患者63例。其中行TAP阻滞置管间断注射局麻药术后镇痛的患者33例,行患者自控静脉镇痛(patient controlled intravenous analgesia, PCIA)的患者30例。纳入标准:患者均18周岁以上;均行自体腹部组织Ⅰ或Ⅱ期乳房再造。排除标准:患者拒绝行术后镇痛;体质量指数(body mass index, BMI)大于40;局部麻醉药或阿片类药物过敏;长期接受镇痛、镇静药物治疗史和有吸毒史、精神病病史、心脏病或肝脏疾病病史。
1.2 术后镇痛方法及疼痛评分方法 所有患者的腹壁皮瓣均需保留神经,通过背阔肌前缘、腹外斜肌后缘和髂嵴定位Petit三角,在手术过程中,同时将导管置入Petit三角,妥善固定于皮肤上,防止活动后导管移位。手术结束后,TAP组患者通过导管注射0.4%罗哌卡因20 ml,每隔8 h间断注射此负荷剂量。PCIA组患者通过自控静脉镇痛泵镇痛,按5 μg/kg的舒芬太尼以0.9%氯化钠注射液稀释至100 ml,设定为按需模式,无背景速度,1ml/次,每次间隔15 min,用尽后可更换止疼泵。两组如镇痛效果欠佳,可于静脉追加吗啡,每次2 mg。本研究疼痛评分方法采用视觉模拟评分法(visual analogue score, VAS),在纸上划一条10 cm的横线,横线的一端为0,表示无痛;另一端为10,表示剧痛;中间部分表示不同程度的疼痛。让患者根据自我感觉在横线上划记号,表示疼痛的程度。
1.3 观察指标 记录各组患者年龄、BMI、术后镇痛相关并发症、术后48 h内阿片类药物的使用量,及术后2、4、8、12、16、20、24、28、32、36、40、44和48 h的疼痛评分。芬太尼的镇痛强度约为吗啡的75~125倍,舒芬太尼的镇痛强度为芬太尼的5~10倍,将舒芬太尼的使用量换算为吗啡进行比较。
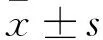
2 结果
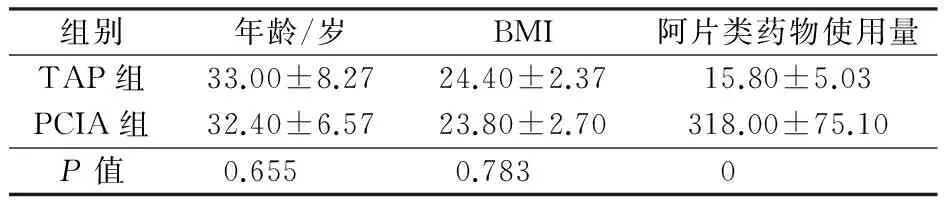
两组患者的年龄、BMI差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术后48 h阿片类药物的使用量TAP组明显少于PCIA组(P<0.05, 表1)。术后48 h各时间点疼痛评分两组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,表2)。
3 讨论
比较两组术后48 h阿片类药物的使用量,可以看出TAP组明显少于PCIA组。两组术后镇痛相关并发症比较,我们可以发现恶心呕吐、呼吸抑制和镇静的发生率TAP组明显低于PCIA组,这与TAP组较少的使用阿片类药物有关;而两组皮肤瘙痒和尿潴留的发生率几乎相同且较低。本研究对比了术后48 h各时间点疼痛评分,我们发现两组术后2、4、8、12、16、20、24、28、32、36、40、44和48 h的疼痛评分均小于3分,其差异无统计学意义,也就是说两种镇痛方法均可以提供有效的术后镇痛效果,曾有报道显示,TAP阻滞可以为腹部供区提供安全有效的术后镇痛。从本研究可以看出,TAP阻滞置管间断注射局麻药术后镇痛与传统的PCIA术后镇痛相比,并发症发生率更低,阿片类药物使用量更少。有报道称,TAP阻滞后发生抽搐[5],本研究中虽未出现,但亦应警惕。同时本研究所有患者在TAP外科置管的过程中无并发症发生,但我们也要考虑到潜在的外科风险。
表1 两组患者的年龄、体质量指数和术后48h阿片类药物使用量比较

组别年龄/岁BMI阿片类药物使用量TAP组33.00±8.2724.40±2.3715.80±5.03PCIA组32.40±6.5723.80±2.70318.00±75.10P值0.6550.7830

表2 两组术后各时间点疼痛评分比较
[1] Gulyam Kuruba SM, Mukhtar K, Singh SK. A randomised controlled trial of ultrasound-guided transversus abdominis plane block for renal transplantation[J]. Anaesthesia, 2014,69(11):1222-1226.
[2] El Hachem L, Small E, Chung P, et al. Randomized Controlled Double-Blind Trial of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block versus Trocar Site Infiltration in Gynecologic Laparoscopy[J]. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2014,Aug 1.
[3] Chandon M, Bonnet A, Burg Y, et al. Ultrasound-Guided Transversus Abdominis Plane Block versus Continuous Wound Infusion for Post-Caesarean Analgesia: A Randomized Trial[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(8):e103971.
[4] Fusco P, Scimia P, Paladini G, et al. Transversus abdominis plane block for analgesia after cesarean delivery. A systematic review[J]. Minerva Anestesiol, 2014 Apr 16.
[5] Weiss E, Jolly C, Dumoulin JL, et al. Convulsions in 2 patients after bilateral ultrasound-guided transversus abdominis plane blocks for cesarean analgesia[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2014,39(3):248-251.
Transversusabdominisplaneblockinpostoperativeanalgesiaofautologousbreastreconstruction
ZHOUHeng,DENGNa,LIANGZuo-di,etal.
(DepartmentofAnesthesiology,TheFirstAffiliatedHospitalofChinaMedicalUniversity,Shenyang110001,China)
ObjectiveTo explore the application of postoperative multimodal analgesia of transversus abdominis plane block in breast reconstruction using the muscle-sparing transversus abdominus myocutaneous flaps.MethodsThis study is a retrospective analysis designed to test the effectiveness of a transversus abdominis plane catheter delivering intermittent local anesthetic and patient controlled intravenous analgesia in reducing postoperative abdominal pain following abdominal tissue breast reconstruction. The objective of this study is to compare the mean total opioid consumption, visual analogue score and the incidence of postoperative analgesia related complications in the first postoperative 48 hours between the two groups.ResultsThe analgesic effect of two groups is almost the same, but the total opioid consumption and incidence of postoperative analgesia related complications of transversus abdominis plane group is lower than patient controlled intravenous analgesia group.ConclusionThe postoperative analgesia of breast reconstruction using the muscle-sparing transversus abdominus myocutaneous flaps by transversus abdominis plane catheter could provide the same analgesic effect to traditional postoperative analgesia methods. It can provide some advantage which traditional postoperative analgesia can′t, and can be applied in the clinical work.
Postoperative analgesia; Breast reconstruction; Transversus abdominis plane block
110001 辽宁 沈阳,中国医科大学附属第一医院 麻醉科(周 珩, 梁佐迪,刘炜炜,蔡大升);中国医科大学附属第四医院 肿瘤内科(邓 娜)
周 珩(1982-),男,辽宁大连人,主治医师,硕士.
10.3969/j.issn.1673-7040.2014.11.016
R655.8
A
1673-7040(2014)11-0685-02
2014-10-15)
