滤泡辅助性T细胞的研究进展①
2014-02-06张俊美中南大学湘雅医院神经内科长沙410008
赵 敏 张俊美 李 静 (中南大学湘雅医院神经内科,长沙 410008)
滤泡辅助性T细胞的研究进展①
赵 敏 张俊美 李 静 (中南大学湘雅医院神经内科,长沙 410008)
生发中心(Germinal center,GC)是次级淋巴组织(如淋巴结、脾、扁桃体、Peyer斑)淋巴滤泡中的特殊结构。在GC内B细胞经历克隆增殖、体细胞高频突变、抗体类别转换、抗体亲和力成熟等过程,最终分化为长寿命记忆性B细胞和浆细胞。
众所周知,GC形成、抗原特异性记忆性B细胞和浆细胞的生成需要辅助性T细胞(helper T lymphocyte,Th细胞)的参与。因为Th2细胞可以分泌IL-4从而诱导B细胞增殖、抗体类别转换和抗体产生,所以Th2细胞曾被认为是辅助B细胞的主要Th细胞。但有研究证实,IL-4缺乏的小鼠仍然可以形成GC并产生针对T细胞依赖抗原的抗体[1],因此人们对Th2细胞辅助B细胞的作用产生了质疑。
2000年Schaerli等和Breitfeld等均在人的扁桃体发现了一种新的CD4+T细胞亚群,该细胞亚群高表达趋化因子受体CXCR5,后者在趋化因子CXCL13的趋化下使细胞定位于淋巴滤泡,进而辅助B细胞增殖、分化、产生抗体、参与体液免疫应答等,并将此群细胞命名为滤泡辅助性T细胞(Follicular helper T cells,Tfh 细胞)[2,3]。现在 Tfh 细胞作为一种不同于Th1细胞、Th2细胞、Th17细胞、Treg细胞的CD4+T细胞亚群已经被人们接受。由于Tfh细胞独特的表面标志、定位、功能及与疾病的密切关系等,近年来成为研究的热点。本文就Tfh细胞最新的研究进展做一综述。
1 参与Tfh细胞功能的主要分子
Tfh细胞功能的实现与其特殊的表面标记物、细胞因子及转录因子密不可分(见表1)。
1.1 CXCR5 CXCR5是Tfh细胞最重要的表面标记物。CD8+T细胞、初始CD4+T细胞及完全极化的Th1、Th2、Th17细胞不表达 CXCR5,经抗原活化的CD4+T细胞可短暂表达CXCR5,但只有Tfh细胞可以相对稳定地表达CXCR5。另外,成熟的B细胞高表达CXCR5。CXCR5的配体为 CXCL-13。CXCL-13主要由滤泡树突状细胞(follicular dendritic cell,FDC)产生[4];有研究报道,Tfh细胞本身也能合成、分泌CXCL-13[5]。在CXCL-13趋化下Tfh细胞迁移至淋巴滤泡,实现对B细胞的直接辅助作用。
1.2 ICOS 诱导性共刺激分子(Inducible co-stimulator,ICOS)即 CD278,属 CD28家族成员,诱导性表达于活化的T细胞(主要是GC的Tfh细胞)表面。ICOS的配体为ICOSL,后者组成性表达于B细胞和单核细胞等抗原提呈细胞(Antigen-presenting cell,APC)表面。Tfh细胞表面 ICOS与 B细胞表面ICOSL的相互结合对Tfh细胞的产生和维持、GC及记忆性B细胞的形成等起了重要作用。Akiba等[6]研究表明,缺乏ICOS的小鼠体内Tfh细胞数量减少、生发中心形成受影响、B细胞成熟及抗体类别转换发生障碍。
1.3 PD-1 程序性死亡-1分子(Programmed death-1,PD-1)又称CD279,亦属CD28家族成员,主要表达于活化的T细胞表面,是一种抑制性受体。有研究表明,在慢性病毒性感染性疾病和癌症中PD-1参与了免疫耐受、CD8+细胞毒性T细胞的“耗竭”,因此PD-1在免疫应答中发挥了负性调节作用[7,8]。PD-1的配体为PD-L1和PD-L2,这两种配体在包括B细胞在内的多种细胞表面都有表达。与其他T细胞亚群相比,Tfh细胞表达PD-1的水平最高[9]。Tfh细胞表面的PD-1和GC-B细胞表面的PD-1配体结合后可以产生抑制GC-B细胞的信号[10]。另外,有研究报道,通过调节PD-1可以影响GC的生成、高亲和力抗体及长寿命浆细胞的产生[11]。
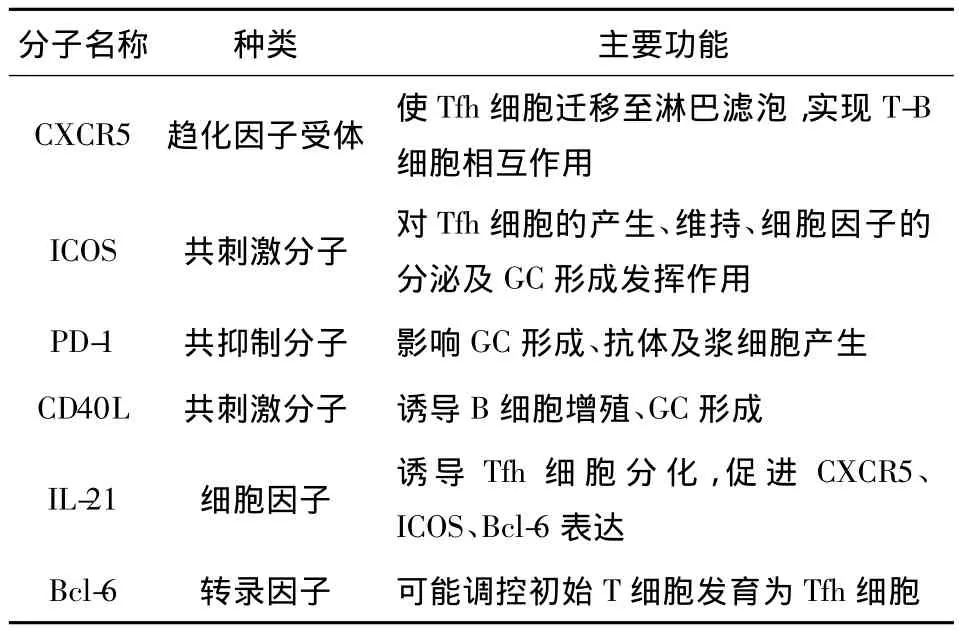
表1 参与Tfh细胞功能的主要分子Tab.1 Main molecular involved in function of Tfh
1.4 CD40L CD40L是CD40的配体,它是肿瘤坏死因子超家族中的一员,高表达于CD4+Th细胞表面。Tfh细胞表面的CD40L与B细胞表面的CD40结合,可诱导B细胞增殖、GC形成等[12]。
1.5 IL-21 IL-21主要由活化的Tfh细胞、Th17细胞和NK T细胞分泌,其中Tfh细胞分泌此细胞因子的量最高。IL-21的配体(IL-21R)主要表达于Tfh细胞、Th17细胞、B细胞、NK细胞和DC。其中B细胞是IL-21作用的最主要靶细胞。IL-21在促进B细胞增殖、抗体类别转换及抗体分泌细胞产生等方面发挥重要作用[13,14]。另外,IL-21通过自分泌的方式促进Tfh细胞表面表达CXCR5、ICOS,从而诱导Tfh细胞分化、向GC迁移及与B细胞相互作用[15]。但是有研究表明,IL-21和IL-6同时存在时才能诱导Tfh细胞分化,仅IL-21或IL-6存在不能诱导 Tfh 细胞分化[16]。
1.6 Bcl-6 转录因子B细胞淋巴瘤6(B-cell lymphoma 6,Bcl-6)是表达于Tfh细胞,在Th1细胞及Th2细胞中不表达[17]。目前关于初始T细胞分化为Tfh细胞由何种转录因子决定尚不明确,有研究表明,Bcl-6在上述过程中发挥了重要作用[18]。Bcl-6缺陷的小鼠不能形成Tfh细胞,而其他CD4+T细胞亚群的形成却不受影响[19]。相反,B淋巴细胞诱导的成熟蛋白-1(B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein 1,Blimp-1)作为一种转录因子,可抑制Bcl-6的表达及Tfh细胞的分化[20]。因此,Bcl-6和Blimp-1的平衡决定了Tfh细胞的分化。
2 Tfh细胞与其他免疫细胞的相互关系
许多研究证实Tfh细胞与Th1细胞、Th2细胞、Th17 细胞、CD4+Treg 细胞有密切关系[21-26],近年来有研究表明,Tfh细胞与滤泡调节性T细胞(Follicular regulatory T cells,Tfr细胞)、CD8+调节性 T 细胞(CD8+regulatory T cells,CD8+Treg 细胞)、滤泡辅助自然杀伤T细胞(NKTfh细胞)在对GC-B细胞的作用中存在相互关系(见图1)。
2.1 Tfh细胞与Tfr细胞 Tfr细胞是一类新发现的专职调节GC的调节性T细胞亚群,它同时高表达CXCR5、转录因子 Foxp3及 Bcl-6,具有 nTreg细胞及Tfh细胞的双重特性,已在小鼠脾脏、淋巴结以及人类扁桃体的淋巴滤泡和GC检测到Tfr细胞的存在。研究已证实,Tfr细胞起源于外周nTreg,在机体的免疫系统中,有一部分CXCR5-Foxp3+nTreg细胞表达转录因子Bcl-6,启动了Bcl-6-CXCR5轴的反应,使其在获得CXCR5表型的过程中逐渐分化为Tfr细胞,在CXCL-13的趋化作用下被募集至淋巴滤泡,抑制GC中Tfh细胞的增殖、B细胞的分化、抗体亲和力的成熟以及浆细胞的形成,具有重要的免疫抑制功能[27-29]。Tfr细胞的发现使人们对T细胞与B细胞的相互作用机制有了进一步的了解,并为自身免疫性疾病的治疗及免疫耐受的维持提供了新思路[30,31]。
2.2 Tfh细胞与CD8+Treg细胞 以往人们对Treg细胞的研究主要针对CD4+Treg细胞,对CD8+Treg细胞的研究却很少。Kim等在小鼠的脾脏及淋巴结中发现一群CD8+Treg细胞,它可以抑制GC中Qa-1+Tfh细胞。与传统的CD8+细胞毒性T细胞不同,该群 CD8+Treg细胞高表达 CD44、ICOSL、CXCR5,因此可以迁移至GC并对Qa-1+Tfh细胞发挥抑制作用。GC中 CD44+ICOSL+CXCR5+CD8+Treg细胞的发现使人们对Tfh细胞与其他细胞的关系有了新的认识,为免疫性疾病的治疗提供了可能的新方法[32-34]。
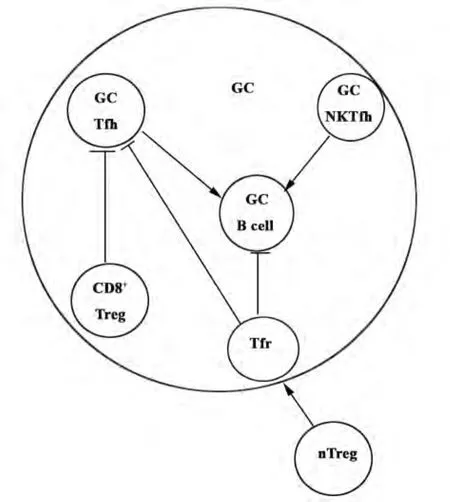
图1 GC中各T细胞亚群对B细胞的作用及各亚群间的相互关系Fig.1 T cell subsets effect on B cell and their interrelationship in GC
2.3 Tfh细胞与 NKTfh细胞 自然杀伤 T细胞(Natural killer T cells,NKT细胞)是一类表面既表达T细胞受体又表达NK细胞受体的天然免疫细胞,能识别CD1d提呈的脂类抗原,辅助B细胞活化。有研究者在GC中发现了一群PD-1hiCXCR5+NKTfh细胞,这群细胞能与识别相同抗原的B细胞相互作用,促进早期GC形成、B细胞亲和力成熟及IgG生成。虽然NKTfh细胞与Tfh细胞在表型上相似,都表达PD-1、CXCR5,且分化过程都依赖转录因子Bcl-6等。但是,NKTfh细胞与Tfh细胞功能有所不同,前者对B细胞的辅助不影响记忆B细胞的形成,在针对病原体的快速反应及早期抗感染过程可能发挥重要作用[35-39]。
3 外周血中CXCR5+CD4+T细胞的相关研究
健康人外周血中可以检测到CXCR5+CD4+T细胞[40],那么这种细胞与Tfh细胞有什么关系呢?Mortia等证实,健康人外周血CXCR5+CD4+T细胞具有与 Tfh细胞相似的功能,但此细胞高表达CD62L和趋化因子CCR7,而低表达Tfh细胞活性分子ICOS及CD69,说明此种细胞处于“静息状态”,可以认为是Tfh细胞在外周血中的记忆部分[41]。研究表明,与健康对照组相比,系统性红斑狼疮、类风湿性关节炎、自身免疫性甲状腺疾病、重症肌无力、慢性病毒性肝炎、多发性硬化等患者外周血中CXCR5+CD4+T细胞的数量及功能异常,说明CXCR5+CD4+T细胞参与了这些疾病的发生[42-48]。
Mortia等还证实,人外周血中CXCR5+CD4+T细胞包含三个亚型(CXCR3+CCR6-Th1样、CXCR3-CCR6-Th2样、CXCR3-CCR6+Th17 样),但只有CXCR3-CCR6-Th2样、CXCR3-CCR6+Th17样两个亚型可以有效辅助B细胞产生抗体,而CXCR3+CCR6-Th1样亚型不能辅助B细胞产生抗体。与健康对照组相比,儿童皮肌炎患者外周血中CXCR5+CD4+T细胞/CD4+T细胞无变化,Th1样细胞/CXCR5+CD4+T细胞下降,Th2样细胞/CXCR5+CD4+T细胞及Th17样细胞/CXCR5+CD4+T细胞上升,且CXCR5+CD4+T细胞/CD4+T细胞与浆母细胞数无相关性,(Th2样+Th17样)/Th1样细胞与浆母细胞数有相关性[41];而在干燥综合征患者外周血中Th1样细胞/CD4+T细胞及Th2样细胞/CD4+T细胞不变,CXCR5+CD4+T细胞/CD4+T细胞及Th17样细胞/CD4+T细胞上升,但只有Th17样细胞/CD4+T细胞与抗体水平呈正相关[49],说明外周血中CXCR5+CD4+T细胞只有部分亚群参与了某些疾病的发生,从而为这些疾病的治疗提供了新思路。
4 Tfh细胞与疾病
Tfh细胞在辅助B细胞产生抗体过程中起了关键性作用,许多研究均证实Tfh细胞数量及功能紊乱与多种疾病的发生有关。
4.1 Tfh细胞与自身免疫性疾病 多种小鼠模型均表明Tfh细胞数量增加及功能增强参与了自身免疫性疾病的发生。在获得性系统性红斑狼疮小鼠模型中,由于Tfh细胞分化的负性调节蛋白——Roquin蛋白突变缺失,导致Tfh细胞数量增高,最终导致系统性红斑狼疮的发生[50]。在6-磷酸葡萄糖异构酶诱导的小鼠关节炎模型中Tfh细胞的数量也明显增加,而当阻断ICOS/ICOSL相互作用后Tfh细胞数量减少,关节炎的严重程度减轻[51]。另外,Aoki等[52]用 NTx-PD-1-/-小鼠建立自身免疫性肝炎(Autoimmunological hepatitis,AIH)模型时观察到小鼠脾脏GC增大,其内有大量表达ICOS、IL-21、Bcl-6等的CD4+T细胞浸润,后者大量分泌的IL-21可促使CD8+T细胞活化增殖,从而导致AIH的发生。当ICOS或IL-21被阻断后,小鼠Tfh细胞形成受阻且不能诱导AIH的发生。
4.2 Tfh细胞与免疫缺陷性疾病 如前所述,Tfh细胞数量增加及功能增强可以导致自身免疫性疾病的发生。相反,Tfh细胞数量减少及功能抑制与免疫缺陷性疾病的发生密切相关。有研究表明,当人ICOS基因缺陷时,GC形成障碍,并导致常见变异型免疫缺陷病(Common variable immunodeficiency,CVID)[53]。另外,X-连锁淋巴增殖性疾病(X-linked lymphoproliferative disease,XLP)患者体内 Tfh细胞存在功能缺陷,ICOS表达下调,不能有效辅助B细胞,从而导致低丙种球蛋白血症及反复感染。Coraglia等还从XLP患者体内分离出Tfh细胞,并且证实Tfh细胞存在功能异常[54]。
4.3 Tfh细胞与感染性疾病 以往认为,Th1细胞主要分泌IL-2、IFN-γ等细胞因子,通过活化巨噬细胞来清除细胞内的病原体;Th2细胞主要分泌IL-4、IL-5等细胞因子,在对寄生虫的清除方面起重要作用并参与变态反应。在淋巴细胞性脉络丛脑膜炎病毒(Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus,LCMV)感染急性期,CD4+T细胞产生大量Th1型细胞因子,从而有利于病毒的控制和清除;但在感染慢性期,Bcl-6表达上调,诱导Th1细胞向Tfh细胞转化,最终表现为病毒的持续复制[55,56]。有研究发现,小鼠被蠕虫感染后Th2细胞能向Tfh细胞转化,说明Tfh细胞可能参与了蠕虫感染后的快速免疫反应[57]。有研究表明,SIV感染猕猴模型GC中Tfh细胞和B细胞的数量均增加且增加的程度与外周血中SIV抗体水平相关,提示Tfh细胞可能参与了感染性疾病的发生[58]。
5 结语
Tfh细胞作为一种新的CD4+T细胞亚群,与多种免疫细胞及疾病的发生密切相关,从而为这些疾病的诊断及治疗提供了新思路。然而仍有许多问题亟待解决,例如Tfh细胞特征性的转录因子是什么?人外周血中CXCR5+CD4+T细胞来源于哪里?人外周血中CXCR5+CD4+T细胞是否还存在其他亚群(Foxp3+Treg样等)?如何通过调控Tfh细胞的数量及功能来治疗人类疾病?随着对Tfh细胞研究的不断深入,相信以上问题终将被解决并为人类疾病的诊断及治疗带来福音!
[1] Kopf M,Le Gros G,Coyle AJ,et al.Immune responses of IL-4,IL-5,IL-6 deficientmice[J].Immunol Rev,1995,148:45-69.
[2] Schaerli P,Willimann K,Lang AB,et al.CXC chemokine receptor 5 expression defines follicular homing T cellswith B cell helper function[J].JExp Med,2000,192(11):1553-1562.
[3] Breitfeld D,Ohl L,Kremmer E,et al.Follicular B helper T cells express CXC chemokine receptor 5,localize to B cell follicles,and support immunoglobulin production[J].JExp Med,2000,192(11):1545-1552.
[4] Cyster JG,Ansel KM,Reif K,et al.Follicular stromal cells and lymphocyte homing to follicles[J].Immunol Rev,2000,176:181-193.
[5] Vermijlen D,Ellis P,Langford C,et al.Distinct cytokine-driven responses of activated blood gammadelta T cells:insights into unconventional T cell pleiotropy[J].J Immunol,2007,178(7):4304-4314.
[6] Akiba H,Takeda K,Kojima Y,etal.The role of ICOS in the CXCR5+follicular B helper T cellmaintenance in vivo[J].JImmunol,2005,175(4):2340-2348.
[7] Kaufmann DE,Walker BD.PD-1 and CTLA-4 inhibitory cosignaling pathways in HIV infection and the potential for therapeutic intervention[J].J Immunol,2009,182(10):5891-5897.
[8] Haymaker C,Wu R,Bernatchez C,et al.PD-1 and BTLA and CD8(+)T-cell“exhaustion”in cancer:“Exercising”an alternative viewpoint[J].Oncoimmunology,2012,1(5):735-738.
[9] Chen M,Guo Z,Ju W,et al.The development and function of follicular helper T cells in immune responses[J].CellMol Immunol,2012,9(5):375-379.
[10] Riella LV,Paterson AM,Sharpe AH,et al.Role of the PD-1 pathway in the immune response [J].Am JTransplant,2012,12(10):2575-2587.
[11] Good-Jacobson KL,Szumilas CG,Chen L,et al.PD-1 regulates germinal center B cell survival and the formation and affinity of long-lived plasma cells [J].Nat Immunol,2010,11(6):535-542.
[12] Oxenius A,Campbell KA,Maliszewski CR,et al.CD40-CD40 ligand interactions are critical in T-B cooperation butnot for other anti-viral CD4+T cell functions[J].J Exp Med,1996,183(5):2209-2218.
[13] Kuchen S,Robbins R,Sims GP,et al.Essential role of IL-21 in B cell activation,expansion,and plasma cell generation during CD4+T cell-B cell collaboration [J].J Immunol,2007,179(9):5886-5896.
[14] Yoon SO,Zhang X,Berner P,et al.IL-21 and IL-10 have redundant roles but differential capacities at different stages of plasma cell generation from human germinal center B cells[J].J Leukoc Biol,2009,86(6):1311-1318.
[15] Nurieva RI,Chung Y.Understanding the development and function of T follicular helper cells[J].Cell Mol Immunol,2010,7(3):190-197.
[16] Eto D,Lao C,DiToro D,et al.IL-21 and IL-6 are critical for different aspects of B cell immunity and redundantly induce optimal follicular helper CD4 T cell(Tfh)differentiation[J].PLoS One,2011,6(3):e17739.
[17] Chtanova T,Tangye SG,Newton R,et al.T follicular helper cells express a distinctive transcriptional profile,reflecting their role as non-Th1/Th2 effector cells that provide help for B cells[J].J Immunol,2004,173(1):68-78.
[18] Poholek AC,Hansen K,Hernandez SG,et al.In vivo regulation of Bcl6 and T follicular helper cell development[J].JImmunol,2010,185(1):313-326.
[19] Nurieva RI,Chung Y,Martinez GJ,et al.Bcl6 mediates the development of T follicular helper cells[J].Science,2009,325(5943):1001-1005.
[20] Johnston RJ,Poholek AC,DiToro D,etal.Bcl6 and Blimp-1 are reciprocal and antagonistic regulators of T follicular helper cell differentiation[J].Science,2009,325(5943):1006-1010.
[21] Fahey LM,Wilson EB,Elsaesser H,et al.Viral persistence redirects CD4 T cell differentiation toward T follicular helper cells[J].JExp Med,2011,208(5):987-999.
[22] Nakayamada S,Kanno Y,TakahashiH,etal.Early Th1 cell differentiation ismarked by a Tfh cell-like transition[J].Immunity,2011,35(6):919-931.
[23] Glatman ZA,Taylor JJ,King IL,et al.T follicular helper cells differentiate from Th2 cells in response to helminth antigens[J].JExp Med,2009,206(5):991-999.
[24] Bauquet AT,Jin H,Paterson AM,etal.The costimulatorymolecule ICOS regulates the expression of c-Maf and IL-21 in the development of follicular T helper cells and TH-17 cells[J].Nat Immunol,2009,10(2):167-175.
[25] Nurieva RI,Chung Y,Hwang D,etal.Generation of T follicular helper cells ismediated by interleukin-21 but independent of T helper 1,2,or 17 cell lineages[J].Immunity,2008,29(1):138-149.
[26] Tsuji M,Komatsu N,Kawamoto S,et al.Preferential generation of follicular B helper T cells from Foxp3+T cells in gut Peyer's patches[J].Science,2009,323(5920):1488-1492.
[27] Wollenberg I,Agua-Doce A,Hernandez A,et al.Regulation of the germinal center reaction by Foxp3+follicular regulatory T cells[J].J Immunol,2011,187(9):4553-4560.
[28] Linterman MA,Pierson W,Lee SK,et al.Foxp3+follicular regulatory T cells control the germinal center response[J].Nat Med,2011,17(8):975-982.
[29] Chung Y,Tanaka S,Chu F,et al.Follicular regulatory T cells expressing Foxp3 and Bcl-6 suppress germinal center reactions[J].Nat Med,2011,17(8):983-988.
[30] Campbell DJ,Koch MA.Treg cells:patrolling a dangerous neighborhood[J].Nat Med,2011,17(8):929-930.
[31] Papatriantafyllou M.Regulatory T cells:Pursuing a germinal cen-tre career[J].Nat Rev Immunol,2011,11(9):572.
[32] Kim HJ,Verbinnen B,Tang X,et al.Inhibition of follicular T-helper cells by CD8(+)regulatory T cells is essential for self tolerance[J].Nature,2010,467(7313):328-332.
[33] Kim HJ,Cantor H.Regulation of self-tolerance by Qa-1-restricted CD8(+)regulatory T cells[J].Semin Immunol,2011,23(6):446-452.
[34] Leavenworth JW,Tang X,Kim HJ,etal.Amelioration of arthritis through mobilization of peptide-specific CD8+regulatory T cells[J].JClin Invest,2013,123(3):1382-1389.
[35] Lehuen A,Fazilleau N.Innate iNKT cell help to B cells:fast but does not last[J].Nat Immunol,2012,13(1):11-13.
[36] Leavy O.Natural killer T cells:More help for B cells[J].Nat Rev Immunol,2012,12(1):5.
[37] Chang PP,Barral P,Fitch J,et al.Identification of Bcl-6-dependent follicular helper NKT cells that provide cognate help for B cell responses[J].Nat Immunol,2012,13(1):35-43.
[38] King IL,Fortier A,Tighe M,et al.Invariant natural killer T cells direct B cell responses to cognate lipid antigen in an IL-21-dependentmanner[J].Nat Immunol,2012,13(1):44-50.
[39] Tonti E,Fedeli M,Napolitano A,et al.Follicular helper NKT cells induce limited B cell responses and germinal center formation in the absence of CD4(+)T cell help [J].J Immunol,2012,188(7):3217-3222.
[40] 张春梅,张 赟,张 圆,等.流式细胞术鉴定人外周血滤泡辅助性T细胞[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2009,25(11):1063-1064.
[41] Morita R,Schmitt N,Bentebibel SE,et al.Human blood CXCR5(+)CD4(+)T cells are counterparts of T follicular cells and contain specific subsets that differentially support antibody secretion[J].Immunity,2011,34(1):108-121.
[42] Simpson N,Gatenby PA,Wilson A,et al.Expansion of circulating T cells resembling follicular helper T cells is a fixed phenotype that identifies a subset of severe systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Arthritis Rheum,2010,62(1):234-244.
[43] Ma J,Zhu C,Ma B,et al.Increased frequency of circulating follicular helper T cells in patientswith rheumatoid arthritis[J].Clin Dev Immunol,2012,2012:827480.
[44] Zhu C,Ma J,Liu Y,et al.Increased frequency of follicular helper T cells in patientswith autoimmune thyroid disease[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2012,97(3):943-950.
[45] Saito R,Onodera H,Tago H,etal.Altered expression of chemokine receptor CXCR5 on T cells of myasthenia gravis patients[J].JNeuroimmunol,2005,170(1-2):172-178.
[46] Luo C,Li Y,Liu W,etal.Expansion of circulating counterparts of follicular helper T cells in patientswithmyasthenia gravis[J].JNeuroimmunol,2013,256(1-2):55-61.
[47] Feng J,Lu L,Hua C,et al.High frequency of CD4+CXCR5+TFH cells in patients with immune-active chronic hepatitis B[J].PLoSOne,2011,6(7):e21698.
[48] Christensen JR,Bornsen L,Ratzer R,et al.Systemic inflammation in progressivemultiple sclerosis involves follicular T-helper,Th17-and activated B-cells and correlates with progression [J].PLoSOne,2013,8(3):e57820.
[49] Li XY,Wu ZB,Ding J,et al.Role of the frequency of blood CD4(+)CXCR5(+)CCR6(+)T cells in autoimmunity in patients with Sjogren's syndrome [J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2012,422(2):238-244.
[50] DongW,Zhu P,Wang Y,etal.Follicular helper T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus:a potential therapeutic target[J].Autoimmun Rev,2011,10(6):299-304.
[51] Frey O,Meisel J,Hutloff A,et al.Inducible costimulator(ICOS)blockade inhibits accumulation of polyfunctional T helper1/T helper 17 cells and mitigates autoimmune arthritis[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2010,69(8):1495-1501.
[52] Aoki N,Kido M,Iwamoto S,et al.Dysregulated generation of follicular helper T cells in the spleen triggers fatal autoimmune hepatitis in mice [J].Gastroenterology,2011,140(4):1322-1333.
[53] Warnats K,Bossaller L,Salzer U,et al.Human ICOSdeficiency abrogates the germinal center reaction and provides amonogenicmodel for common variable immunodeficiency [J].J Blood,2006,10(8):3045-3052.
[54] Coraglia A,Felippo M,Schierloh P,et al.CD4+T Lymphocytes with follicular helper phenotype(T(FH))in patients with SH2D1A deficiency(XLP)[J].Clin Immunol,2011,14(3):357-364.
[55] Fahey LM,Wilson EB,Elsaesser H,et al.Viral persistence redirects CD4 T cell differentiation toward T follicular helper cells[J].JExp Med,2011,208(5):987-999.
[56] Harker JA,Lewis GM,Mack L,et al.Late interleukin-6 escalates T follicular helper cell responses and controls a chronic viral infection[J].Science,2011,334(6057):825-829.
[57] Zaretsky AG,Taylor JJ,King IL,et al.T follicular helper cells differentiate from Th2 cells in response to helminth antigens[J].JExp Med,2009,206(5):991.
[58] Hong JJ,Amancha PK,Rogers K,et al.Spatial alterations between CD4(+)T follicular helper,B,and CD8(+)T cells during simian immunodeficiency virus infection:T/B cell homeostasis,activation,and potentialmechanism for viral escape[J].J Immunol,2012,188(7):3247-3256.
[收稿2013-06-25 修回2013-07-23]
(编辑 许四平)
R392.12
A
1000-484X(2014)05-0700-05
10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2014.05.030
①本文受国家自然科学基金(No.81271325)资助。
赵 敏(1987年-),女,主要从事重症肌无力研究。
及指导教师:李 静(1970年-),女,医学博士,副主任医师,硕士生导师,主要从事神经免疫学研究,E-mail:jing_neurology@hotmail.com。
