悬钩子属植物化学成分及药理活性研究进展
2011-11-23孟祥娟热增才旦折改梅姜艳艳
孟祥娟,刘 斌,热增才旦,折改梅,姜艳艳
北京中医药大学,北京100102
悬钩子属植物化学成分及药理活性研究进展
孟祥娟,刘 斌*,热增才旦,折改梅,姜艳艳
北京中医药大学,北京100102
本文对近10年来悬钩子属植物的化学成分和药理活性研究进行了综述,为该属植物的进一步开发利用提供参考。悬钩子属植物的化学成分主要包括黄酮、萜、鞣质、甾等。药理活性主要包括抗菌、抗炎、抗肿瘤、抗氧化、抗过敏、保肝、镇痛等。
悬钩子属;黄酮;萜;鞣质;抗肿瘤;抗过敏;保肝
悬钩子属(Rubus L.)是蔷薇科(Rosaceae)蔷薇亚科的一个大属,现已知750余种,分布于全世界,集中分布于北美和东亚。我国有200余种,南北各省均有,主要分布于长江以南及西北地区[1]。该属许多植物在我国传统中医药中的应用十分广泛,如覆盆子具有益肾、固精、缩尿的功效,用于肾虚遗尿、小便频数、阳痿早泄、遗精滑精;山莓具有活血、止血、祛风利湿的功效,用于吐血、便血、肠炎、痢疾、风湿关节痛、跌打损伤、月经不调、白带,其叶可消肿解毒,外用治痈疖肿毒;茅莓散瘀止痛、清热解毒、祛风除湿;高粱泡根疏风清热、凉血活血,用于月经不调、崩漏、白带、闭经、胎动不安等症;寒莓根清热解毒、凉血止痛[2]。近年来,国内外许多学者对本属植物进行了一系列化学成分和药理活性研究,发现悬钩子属植物含有多种化学成分,具有多种药理作用,药用价值很高,对调节机体的生命活动及医疗保健作用有重要意义。
1 化学成分
该属植物化学成分的系统研究始于20世纪70年代末80年代初,迄今为止,国内外化学工作者已从该属植物川莓R.setchuenensis Bur.(1)、茅莓R.parvifolius L.(2)、木莓R.swinhoei Hance(3)、寒莓R.buergeri Mip.(4)、山莓R.corchorifolius L.(5)、钻地风R.ellipticus Smith var.obcordatus Focke(6)、覆盆子R.chingii Hu(7)、红树莓R.idaeus L.(8)、黑草莓 R.ursinus L.(9)、黑莓 R.allegheniensis Port.(10)、榆叶黑莓R.ulmifolius Schott.(11)、广西甜茶R.suavissimus S.(12)、灰毛泡 R.irenaeus Focke (13)、毛萼梅R.chroosepalus Focke(14)、乌泡子R.parkeri Hance(15)、白叶莓R.innominatus S.(16)、粗叶悬钩子R.alceaefolius Poir(17)、粉枝莓R.biflorus Buch.(18)、紫色悬钩子R.irritans Focke(19)、菰帽悬钩子R.pileatus Focke(20)、黄果悬钩子R.xanthocarpus Bureau et Franch(21)、红毛悬钩子R.pinfaesis Levl.et Vant.(22)、灰白毛莓 R.tephrodes Hance(23)、托盘R.crataegiflolius Bge.(24)、秀丽莓R.amabilis Focke(25)、蓬蘽 R.hirsutus Thunb.(26)、二花悬钩子R.biflorus Buch.(27)、空心泡R.rosaefolius Smith(28)、R.pinnatus Willd.(29)、R.rigidus Sm.(30)、插田泡R.coreanus Miq.(31)、裂叶悬钩子R.laciniatus Willd.(32)、刺悬钩子R.pun-gens Camb.(33)、R.sanctus Schreb.(34)等植物中分离得到多种化学成分,主要包括黄酮、萜、鞣质、甾,以及少量醌、有机酸、生物碱等[3]。
1.1 黄酮类
刘明生等[4]已对1999年之前从该属植物中分离得到的黄酮类化合物进行了综述。近10年来从该属植物中分离得到的黄酮类化合物基本骨架见图1,结构见表1。
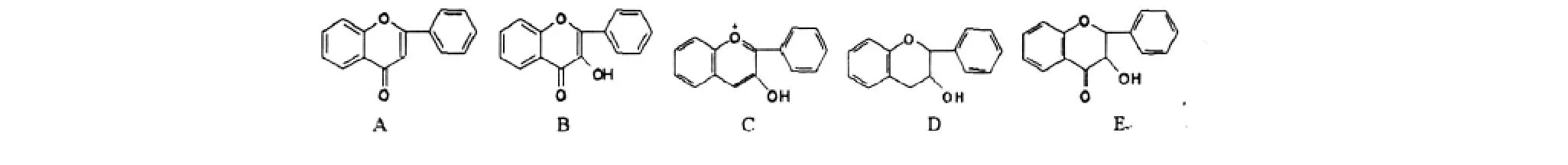
图1 悬钩子属植物中的黄酮类化合物基本骨架Fig.1 Structure of flavones isolated from Rubus L.

表1 悬钩子属植物中的黄酮类化合物Table 1 Flavones isolated from Rubus L.
1.2 萜类
悬钩子属植物中的萜类化合物主要包括二萜、三萜以及少数单萜[4]。根据母核结构,二萜类化合物可分为半日花烷型和贝壳杉烷型,三萜类化合物主要为齐墩果烷型和乌苏烷型,少数为羽扇豆烷型。
1.2.1 二萜类
傅正生等[3]综述了1999年之前从该属植物中分离得到的半日花烷型二萜类化合物,该类二萜属于对映-半日花烷型,主要存在于覆盆子叶、灰毛果莓果实、广西甜茶叶和果实中。其后未从该属植物中分离得到新的该类型二萜成分。
Takashi Tanaka等[3]从广西甜茶叶中分离得到贝壳杉烷型二萜苷Rubusoside(13-O-β-D-glucosylsteviol),系首个从该属植物中分离得到的贝壳杉烷型二萜苷。近10年来从该属植物中分离得到的贝壳杉烷型二萜类化合物的基本骨架见图2,结构见表2。
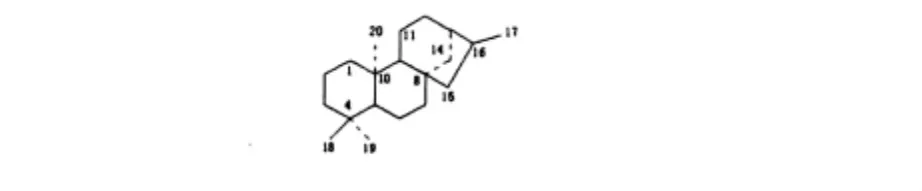
图2 贝壳杉烷型二萜类化合物基本骨架Fig.2 Structure of the Kaursane-type diterpenes
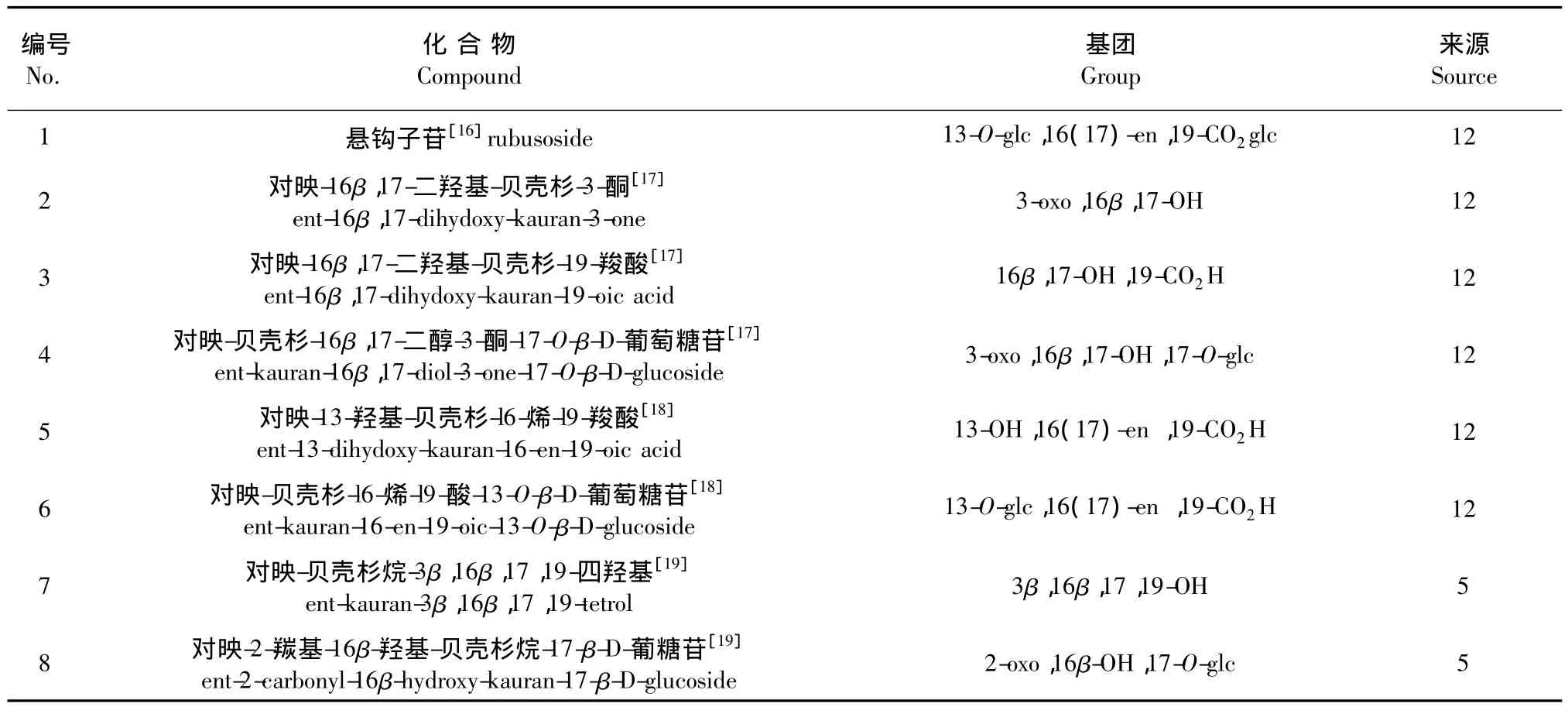
表2 悬钩子属植物中贝壳杉烷型二萜类化合物Table 2 The Kaursane-type diterpenes isolated from Rubus L.
1.2.2 三萜类
日本学者通过对本属39种植物叶的研究,提出19α-羟基乌苏酸-28-β-D-葡萄糖酯苷型三萜在本属植物中具有分类学意义[4]。近年来国内外化学工作者相继对该属植物的三萜类成分做了进一步研究,从中分离出一系列三萜类化合物,其基本骨架见图3~5,结构见表3~5。
另外,Hao XJ等[22]从刺悬钩子地上部分得到了新的乌苏烷型三萜苷二聚体Rubupungenosides A和Rubupungenosides B。
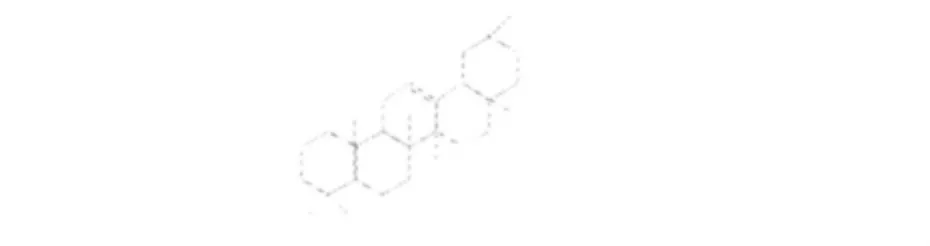
图3 齐墩果烷型三萜类化合物基本骨架Fig.3 Structure of the oleane-type triterpenes

表3 悬钩子属植物中齐墩果烷型三萜类化合物Table 3 The oleane-type triterpenes isolated from Rubus L.

齐墩果酸[23]oleanolia acid 3β-OH,12-en,28-CO2H 20 5 arjunolic acid[24]2α,3β,19α-(OH)3,12-en,28-CO2H 3 4寒莓酸甲酯[25]methyl buergericate 2α,3α,19α,24-(OH)4,12-en,28-CO2CH3 4 7 canmelliagenin A[26]3β,16α,22α(OH)3,12-en,28-CH2OH 2 6 3β,16α,22α-(OH)3,12-en,23,28-CH2OH 2 9 sericoside[27]2α,3β,19α,24-(OH)4,12-en,28-CO2glc 6 8 canmelliagenin C[26]10 sericic acid[27]2α,3β,19α,24-(OH)4,12-en,28-CO2H 6 11 buergericic acid[27] 2α,3α,19α,24-(OH)4,12-en,28-CO2H 6 12 crataegioside[28] 3β,19α,23-(OH)3,12-en,28-CO2glc 24 13 arjunglucoside I[28] 2α,3β,19α,23-(OH)4,12-en,28-CO2glc 24 14 2α,3β,19α-三羟基齐墩果-12-烯-23-酸-28-葡萄糖苷[28]2α,3β,19α-trihydroxyolean-12-en-23-oic acid-28-β-D-glucoside 2α,3β,19α-(OH)3,12-en,23-COOH,28-CO2glc 24
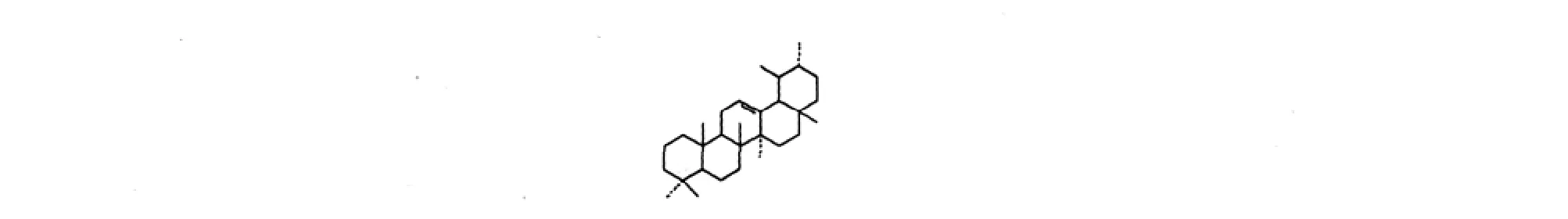
图4 乌苏烷型三萜类化合物基本骨架Fig.4 Structure of the ursane-type triterpenes

表4 悬钩子属植物中乌苏烷型三萜类化合物Table 4 The ursane-type triterpenes isolated from Rubus L.

18 覆盆子酸[32]fupenzic acid 2α,19α-(OH)2,3-oxo,1,12-dien,28-CO2H 16 19 2α,19α-二羟基-3-氧-乌索-12-烯-28-酸[32]2α,19α-dihydroxylurs-12-en-3-oxo-28-oic acid 2α,19α-(OH)2,3-oxo,12-en,28-CO2H 16 20 2α,3α-二羟基乌索-12,18-二烯-28-酸[32]2α,3α-dihydroxylurs-12,18-dien-28-oic acid 2α,3α-(OH)2,12,18-dien,28-CO2H 16 21 2α,3α-二羟基乌索-12,19-二烯-28-酸[32]2α,3α-dihydroxylurs-12,19-dien-28-oic acid 2α,3α-(OH)2,12,19-dien,28-CO2H 16 22 3β,19α-二羟基乌索-12-稀-28-葡萄糖苷[25]3β,19α-dihydroxylurs-12-en-28-oic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranoside 3β,19α-(OH)2,12-en,28-CO2glc 4 23 坡曼酸-3-阿拉伯糖苷[25]3-O-β-D-arabinopyranosyl pomolic acid 3-O-β-ara,19α-(OH)2,12-en,28-CO2H 4 24 2α,3β-二羟基乌苏-12,19-二烯-23,28-二酸[33]2α,3β-dihydroxylurs-12,19-dien-23,28-dioic acid 2α,3β-(OH)2,12,19-dien,23,28-(CO2H)2 14 25 rubusside A[34] 3,23-O-butylidene,2α,19α-(OH)2,12-en,28-CO2glc 10 26 委陵菜酸[35]tormentic acid 2α,3β,19α-(OH)3,12-en,28-CO2H 28 27 28-methoxytormentic acid[35] 2α,3β,19α-(OH)3,12-en,28-CO2CH3 28 28 rubuside A[27]2α,3β-(OH)2,12,18-dien,28-CO2glc 6 29 rubuside B[27]2α,3α-(OH)2,12,18-dien,28-CO2glc 6 30 rubuside C[27]2α,3α,23-(OH)3,12,18-dien,28-CO2glc 6 31 rubuside D[27]2α,3β-(OH)2,12,19-dien,28-CO2glc 6 32 rubuside E[27]2α,3α-(OH)2,12,19-dien,28-CO2glc 6 33 rubuside F[27]2α,3β-(OH)2,12,19(29)-dien,28-CO2glc 6 34 rubuside G[27]2α,3α-(OH)2,11,13(18)-dien,28-CO2glc 6 35 rubuside H[27]2α,3β,23-(OH)3,11,13(18)-dien,28-CO2glc 6 36 rubuside J[27]2α,3α,19α-(OH)3,12-en,23-CHO,28-CO2H 6 37 2α,3β,23-三羟基乌索-12,18-二烯-28-葡萄糖苷[27]2α,3β,23-trihydroxyurs-12,18-dien-28-oic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranoside 2α,3β,23-(OH)3,12,18-dien,28-CO2glc 6 38 2α,3β,23-三羟基乌索-12,19-二烯-28-葡萄糖苷[27]2α,3β,23-trihydroxyurs-12,19-dien-28-oic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranoside 2α,3β,23-(OH)3,12,19-dien,28-CO2glc 6 39 alpinoside[27]2α,3α-(OH)2,12,19(29)-dien,28-CO2glc 6 40 quadranoside VIII[27] 2α,3β,23-(OH)2,12,19(29)-dien,28-CO2glc 6 41 sericoside[27] 2α,3β,19α,24-(OH)4,12-en,28-CO2glc 6 42 pinfaensin[27] 2α,3β,19α-(OH)3,12-en,23-CHO,28-CO2H 6 43 苦莓苷F2[27]niga-ichigoside F2 2α,3α,19α,23-(OH)4,12-en,28-CO2glc 6 44 4-epi-niga-ichigoside F1[27] 2α,3β,19α,23-(OH)4,12-en,28-CO2glc 6 45 trachelosperoside A1[27] 2α,3β,19α-(OH)3,12-en,24-CO2H,28-CO2glc 6 46 pedunculoside[27] 3β,19α,23-(OH)3,12-en,28-CO2glc 6 47 ziyu-glycoside[27] 19α-OH,3-ara,28-CO2glc 6

48 1α,2α,3β,19α-四羟基乌索-12-烯-28-酸[27]1α,2α,3β,19α-tetrahydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid 1α,2α,3β,19α-(OH)4,12-en,28-CO2H 6 49 2α,3β,19α-三羟基乌索-12-烯-23,28-二酸[27]2α,3β,19α-trihydroxyurs-12-en-23,28-dioic acid 2α,3β,19α-(OH)3,12-en,23,28-(CO2H)2 6
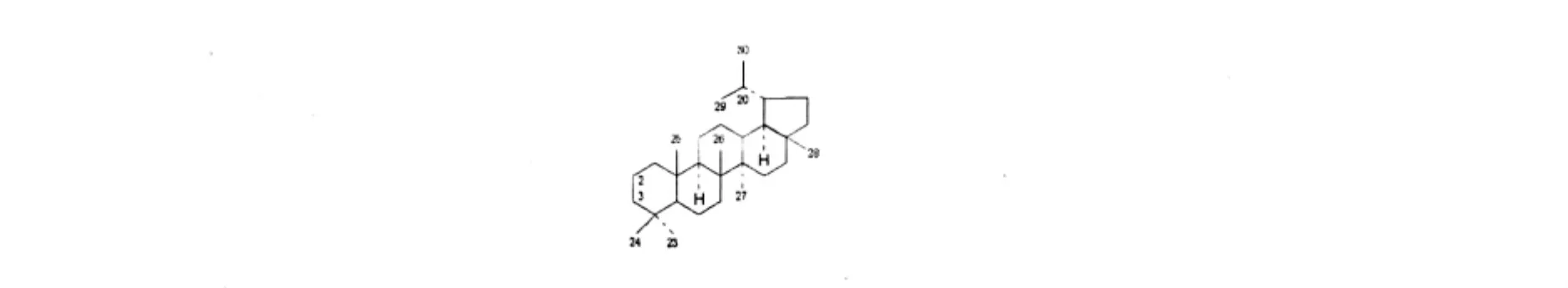
图5 羽扇豆烷型三萜类化合物基本骨架Fig.5 Structure of the lupane-type triterpenes

表5 悬钩子属植物中羽扇豆烷型三萜类化合物Table 5 The lupane-type triterpenes isolated from Rubus L.
1.3 鞣质类
从悬钩子属植物中分离得到的鞣质主要是可水解鞣质,包括没食子鞣质、逆没食子鞣质、可水解鞣质低聚体和咖啡鞣质等。
赵庆春等[36]从粗叶悬钩子中分离到一个新的鞣质sanguiin H-2 ethyl ester及1,2,3,4,6-五-没食子酰葡萄糖(1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucopyranose)和1,2,3,6-四-没食子酰葡萄糖(1,2,3,6-tetra-O-galloyl-β-D-glucopyranose)。Haizhou Li等[37]从甜茶提取物中分离到6个新的可水解鞣质和7个已知鞣质成分。6个新的可水解鞣质均属逆没食子鞣质及其低聚体和衍生物,分别是Rubusuaviins A~F,其中,Rubusuaviin A的结构是1-O-galloyl-2,3-O-(S)-HHDP-4,6-O-(S)-sanguisorboyl-β-D-glucopyranose;Rubusuaviins B、C和E分别是逆没食子鞣质的二、三、四聚体;Rubusuaviins D和F分别是Rubusuaviins C and E的衍生物。7个已知鞣质分别是pedunculagin、1(β)-O-galloyl pedunculagin、strictinin、sanguiin H-5、lambertianin A、sanguiin H-6和1-desgalloyl sanguiin H-6;Sahar A.M.Hussein等[38]从Rubus sanctus的地上部分分离出1个新鞣质2,3-O-hexahhexahydroxydiphenoyl-4,6-O-sanguisorboyl-(α/ β)-glucose和2个已知鞣质2,3-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-(α/β)-glucose、bis-2,3,4,6-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-(α/β)-glucose。
1.4 甾类
悬钩子属植物所含甾类化合物主要有植物甾醇、C21甾等。黄可新等[39]从川莓中分离出胡萝卜苷-6’-棕榈油酯;阮金兰等[40]从黑草莓果实冻干粉的正丁醇提取部分分离得到△5,22-豆甾烯醇﹑β-谷甾醇和胡萝卜苷;王明奎等[32]从白叶莓根分离得到β-谷甾醇和胡萝卜苷;Márcia Kanegusuku等[35]从空心泡中分离得到豆甾醇(stigmasterol)﹑(3β,24R)-麦角甾-5-烯-3-醇 (campesterol)。Xiaochun chen等[5]从秀丽莓中分离得到1个C21甾体化合物3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-3β,15α-dihydroxypregn-5-en-20-one。
1.5 其它类
Guido Flamini等[41]从榆叶黑莓中分离到3个新的蒽醌类化合物rubanthrone A、B和C;Sahar A.M.Hussein等[38]从R.sanctus Schreb.的地上部分分离出2个新的天然咖啡酰酯3,6-di-O-caffeoyl-(α/ β)-glucose和 1-O-caffeoyl-β-xylose;Xiaochun chen等[5]从秀丽莓中分离得到(-)-secoisolariciresinol-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside和(+)-pinoresinol-O-β-D-glucopyranoside;赵庆春等[36]从粗叶悬钩子中分离得到1个新的酚酸类化合物rubuphenol及鞣花酸(ellagic acid)和没食子酸乙酯(ethyl gallate)。L.Panizzi等[6]从榆叶黑莓中分离得到没食子酸、阿魏酸;Silvia Martini等[12]自榆叶黑莓中分离得到鞣花酸、咖啡酸、香豆酸;Gudej J等[7]从红树莓叶中分离得到没食子酸甲酯;谢一辉等[42]自华东覆盆子中分离得到对羟基间甲氧基苯甲酸和对羟基苯甲酸。
2 药理作用
2.1 抗菌作用
黑莓叶的提取物对幽门螺杆菌具有明显的抗菌活性,尤其是从黑莓中提取分离得到的鞣花酸类成分和黄酮类成分抗菌活性显著,其最低杀菌浓度远远小于黑莓叶粗提物[12]。Guido Flamini等[41]从榆叶黑莓中分离得到的rubanthrone A在浓度为4.5 mg/ml时表现出对金黄色葡萄球菌显著的抗菌活性。兴安悬钩子R.chamaemorus Linn.叶的甲醇提取物对某些革兰氏阳性、革兰氏阴性菌和白色念珠菌具有显著的抗菌活性[43]。
2.2 抗炎作用
Choi J[44]等人研究了插田泡果实的提取物对小鼠和大鼠的抗炎活性,结果显示,从插田泡果实分离到的苦莓苷F1和23-hydroxytormentic acid均有显著的抗炎作用,且23-hydroxytormentic acid比苦莓苷F1具有更高的抗炎活性。
2.3 抗肿瘤作用
茅莓总皂苷对体内、外黑色素瘤细胞有抑制作用,通过促进黑色素瘤细胞凋亡而发挥抗肿瘤活性,并呈量效依赖关系[45]。
Choi SH等[46]研究了托盘根甲醇提取物对MCF-7人乳腺癌细胞生长周期的影响,结果表明托盘根甲醇提取物具有显著的诱导癌细胞凋亡活性,并能显著抑制 MCF-7人乳腺癌细胞的扩散,对MCF-7人乳腺癌细胞的生长有很强的抑制效应。另外,R.coreanum的水提取物能抑制人结肠癌细胞TH-29的增殖,并能促进该细胞的凋亡[47]。
2.4 抗氧化作用
Hyun Kyoung Ju等[48]对覆盆子中酚酸的含量及相关的抗氧化活性在其发酵前后的变化进行了研究。结果显示,覆盆子所含的酚酸具有显著的抗氧化活性,经过发酵过程后不仅含量有了提高,其清除自由基能力也大大增强。插田泡种子乙醇提取物对DPPA·,H2O2等有较强的清除能力,尤其是发酵后的种子乙醇提取物比新鲜种子具有更高的抗氧化活性[49]。
2.5 抗过敏作用
方耀高等[50]对广西甜茶提取物的抗过敏作用进行了研究。结果表明,广西甜茶提取物能显著抑制2,4-二硝基氟苯诱发的小鼠耳肿胀及血管通透性增高、绵羊红细胞诱发的小鼠迟发型过敏反应足跖肿胀,减轻小鼠异种被动皮肤过敏反应,而表现出显著的抗过敏作用,其作用机制可能与抑制肥大细胞释放组胺有关。
刺莓R.croceacanthus Leveille甲醇提取物能抑制肥大细胞介导的过敏样反应,具有很高的抗过敏活性[51]。
2.6 保肝作用
R.sanctus Schreb.乙醇提取物能显著抑制四氯化碳诱导的细胞死亡效应,减少谷胱甘肽消耗量,对四氯化碳诱导的小鼠离体肝细胞毒性损伤有显著保护作用[52]。
洪振丰等[53]采用CCl4致小鼠急性肝损伤模型,通过测定血清中谷丙转氨酶(ALT)、谷草转氨酶(AST)、肝组织损伤程度,以及肝组织中细胞色素CYP2E1和CYP3A1的mRNA表达,研究粗叶悬钩子总生物碱对模型大鼠急性肝损伤药物代谢酶的影响。结果表明,粗叶悬钩子总生物碱可显著降低ALT和AST水平,保护肝细胞免受伤害,并抑制细胞色素CYP2E1和CYP3A1在肝组织中的mRNA表达。
2.7 镇痛作用
空心泡地上部分提取物具有很强的镇痛作用,其中28-methoxytormentic acid的镇痛活性强于阿司匹林和对乙酰氨基酚数倍[35]。从R.imperialis中分离得到的苦莓苷F1也具有显著的镇痛效果[54]。
2.8 其它作用
从插田泡的未成熟果实中分离得到的苦莓苷F1和23-hydroxytormentic acid具有较好的抗风湿作用[30];茅莓总皂苷具有较好的抗脑缺血作用[55];从广西甜茶水提取物中分离得到的没食子酸具有显著的抗血管生成活性[56]。从茅莓根中分离得到的甜叶苷R1对多巴胺能神经元有保护作用[57]。插田泡果实乙醇提取物能加强成骨细胞的功能,对骨质疏松症和骨炎性疾病具有一定的预防作用[58]。
3 讨论
悬钩子属植物含有黄酮、萜、鞣质、甾、醌、生物碱、有机酸等多种化学成分,具有抗菌、抗炎、抗肿瘤、抗氧化、抗过敏、保肝、镇痛等多方面的药理活性,具有很高的医疗保健价值,且在我国传统中医药中应用广泛。但如何在广泛搜集整理民间治疗经验的基础上,确切地阐明该属植物的活性成分及其作用机制,并将其开发应用于临床是一个亟待解决的问题。进一步加强对该属植物有效成分药理活性、作用机制、构效关系、结构修饰改造等的多学科研究和关联分析,对该属植物成分的有效利用和新的药物先导化合物的发现具有重要意义。
1 Delectis Florae Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae,Agendae Academiae Sinicae Edita(中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会).Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sin(中国植物志),Tomus 57.Beijing:Science Press,1985.10-218.
2 Sun CQ(孙长清),et al.The exploitation and utilization of raspberry(Rubus L.).Guihaia(广西植物),2004,24:578-582.
3 Fu ZS(傅正生),et al.The progress of chemical composition and bioactivity of Rubus L..Nat Prod Res Dev(天然产物研究与开发),2001,13:86-91.
4 Liu MS(刘明生),et al.The research of chemical composition of Rubus L..Lishizhen Med Mat Med Res(时珍国医国药),1999,11:866-867.
5 Chen XC,et al.Pregnane glycoside,lignan glycosides,triterpene glycosyl ester and flavonoid glycosides from Rubus amabilis.Planta Medica,2001,67:270-273.
6 Panizzi L,et al.In vitro antimicrobial activity of extracts and isolated constituents of Rubus ulmifolius.J Ethnopharmacol,2002,79:165-168.
7 Gudej J.Kaempferol and quercetin glycosides from Rubus idaeus L.leaves.Acta Pol Pharm,2003,60:313-315.
8 Robert Byamukama,et al.Anthocyanins from fruits of Rubus pinnatus and Rubus rigidus.J Food Compos Anal,2005,18: 599-605.
9 Ku CS,Mun SP.Optimization of the extraction of anthocyanin from Bokbunja(Rubus coreanus Miq.)marc produced during traditional wine processing and characterization of the extracts.Bioresour Technol,2008,99:8325-8330.
10 Wang Y(汪瑗),et al.Analysis of flavones in Rubus parvifolius Linn by high performance liquid chromatography combined with electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry and thin-layer chromatography combined with fourier transform surface enhanced raman spectroscopy.Chin J Anal Chem(分析化学),2006,34:1073-1077.
11 Venskutonis PR,et al.Radical scavenging activity and composition of raspberry(Rubus idaeus)leaves from different locations in Lithuania.Pitoterapia,2007,78:162-165.
12 Silvia Martini,et al.Antimicrobial activity against Helicobacter pylori strains and antioxidant properties of blackberry leaves(Rubus ulmifolius)and isolated compounds.Int J Antimicrob Agents,2009,34:50-59.
13 Kang SH(康淑荷),Zheng SZ(郑尚珍).Two new flavones from Rubus biflorus Buch.Acta Pharm Sin(药学学报),2007,42:1288-1291.
14 Määttä-Riihinen KR,et al.Identification and quantification of phenolic compounds in berries of Fragaria and Rubus species (family Rosaceae).J Agric Food Chem,2004,52:6178-6187.
15 Carle R,et al.A novel zwitterionic anthocyanin from evergreen blackberry(Rubus laciniatus Willd.).J Agric Food Chem,2002,50:396-399.
16 Du JW(杜晋伟),et al.The research of chemical composition of Rubus suavissimus S.Lee.China Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药),2007,38:346-348.
17 Wang JX(王剑霞),Lv HC(吕华冲).Studies on the diterpenoids of Rubus suavissimus S.Lee.Lishizhen Med Mat Med Res(时珍国医国药),2008,19:664-665.
18 Wang JX(王剑霞),Lv HC(吕华冲).Studies on the chemical constituents of Rubus suavissimus S.Lee.J Chin Med Mater(中药材),2007,30:800-802.
19 Zhang M(张敏),et al.Isolation and identification of two new diterpenoid from Rubus corchorifolius L..Acta Pharm Sin(药学学报),2007,42:1155-1158.
20 Liu R(刘戎),et al.Chemical constituents from root of Rubus irenaeus.China Tradit Herb Drugs(中草药),2003,34:394-396.
21 Kang SH(康淑荷),et al.Triterpenoids and steroids of root of Rubus biflorus.J Chin Med Mater(中药材),2008,31: 1669-1670.
22 Hao XJ,et al.Rubupungenosides A and B,two novel triterpenoid saponin dimers from the aerial parts of Rubus pungens.J Nat Prod,2000,63:851-854.
23 Wang BG(王斌贵),Jia ZJ(贾忠建).Studies on the chemical constituents of two species of raspberry(Rubus L.).China Tradit Herb Drugs(中草药),1999,30:83-87.
24 Zhao WQ(赵卫权),et al.Studies on chemical constituents in radicular part of Rubus swinhoei.China Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药),2001,32:874-875.
25 Deng Y(邓烨),et al.Triterpenoids from Rubus buergeri.Acta Bot Sin(植物学报),2001,43:644-646.
26 Du SH(都述虎),et al.Isolation and identification of chemical constituents from Rubus Parvifolius L..Chin J Nat Med (中国天然药物),2005,3:17-20.
27 Li W,et al.Triterpenoid saponins from Rubus ellipticus var.obcordatus.J Nat Prod,2009,72:1755-1760.
28 Jung SW,et al.A triterpene glucosyl ester from the roots of Rubus crataegifolius.Arch Pharmacal Res,2001,24:412-415.
29 Zuo GY(左国营),et al.Triterpenoids from the roots of Rubus obcordatus(Rosaceae).Acta Bot Yunnan(云南植物研究),2008,30:381-385.
30 Nam JH,et al.The anti-gastropathic and anti-rheumatic effect of niga-ichigoside F1 and 23-hydroxytormentic acid isolated from the unripe fruits of Rubus coreanus in a rat model.Biol Pharm Bull,2006,29:967-970.
31 Tan MX(谭明雄),et al.Studies on the chemical constituents from the Chinese traditional medicine Rubus parvifolius.Guihaia(广西植物),2003,23:282-284.
32 Wang MK(王明奎),et al.Studies on chemical constituents from root of Rubus innominatus.China Tradit Herb Drugs(中草药),2003,34:295-297.
33 Liu R(刘戎),et al.Chemical constituents from the root of Rubus chroosepalus.Acta Pharm Sin(药学学报),2001,36: 38-41.
34 Ono M,et al.A new triterpene glucosyl ester from the fruit of the Blackberry(Rubus allegheniensis).Chem Pharm Bull,2003,51:200-202.
35 Kanegusuku M,et al.Phytochemical and analgesic activity of extract,fractions and a 19-hydroxyursane-type triterpenoid obtained from Rubus rosaefolius(Rosaceae).Biol Pharm Bull,2007,30:999-1002.
36 Cui CB,et al.Two new and four known polyphenolics obtained as new cell-cycle inhibitors from Rubus Aleaefolius Poir.J Asian Nat Prod Res,2002,4:243-252.
37 Haizhou Li,et al.Rubusuaviins A-F,monomeric and oligomeric ellagitannins from Chinese Sweet Tea and their α-amylase inhibitory activity.Chem Pharm Bull,2007,55:1325-1331.
38 Hussein SA,et al.Caffeoyl sugar esters and an ellagitannin from Rubus sanctus.Phytochemistry,2003,63:905-911.
39 Huang KX(黄可新),et al.Chemical constituents from Rubus setchuenensis.Chin J Appl Environ Biol(应用与环境生物学报),2000,6:194-196.
40 Ruan JL(阮金兰),Zhao XY(赵晓亚),John M Cassady,et al.Study on the constituents from freeze-dried Power of blackberries(Rubus ursinus).J Chin Med Mater(中药材),2001,24:645-647.
41 Guido Flamini,et al.Three anthrones from Rubus ulmifolius.Phytochemistry,2002,59:873-876.
42 Xie YH(谢一辉),et al.Studies on the chemical constituents from Fructus Rubi.J Chin Med Mater(中药材),2005,28: 99-100.
43 Goslinska O,Thiem B.Antimicrobial activity of Rubus chamaemorus leaves.Fitoterapia,2004,75:93-95.
44 Choi J,et al.Antinociceptive and antiinflammatory effects of Niga-ichigoside F1 and 23-hydroxytormentic acid obtained from Rubus coreanus.Biol Pharm Bull,2003,26:1436-1441.
45 Zhen ZJ(郑振洨),et al.Antitumour effect of total saponins of Rubus parvifolius on malignant melanoma.China J Chin Mat Med(中国中药杂志),2007,32:2055-2057.
46 Choi SH,et al.Activity of crude extract of Rubus crataegifolius roots as a potent apoptosis inducer and DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor.Arch Pharmacal Res,2000,23:338-343.
47 Kim EJ,et al.Induction of apoptosis by the aqueous extract of Rubus coreanum in HT-29 human colon cancer cells.Nutrition,2005,21:1141-1148.
48 Ju HK,et al.Characterization of increased phenolic compounds from fermented Bokbunja(Rubus coreanus Miq.)and related antioxidant activity.J Pharm Biomed Anal,2009,49: 820-827.
49 Ku CS,Mun SP.Antioxidant activities of ethanol extracts from seeds in fresh Bokbunja(Rubus coreanus Miq.)and wine processing waste.Bioresour Technol,2008,99:503-4509.
50 Fang YG(方耀高),et al.Anti-allergic effects of Rubus suavissimus extract.J Chin Med Mater(中药材),2008,31:710-714.
51 Choi IY,et al.Rubus croceacanthus Leveille inhibits mast cellmediated anaphylactic-like reaction and tumor necrosis factoralpha secretion.Biol Pharm Bull,2004,27:1359-1363.
52 Abdel-Naim AB,et al.Rubus sanctus protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced toxicity in rat isolated hepatocytes:isolation and characterization of its galloylated flavonoids.J Pharm Pharmacol,2009,61:1511-1520.
53 Hong ZF(洪振丰),et al.Effect of total alkaloids of Rubus alceaefolius poiron on gene expressions of CYP2E1 and CYP3A1 in rats with acute liver injury.Chin J Integr Tradit West Med(中国中西医结合杂志),2009,29:711-715.
54 Ardenghi JV,et al.Analysis of the mechanism of antinociceptive action of niga-ichigoside F1 obtained from Rubus imperialis(Rosaceae).J Pharm Pharmacol,2006,58:1669-1675.
55 Wang JS(王继生),et al.Effect of total saponins of Rubus parviflolius(TSRP)on change of hydrated amount and bloodbrain barrier in rats during focal cerebral ischemic/reperfusion.Chin J Chin Mat Med(中国中药杂志),2007,32: 2166-2169.
56 Greenway FL,et al.Gallic acid is partially responsible for the antiangiogenic activities of Rubus leaf extract.Phytother Res,2006,20:806-813.
57 Yu ZY(于占洋),et al.Isolation and identification of suavissimoside R1 from roots of Rubus parvifollus used for protecting dopaminergic neurons against MPP+toxicity.J Chin Med Mater(中药材),2008,31:554-557.
58 Choi EM,Lee KH.Rubus coreanus Miq.extract promotes osteoblast differentiation and inhibits bone-resorbing mediators in MC3T3-E1 cells.Am J Chin Med,2006,34:643-654.
Progress of Chemical Constituents and Pharmacology of Genus Rubus
MENG Xiang-juan,LIU Bin*,RE Zeng-cai-dan,SHE Gai-mei,JIANG Yan-yan
Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing 100102,China
The chemical constituents and pharmacology of Rubus in the latest 10 years were summarized to supply the scientific basis for further exploitation of Rubus.Flavonoids,terpenoids,tannins and steroids are the main constituents of Rubus.It has wide range of pharmacological effects including antibiosis,antiinflammatory,antitumor,antioxidant,anti-allergic,hepatoprotective and antinociceptive.
Rubus L.;flavonoids;terpenoids;tannins;antitumor;anti-allergic;hepatoprotective
1001-6880(2011)04-0767-10
2009-12-28 接受日期:2010-04-08
*通讯作者 Tel:86-10-84738629;E-mail:liubinyn67@163.com
R284.2
A
