SOCS1基因沉默对人胰腺癌细胞增殖和干扰素-γ敏感性的影响
2014-07-05吕清林陈黎萍
吕清林 王 娟 陈黎萍
SOCS1基因沉默对人胰腺癌细胞增殖和干扰素-γ敏感性的影响
吕清林 王 娟 陈黎萍
目的 在人胰腺癌细胞中观察细胞因子信号转导抑制因子1(SOCS1)沉默对细胞增殖及干扰素-γ (IFN-γ)敏感性的影响,探讨SOCS1作为胰腺癌治疗靶点的可能。方法Western blot及PCR验证SOCS1干扰序列沉默人胰腺癌细胞系PANC1中SOCS1的表达;给予IFN-γ刺激后,采用Western blotting方法观察转录激活因子(STAT)1及磷酸化STAT(pSTAT)1的变化;采用定量PCR的方法观察IFN-γ调节因子1(IRF-1)表达水平变化;MTT法检测胰腺癌细胞对IFN-γ敏感性的变化;细胞计数的方法观察细胞的增殖速度;采用流式细胞术的方法检测细胞周期的变化。结果将SOCS1干扰序列转染PANC1细胞后,SOCS1 mRNA及蛋白表达水平均明显下降。沉默SOCS1表达后,pshSOCS1-PANC1组细胞的IRF-1 mRNA水平及pSTAT1蛋白表达水平均显著升高(P<0.05),IFN-γ 对PANC1细胞的半数抑制浓度(IC50)显著降低(P<0.01);转染72 h后PANC1细胞数量较对照组显著减少(P<0.05);SOCS1表达抑制后PANC1细胞G0/G1期细胞比例明显升高,而S期和G2/M期细胞比例明显减小,与对照组比较差异均有统计学意义。结论SOCS1表达抑制后,人胰腺癌细胞株PANC1的增殖能力下降,并且对IFN-γ的敏感性增强。
胰腺肿瘤;癌;基因沉默;细胞增殖;干扰素Ⅱ型;转染;半数抑制浓度;细胞因子信号转导蛋白抑制因子
细胞因子信号转导抑制因子1(SOCS1)属于SOCS家族成员,可通过Janus激酶细胞信号转导及转录活化因子(JAK-STAT)细胞信号传导通路调节细胞因子的分泌[1],对白细胞介素(IL)-6[2]、干扰素(IFN)-γ[3]等细胞因子的信号传导起着负性调控作用。SOCS1还可通过负反馈调节经Toll样受体(TLR)传导信号通路,调节细胞的分化与成熟[4]。SOCS1基因沉默有利于树突状细胞(dendritic cell,DC)的活化,表现为成熟表型,且在小鼠体内引起明显的抗肿瘤免疫[5];另外,在胰腺癌[6]、前列腺癌[2]等肿瘤中发现了SOCS1的异常表达。研究表明miR-155可通过下调SOCS1增强STAT3信号通路活性影响胰腺癌细胞的侵袭和转移[6],抑制SOCS1的表达能增强角质细胞和成神经管细胞瘤细胞对IFN-γ的敏感性[7]。INF-γ是恶性肿瘤免疫治疗的一种重要方法,SOCS1可通过负反馈调节IFN-γ信号通路影响IFN-γ对细胞的作用。为进一步验证SOCS1 与IFN-γ作用的关系,本研究通过沉默人胰腺癌PANC1细胞中的SOCS1基因,以考察SOCS1对细胞增殖与IFN-γ敏感性的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 主要试剂与仪器 人胰腺癌细胞株PANC1购自中科院培养物保藏委员会细胞库;10%胎牛血清购自杭州四季青生物材料研究所;RPMI 1640培养基购自美国Gibco;BLOCK-iT™U6 RNAi Entry Vector试剂盒、Lipo2000、Trizol购自美国Invitrogen;IFN-γ购自美国Peprotech;Real-time PCR试剂盒购自TaKaRa公司;2×Taq PCR MasterMix PCR扩增试剂盒购自北京TIANGEN公司;STAT1、p-STAT1抗体购自Abcam;SOCS-1抗体购自Millipore;β-actin抗体购自北京中杉金桥;氟尿嘧啶购自Sigma;相关引物设计与合成委托上海生工生物工程有限公司完成。PCR仪为美国Gene Amp PCR system 9600;FA Csort流式细胞仪(BD,US);GDS800分析系统软件(UVP,US)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 构建pshSOCS1载体 参考文献[8]获得SOCS1干扰序列。将合成好的shRNA寡核苷酸序列退火形成双链DNA片段与ENTR/U6载体连接,构建成pshSOCS1载体。
1.2.2 细胞培养及转染 实验分组:对照组为未转染重组质粒的PANC1细胞(PANC1组),实验组为转染重组质粒psh-SOCS1的PANC1细胞(pshSOCS1-PANC1组)。人胰腺癌细胞株PANC1常规培养于含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养液中,于37℃饱和湿度5%CO2培养箱中,3~4 d传代1次。取对数生长期细胞,按一定浓度接种培养用于实验。转染前1 d铺于6孔板中。转染4 h后更换含血清培养基继续培养。Lipo2000转染细胞的具体方法参考说明书。转染48 h 后IFN-γ再刺激4 h。
1.2.3 RT-PCR检测mRNA水平 收集转染后48 h的细胞及未转染细胞,用Trizol提取细胞总RNA,使用MMLV逆转录酶逆转录为cDNA,以各组cDNA为模板,加入缓冲液引物等进行PCR,各样本重复3次,GAPDH为内参照。SOCS1,PF:ATGCAGTCTCCACAGCAGCAGAG;PR:CGAACGGAATGTGCGGAAGTG。 IFN-γ调 节 因 子 1(IRF-1),PF: TCTTCCCTCTTCCACTCGGAGTCG;PR:CTTCTGACCCATGCCCACCA。GAPDH,PF:GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTC,PR:GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC。反应体系为50 μL,反应条件:95℃5 min预变性,94℃30 s变性,退火(SOCS1:60℃;IRF-1:56℃;GAPDH:55℃)30 s,72℃1 min延伸,40个循环,72℃7 min。PCR结束后加入上样缓冲液后对产物进行1.5%的琼脂糖电泳,凝胶成像系统观察结果。
1.2.4 Western blotting检测蛋白表达水平 转染后48 h收集细胞及未转染细胞,用冰冷PBS洗2遍,加入细胞裂解液(25 mmol·L-1Tris-HCl,10 mmol·L-1EDTA,体积分数0.01NP-40,150 mmol·L-1氯化钠,质量浓度1 g·L-1苯甲基磺酰氟),冰浴1 h,4℃下14 000 r/min离心25 min,Lowry法测定上清液蛋白浓度。取细胞裂解蛋白50 g,经十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺(SDS-PAGE)凝胶电泳后电转移至PVDF膜;质量分数为0.05的脱脂奶粉封闭PVDF膜1 h,分别加入STAT1、p-STAT1、SOCS1及β-actin抗体,4℃过夜,洗膜后加辣根过氧化物酶标记的羊抗小鼠或兔抗体(1∶5 000稀释),室温孵育2 h;洗膜后加ECL试剂,然后将PVDF膜放入X射线暗盒,压片,显影,定影。用GDS800分析系统对Western blotting条带进行定量分析。
1.2.5 MTT法检测药物敏感性 实验前1 d,取对数生长期细胞按1.0×104个/孔分到96孔板,加入不同浓度的IFN-γ及氟尿嘧啶,药物用DMSO或PBS制备成10 mmol/L储液,使用浓度分别为20、10、5、2.5、1.25和0.625 μmol/L,每个浓度设置6个复孔,培养48 h后,加入4.5 g/L MTT溶液,37℃继续培养5 h,弃上清后每孔加160 μL DMSO后于550 nm波长处测吸光度值,用Prism计算半数抑制浓度(IC50),实验重复3次。
1.2.6 细胞增殖速度测定 将细胞按3×104个/孔铺于96孔板,每个时点设置3个复孔,分别转染6、12、24、48及72 h后,收集细胞,取等体积计数活细胞数量,计算细胞增殖速度。
1.2.7 流式细胞术检测细胞周期 转染后48 h收集上清中细胞及贴壁细胞,PBS洗2次,采用体积分数为0.70的冷乙醇4℃固定24 h,PBS洗2次,碘化丙啶4℃避光染色30 min,用FA Csort流式细胞仪分析。
1.3 统计学方法 采用SPSS 16.0软件进行统计分析,数据以均数±标准差(±s)表示,比较采用t检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 SOCS1干扰效果 转染后48 h,与未转染细胞相比,SOCS1转染后可被有效沉默,见图1;Western blot结果示SOCS1蛋白表达抑制率达90%。
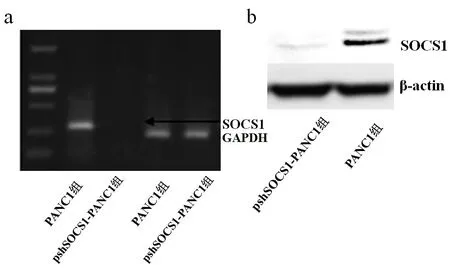
Fig.1 The expression of SOCS1 in PANC1 detected by RT-PCR(a) and Western blot(b)assay图1 RT-PCR(a)及Western blot(b)检测PANC1中SOCS1的表达
2.2 SOCS1沉默对INF-γ信号通路的影响 psh-SOCS1-PANC1组的IRF-1 mRNA表达水平高于PANC1组(t=9.801,P<0.05),见图 2。同时检测STAT1及 pSTAT1的蛋白表达水平,发现 psh-SOCS1-PANC1组的pSTAT1蛋白表达水平高于PANC1组(t=17.714,P<0.01),2组STAT1蛋白表达水平差异无统计学意义(t=1.017,P=0.367),见图3。
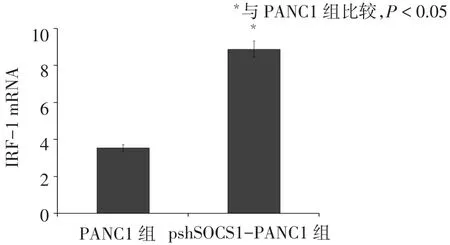
Fig.2 The expression of IRF-1 in PANC1 or pshSOCS1-PANC1 after the stimulation with IFN-γ图2 SOCS1沉默前后IRF-1mRNA表达水平比较
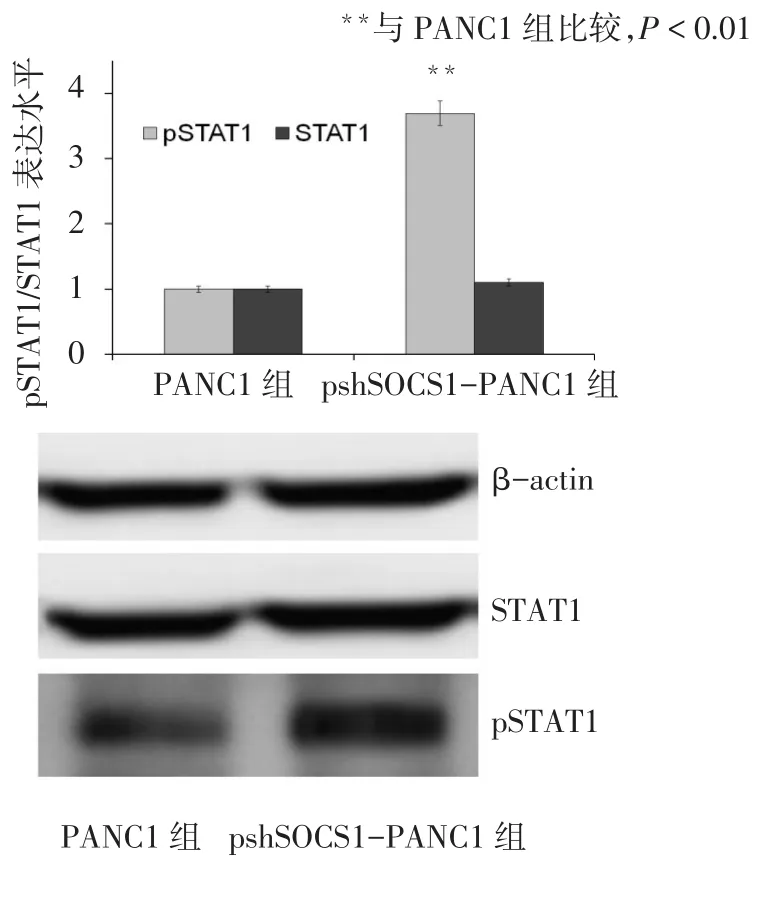
Fig.3 The expression changes of STAT1 and pSTAT1 following the stimulation of IFN-γ图3 SOCS1沉默前后STAT1及pSTAT1表达水平的变化
2.3 SCOS1沉默后细胞对INF-γ的敏感性 与PANC1组比较,pshSOCS1-PANC1组的PANC1细胞对IFN-γ的IC50显著降低(P<0.01),2组细胞对氟尿嘧啶的IC50差异无统计学意义,见表1。
Tab.1 The IC50of drugs for PANC1 cells before and after SOCS1 gene silencing表1 SOCS1沉默前后药物对PANC1细胞IC50的影响(μmol/L,±s)
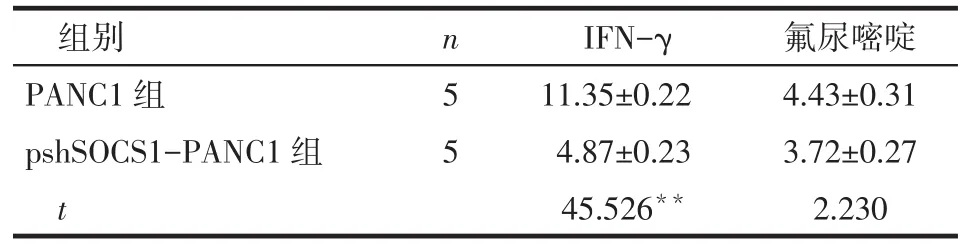
Tab.1 The IC50of drugs for PANC1 cells before and after SOCS1 gene silencing表1 SOCS1沉默前后药物对PANC1细胞IC50的影响(μmol/L,±s)
**P<0.01
?
2.4 细胞增殖情况 转染6~48 h,2组细胞数量无明显差异,72 h,pshSOCS1-PANC1组的细胞数低于PANC1组(t=10.710,P<0.05),见图4。
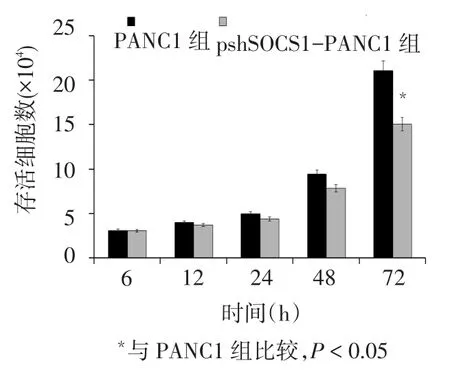
Fig.4 The changes in cell proliferation ability after transfection图4 转染后细胞增殖能力的变化
2.5 SOCS1沉默对细胞周期的影响 与PANC1组比较,pshSOCS1-PANC1组的G0/G1期细胞比例增高(t=4.021,P<0.05),S期、G2/M期细胞比例降低(t分别为4.558、5.328,P<0.05),见图5。
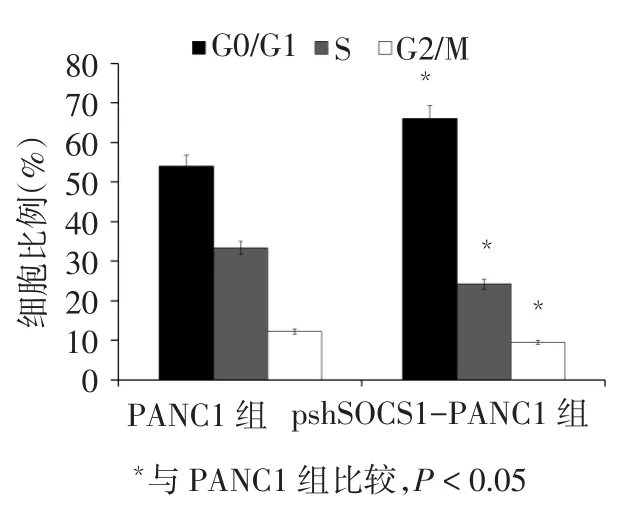
Fig.5 The effect of SCOS1 gene silencing on the cell cycle of PANC1图5 SCOS1沉默对PANC1细胞周期的影响
3 讨论
SOCS1在肿瘤发生、发展中的作用目前存在争议,一方面有证据表明SOCS1低表达可抑制细胞发生恶性转化[2,9],另一方面又有证据提示SOCS1高表达可抑制肿瘤的侵袭及转移[10]。有研究发现乳腺癌中SOCS1的表达高于正常乳腺组织,但在乳腺癌细胞系中SOCS1的表达并未升高[11],在接受去势治疗的前列腺癌患者中,SOCS1的表达降低,而复发患者中SOCS1的表达又升高[6];但在恶性黑色素瘤的转移部位则发现SOCS1表达降低,体外研究也表明过表达SOCS1可抑制黑色素瘤细胞的增殖及转移[10]。本研究以胰腺癌细胞株PANC1为研究对象,发现沉默PANC1细胞中SOCS1表达后可影响细胞周期,使细胞在G0/G1期阻滞,S期细胞比例明显减小,即细胞遗传物质复制的时间延长,可能会抑制细胞的增殖能力,而细胞增殖速度的测定也验证了这种现象。
SOCS1高表达可影响细胞对多种细胞因子的敏感性,如IFN-γ,研究报道在SOCS1基因敲除小鼠中,IFN-α可通过增强CD4-T和CD8-T细胞功能从而发挥抗肿瘤活性[12];SOCS1能够消除干扰素对丙肝病毒复制的抑制作用[13]。IFN-γ主要通过JAK/ STAT通路调节细胞的分化、增殖等功能,而SOCS1 是JAK/STAT通路的重要负性调节分子,在IFN-γ敏感性降低的过程中可能发挥着重要作用。在临床中很多经过IFN-γ治疗的患者会发生IFN-γ抵抗或不敏感,进而限制了IFN-γ的使用。因此,通过沉默细胞中SOCS1的表达从而提高IFN-γ治疗的敏感性可能成为治疗人胰腺癌的重要方法。本研究沉默细胞中SOCS1的表达后,给予IFN-γ刺激可显著增强pSTAT1的表达,也即IFN-γ信号通路信号增强,进而启动目的基因表达,影响肿瘤细胞的生长,另外,IRF-1的表达也增强,结果表明,沉默SOCS1后PANC1细胞对IFN-γ的敏感性增加,为提高胰腺癌免疫治疗效果提供了新的方法。
综上,沉默PANC1中SOCS1的表达可以显著增强IFN-γ的敏感性,也可影响细胞周期,使S期延长,抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖,增强细胞对IFN-γ的敏感性是治疗胰腺癌的一个重要手段,SOCS1可能是影响人胰腺癌免疫治疗效果的重要靶点。
[1]Sun Q,Xiang RL,Yang YL,et al.Suppressor of cytokine signaling1 protects rat pancreatic islets from cytokine-induced apoptosis through Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription pathway[J].Chin Med J(Engl),2013,126(21):4048-4053.
[2]Ge D,Gao AC,Zhang Q,et al.LNCaP prostate cancer cells with autocrine interleukin-6 expression are resistant to IL-6-induced neuroendocrine differentiation due to increased expression of suppressors of cytokine signaling[J].Prostate,2012,72(12):1306-1316.
[3]Satou R,Miyata K,Gonzalez-Villalobos RA,et al.Interferon-γ biphasically regulates angiotensinogen expression via a JAK-STAT pathway and suppressor of cytokine signaling 1(SOCS1)in renal proximal tubular cells[J].FASEB J,2012,26(5):1821-1830.
[4]Mansell A,Smith R,Doyle S L,et al.Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 negatively regulates Toll-like receptor signaling by mediating Mal degradation[J].Nat Immunol,2006,7(2):148-155.
[5]Heo MB,Cho MY,Lim YT.Polymer nanoparticles for enhanced immune response:combined delivery of tumor antigen and small interference RNA for immunosuppressive gene to dendritic cells[J].Acta Biomater,2014,10(5):2169-2176.
[6]Huang C,Li H,Wu W,et al.Regulation of miR-155 affects pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness and migration by modulating the STAT3 signaling pathway through SOCS1[J].Oncol Rep,2013,30 (3):1223-1230.
[7]Laner-Plamberger S,Wolff F,Kaser-Eichberger A,et al.Hedgehog/ GLI signaling activates suppressor of cytokine signaling 1(SOCS1) in epidermal and neural tumor cells[J].PLoS One,2013,8(9): e75317.
[8]Lesinski GB,Zimmerer JM,Kreiner M,et al.Modulation of SOCS protein expression influences the interferon responsiveness of human melanoma cells[J].BMC Cancer,2010,142(10):1-10.doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-142.
[9]Gui Y,Yeganeh M,Cepero-Donates Y,et al.Regulation of MET Receptor Signaling by SOCS1 and its Implications for Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J].Curr Pharm Des,2014,20(17):2922-2923.
[10]Scutti JA,Matsuo AL,Pereira FV,et al.Role of SOCS-1 Gene on Melanoma Cell Growth and Tumor Development[J].Transl Oncol, 2011,4(2):101-109.
[11]Sasi W,Jiang WG,Sharma A,et al.Higher expression levels of SOCS 1,3,4,7 are associated with earlier tumour stage and better clinical outcome in human breast cancer[J].BMC cancer,2010,10 (1):178.
[12]Guenterberg KD,Lesinski GB,Mundy-Bosse BL,et al.Enhanced anti-tumor activity of interferon-alpha in SOCS1-deficient mice is mediated by CD4-and CD8-T cells[J].Cancer Immunol Immunother,2011,60(9):1281-1288.
[13]Shao RX,Zhang L,Hong Z,et al.SOCS1 abrogates IFN's antiviral effect on hepatitis C virus replication[J].Antiviral Res,2013,97(2): 101-107.
(2014-04-14收稿 2014-05-20修回)
(本文编辑 闫娟)
Effects of Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling-1 Silencing on the Proliferation and Interferon Gamma Susceptibility of Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells
LYU Qinglin,WANG Juan,CHEN Liping
The Affiliated Hospital of Liaocheng University,Liaocheng 252000,China
ObjectiveTo detect the changes of cell proliferation and IFN-γ susceptibility of human pancreatic cancer cells after suppressor of cytokine signaling-1(SOCS1)gene silencing,and to explore the SOCS1 as the target of anti-tumor therapy through enhancing the function of IFN-γ.MethodsWestern blot assay,PCR and real-time PCR were used to verify the down regulation of SOCS1 in human pancreatic cancer cell(PANC1)after transfection;subsequently,PANC1 was stimulated with IFN-γ.Western blot assay was also used to detect the expression of signal transducers and activators of transcription(STAT)1 and phosphorylation STAT(pSTAT)1;and the change of IFN-γ susceptibility was detected by MTT assay. Real-time PCR was used to detect the mRNA of interferon regulatory factor-1(IRF-1).Flow cytometry was used to detect the cell cycle.ResultsThe expression levels of SOCS1 mRNA and protein were significantly decreased in small hairpin SCOS1(shSOCS1)transfected PANC1 cells.After the silence of SOCS1,the expression levels of IRF-1 and pSTAT1 increased significantly(P<0.05),and the median inhibitory concentration(IC50)of IFN-γ for PANC1 cells decreased significantly(P<0.01).The cell count of shSOCS1 cells dropped significantly compared with that of control group after the SOCS1 silencing for 72 hours(P<0.05).The cell cycle arrest was promoted at the G0/G1 phase,but the percentage of cells in S phase and G2/M decreased compared to that of control groups(P<0.05).ConclusionAfter the inhibition of SOCS1 gene expression,the proliferation ability of human pancreatic cancer cell line PANC1 decreased,and the sensitivity of PANC1 cells to IFN-γ was enhanced.
pancreatic neoplasms;carcinoma;gene silencing;cell proliferation;interferon type II;transfection;IC50;suppressor of cytokine signaling proteins
R735.9
A
10.3969/j.issn.0253-9896.2014.09.004
山东,聊城,聊城大学医院(邮编252000)
