鹅掌楸属植物化学成分及其生物活性研究进展
2014-05-17杨东婷杨国旭贾爱群
杨东婷,杨国旭,董 伟,贾爱群*
1南京理工大学化工学院;2南京理工大学环境与生物工程学院,南京210014
木兰科鹅掌楸属植物是在中生代侏罗纪就已经出现的一种被子植物,目前全球仅存两个种:北美鹅掌楸(Liriodendron tulipifera L.),主要分布于美国东部和加拿大东南部[1]。中国鹅掌楸[Liriodendron Chinense(Hemsl.)sarg.],星散分布于长江流域以南区域,如江西(庐山)、福建(武夷山)、湖北(房县)等[2],是首批列入《中国珍稀濒危保护植物名录》的国家二类濒危植物。这两个种又被称之为“洲际种对”(Vicariad Species Pairs)[3]。为保护濒危植物,1963年,我国林木育种学家叶培忠教授首次以中国鹅掌楸为母本,与北美鹅掌楸杂交成功选育得到种间杂交种--杂交鹅掌楸[L.chinense(Hemsl.)Sarg.x L.tulipifera L.][4,5],又称杂交马褂木。
鹅掌楸属植物作为传统的药用植物,具有很高的药用价值。《全国中草药汇编》记载以中国鹅掌楸的树皮和树根入药,可祛风除湿,止咳消喘,用于治疗风寒咳嗽,风湿关节痛等病症。北美鹅掌楸树皮亦早期曾被作印第安人用于辅助用药、兴奋剂和退烧药,并且美国内战中北美鹅掌楸树皮的粗提物曾作为喹啉的替代物,用于治疗疟疾[6]。国内外学者对北美鹅掌楸中所含有的化合物及其药理活性进行了较为深入系统的研究,而对中国鹅掌楸植物的研究则相对较少,尤其迄今未见杂交鹅掌楸中化学成分的研究报道。本文对鹅掌楸属植物中分离鉴定得到多种生物碱类、倍半萜内酯类、黄酮类及苯丙素类等化学成分及该属植物部位成分可能的生物活性做一综述。
1 化学成分
1.1 生物碱类(Alkaloids)
生物碱类化合物广泛存在鹅掌楸属植物中。目前,国内外学者已经从北美鹅掌楸的不同部位分离得到46个生物碱,其中大部分为阿朴啡类生物碱及其脱氢、氧化的衍生物,只有少量的生物碱是原阿朴啡类生物碱和四氢小檗碱,见表1。
1.2 倍半萜(Sesquiterpenes)
倍半萜类化合物也存在鹅掌楸属植物中。目前,该属植物中已经发现十余种愈创木烷型、吉马型、桉叶烷型构型的倍半萜类化合物,见表2。
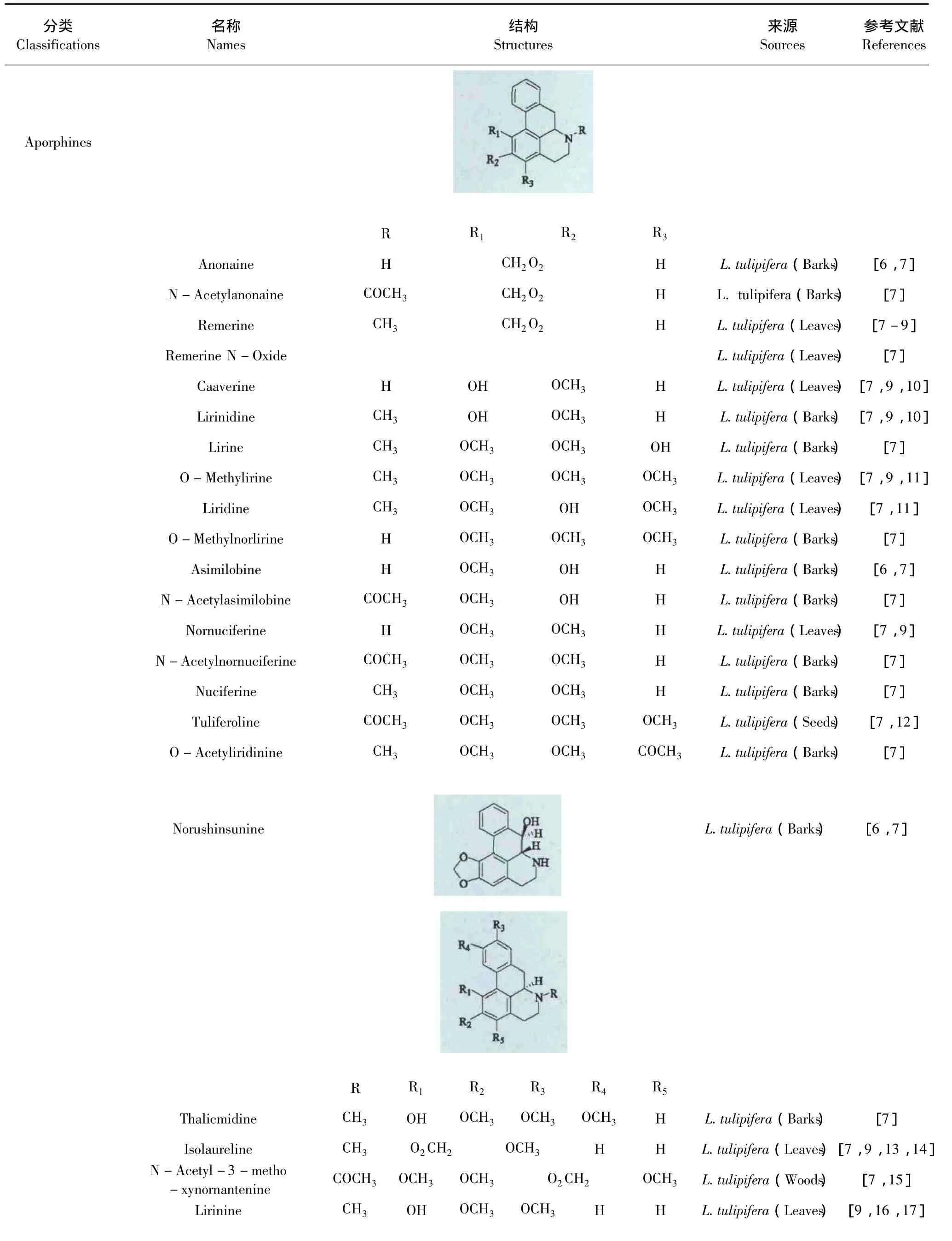
表1 鹅掌楸属植物的生物碱Table 1 Alkaloids of Liriodendron Genus
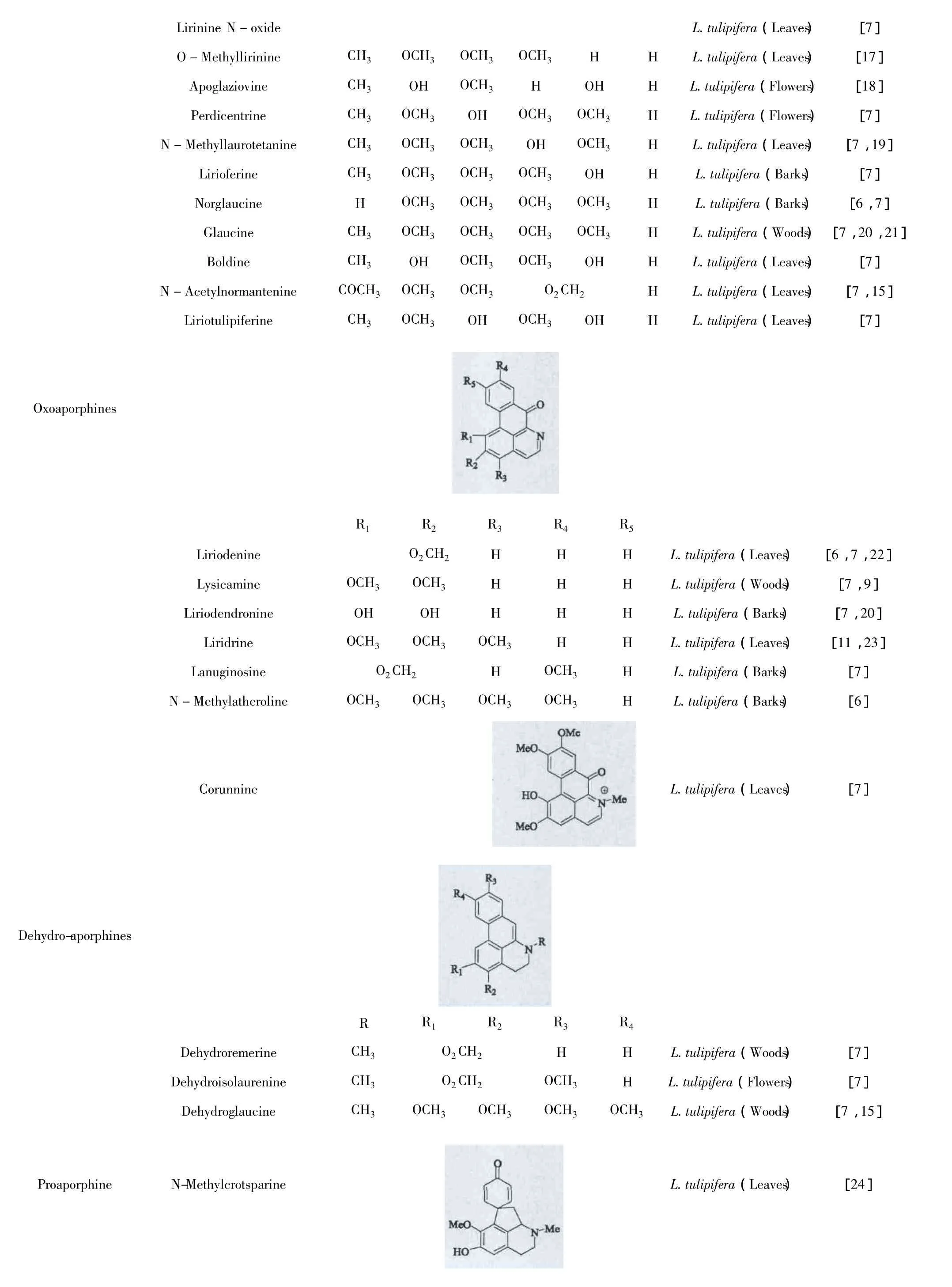
L.tulipifera(Leaves) [7]O -Methyllirinine CH3 OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 H H L.tulipifera(Leaves) [17]Apoglaziovine CH3 OH OCH3 H OH H L.tulipifera(Flowers) [18]Perdicentrine CH3 OCH3 OH OCH3 OCH3 H L.tulipifera(Flowers) [7]N -Methyllaurotetanine CH3 OCH3 OCH3 OH OCH3 H L.tulipifera(Leaves) [7,19]Lirioferine CH3 OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 OH H L.tulipifera(Barks) [7]Norglaucine H OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 H L.tulipifera(Barks) [6,7]Glaucine CH3 OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 H L.tulipifera(Woods) [7,20,21]Boldine CH3 OH OCH3 OCH3 OH H L.tulipifera(Leaves) [7]N -Acetylnormantenine COCH3 OCH3 OCH3 O2CH2 H L.tulipifera(Leaves) [7,15]Liriotulipiferine CH3 OCH3 OH OCH3 OH H L.tulipifera(Leaves) [7]Lirinine N-oxide OxoaporphinesR1 R2 R3 R4 R5 Liriodenine O2CH2 H H H L.tulipifera(Leaves) [6,7,22]Lysicamine OCH3 OCH3 H H H L.tulipifera(Woods) [7,9]Liriodendronine OH OH H H H L.tulipifera(Barks) [7,20]Liridrine OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 H H L.tulipifera(Leaves) [11,23]Lanuginosine O2CH2 H OCH3 H L.tulipifera(Barks) [7]N -Methylatheroline OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 H L.tulipifera(Barks) [6]Corunnine L.tulipifera(Leaves) [7]Dehydro-aporphinesR R1 R2 R3 R4 Dehydroremerine CH3 O2CH2 H H L.tulipifera(Woods) [7]Dehydroisolaurenine CH3 O2 CH2 OCH3 H L.tulipifera(Flowers) [7]Dehydroglaucine CH3 OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 L.tulipifera(Woods) [7,15]Proaporphine N-Methylcrotsparine L.tulipifera(Leaves) [24]
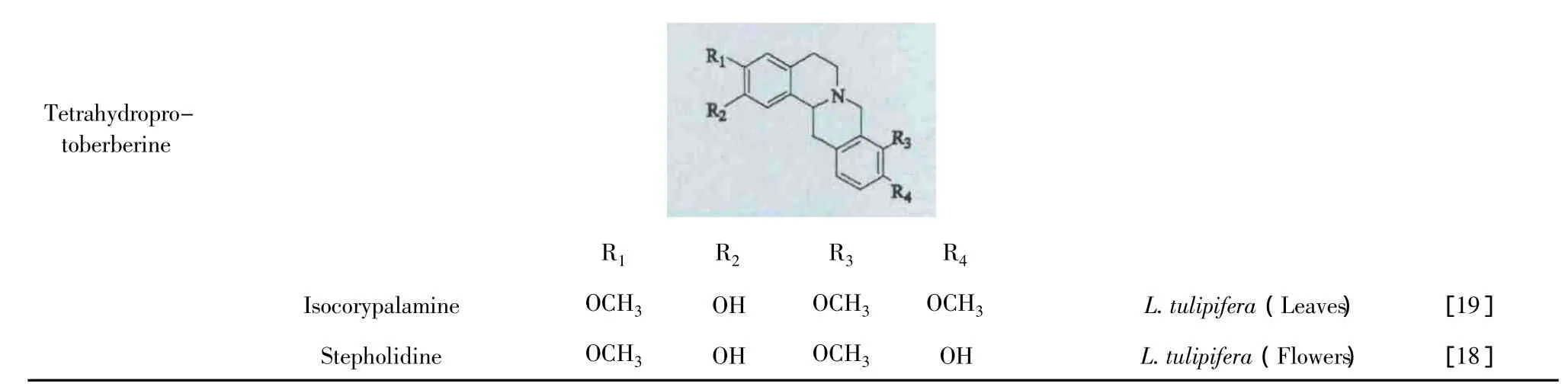
TetrahydroprotoberberineR1 R2 R3 R4 Isocorypalamine OCH3 OH OCH3 OCH3 L.tulipifera(Leaves) [19]Stepholidine OCH3 OH OCH3 OH L.tulipifera(Flowers) [18]
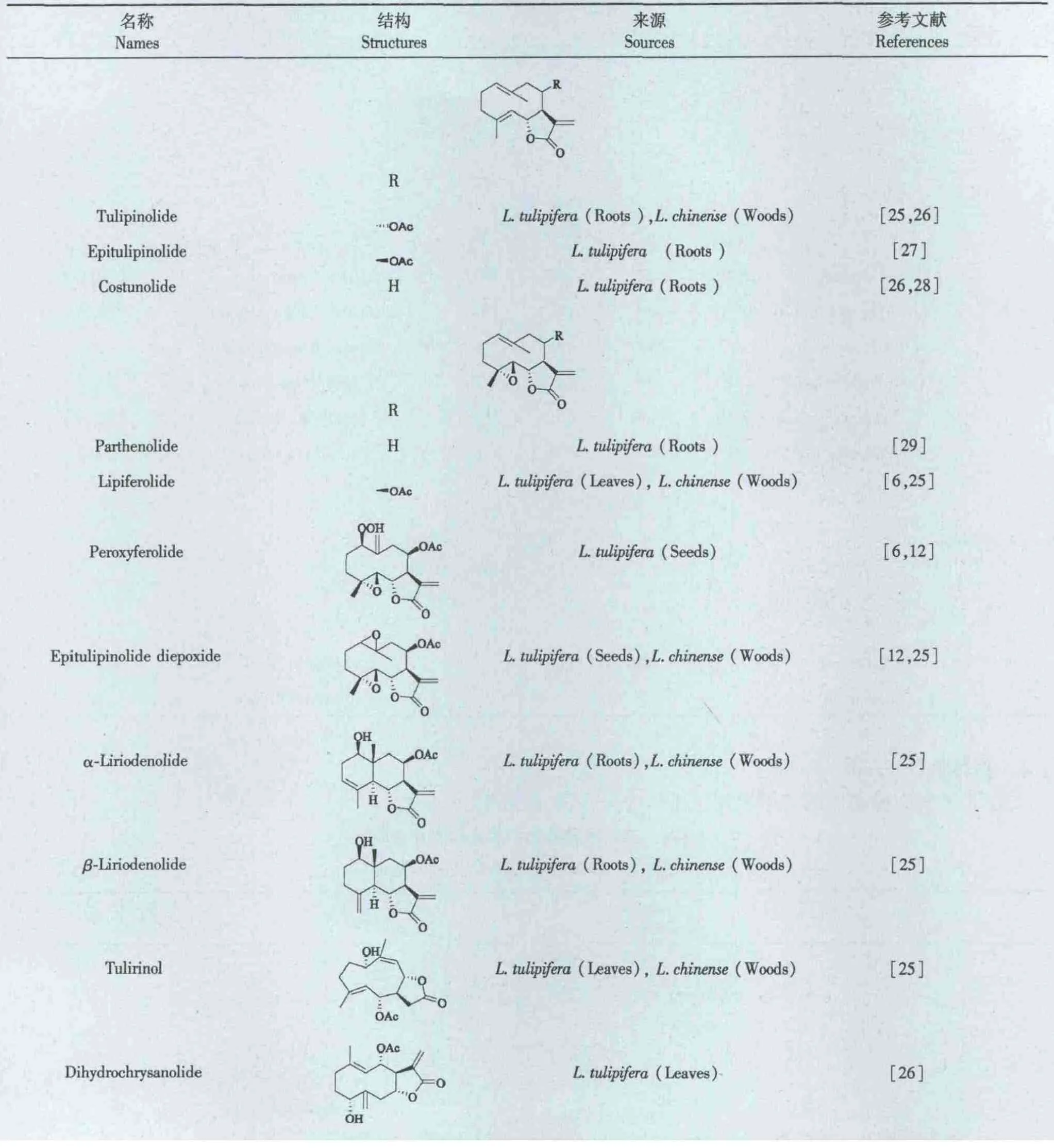
表2 鹅掌楸植物中的倍半萜Table 2 Sesquiterpenes of Liriodendron genus
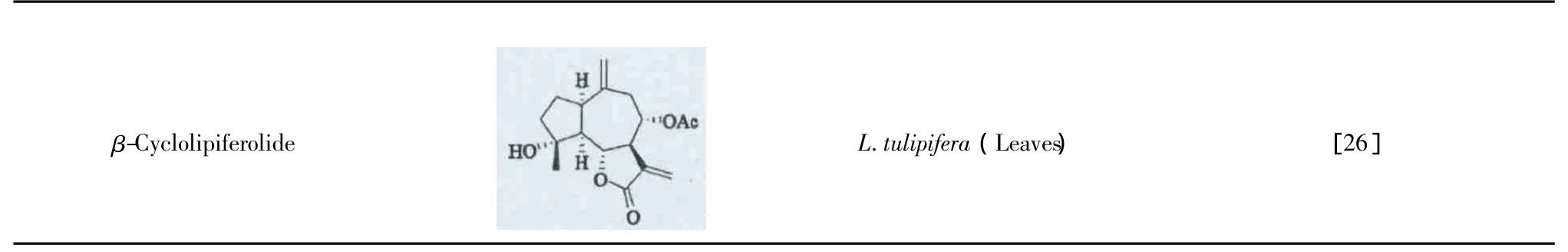
β-CyclolipiferolideL.tulipifera(Leaves) [26]
1.3 苯丙素类(Phenylpropanoid)
苯丙素类化合物主要存在鹅掌楸属植物的茎、叶和种子中。目前,国内外学者已在北美鹅掌楸植物中已经发现木质素类和苯丙素类化合物,见表3。
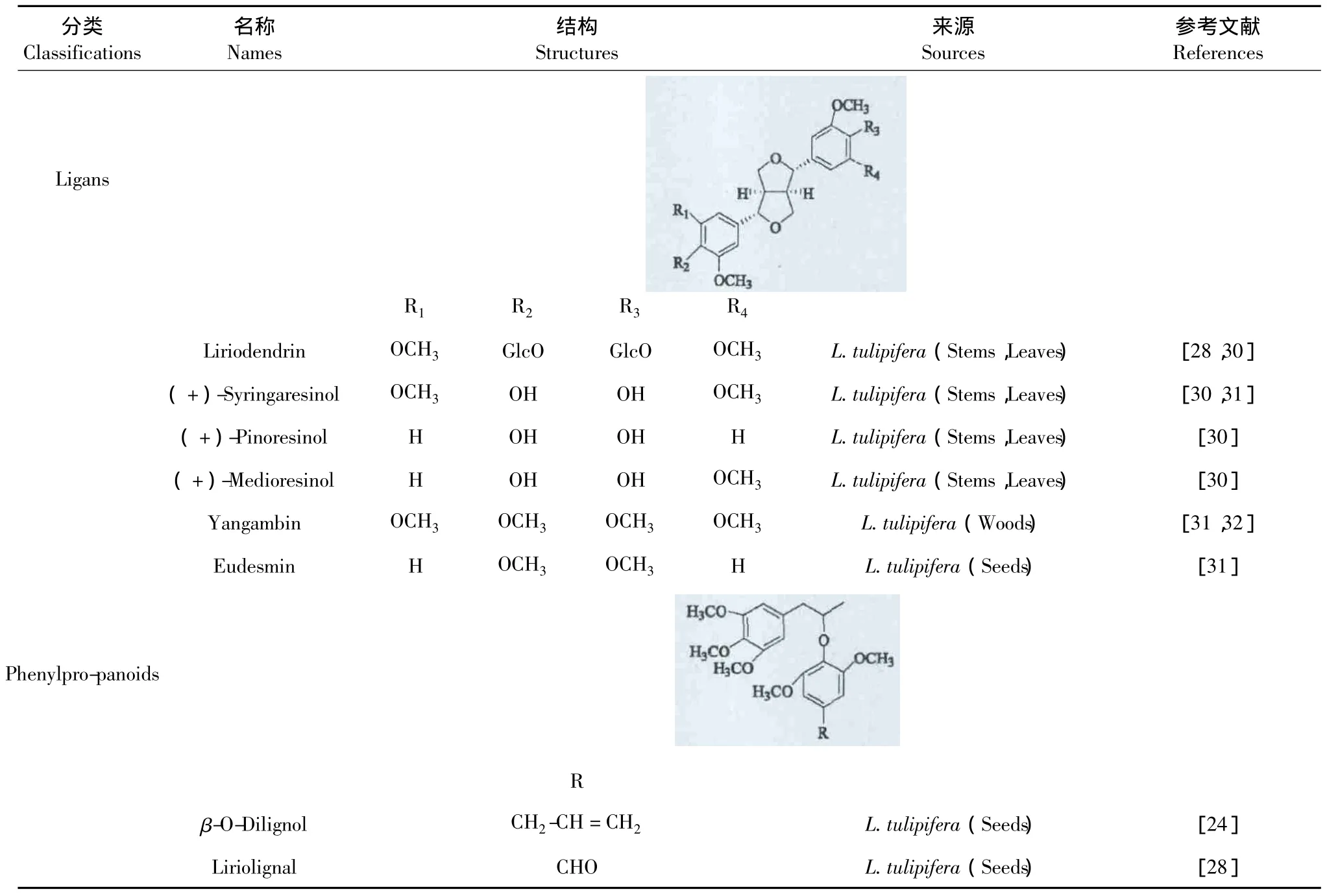
表3 鹅掌楸属植物中的苯丙素类化合物Table 3 Phenylpropanoids of Liriodendron Genus
1.4 甾体类(Steroids)
在北美鹅掌楸植物的茎中发现了甾体类化合物,见表4。
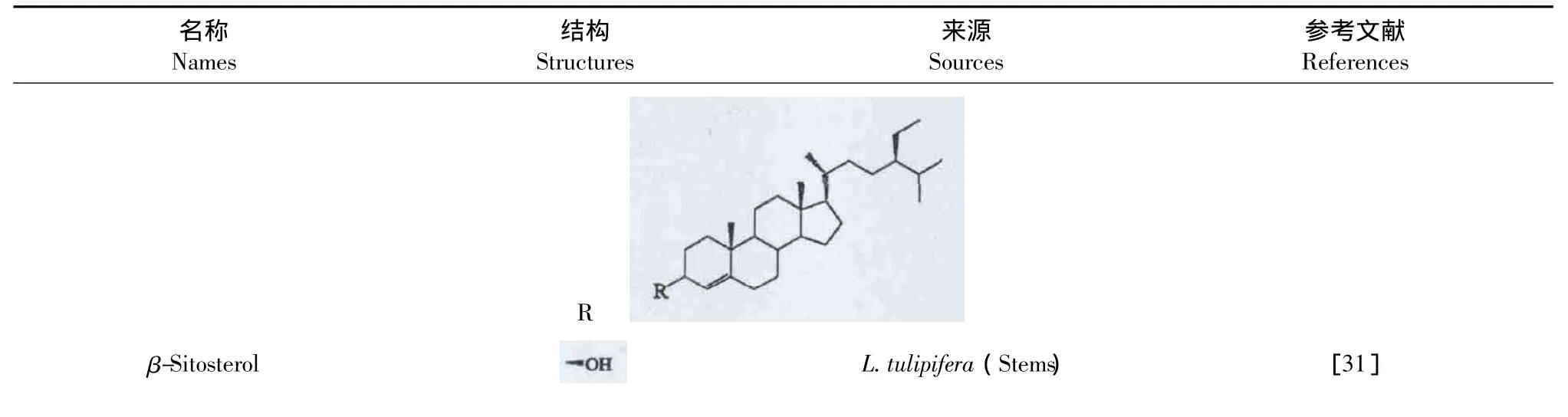
表4 鹅掌楸属植物中的甾体类化合物Table 4 Steroids of Liriodendron Genus

β-Sitostenone =O L.tulipifera(Stems) [31]Stigmasterol L.tulipifera(Stems) [31]Stigmastenone =O L.tulipifera(Stems) [31]
1.5 黄酮类(Flavonoids)
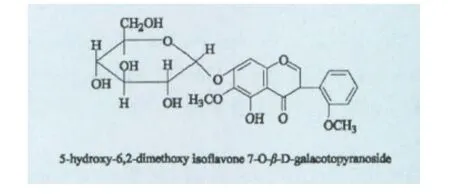
仅在北美鹅掌楸植物中发现了一个黄酮类化合物 5-Hydroxy-6-2-dimethoxy isoflavone 7-O-β-D galacotopyranoside[33],其结构如图所示。
2 生物活性
鹅掌楸属植物及其部位成分含有各种生物活性成分,《全国中草药编汇》中记载鹅掌楸属植物具有祛风除湿,止咳,可用于风湿关节痛,风寒咳嗽。文献报道有抗菌、抗疟疾,抗肿瘤等。
2.1 抗菌活性
李书华和曾超珍分别采用滤纸片观察法和杯碟法表明:中国鹅掌楸的正丁醇部位抑菌性最强,且中国鹅掌楸提取物对金色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)、枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)、大肠埃希杆菌(Escherichia coli)的生长均有较强的抑制效果,其MIC 值分别为 0.0313、0.0625、0.0625 mg/mL[34,35]。
Anonaine对三种革兰氏阳性菌:蜡样芽孢杆菌(Bacillus cereus)、微球菌属(Micrococcus)、金黄色葡萄球菌具有显著的抑菌作用(MIC值≥50 mg/mL)。同时Anonaine也能够有效的抑制真菌如白色念珠菌(Candida albicans)、新型隐球菌(Cryptococcus neoformans)及其他念珠属菌类的生长(MIC值在 62.5 ~1000 mg/mL 之间)[36]。
Liriodenine能够抑制多种革兰氏阳性菌如枯草芽孢杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌及β-溶血链球菌(Beta hemolytic streptococcus)等和革兰氏阴性菌如大肠埃希杆菌、铜绿假单胞菌(Pseudomonas aeruginosa)和志贺痢疾杆菌(Shigella shigae)等的生长。Liriodenine对黄曲霉(Aspergillus flavus)、白色念珠菌、杂色曲霉(Aspergillus versicolor)和黑曲霉(Aspergillus niger)等真菌亦具有显著的细胞毒性[37]。同时,Lysicamine和Liriodenine对表皮葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus epidermidis)和都柏林念珠菌(Candida dubliniensis)具有细胞毒性(MIC值在12.5~100 mg/mL之间)[36]。
2.2 抗疟疾活性
Graziose R等研究发现北美鹅掌楸树皮及树皮的乙醇提取物和叶子的氯仿提取物均具有抗疟原虫活性,其 IC50值分别为 10.9 μg/mL,2.0 μg/mL[6]。
Liriodenine能够抑制利什曼原虫(Leishmania braziliensis和 Leishmania donovani)和恶性疟原虫(Plasmodium falciparum)的生长(其 IC50值分别为21.5、26.16、15 mM)[38,39]。Graziose R 等人从北美鹅掌楸树皮中分离纯化得到六种阿朴啡类生物碱:Asimilobine、Norushinsunine、Norglaucine、Liriodenine、Anonaine、Oxoglaucine,并在体外进行抗疟疾活性实验,实验显示这六种生物碱均具有抗疟疾活性。并且研究显示Dehydroremerine在体外能够抑制恶性疟原虫Plasmodium falciparum W2的生长,其IC50值为0.36 mM。Caaverine亦对利什曼原虫和克氏锥虫具有显著的抑制效果[6]。
2.3 抗肿瘤活性
Jin-Hui Chen等人研究表明中国、北美及杂交鹅掌楸的茎、叶的粗体物对人体乳腺癌细胞MDAMB-231和MCF-7、胃癌细胞SGC-7901、肝癌细胞HuH-7及结肠癌细胞HCT-15都有不同程度的抑制活性[40]。Rao等人亦研究显示北美鹅掌楸根部树皮的醇提物对人的鼻咽癌细胞KB细胞具有强烈的抑制活性[35]。
Anonaine能够抑制人肺癌细胞H1299增殖,扩散迁移以及阻断H1299细胞周期,引起其DNA损伤,进而抑制癌细胞生长[41];同时Anonaine能够上调宫颈癌细胞HeLa细胞中Bax蛋白和p53蛋白表达,促使癌细胞迅速凋亡[42]。
Gerhardt D等人指出Boldine能有效的抑制神经胶质瘤细胞系U138MG、U87-MG和C6的细胞生长,Boldine可能成为治疗神经胶质瘤的一种潜在的抗癌药物[43]。
Liriodenine对人的多种癌细胞生长具有抑制作用。Yang C等人通过实验指出Liriodenine能够抑制癌细胞系MCF-7、NCI-H460和SF-268细胞的生长(其 IC50值分别为 2.19、2.38 和 3.19 mg/mL)[44],且 Liriodenine 可以诱导癌细胞凋亡。同时,Liriodenine分别和金属离子 Mn2+、Fe2+、Co2+和Zn2+形成复合物,增强对癌细胞株的毒性[45,46]。Liriodenine碱银配合物(AgLA2)在体外能够抑制肺癌细胞SPC-A-1增殖,并诱导肺癌细胞凋亡[45]。
Lanuginosine能够抑制肝细胞癌细胞系HepG2和脑癌细胞系 U251的增殖[47],并诱导其凋亡,Caaverine对 HepG2细胞具有强烈的抑制活性[48]。
2.4 神经系统作用活性
Boldine在体外和多巴胺受体结合能力非常强。Boldine和Glaucine在大鼠神经具有抑制功效,表明它们对多巴胺受体可能有拮抗作用,研究显示Boldine在体外对D1-和D2-受体均具有良好的亲和力,但在体内却不能有效的显示对中枢系统多巴胺受体的拮抗作用;而Glaucine在体内有显著的多巴胺受体拮抗作用,但在体外实验中效果却并不明显[49]。
2.5 其他生物活性
除了上述活性外,鹅掌楸属中的阿朴啡生物碱还表现出许多其他生物活性。Lysicamine、Glaucine和 Nornuciferine 具 有 安 眠 镇 静 的 功 效[50,51];Glaucine和Oxoglaucine显示出明显的消炎能力[52];Nuciferine具有较强的抗 HIV活性(IC50值为0.8 mg/mL)[53];N-methylcrotsparine 能够抑制单纯性疱疹病毒 HSV-1、HSV-1-TK、HSV-2(IC50值分别为8.3、7.7、6.7 mg/mL)[54];Anonaine 、Liriodenine、Norshinsunine 具有促使血管舒张作用[42,55],同时,Liriodenine具有抗心率不齐和在心肌缺血再灌注损伤时对心脏和心血管保护的功效[56,57];Liriodenine、Lanuginosine、N-acetylnornuciferine可以抑制由花生四烯酸等引发的血小板聚集[58-60];Boldine能够通过清除活性氧和活性自由基,抑制次黄嘌呤-黄嘌呤氧化镁系统等机理发挥其抗氧化作用[61,62]。
3 结语
鹅掌楸属植物含有结构多样的植物化学成分以及潜在的生物活性成分,开发利用本属植物资源有良好的药学等应用前景。目前从鹅掌楸属植物中所分离得到的部位成分大多具有良好的生物活性,但该属植物尤其中国马褂木中化学成分以及可能的活性物质还没有被系统研究,另外中国马褂木和北美鹅掌楸均为孑遗濒危植物,通过对杂交马褂木中活性成分的研究显得更有意义。总结提出进一步创新性研究想法与思路!
1 Wang ZR(王章荣).The Review and outlook on hybridization in tulip tree breeding in China.JNanjing Forestry Univ,Nat Sci Ed(南京林业大学学报,自科版),2003,3(27):76-78.
2 Liu YH(刘玉壶).Liriodendron.The Flora of China(中国植物志),1996.30,196.
3 Zhu QS(朱秋生),Ye JS(叶金山).Research status and protection countermeasures of relict plant liriodendron spp.Modern Agric Sci Tech(现代农业科技),2010(9):201-206.
4 Zhang FY(张富云),Zhao Y(赵燕).Advance of study on liriodendron.J Yunnan AgricUniv(云南农业大学学报),2005,20:697-701.
5 Doskotch RW,El-Feraly FS.Antitumor agents.II.Tulipinolide,a new germacranolide sesquiterpene,and costunolide.Two cytotoxic substances from Liriodendron tulipifera L..J Pharm Sci,1969,7:877-880.
6 Graziose R,et al.Antiplasmodial activity of aporphine alkaloids and sesquiterpene lactones from Liriodendron tulipifera L..JEthnopharmacol.2011,133:26-30.
7 Ziyaev R,et al.Alkaloids of Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1987,23:521-528.
8 Ziyaev R,et al.Alkaloids of Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1973,4:118-119.
9 Ziyaev R,et al.The dynamics of the accumulation andmutual transformation of alkaloids in Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1975,11:478-481.
10 Ziyaev R,et al.d-Caaverine and a new alkaloid lirinidine from Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1973,9:727-729.
11 Abdusamatov A,et al.Alkaloids of Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1975,11:829-830.
12 Muhammad I,Hufford CD.Phenylpropanoids,sesquiterpenes,and alkaloids from the seeds of Liriodendron tulipifera.Nat Prod,1989,52:1177-1179.
13 Ziyaev R,et al.d-Isolaureline-a new alkaloid from Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1974,10:685.
14 Ziyaev R,et al.Alkaloids of Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1977,13:602-603.
15 Hufford CD,Morgan JM.Synthesis of(±)3-Methoxy-N-acetylnornantenine.JOrgan Chem,1976,41:375-376.
16 Ziyaev R,et al.Lirinine-a new alkaloid from Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1973,9:59-61.
17 Ziyaev R,etal.Alkaloids of Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1973,9:475-476.
18 Ziyaev R,etal.Alkaloids of Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1991,27:516-517.
19 Ziyaev R,et al.N-methyllaurotetanine and Isocorypalmine from Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1986,22:490.
20 Senter PD,Chen C.Liriodendronine,an oxoaporphine pigment from discolored sapwood of Liriodendron tulipifera.Phytochemistry,1977,16:2015-2017.
21 Cohen J,et al.The alkaloids of Liriodendron tulipifera L.The structure and synthesis of the unnamed yellow alkaloid and the isolation of d-glaucine.J Organ Chem,1961,26:4143-4144.
22 Jin CM,et al.Liriodenine inhibits dopamine biosynthesis and L-DOPA-induced dopamine content in PC12 cells.Archivesof Pharmacal Research,2007,30:984-990.
23 Abdusamatov A,et al.Alkaloids of the wood of Liriodendron tulipifera.Chem Nat Comp,1974,10:126-127.
24 Barbosa P,et al.Allelochemicals in foliage of unfavored tree hosts of the gypsy moth,Lymantria dispar L..Journal of Chemical Ecology,1990,16:1719-1730.
25 Dong Y,et al.Sesquiterpenes with quinone reductase-inducing activity from Liriodendron chinense.Nat Prod Commun,2009,4:467-468.
26 Doskotch RW,et al.Six additional sesquiterpene lactones from Liriodendron tulipifera.JNat Prod,1983,46:923-929.
27 Doskotch RW,El-Feraly FS.Antitumor agents.IV.Structure of tulipinolide and epitulipinolide cytotoxic sesquiterpenes from Liriodendron tulipifera L..J Organ Chem,1970,35:1928-1936.
28 Li SS(李石生),et al.Phytochemical and chemotaxonomic studies on liriodendron chinense and paramichelia baillonii(Magnoliaceae),Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究),2001,23:115-120.
29 Frankfater C,et al.Processing of a sesquiterpene lactone by papilio glaucus caterpillars.JChem Ecology,2005,31:2541-2550.
30 Katayama T,Ogaki A.Biosynthesis of(+)-syringaresinol in Liriodendron tulipifera I:Feeding experiments withl-[U-14C]phenylalanine and [8-14C]sinapyl alcohol.JWood Science,2001,47:41-47.
31 LiW,et al.Biofunctional constituents from Liriodendron tulipifera with antioxidants and anti-Melanogenic properties.Int JMol Sci,2013,14:1698-1712.
32 Fine P,et al.Chemical characterization of fine particle emissions from the fireplace combustion of woods grown in the southern United States.Environmental Science & Technology,2002,36:1442-1451.
33 Lapc∨ík O.Isoflavonoids in non-leguminous taxa:a Rarity or a Rule?Phytochemistry,2007,68:2909-2916.
34 Li SH(李书华),et al.Inhibitory effect of Liriodendron bark.Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences(江苏农业科学),2008(3):113-115.
35 Zeng CC(曾超珍),Liu ZX(刘志祥).Bacteriostatic activity and stability of extracts from Liriodendron chinense.Hubei Agric Sci(湖北农业科学),2009,5:1221-1224.
36 Costa EV,et al.Alkaloids from the bark of guatteria hispida and their evaluation as antioxidant and antimicrobial agents.JNat Prod,2010,73:1180-1183.
37 Rahman MM,et al.Antibacterial and cytotoxic compounds from the bark of Cananga odorata.Fitoterapia,2005,76:756-761.
38 Costa EV,et al.A pyrimidine-β-carboline and other alkaloids from Annona foetida with Antileishmanial Activity.J Nat Prod,2006,69:292-294.
39 Del Rayo Camacho M,etal.Oxoaporphine alkaloids and quinones from Stephania dinklagei and evaluation of their antiprotozoal activities.Planta Med,2000,66:478-480.
40 Chen JH,et al.In vitro tumor cytotoxic activities of extracts from three Liriodendron plants.Pak J Pharm Sci,2013,26:233-237.
41 Chen B,et al.(-)-Anonaine induces DNA damage and inhibits growth and migration of human lung carcinoma H1299 cells.JAgric Food Chem,2011,59:2284-2290.
42 Chen C,et al.(-)-Anonaine induces apoptosis through baxand caspase-dependent pathways in human cervical cancer(HeLa)cells.Food and Chemical Toxicology,2008,46:2694-2702.
43 Gerhardt D,et al.Boldine:A potential new Antiproliferative drug against glioma cell lines.Investigational New Drugs,2009,27:517-525.
44 Yang C,et al.Secondary metabolites and cytotoxic activities from the stem bark of Zanthoxylum nitidum.Chemistry &Biodiversity,2009,6:846-857.
45 Liu HG(刘华钢),etal.Apoptosis-inducing effects of AgLA2 on SPC-A-1 cells and itsmechanism in vitro.Chineses Pharma Cological Bulletin(中国药理学通报),2008,24:1449-1452.
46 Zhen-Feng C,etal.Potential new inorganic antitumour agents from combining the anticancer traditional chinese medicine(TCM)liriodenine with metal ions,and DNA binding studies.Dalton transactions,2009(2):262-772.
47 Mohamed SM,et al.Cytotoxic and antiviral activities of aporphine alkaloids of Magnolia grandiflora L..Natural Product Research,2010,24:1395-1402.
48 Fournet A,et al.Phytochemical and antiprotozoal activity of Ocotea lancifolia.Fitoterapia,2007,78:382-384.
49 Asencio M,etal.Biochemical and behavioral effects of boldine and glaucine on dopamine systems.Pharmacology,Biochemistry and Behavior,1998,62:7-13.
50 Han BH,Park MH.Sedative activity and the active components of Zizyphi fructus.Archives of Pharmacal Research,1987,10:208-211.
51 Nishiyama Y,et al.Antinociceptive effects of the extracts of Xylopia parviflora bark and its alkaloidal components in experimental animals.JNatMed,2010,64:9-15.
52 Remichkova M,etal.Toll-like receptor-mediated anti-inflammatory action of glaucine and oxoglaucine.Fitoterapia,2009,80:411-414.
53 Kashiwada Y,et al.Anti-HIV benzylisoquinoline alkaloids and flavonoids from the leaves of Nelumbo Nucifera,and structure-activity correlations with related alkaloids.Bioorganic Med Chem,2004,13:443-448.
54 Nawawi A,et al.Anti-herpes simplex virus activity of alkaloids isolated from Stephania cepharantha.Biological Pharm Bull,1999,22:268-274.
55 Chulia S,et al.Vasodilator effects of liriodenine and norushinsunine,two aporphine alkaloids isolated from annona cherimolia,in rat aorta.Pharm,1995,50:380-387.
56 Chang W,et al.The vascular and cardioprotective effects of liriodenine in ischemia-reperfusion injury via NO-dependent pathway.Nitric Oxide,2004,11:307-315.
57 Chang G,et al.Electrophysiological mechanisms for antiarrhythmic efficacy and positive inotropy of liriodenine,a natural aporphine alkaloid from fissistigma glaucescens.British J Pharm,1996,118:1571-1583.
58 Chang F,et al.Two new 7-dehydroaporphine alkaloids and antiplatelet Action aporphines from the leaves of Annona purpurea.Phytochemistry,1998,49:2015-2018.
59 Jantan I,et al.Antiplatelet activity of aporphine and phenanthrenoid alkaloids from Aromadendron elegans Blume.Phytotherapy Research,2006,20:493-496.
60 Pyo MK,etal.Antiplateletactivities of aporphine alkaloids isolated from leaves of Magnolia obovata.Planta Medica,2003,69:267-269.
61 Konrath EL,et al.Antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties of boldine on hippocampal slices exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation in vitro.Neuro Toxicology,2008,29:1136-1140.
62 Santanam N,et al.A novel alkaloid antioxidant,boldine and synthetic antioxidant,reduced form of RU486,inhibit the oxidation of LDL in vitro and atherosclerosis in vivo in LDLR-/-mice.Atherosclerosis,Amsterdam,Netherlands,2004,173:203-210.
