脑得生片物质基础的HPLC-DAD-MSn分析
2012-11-29陈慧贞李云飞钟敬华范骁辉
陈慧贞,李云飞,钟敬华,范骁辉
(浙江大学药学院,浙江杭州 310058)
近年来,随着中医药现代化和国际化进程,中药在全球的应用日益广泛,并受到了各国药品监管部门及药物研发人员的普遍关注[1-2]。由于中药化学组成复杂,如何进行有效地控制中药质量随之成为中药研究和监管部门的重要课题[3-4]。显然,开展中药的化学物质基础研究,鉴定出其所含的主要化学成分应是建立科学质量控制方法的先决条件[5-7]。
脑得生片是一种临床上常用于治疗脑动脉硬化、缺血性脑卒中和脑出血后遗症等的复方制剂[8],其主要由三七、川芎、葛根、红花和山楂5种药材制成。目前,已有文献研究了葛根[4,9-10]、红花[11-13]、三七[14-15]、川芎[16-18]和山楂[19-21]等药材的活性成分,并有研究人员采用高效液相(HPLC)或高效毛细管电泳(HPCE)法建立了脑得生片中的葛根素的检测方法[4,22-24]。但至今为止,鲜见同时鉴定脑得生片中多种成分的报道,导致该制剂的化学物质基础仍不明确,制约了其质量的进一步提升。
LC-ESI-MSn联用技术拥有强大的分离能力,可有效分离中药的复杂成分,进而通过质谱检测器获取其多级碎片信息,实现化合物的推断鉴定,被认为是中药等复杂物质体系的重要分析方法[25-28]。显然,采用 LC-ESI-MSn联用技术对中药进行定性分析,明确其化学物质基础,对于进一步开展药效物质基础研究或提高其质量标准具有重要意义。为此,本研究采用HPLC-DADESI-MSn联用技术建立脑得生片中多种成分同时鉴定方法,开展其化学物质基础研究。
1 实验部分
1.1 仪器与试剂 Agilent 1100/LC/DAD/MS系统(安捷伦公司,美国),含在线真空脱气机、四元泵、自动进样器、柱温箱、光电二极管阵列检测器(DAD)、电喷雾接口(ESI)和Finnigan LCQ-DECA XP Plus离子阱质谱仪(赛默飞公司,美国)。Thermo Finnigan Xcalibur 1.3工作站。
实验试剂:乙腈(色谱纯,默克公司,德国)、甲醇和甲酸(分析纯,杭州试剂公司,中国),以及 Milli-Q水(密理博公司,法国)。葛根素、大豆苷、三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Rg1、人参皂苷Re、人参皂苷Rb1、人参皂苷Rc、人参皂苷Rb2和人参皂苷Rd对照品购于中国药品生物制品检定所,经HPLC鉴定纯度超过98%,甲醇溶液中稳定。脑得生片由吉林春光制药有限公司提供。药材三七、川芎、葛根、红花和山楂由杭州中药材饮片厂提供。
1.2 样品制备 脑得生片供试品的制备:取脑得生片1 g,去糖衣后,研成细粉,加甲醇-水溶液(体积比1∶1)20 ml,超声提取 45 min,提取液过滤,滤液 12 000 r·min-1,离心 15 min,即得。
1.2.1 药材供试品制备 原药材粉末各取5 g,加水50 ml,加热至 100℃,回流提取 2 次,每次1.5 h,每次50 ml,合并2次滤液。滤液在60℃条件下,旋转蒸发仪蒸干。残渣用50 ml的水溶解。溶液过0.45 μm滤膜,即得。
1.2.2 色谱条件 色谱柱:Agilent Zorbax SBC18柱(4.6 mm ×250 mm,i.d,5 μm)。流动相:0.05%甲酸(A)和乙腈(B),梯度洗脱 0 min,5%B;15 ~30 min,10%B;60 min,20%B;75 min,30%B;85 min,40%B;100 min,60%B。流速:0.5 ml·min-1。DAD 检测器:190~400 nm进行全波长扫描,同时选择3个不同波长作为检测波长,分别为203 nm、254 nm和280 nm。柱温:40℃;进样体积:15μL。
1.2.3 质谱检测条件 MS同时记录总离子流(TIC)色谱图。离子极性:ESI(+/-);扫描范围:100~2000;毛细管温度:350℃;干燥气(N2)流速:30 L·min-1,辅助气体(N2)流速为10 L·min-1;毛细管电压:20 V;裂解电压:3.0 kV。离子宽度为2.0的母离子进行多级质谱分析。
2 数据分析
2.1 HPLC-DAD分析 根据中国药典(2005版)对脑得生片生产过程的记载,脑得生片中的主要化学成分是由三七、葛根、红花和山楂4种药材的水溶性成分和川芎中的挥发油组成[8]。考虑到 HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn联用技术的特点,本研究暂不将挥发油作为研究对象。预实验表明,脑得生片中的主要化学成分是黄酮、皂苷和酚酸3类化学成分。文献研究表明,三萜类皂苷的紫外最大吸收波长在203 nm处[29-30],酚酸的紫外最大吸收波长在210 nm和280 nm处[31-32],黄酮的紫外最大吸收波长在250 nm和275 nm处[33-36]。因此,可以根据化合物的特征紫外吸收图快速推断鉴定化合物的母核类型。
图1为脑得生片色谱图(图1A-C)与三七提取物、葛根提取物、红花提取物和山楂提取物的色谱图进行对照(图1D-G),脑得生片中的主要化合物色谱峰可以从各药材提取物色谱峰中找到归属。

图1 脑得生片及药材在不同波长下的HPLC-UV色谱图Fig.1 HPLC-UV chromatogram of Naodesheng tablet and extracts of herbs
2.2 对照品的HPLC-MS分析 9个对照品直接进样用于ESI-MS参数优化,葛根素、大豆苷、三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Re、人参皂苷Rg1、人参皂苷Rb1、人参皂苷Rc、人参皂苷Rb2和人参皂苷Rd。标准品经过ESI离子源电离成碎片离子,相应的碎片离子经过碰撞、诱导及解离(CID),获取相应的二级质谱数据和多级质谱数据。通过二级质谱和多级质谱数据可以获得9个对照品的裂解模式。这可以用于脑得生片中具有相似母核化合物的鉴定。在ESI电离过程中,所有对照品的准分子离子峰是失去质子的[M-H]-,三萜类皂苷的准分子离子峰是加合AcO-离子后的加合离子[M+AcO]-。9个对照品的分子量、二级质谱数据和多级质谱获得的主要裂解碎片见表1。
2.3 脑得生片HPLC-DAD-MSn分析 脑得生片的LC-MS数据用Matlab 7.0进行噪音平滑处理。图2为脑得生片203 nm波长处的HPLCUV色谱图(图2A)和总离子流图(图2B)。
由于脑得生片总离子流图的信噪比较低,很难将TIC色谱图的组分或色谱峰与对照品的质谱数据进行对照。为此,本研究先用CODA-DW法消除噪声干扰[37],滤噪后的总离子流图见图2C。
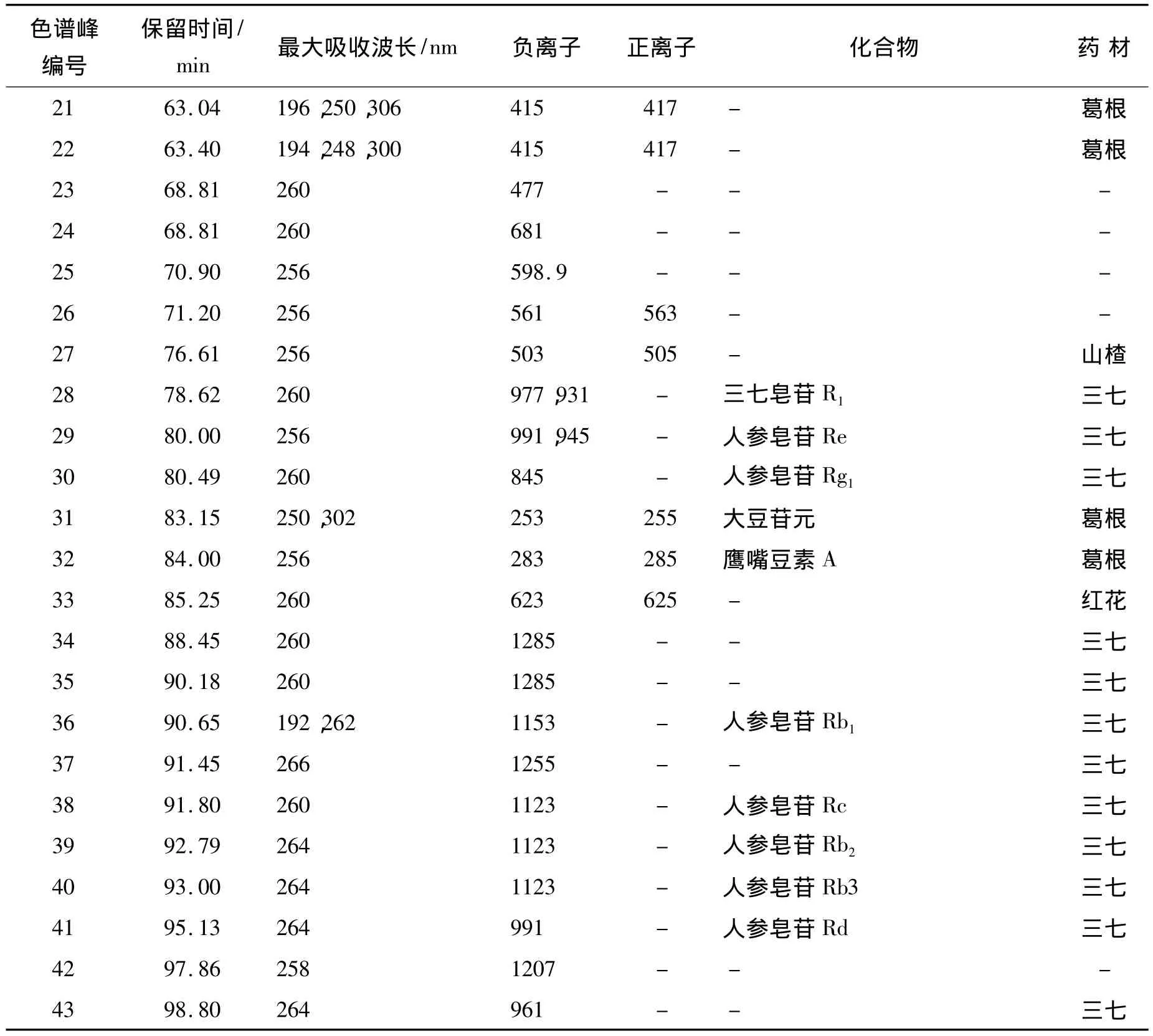
将脑得生片与药材提取物的HPLC-UV和HPLC-MS色谱图进行对比,制剂中大多数的色谱峰可以在原药材提取物的色谱图中找到归属。10、16、28、29、30、36、38、39 和 41 号色谱峰可以通过色谱峰的保留时间、紫外吸收光谱图和对照品的m/z值进行鉴定。脑得生片化学物质的推断鉴定结果见表2。

图2 脑得生片在203 nm处的HPLC-UV色谱图和总离子流图Fig.2 HPLC-UV chromatogram(203 nm)and total ion current chromatogram of Naodesheng tablet

表1 对照品一级质谱和多级质谱分析后的母离子和主要裂解离子Table 1 The precursor ion and main fragment ions of the reference compounds in MS and MSn analysis

表2 脑得生片中色谱峰HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS鉴定结果Table 2 HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS identification of Naodesheng tablet
续表2
由于缺少对照品,本研究通过各个色谱峰的特征紫外吸收图、一级质谱、二级质谱和三级质谱的裂解碎片和前述9个对照品的各级质谱裂解离子和裂解规律及文献数据来鉴定其它色谱峰[4,12,38-41]。
经上述方法推断鉴定,2、3、7、8、12、14、18、20、31、32和40号色谱峰分别为红花黄色素A、4'-O-葡萄糖葛根素、3'-羟基葛根素、大豆苷元-8-C-芹菜糖基(1-6)葡萄糖苷、3'-甲氧基葛根素、3'-甲氧基-6″-O-木糖葛根素、5,7-三羟基异黄酮-7-糖苷、葛根苷A、大豆苷元、鹰嘴豆素A和人参皂苷Rb3(表2)。12号色谱峰的准分子离子峰[M-H]-的m/z是445。据此推测12号色谱峰的分子质量应是446,与化合物3'-甲氧基葛根素的分子量相同。对该准分子离子进行二级质谱分析,产生脱去120 Da的碎片离子基峰,碎片离子的m/z为325(图3)。这是碳苷类化合物的特征裂解途径[39]。12号色谱峰的最大紫外吸收波长在204 nm和250 nm。这些数据与文献相符[4,39]。据此推测12号色谱峰是3'-甲氧基葛根素。
32号色谱峰的准分子离子峰[M-H]-的m/z是283。对此准分子离子进行二级质谱分析,产生缺失一个甲基的碎片离子基峰[M-H-15]-,碎片离子的m/z是268。这些数据与文献[4]的信息一致,推测32号色谱峰是鹰嘴豆素A。
3号和14号色谱峰的准分子离子峰[M+H]+的m/z是579。然而,2个色谱峰的质谱裂解途径不同。3号色谱峰的二级质谱的碎片离子基峰[M+H-162]+是缺失一个葡萄糖基获得的,m/z是417;14号色谱峰的二级质谱的碎片离子基峰[M+H-132]+是缺失一个木糖基或芹菜糖基获得的,碎片离子的m/z是447。2个色谱峰的三级质谱显示2个碎片离子基峰都缺失1个120 Da的中性片段,可以判断这2个化合物是碳苷类化合物。将数据与文献[39-40]进行对照,3号色谱峰是4'-O-葡萄糖葛根素,14号色谱峰是3'-甲氧基-6″-O-木糖葛根素。
其它色谱峰,例如:4、17、23、24、25、26 和 42号色谱峰未从药材提取物中找到对应的色谱峰。这些色谱峰极有可能是在产品生产或是在样品制备过程中产生的中间产物。另外,药厂实际生产时所用的药材可能与实验中使用的有差异。由于母离子峰度较低,1、9、15、21、22、27、33、34、35、37和43号色谱峰的三级质谱未得到很好检测。由于缺少文献数据的验证,5、6和19号色谱峰无法鉴别。上述提到的色谱峰的m/z值、紫外吸收光谱图和对应的药材和各色谱峰的数据见表2,已鉴定化合物的结构式见图4。

图3 12号色谱峰的ESI图Fig.3 ESI spectra of peak 12

图4 脑得生片中已鉴定化合物的结构式Fig.4 Structure of the identified compounds in Naodesheng tablet
3 结论
本研究运用HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn联用技术检测和鉴定脑得生片中的化合物。根据化合物的保留时间,紫外吸收光谱图和各级质谱数据,成功推断鉴定了22个化合物,初步明确了脑得生片的化学物质基础。这一研究结果为后续提高脑得生片质量控制标准提供了基础数据,有助于开展其药效物质基础研究。
[1]NORMILE D.Asian medicine.The new face of traditional Chinese medicine [J].Science,2003,299(5604):188-190.
[2]EISENBERG D M,DAVIS R B,ETTNER S L,et al.Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States,1990-1997:results of a follow-up national survey[J].JAMA,1998,280(18):1569-1575.
[3]CALIXTO J B.Efficacy,safety,quality control,marketing and regulatory guidelines for herbal medicines(phytotherapeutic agents)[J].Braz J Med Biol Res,2000,33(2):179-189.
[4]CHENG Yi-yu,FAN Xiao-hui,YE Zheng-liang,et al.Multiple chromatographic fingerprinting and its application to the quality control of herbal medicines[J].Anal Chim Acta,2006,555(2):217-224.
[5]ZHANG Hai-jiang,WU Yong-jiang,CHENG Yi-yu.Analysis of'SHENMAI'injection by HPLC/MS/MS[J].J Pharm Biomed Anal,2003,31(1):175-183.
[6]ZHU You-ping,WOERDENBAG H J.Traditional Chinese herbal medicine [J].Pharm World Sci,1995,17(4):103-112.
[7]MA Ming,FENG Fang,SHENG Yu-lan,et al.Development and evaluation of an efficient HPLC/MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of pseudoephedrine and cetirizine in human plasma:application to phase-I pharmacokinetic study[J].J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci,2007,846(1-2):105-111.
[8]State Pharmacopoeia Committee of People's Republic of China(食品药品监督管理局).Chinese Pharmacopoeia:version 2005(中国药典2005版)[M].Chemical Industry Press(in Chinese)
[9]TIAN Hong-zhen,WANG Hua,GUAN Ya-feng.Separation and identification of isoflavonoids in Pueraria lobata extracts and its preparations by reversed-phase capillary liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography(色谱),2005,23(5):477-481.(in Chinese)
[10]LI Xiao-ming,YANG Bin,HUANG Lu-qi(李晓明,杨 滨,黄璐琦).Identification of isoflavones in the roots of Pueraria lobat with HPLC-MS[J].China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica(中国中药杂志),2008,33(11):1337-1339.(in Chinese)
[11]WANG Ruo-jing,YANG Bin(王若菁,杨 滨).Survey of study on the chemical constituents and quality control of Flos Carthami.[J].Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae(中国实验方剂学杂志),2007,13(5):65-69.(in Chinese)
[12]JIN Yu,XIAO Yuan-sheng,ZHANG Fei-fang,et al.Systematic screening and characterization of flavonoid glycosides in Carthamus tinctorius L.by liquid chromatography/UV diode-array detection/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry[J].J Pharm Biomed Anal,2008,46(3):418-430.
[13]JIN Yu,ZHANG Xiu-li,SHI Hui,et al.Characterization of C-glycosyl quinochalcones in Carthamus tinctorius L.by ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time-offlight mass spectrometry[J].Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom,2008,22(8):1275-1287.
[14]KITE G C,HOWES M J,LEON C J,et al.Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry of malonylginsenosides in the authentication of ginseng[J].Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom,2003,17(3):238-244.
[15]LI Lie,ZHANG Jin-lan,SHENG Yu-xin,et al.Simultaneous quantification of six major active saponins of Panax notoginseng by high-performance liquid chromatography-UV method [J].J Pharm Biomed Anal,2005,38(1):45-51.
[16]KONG Liang,YU Zhi-yian,BAO Yong-ming,et al.Screening and analysis of an antineoplastic compound in Rhizoma Chuanxiong by means of in vitro metabolism and HPLC-MS [J].Anal Bioanal Chem,2006,386(2):264-274.
[17]TENG Jiu-wei,LI De-liang,LUO An-dong(滕久委,李 德 良,罗 安 东).Identification and characterization of supercritical fluid extracts of Rhizoma Chuanxiong by high performance liquid chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Instrumental Anaysis(分析测试学报),2007,26(3):356-359.(in Chinese)
[18]KONG Liang,YU Zhi-yuan,ZHOU Han-fa,et al(孔 亮,于志远,邹汉法,等).Determination of the active ingredients in Rhizoma Chuanxiong by high performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry(分析化学),2004,11(11):1501-1504.(in Chinese)
[19]RAYYAN S,FOSSEN T,SOLHEIM N H,et al.Isolation and identification of flavonoids,including flavone rotamers,from the herbal drug'Crataegi folium cum flore'(hawthorn)[J].Phytochem Anal,2005,16(5):334-41.
[20]GUO Yong-xue,LI Nan,YANG Mei-yan,et al(郭永学,李 楠,杨美燕,等).Progress on chemical constituents and analytical methods of flavones of crataegus.L [J].Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine(中成药),2005,27(1):112-115.(in Chinese)
[21]SHI Xiang-yu,MA Yin-hai(石香玉,马银海).Determination of six organic acids in C.pinnatifida Bunge by high performance liquid chromatography based on matrix solid phase dispersion [J].Food Science(食品科学),2008,29(2):297-299.(in Chinese)
[22]SHEN Chun-xiang,YANG Bing-xun,CHEN Lizhuan(沈春香,杨兵勋,陈立钻).Determination of puerarin in Naodesheng tablets by HPLC [J].The Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy(中国现代应用药学),2006,23(3):223-225.(in Chinese)
[23]SUN Li-hua,HU Yong-ming,ZOU De-lu,et al(孙立华,胡永明,邹德禄,等).Determination of puerarin in radix puerariae and Naodesheng tablets by HPCE [J]. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Sciences(中国药学杂志),2000,35(10):694-696.(in Chinese)
[24]WANG Jun-yong,LIANG Sheng-wang,FU Li-jiao,et al(王 俊 永,梁 生 旺,付 利 娇,等).Determination the content of isoflavones in Naodesheng tablets[J].China Pharmacis(中国药师),2008,11(4):423-425.(in Chinese)
[25]CHENG Y Y,LU Y,YU K,et al.Development of an HPLC-UV-ELSD method for quantification of multiple components of a Chinese medicine made from Radix salvia miltiorrhiza and Panax notoginseng[J].Chromatographia,2007,65(1-2):19-24.
[26]CHANG Y W,YAO H T,CHIEN D S,et al.Highperformance liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of multiple active components in Sheng-Mai San,a prescription of traditional Chinese medicine[J].Phytochem Anal,2008,19(3):258-265.
[27]LI Yun-fei, QU Hai-bing, CHENG Yi-yu.Identification of major constituents in the traditional Chinese medicine“QI-SHEN-YI-QI”dropping pill by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array detection-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry[J].J Pharm Biomed Anal,2008,47(2):407-412.
[28]XU S J,YANG L,ZENG X,et al.Characterization of compounds in the Chinese herbal drug Mu-Dan-Pi by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization mass spectrometry [J].Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom,2006,20(22):3275-3288.
[29]TAI Jian-dong,LUO Xu-biao,YAN Liu-shui,et al(邰建东,罗旭彪,颜流水,等).Simultaneous determination of seven compounds of saponins in Panax Notoginseng by HPLC [J].China Pharmacis(中国药师),2008,11(12):1411-1413.(in Chinese)
[30]YANG Nan-lin,WU Yong-jiang,CHENG Yi-yu,et al(杨南林,吴永江,程翼宇,等).Simultaneous determination of Notoginseng R1,Ginsensoide R1,Rg1and Rdin Panax Notoginseng Herb using reversed phase high performance liquid chromatographic method[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry(分析化学研究简报),2003,31(6):731-734.(in Chinese)
[31]LI Jian-zhong(李建中).Analysis of active in Chinese Hawthorn fruits by using HPLC[D].河北保定:河北农业大学,2004.(in Chinese)
[32]LIU Wen-min(刘文民).Analysis of active in Chinese Hawthorn fruits by using HPLC and HPCE[D].河北保定.河北农业大学,2002.(in Chinese)
[33]CHEN Shu-he,CHEN Li-dan,BA Sai,et al(陈树和,陈丽炟,巴 塞,等).Study on HPCE Fingerprints of total flavonoids from Pueraria lobata.[J].China Pharmacy(中 国 药 房),2010,21(39):3709-3711.(in Chinese)
[34]LUO Lan,GAO Shu-juan,WANG Shu-mei,et al(罗兰,高淑娟,王淑美,等).Determination of pueraria isoflavones content in effective parts of Naomaitong.[J].Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine(中成药),2010,32(4):604-606.(in Chinese)
[35]ZHAO Ming-bo,DENG Xiu-lan,WANG Ya-ling,et al(赵明波,邓秀兰,王亚玲,等).Establishment of chromatographic fingerprint and quality assessment of Carthamus tinctorius L.by high performance liquid chromatography.[J].Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica(药学学报),2004,39(3):212-216.(in Chinese)
[36]XIE Guo-xiang,QIU Ming-feng,ZHANG Han-jie,et al(谢国祥,邱明丰,张汉杰,等).Fingerprint of Carthamus Tinctorius L.by HPLC.[J].Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine(中成药),2004,39(3):212-216.(in Chinese)
[37]WINDIG W.The use of the Durbin-Watson criterion for noise and background reduction of complex liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry data and a new algorithm to determine sample differences[J].Chemometr Intell Lab,2005,77(1-2):206-214.
[38]DONG Ying,XU Bin,LIN Lin,et al(董 英,徐斌,林 琳,等).Advances in studies on chemical components of Pueraria DC.[J].Food and Machinery(食品与机械),2005,(6):85-88.(in Chinese)
[39]ZHANG Yan(张 岩).Construction of Multi-Components Library and investigation of estrogenic activities of Kudzu Root[D].大连:大连化学物理研究所,2005.(in Chinese)
[40]CHI Ji-fei(迟 霁 菲).Research of chemical composition and quality control methods in radix puerariae[D].沈阳:沈阳药科大学,2006.(in Chinese)
[41]WAN J B,LAI C M,LI S P,et al.Simultaneous determination of nine saponins from Panax Notoginseng using HPLC and pressurized liquid extraction [J].J Pharm Biomed Anal,2006,41(1):274-279.
