幽门螺杆菌相关胃外疾病研究进展
2024-07-08刘晋阳陈峥宏马牧溪林永帅谭伟伟
刘晋阳 陈峥宏 马牧溪 林永帅 谭伟伟


摘要:幽门螺杆菌(Hp)是一种常见的胃肠道感染的革兰氏阴性杆菌,主要存在于胃上皮细胞表面和黏液中,与胃溃疡、胃癌和胃黏膜等相关淋巴瘤有关。研究表明Hp可诱发或加重某些胃外疾病,还与新型冠状病毒感染发生有关,因此Hp可能通过刺激机体产生炎症因子或发生交叉免疫反应,间接或直接地参与胃外疾病的发生和发展,同时Hp还可进入念珠菌内,持续释放毒素,且发挥躲避免疫系统识别和药物杀菌作用。本文总结近年国内外对Hp相关胃外疾病的研究报道,旨在引起临床工作者对Hp相关胃外疾病的重视,积极地掌握Hp的感染相关学科知识,从而科学制订避免Hp加重或诱发其他疾病的对策。
关键词:幽门螺杆菌;胃外疾病;交叉免疫反应;新型冠状病毒感染
中图分类号: R573 文献标识码: A 文章编号:1000-503X(2024)03-0414-11
DOI:10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.15698
Research Progress of Helicobacter pylori-Associated Extragastric Diseases
LIU Jinyang 2,CHEN Zhenghong3,4,MA Muxi5,LIN Yongshuai 2,TAN Weiwei 2
1Clinical Medicine School,Guizhou Medical University,Guiyang 55000 China
2Department of Urology,The Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University,Guiyang 55000 China
3Helicobacter pylori and Intestinal Microecology Joint Laboratory/Department of Urology,The Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University,Guiyang 55000 China
4Key Laboratory of Pathogenic Biology Characteristics,Guizhou Provincial Department of Education,Guiyang 55000 China
5Central Hospital of Yicheng District in Zhumadian,Zhumadian,Henan 463000,China
Corresponding author:CHEN Zhenghong Tel:13985006815,E-mail:chenzhenhong@gmc.edu.cn
ABSTRACT:Helicobacter pylori (Hp) is a common Gram-negative bacillus causing gastrointestinal infections.It mainly exists on the surface of gastric epithelial cells and in mucus and is associated with gastric ulcers,gastric cancer,and gastric mucosa-associated lymphomas.Studies have shown that Hp can induce or exacerbate certain extragastric diseases and is associated with the occurrence of coronavirus disease 2019.It is hypothesized that Hp may be indirectly or directly involved in the occurrence and development of diseases by stimulating the production of inflammatory cytokines or inducing cross-immune reactions.In addition,Hp can enter Candida to release toxins continuously and play a role in escaping the recognition of the host immune system and the bactericidal effect of drugs.This article reviews the research progress in Hp-associated extragastric diseases in recent years,aiming to draw the attention of clinical workers to Hp-associated extragastric diseases and enrich the knowledge about Hp infection for formulating countermeasures to avoid the aggravation or triggering of other diseases by Hp.
Key words:Helicobacter pylori;extragastric diseases;cross-immune reaction;coronavirus disease 2019
Acta Acad Med Sin,2024,46(3):414-424
幽门螺杆菌(Helicobacter pylori,Hp)在全球范围内的感染率超过50%,尤其是在发展中国家的感染率明显高于发达国家[1-2]。除了胃内疾病,越来越多的证据表明,Hp的感染与心血管系统、免疫系统和神经系统等系统疾病相关,有研究报道Hp与新型冠状病毒肺炎和阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimers disease,AD)等有关[3-7]。Hp的感染使得治疗某些疾病变得较为复杂,而医务工作者在患者感染Hp早期又会忽略Hp与某些胃外疾病的关系,可造成感染Hp患者原有某些疾病加重。
近日有研究指出:Hp能与念珠菌形成原核-真核共生物,即Hp内化念珠菌,不仅在念珠菌内的Hp可持续释放毒力因子于胞外,对局部组织或全身产生致炎作用,并且念珠菌内的Hp还具有躲避抗生素的作用[8-9]。部分Hp感染者无明显症状,患者往往得不到及时的治疗,且Hp持续产生毒力因子还可影响胃外疾病发生和发展[10]。因此,本文总结了与Hp相关的部分胃外疾病,简述Hp导致部分胃外疾病的发生机制,旨在打开Hp治疗的的临床思路,揭示对Hp某些毒力因子干预的重要性。
1 Hp致病机制
Hp是一种革兰氏阴性杆菌,菌体呈螺旋形,其致病性与其鞭毛、黏附素、细胞毒素相关,也与细胞毒素相关基因A(cytotoxin associated gene A,CagA)和空泡毒素相关基因A(vacuolating cytotoxin,VacA)有关[11]。
1.1 CagA致病机制
CagA蛋白是最有代表性的毒力因子,由CagA编码的、相对分子质量为120×103~140×103的免疫显性蛋白,可通过四型分泌系统进入真核生物细胞,诱导细胞形态发生改变[12]。附着在胃黏膜上皮细胞上的Hp可通过革兰氏阴性细菌四型分泌系统将CagA蛋白注入上皮细胞,磷酸化后的CagA蛋白结合真核磷酸酶SHP-2重塑胃黏膜上皮细胞骨架,使上皮细胞异常增殖和运动,最新研究指出:(1)CagA蛋白可上调circRNA表达产物circMAN1A2,促进胃黏膜上皮细胞癌变;(2)CagA蛋白还可破坏Wnt/PCP平面细胞极性通路信号传导,促使幽门腺基底细胞增殖异常[13-14]。
1.2 VacA致病机制
除了CagA蛋白,VacA蛋白同样是Hp产生的重要毒力因子,但与CagA蛋白不同,VacA蛋白几乎存在于所有Hp菌株中。VacA蛋白对宿主细胞具有多种功能,其中最具有代表性的是其诱导细胞内空泡样变性,故名——空泡毒素,但目前对空泡样变的机制尚存争议,有学者认为与VacA蛋白阴离子选择性通道的形成有关[15]。VacA蛋白可上调促凋亡蛋白Bax和内源性线粒体膜电压依赖性阴离子通道的表达,导致细胞色素C的释放,诱导宿主细胞凋亡。近日有研究报道了VacA蛋白可通过核因子-κB信号通路促进白细胞介素(interleukin,IL)-1β和肿瘤坏死因子-α等炎症因子的分泌,加重局部炎症和细胞损伤。
1.3 其他致病机制
Hp的致病机制还有以下3种:(1)Hp的鞭毛为其提供动力,鞭毛的转动可促使Hp通过胃壁的黏液层,能长期定存于胃中;目前有学者针对Hp的动力系统研发出“抗动力”毒素,可抑制鞭毛运动和鞭毛蛋白转录,并辅助抗生素治疗,开拓了Hp治疗新途径[16]。(2)Hp的脂多糖中路易斯抗原的表达能模仿宿主抗原,从而帮助其逃过机体免疫识别。(3)Hp的外膜囊泡与其他毒力因子产生协同作用,在诱导IL-8、调节应激纤维活性和影响细胞连接中发挥作用。
2 呼吸系统疾病
2.1 肺癌
肺癌是我国死亡率最高的癌症,通常可分为非小细胞肺癌和小细胞肺癌,肺癌的病因至今仍不明朗,但有研究报道了某些病原微生物(如Hp等多种病毒和细菌)与肺癌有关[17]。一项数据表明:Hp的感染与某些肿瘤标志物水平有关,在感染Hp的肺癌患者中,其癌胚抗原(carcinoembryonic antigen,CEA)水平更高,而甲胎蛋白和CA724会偏低[18]。CEA水平的升高可间接反映癌症的进展或复发,因此Hp有可能在某些特定的癌症中发挥作用,特别是感染Hp的患者,Hp可能会影响患者肿瘤标志物水平的变化。对待罹患肺癌且感染Hp的患者,有研究发现了一些“量体裁衣”的药物,如生物相容性银纳米颗粒即可靶向破坏肺癌细胞,又可抑制Hp[19]。有研究者指出Hp的感染会使接受免疫治疗的非小细胞肺癌患者体内干扰素和IL-6表达显著降低,影响癌症患者免疫治疗的疗效,这些有可能与Hp毒力因子VacA蛋白抑制骨髓细胞活性有关[20]。
2.2 关于Hp与肺癌的思考
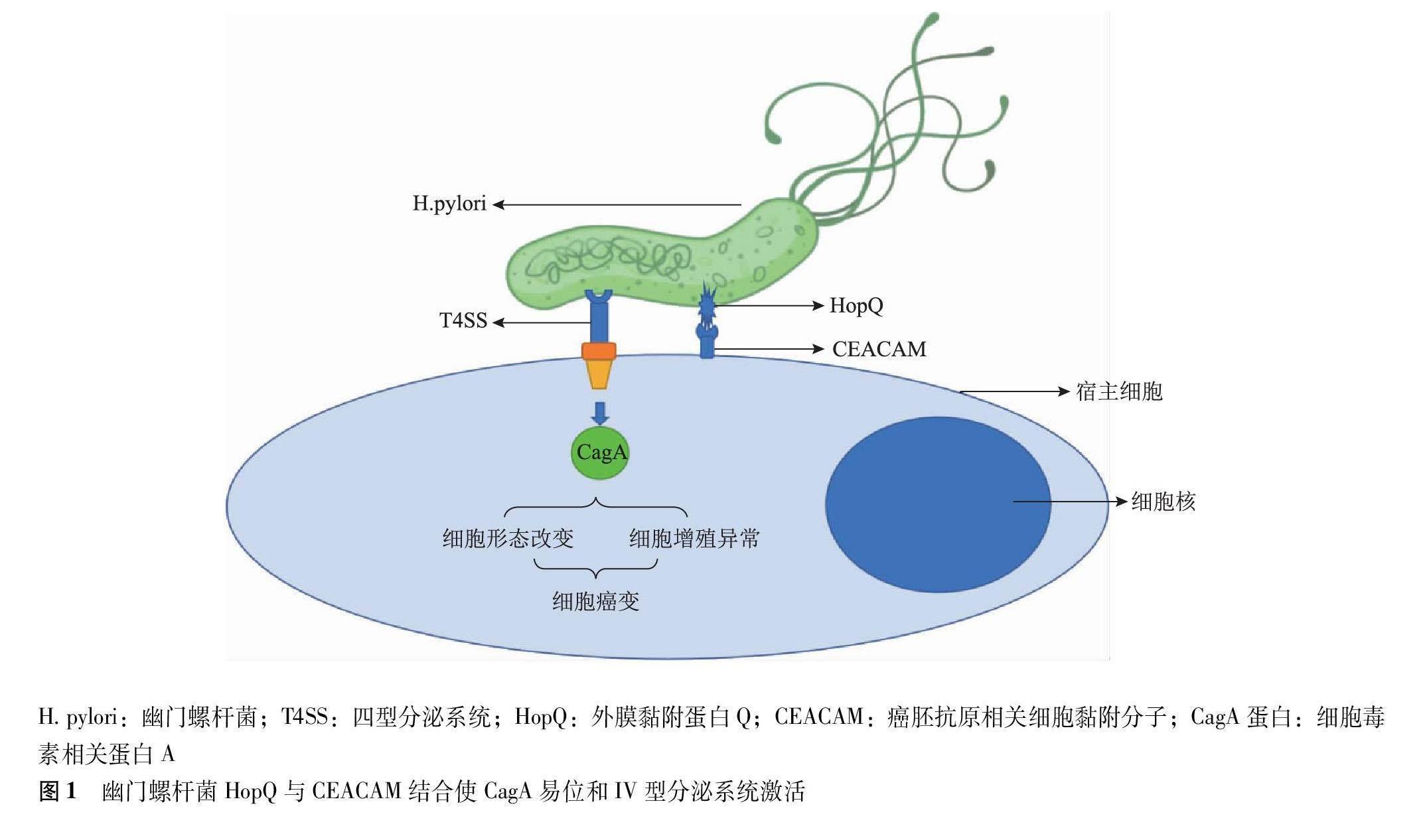
有研究表明:(1)在使用抗生素一段时间后,Hp毒力因子的表达才会下降,甚至某些Hp耐药菌株会因抗生素的使用而导致CagA表达上调。为减少毒力因子对机体影响,在根治Hp时,中和体内残存的毒素可纳入辅助治疗Hp的并行思路[21]。(2)为提高癌症患者生存率、合理解读健康人或肿瘤患者血清肿瘤标志物水平,应重视主动预防和筛查Hp;但值得注意的是Hp的根治并不能恢复Hp引起的肿瘤免疫低疗效现象,但因为Hp与机体特异性免疫有关,所以研究者建议把Hp血清学检查结果纳入对非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗的预期疗效评估中[20]。(3)目前关于Hp对免疫治疗的抑制作用仅局限于非小细胞肺癌,对其他需免疫治疗的癌症是否具备同样抑制作用仍有待进一步研究。(4)Hp感染的肺癌患者CEA水平较高,由此推测Hp外膜黏附蛋白Q与CEA高度亲和性有关:高表达水平CEA的细胞有助于促进与外膜黏附蛋白Q的结合,介导四型分泌系统将CagA蛋白注入宿主细胞中发生易位,对机体产生更强的致癌活性[22]。目前尚缺乏准确阐述Hp上调CEA的数据,有望作为下个阶段研究热点(图1)。
2.3 新型冠状病毒感染
新型冠状病毒感染被认为是最致命流行病之一,其通过结合血管紧张素转化酶-2受体进入细胞,从而导致以发热、咳嗽为主的一系列临床症状[23]。有研究指出Hp可上调机体肠道细胞血管紧张素转化酶-2受体的表达,导致更多的病毒进入细胞,使这类患者消化道症状(如腹痛、腹泻等)相较未感染Hp的新型冠状病毒感染患者更重[24]。此外,Hp还可刺激机体产生大量炎症介质(如肿瘤坏死因子-α和IL-8等),这些炎症因子与病毒一同介导急性肺损伤[25]。除了感染阶段,有研究表明在治疗Hp时,质子泵抑制剂(proton pump inhibitor,PPI)的使用会增大新型冠状病毒肺炎的易感性,且与患者严重临床症状有关,这可能与PPI会增加嗜铬粒蛋白A血浆水平有关[26-27]。另一方面嗜铬粒蛋白A水平可作为早期预测新型冠状病毒感染患者死亡的独立因子:重症患者血浆嗜铬粒蛋白A水平明显升高,这可能与嗜铬粒蛋白A参与血管重塑和全身免疫反应有关[28]。
3 神经系统疾病
3.1 AD
由于Hp不直接侵犯神经系统,所以早年医学研究忽略了Hp对神经系统疾病的影响。AD是一种神经系统退行性疾病,其特点是大脑皮层和皮层下区域神经元丢失,近几年有学者开始研究AD与病原微生物感染的关系,Hp感染也逐渐证明为AD诱因[29-30]。
有学者认为Hp与AD存在间接关联[31]。Hp诱发AD的发生和发展机制推测如下:(1)革兰氏阴性细菌释放的外膜囊泡可携带毒力因子,而Hp的外膜囊泡可通过血脑屏障,诱导神经胶质细胞的激活和神经元功能的障碍,加速AD的形成[32]。(2)Hp的脲酶具有促炎活性和激活免疫系统的能力,从而诱发神经系统的炎症和神经系统退行性变的发生[33]。(3)Hp可导致患者肠道黏膜的通透性增加,肠道菌群结构异常会成为诱发AD的关键启动因素[34]。有日本学者通过尿液检测分析发现Hp与AD之间无明显关联,故Hp与AD之间的关系还需更多大样本的试验去证明[35]。
3.2 其他神经系统疾病
Hp与神经系统其他疾病的关系及可能机制见表1。
3.3 Hp的治疗对神经系统疾病的意义
Hp相关神经系统疾病均说明Hp感染所导致的疾病已不仅局限于消化系统内,也是影响其他疾病发生发展的原因,如Hp有可能成为大部分神经系统疾病诱因。已有的病例与研究揭示了Hp治疗在神经系统疾病中的重要性:(1)大部分Hp的外膜囊泡是在患者感染Hp 3周以后才被检测到,表明早期检测和根治Hp的重要性[32]。(2)目前已有的研究证明肠道菌群与神经系统直接相关,有学者将二者关系形象地称之为脑肠轴-肠道神经系统与中枢神经系统通过多边机制相互联系,其中也包括肠道微生物的参与,而Hp可影响肠道原有菌群,参与Hp相关神经系统疾病发生发展[44-45]。也有学者提出益生菌可有效治疗神经系统疾病的假设,这一假设也得到了后来的研究证实:如长期口服益生菌的AD小鼠可有效延缓疾病的进展,同样益生菌的服用还有助于减少Hp所带来的不良反应[46-47]。
4 生殖系统与Hp
4.1 Hp传播途径
Hp的传统传播途径被认为是粪-口与口-口两种[48]。早在2008年便有学者提出Hp可通过性传播的假设,随后有研究发现Hp在性伴侣之间的感染率明显高于对照组,推测Hp可通过性传播[49-50],理由如下:(1)对人体唾液及拔除的牙齿标本进行细菌培养,通过PCR扩增技术后检测到了Hp特异性核酸,说明Hp有可能存在于口腔中[51-52]。(2)从女性阴道取出的阴道分泌物进行培养,通过PCR扩增后,仍可检测到Hp特异性核酸,说明Hp有可能存在于女性阴道中[53]。Hp有可能通过性传播,甚至是母婴垂直传播,因此明确Hp具体传播途径,有助于科学防治Hp,减少Hp胃外疾病的发生。但有关Hp可通过性传播的结论尚缺可信度:在性伴侣之间Hp感染率的研究中,仅测定性伴侣间Hp阳性率,而未确定Hp的基因同源性,应通过PCR扩增目的基因并通过基因测序技术比对性伴侣间Hp的特异性基因序列[50]。目前可明确的是Hp容易以家庭为单位,在家族成员中传播,所以Hp筛查和防治应以家庭为单位[54]。
4.2 Hp形成真核-原核共生物
念珠菌是一种生活在女性阴道的真菌,近日有学者从女性阴道分泌物中的念珠菌内检测到Hp的特异性核酸[55]。有研究者发现胃内Hp可催化尿素产生氨气,降低胃内的酸性,而阴道中尿素含量低,Hp为躲避不利因素,可进入念珠菌内形成真核-原核共生物即Hp内化念珠菌,念珠菌还可增强细菌的致病性,体外实验也同样发现Hp为躲避不利条件会进入念珠菌证据[55-58]。念珠菌内的Hp同样可释放CagA蛋白于念珠菌之外,表明念珠菌内的Hp有可能产生毒力因子引起胃外疾病,因此Hp的治疗与筛查不应只局限于胃内Hp,为降低Hp的复发,还应根治机体其他部位Hp与念珠菌内形成的真核原核共生物(图2)。有研究发现在缺乏营养的情况下念珠菌的细胞壁会发生改变,使Hp难以进入,这为杜绝Hp内化念珠菌的形成提供新的思路[56]。
4.3 男性不育
男性不育发病机制复杂,迄今为止仍有大量患者病因不明[59-60]。有学者认为Hp的感染与男性不育有关,在Hp感染的人群中精子活力、浓度和生育指数都有降低[61-62]。有研究者在单纯雄激素去除治疗前列腺癌患者中发现同时感染了Hp的患者死亡率降低,因此推测Hp可能影响男性体内雄激素水平[63]。有研究发现精子鞭毛的主要成分微管蛋白与Hp的鞭毛蛋白、CagA蛋白和VacA蛋白存在部分结构同源性,这表明Hp有可能刺激人体产生交叉免疫反应,诱导机体产生抗精子抗体,使患者精子质量下降[64]。然而,Feng等[65]研究显示,Hp的感染与精子活力及精子浓度无明显关联,但可以明确的是Hp患者经抗菌治疗后,其精子质量有所改善。
4.4 特殊人群Hp治疗
鉴于妊娠期Hp对胎儿及母体的影响,早期检测并治疗Hp尤为重要。Hp的治疗目前推荐的是两种抗生素+PPI+铋剂,但由于妊娠期的特殊性,抗生素使用需更加小心,除了已知药物透过胎盘屏障对胎儿造成影响,某些抗生素妊娠期服用还会造成母乳中IgG含量下降,降低新生儿抵抗力[66]。PPI的使用有增大妊娠期女性先兆子痫、妊娠糖尿病的风险[67]。体外实验表明:泮托拉唑可增加精子蛋白质磷酸化和阻止精子细胞膜电位超极化,从而抑制精子获能[68]。埃索美拉唑作为新一代的PPI,有研究发现患者在服用60 min后,其活动精子的总数减少[69]。鉴于PPI使用的不良反应,妊娠期或近期有生育需求患者其Hp治疗用药需谨慎。有研究表明益生菌可辅助治疗Hp,理由如下:(1)妊娠期服用益生菌,可降低先兆子痫、妊娠期糖尿病的发病率[70]。(2)男性不育患者服用益生菌,可通过改善肠道菌群起到提高精液质量,辅助治疗男性不育的作用[71]。(3)益生菌的使用可增强抗生素疗效,减少Hp复发的可能性[72]。
5 心血管系统疾病
Hp与心血管疾病存在联系的观点早在20世纪便陆续有学者提出过(图3)。目前有关Hp与心血管疾病联系相关探索也从一开始的统计学研究转变为病因研究,而对病因研究最多的疾病是高血压病和冠心病(coronary heart disease,CHD)。
5.1 高血压病
高血压病系以体循动脉血压升高(收缩压≥140 mmHg或舒张压≥90 mmHg)(1 mmHg=0.133 kPa)为主要特征,可伴有心、脑、肾等器官功能衰竭或器质性损害的临床综合征。近年有研究对高血压病因进行了总结与分析:(1)有学者认为Hp可刺激机体释放C反应蛋白和IL等炎症因子,从而诱导血管内皮功能障碍,引发动脉血压升高[78]。(2)Hp感染的患者,血液中纤维蛋白原含量升高,而纤维蛋白原作为血管炎症因子可诱导血管收缩使外周血管压力升高,从而诱发高血压病[79]。Hp与高血压病存在某些间接或直接的关系,加之Hp日益增长的耐药性,目前研究者发现了治疗高血压病的老药新用途:如二氢吡啶类药物是治疗高血压病常用药,有研究发现二氢吡啶类药物不仅能影响Hp在胃内的定植,还具有一定的抗Hp活性,且杀菌活性相当于甲硝唑等抗生素,这样一方面减少抗生素使用带来肠道菌群紊乱的后遗症,另一方面相较新药物更具安全和可靠价值,因此二氢吡啶类药物替代抗生素治疗感染Hp的高血压病患者成为可能[80]。
5.2 CHD
CHD是由于冠状动脉粥样硬化病变而引起血管腔狭窄或阻塞,从而诱发心肌缺血、缺氧或坏死而导致的心脏病。Hp与CHD关系也越来越被科学界关注,而研究的重点集中在Hp的毒力因子上。
Hp产生的CagA蛋白可通过刺激机体活性氧的异常产生,导致低密度脂蛋白升高,还会诱发血管内皮的炎症,此外CagA蛋白还有助于刺激泡沫细胞的形成和通过NLRP3-IL1β信号通路促进动脉粥样硬化,共同促进CHD形成[81-82]。鉴于Hp与CHD的关系,临床上可早期检测某些生物分子,用于评估Hp患者CHD的发生率和干预CHD形成。如有学者发现甘油三酯和C反应蛋白之间的关系,通过建立数学模型监测和早期诊断Hp阳性患者CHD的情况[83]。除了预防,在治疗Hp方面上年龄和性别也尤为重要,根治Hp对CHD的预防效果取决于患者的年龄和性别,对于感染Hp的男性患者,年龄≤65岁根治Hp对能有效减少CHD的发生,故建议男性为预防CHD应尽早筛查Hp[84]。
6 内分泌系统疾病
6.1 糖尿病
糖尿病是一种以高血糖为特征的慢性代谢性疾病,主要发病机制是由于胰岛素的分泌缺陷或生物作用受损,长期的血糖升高导致肾脏、眼和心脏等重要器官出现一系列并发症。糖基化血红蛋白是判断近期血糖控制水平最有价值的指标之一,是由血红蛋白与葡萄糖发生非酶促反应、不可逆性结合的产物。来自我国一项9000多人的队列研究显示,长期的Hp感染会升高糖基化血红蛋白水平,但遗憾的是该研究并未揭示Hp导致胰腺功能障碍的病理生理机制[85]。有学者推测Hp导致胰腺功能障碍的病理生理机制可能是以下两点:(1)Hp可诱导胃黏膜腺体组织病理学改变——幽门化生、胃壁细胞减少,这种改变也同样可能发生在胰腺中,使胰腺腺泡导管化生,从而导致胰腺功能障碍,造成其功能异常[86]。(2)Hp刺激机体产生的炎症因子IL-6、肿瘤坏死因子等会影响生长抑素释放及胰岛B细胞胰岛素释放,从而造成胰岛素抵抗[87]。Esmaeili Dooki等[88]研究显示,Hp的感染与年龄在5~15岁的儿童糖尿病患者无明显关联。目前Hp与糖尿病的联系并没有定论,但有趣的是治疗Hp的PPI可通过激活过氧化酶体增殖物激活受体γ,增强胰岛素敏感基因的表达,从而增强达格列净治疗糖尿病疗效[89]。
6.2 甲状腺疾病
甲状腺分泌的激素主要包括三碘甲状腺原氨酸和甲状腺素,对基础代谢、机体生长发育至关重要。Zhang等[90]研究表明,Hp的感染会增加中老年女性罹患亚临床甲状腺功能亢进的风险。Silva等[91]研究证实,Hp的感染与儿童甲状腺功能减退有关,还有可能与Hp的CagA蛋白和甲状腺滤泡存在交叉免疫反应有关。上述研究存在以下问题:(1)Zhang等[90]试验并未排除老年女性甲状腺功能随年纪增大而发生减退的可能,且甲状腺疾病与饮食、地域关系密切,故探究Hp与甲状腺疾病的联系应排除饮食与性别的干扰。(2)Silva等[91]研究并未阐明儿童感染Hp及罹患甲状腺功能减退的先后顺序,即患儿是否发生甲状腺功能减退后感染的Hp:甲状腺激素可调节先天性免疫和适应性免疫中中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞和自然杀伤细胞等激活、分化和增殖,甲状腺功能减退患儿分泌甲状腺激素减少,对Hp等病原微生物易感性增高[92]。已有研究表明,Hp可通过分子模拟、多克隆抗体激活及毒力因子CagA蛋白高度免疫活性诱导机体免疫损伤和调节机体免疫反应,具有启动自身免疫性疾病的可能性[93]。
7 总结和展望
Hp感染人体后会出现某些胃外临床表现,消化系统内的Hp产生的毒力因子可通过血液循环到达全身各部位,毒力因子可影响肺癌CEA水平和诱导神经系统发生退行性病变等,表明Hp的治疗和筛查不仅应综合考量全身情况,还应充分考虑毒力因子和宿主机体环境相互影响的结果。本文系统地阐述了Hp毒力因子对机体的直接影响、Hp所引起机体交叉免疫反应和治疗Hp的一线药物等方面进展,旨在进一步完善感染Hp时出现的临床表现和治疗Hp综合方案。Hp可直接感染人体,也能联合其他病原体(例如念珠菌等)共同感染人体,诱发不同胃外系统的疾病。Hp有许多不同的毒株,且不同亚型Hp在胃外疾病的发生发展中的作用也不相同,但首先明确Hp具体毒株及其相关毒力因子与不同胃外系统的疾病之间的关系以及胃外系统疾病发病机制和治疗方法,为临床工作者科学制订Hp相关胃外疾病的对策提供帮助。
利益冲突 所有作者声明无利益冲突
作者贡献声明 刘晋阳:研究思路的提出,文献检索、论文起草和修订;马牧溪:文献筛选,资料的提取与整理;林永帅:数据搜集、分析、解释工作;谭伟伟:能按编辑部的修改意见进行核修,对学术问题进行解答;陈峥宏:论文的修订、质量控制及终审和定稿,并同意対研究工作诚信负责
参 考 文 献
[1]Ding SZ,Du YQ,Lu H,et al.Chinese consensus report on family-based Helicobacter pylori infection control and management (2021 edition)[J].Gut,2022,71(2):238-253.DOI:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325630.
[2]Magsi I,Hussain KS,Kumar C,et al.Response of Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment in patients with normal and below-normal serum vitamin D levels[J].Cureus,202 13(4):e14777.DOI:10.7759/cureus.14777.
[3]Chung J,Min KW,Son BK,et al.Association between histological severity of Helicobacter pylori infection and cardiovascular risk scores in the Korean population[J].Atherosclerosis,202 333:124-130.DOI:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.08.019.
[4]Cuan-Baltazar Y,Soto-Vega E.Microorganisms associated to thyroid autoimmunity[J].Autoimmun Rev,2020,19(9):102614.DOI:10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102614.
[5]Baj J,Forma A,Flieger W,et al.Helicobacter pylori Infection and extragastric diseases-A focus on the central nervous system[J].Cells,202 10(9):2191.DOI:10.3390/cells10092191.
[6]Franceschi F,Covino M,Roubaud BC.Review:Helicobacter pylori and extragastric diseases[J].Helicobacter,2019,24 Suppl 1:e12636.DOI:10.1111/hel.12636.
[7]Papagni ME,Brindicci VF,Cristofori F,et al.The role of Helicobacter pylori infection in coronavirus disease 2019,cause or coincidence[J].J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr,202 73(4):e106.DOI:10.1097/MPG.0000000000003175.
[8]Chen X,Zhou X,Liao B,et al.The cross-kingdom interaction between Helicobacter pylori and Candida albicans[J].PLoS Pathog,202 17:e1009515.DOI:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009515.
[9]Hiengrach P,Panpetch W,Chindamporn A,et al.Helicobacter pylori,potected from antibiotics and stresses inside candida albicans vacuoles,cause gastritis in mice[J].Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(15):8568.DOI:10.3390/ijms23158568.
[10]Reshetnyak VI,Burmistrov AI,Maev IV.Helicobacter pylori:commensal,symbiont or pathogen[J].World J Gastroenterol,202 27(7):545-560.DOI:10.3748/wjg.v27.i7.545.
[11]Imoto I,Oka S,Katsurahara M,et al.Helicobacter pylori infection:is there circulating vacuolating cytotoxin A or cytotoxin-associated gene A protein[J].Gut Pathog,2022,14(1):43.DOI:10.1186/s13099-022-00519-8.
[12]Tomb JF,White O,Kerlavage AR,et al.The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori[J].Nature,1997,388(6642):539-547.DOI:10.1038/41483.
[13]Guo R,Cui X,Li X,et al.CircMAN1A2 is upregulated by Helicobacter pylori and promotes development of gastric cancer[J].Cell Death Dis,2022,13(4):409.DOI:10.1038/s41419-022-04811-y.
[14]Takahashi-Kanemitsu A,Lu M,Knight CT,et al.The Helicobacter pylori CagA oncoprotein disrupts Wnt/PCP signaling and promotes hyperproliferation of pyloric gland base cells[J].Sci Signal,2023,16(794):eabp9020.DOI:10.1126/scisignal.abp9020.
[15]Palframan SL,Kwok T,Gabriel K.Vacuolating cytotoxin A (vaca),a key toxin for Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis[J].Front Cell Infect Microbiol,2012,2:92.DOI:10.3389/fcimb.2012.00092.
[16]Suerbaum S,Coombs N,Patel L,et al.Identification of antimotilins,novel inhibitors of Helicobacter pylori flagellar motility that inhibit stomach colonization in a mouse model[J].mBio,2022,13(2):e0375521.DOI:10.1128/mbio.03755-21.
[17]Yoon HS,Shu XO,Cai H,et al.Associations of lung cancer risk with biomarkers of Helicobacter pylori infection[J].Carcinogenesis,2022,43(6):538-546.DOI:10.1093/carcin/bgac047.
[18]Xu MY,Cao B,Chen Y,et al.Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and tumor markers:an observational retrospective study[J].BMJ Open,2018,8(8):e022374.DOI:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022374.
[19]Saravanakumar K,Chelliah R,MubarakAli D,et al.Unveiling the potentials of biocompatible silver nanoparticles on human lung carcinoma A549 cells and Helicobacter pylori[J].Sci Rep,2019,9(1):5787.DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-42112-1.
[20]Oster P,Vaillant L,Riva E,et al.Helicobacter pylori infection has a detrimental impact on the efficacy of cancer immunotherapies[J].Gut,2022,71(3):457-466.DOI:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323392.
[21]Kobatake T,Ogino K,Sakae H,et al.Antibacterial effects of disulfiram in Helicobacter pylori[J].Infect Drug Resist,202 14:1757-1764.DOI:10.2147/IDR.S299177.
[22]Nguyen QA,Schmitt L,Mejías-Luque R,et al.Effects of Helicobacter pylori adhesin HopQ binding to CEACAM receptors in the human stomach[J].Front Immunol,2023,14:1113478.DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1113478.
[23]Wan Y,Shang J,Graham R,et al.Receptor recognition by the novel coronavirus from Wuhan:an analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS coronavirus[J].J Virol,2020,94(7):e00127-20.DOI:10.1128/JVI.00127-20.
[24]Balamtekin N,Artuk C,Arslan M,et al.The effect of Helicobacter pylori on the presentation and clinical course of coronavirus disease 2019 infection[J].J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr,202 72(4):511-513.DOI:10.1097/MPG.0000000000003005.
[25]Gonzalez I,Lindner C,Schneider I,et al.Inflammation at the crossroads of Helicobacter pylori and COVID-19[J].Future Microbiol,2022,17(2):77-80.DOI:10.2217/fmb-2021-0250.
[26]Lee SW,Ha EK,Yeniova A,et al.Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors:a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching[J].Gut,202 70(1):76-84.DOI:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248.
[27]Sciorati C,De Lorenzo R,Lorè NI,et al.The elusive role of proton pump inhibitors in COVID-19:Can plasma Chromogranin A levels hold the key[J].Pharmacol Res,2023,187:106601.DOI:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106601.
[28]De LR,Sciorati C,Ramirez GA,et al.Chromogranin A plasma levels predict mortality in COVID-19[J].PLoS One,2022,17(4):e0267235.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0267235.
[29]Nemergut M,Batkova T,Vigasova D,et al.Increased occurrence of Treponema spp.and double-species infections in patients with Alzheimers disease[J].Sci Total Environ,2022,844:157114.DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157114.
[30]Beydoun MA,Beydoun HA,Weiss J,et al.Helicobacter pylori,periodontal pathogens,and their interactive association with incident all-cause and Alzheimers disease dementia in a large national survey[J].Mol Psychiatry,202 26(10):6038-6053.DOI:10.1038/s41380-020-0736-2.
[31]Fu P,Gao M,Yung KKL.Association of intestinal disorders with Parkinsons disease and Alzheimers disease:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J].ACS Chem Neurosci,2020,11(3):395-405.DOI:10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00607.
[32]Xie J,Li Q,Haesebrouck F,et al.The tremendous biomedical potential of bacterial extracellular vesicles[J].Trends Biotechnol,2022,40(10):1173-1194.DOI:10.1016/j.tibtech.2022.03.005.
[33]Uberti AF,Callai-Silva N,Grahl MVC,et al.Helicobacter pylori Urease:potential contributions to Alzheimers disease[J].Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(6):3091.DOI:10.3390/ijms23063091.
[34]Ju Z,Shen L,Zhou M,et al.Helicobacter pylori and Alzheimers disease-related metabolic dysfunction:activation of TLR4/Myd88 inflammation pathway from p53 perspective and a case study of low-dose radiation intervention[J].ACS Chem Neurosci,2022,13(7):1065-1081.DOI:10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00082.
[35]Shiota S,Murakami K,Yoshiiwa A,et al.The relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and Alzheimers disease in Japan[J].J Neurol,201 258(8):1460-1463.DOI:10.1007/s00415-011-5957-5.
[36]Zhong R,Chen Q,Zhang X,et al.Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with a poor response to levodopa in patients with Parkinsons disease:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].J Neurol,2022,269(2):703-711.DOI:10.1007/s00415-021-10473-1.
[37]Bai F,Li X.Association of Helicobacter pylori treatment with Parkinsonism and related disorders:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Life Sci,202 281:119767.DOI:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119767.
[38]Smeyne RJ,Noyce AJ,Byrne M,et al.Infection and Risk of Parkinsons Disease[J].J Parkinsons Dis,202 11(1):31-43.DOI:10.3233/JPD-202279.
[39]Nyholm D,Hellstrm PM.Effects of Helicobacter pylori on levodopa pharmacokinetics[J].J Parkinsons Dis,202 11(1):61-69.DOI:10.3233/JPD-202298.
[40]Arjmandi D,Abdollahi A,Ardekani A,et al.Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of multiple sclerosis:an updated meta-analysis[J].Helicobacter,2022,27(6):e12927.DOI:10.1111/hel.12927.
[41]Kountouras J,Papaefthymiou A,Gavalas E,et al.Helicobacter pylori infection as a potential risk factor for multiple sclerosis[J].Med Hypotheses,2020,143:110135.DOI:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110135.
[42]Cavestro C,Prandi G,Manildo M,et al.A cross-sectional study on the association between Helicobacter pylori infection and headache[J].Neurol Sci,2022,43(10):6031-6038.DOI:10.1007/s10072-022-06153-1.
[43]Arzani M,Jahromi SR,Ghorbani Z,et al.School of advanced studies of the european headache federation (EHF-SAS).Gut-brain axis and migraine headache:a comprehensive review[J].J Headache Pain,2020,21(1):15.DOI:10.1186/s10194-020-1078-9.
[44]Baj J,Forma A,Flieger W,et al.Helicobacter pylori infection and extragastric dseases-a focus on the central nervous system[J].Cells,202 10(9):2191.DOI:10.3390/cells10092191.
[45]Bai X,Jiang L,Ruan G,et al.Helicobacter pylori may participate in the development of inflammatory bowel disease by modulating the intestinal microbiota[J].Chin Med J (Engl),2022,135(6):634-638.DOI:10.1097/CM9.0000000000002008.
[46]Aaldijk E,Vermeiren Y.The role of serotonin within the microbiota-gut-brain axis in the development of Alzheimers disease:a narrative review[J].Ageing Res Rev,2022,75:101556.DOI:10.1016/j.arr.2021.101556.
[47]He C,Xie Y,Zhu Y,et al.Probiotics modulate gastrointestinal microbiota after Helicobacter pylori eradication:a multicenter randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial[J].Front Immunol,2022,13:1033063.DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1033063.
[48]Duan M,Li Y,Liu J,et al.Transmission routes and patterns of Helicobacter pylori[J].Helicobacter,2023(1):e12945.DOI:10.1111/hel.12945.
[49]Head S.Helicobacter pylori infection:a sexually transmitted disease[J].BMJ,2008,337:a2077.DOI:10.1136/bmj.a2077.
[50]Sgambato D,Visciola G,Ferrante E,et al.Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in sexual partners of H.pylori-infected subjects:role of gastroesophageal reflux[J].United European Gastroenterol J,2018,6(10):1470-1476.DOI:10.1177/2050640618800628.
[51]Hamada M,Nomura R,Matayoshi S,et al.Detection of Helicobacter pylori from extracted teeth of a patient with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura[J].Microorganisms,2022,10(11):2285.DOI:10.3390/microorganisms10112285.
[52]Hamada M,Nomura R,Ogaya Y,et al.Potential involvement of Helicobacter pylori from oral specimens in overweight body-mass index[J].Sci Rep,2019,9(1):4845.DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-41166-5.
[53]Sánchez-Alonzo K,Matamala-Valdés L,Parra-Sepúlveda C,et al.Intracellular presence of Helicobacter pylori and its virulence-associated genotypes within the vaginal yeast of term pregnant women[J].Microorganisms,202 9(1):131.DOI:10.3390/microorganisms9010131.
[54]Chang YW,Han YS,Lee DK,et al.Role of Helicobacter pylori infection among offspring or siblings of gastric cancer patients[J].Int J Cancer,2002,101(5):469-474.DOI:10.1002/ijc.10637.
[55]Sánchez-Alonzo K,Parra-Sepúlveda C,Vega S,et al.In vitro incorporation of Helicobacter pylori into Candida albicans caused by acidic pH stress[J].Pathogens,2020,9(6):489.DOI:10.3390/pathogens9060489.
[56]Sánchez-Alonzo K,Silva-Mieres F,Arellano-Arriagada L,et al.Nutrient deficiency promotes the entry of Helicobacter pylori cells into Candida yeast cells[J].Biology (Basel),202 10(5):426.DOI:10.3390/biology10050426.
[57]Yang T,Li J,Zhang Y,et al.Intracellular presence of Helicobacter pylori antigen and genes within gastric and vaginal Candida[J].PLoS One,2024,19(2):e0298442.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0298442.
[58]Abrantes PMDS,Africa CWJ.Measuring Streptococcus mutans,Streptococcus sanguinis and Candida albicans biofilm formation using a real-time impedance-based system[J].J Microbiol Methods,2020,169:105815.DOI:10.1016/j.mimet.2019.105815.
[59]Assidi M.Infertility in men:advances towards a comprehensive and integrative strategy for precision theranostics[J].Cells,2022,11(10):1711.DOI:10.3390/cells11101711.
[60]Corsini C,Boeri L,Candela L,et al.Is there a relevant clinical impact in differentiating idiopathic versus unexplained male infertility[J].World J Mens Health,2023,41(2):354-362.DOI:10.5534/wjmh.220069.
[61]
El-Garem Y,El-Sawy M,Mostafa T.et al.Seminal Helicobacter pylori treatment improves sperm mtility in infertile asthenozoospermic men[J].Urology,2014,84(6):1347-1350.DOI:10.1016/j.urology.2014.09.004.
[62]Moretti E,Figura N,Campagna MS,et al.Infectious burden and semen parameters[J].Urology,2017,100:90-96.DOI:10.1016/j.urology.2016.10.032.
[63]Liu JM,Wu CT,Hsu RJ,et al.Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and mortality risk in prostate cancer patients receiving androgen deprivation therapy:a real-world evidence study[J].Cancer Med,202 10(22):8162-8171.DOI:10.1002/cam4.4318.
[64]Youssefi M,Tafaghodi M,Farsiani H,et al.Helicobacter pylori infection and autoimmune diseases;Is there an association with systemic lupus erythematosus,rheumatoid arthritis,autoimmune atrophy gastritis and autoimmune pancreatitis?A systematic review and meta-analysis study[J].J Microbiol Immunol Infect,202 54(3):359-369.DOI:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.08.011.
[65]Feng C,Lv PP,Huang CC,et al.Sperm parameters and anti-Müllerian hormone remain stable with Helicobacter pylori infection:a cross-sectional study[J].BMC Urol,2020,20(1):188.DOI:10.1186/s12894-020-00725-z.
[66]Ding Y,Yao X,Zhang H,et al.Maternal antibiotic treatment during pregnancy attenuates the transport and absorption of maternal antibody IgG through TLR4 and TLR2 receptor[J].Front Microbiol,2023,14:1109273.DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1109273.
[67]Breddels EM,Simin J,Fornes R,et al.Population-based cohort study:proton pump inhibitor use during pregnancy in Sweden and the risk of maternal and neonatal adverse events[J].BMC Med,2022,20(1):492.DOI:10.1186/s12916-022-02673-x.
[68]Escoffier J,Arnaud B,Kaba M,et al.Pantoprazole,a proton-pump inhibitor,impairs human sperm motility and capacitation in vitro[J].Andrology,2020,8(6):1795-1804.DOI:10.1111/andr.12855.
[69]Kumar A,Kumar R,Flanagan J,et al.Esomeprazole reduces sperm motility index by targeting the spermic cholinergic machinery:a mechanistic study for the association between use of proton pump inhibitors and reduced sperm motility index[J].Biochem Pharmacol,2020,182:114212.DOI:10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114212.
[70]Obuchowska A,Gorczyca K,Standyo A,et al.Effects of probiotic supplementation during pregnancy on the future maternal risk of metabolic syndrome[J].Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(15):8253.DOI:10.3390/ijms23158253.
[71]Hao Y,Feng Y,Yan X,et al.Gut microbiota-testis axis:FMT improves systemic and testicular micro-environment to increase semen quality in type 1 diabetes[J].Mol Med,2022,28(1):45.DOI:10.1186/s10020-022-00473-w.
[72]Ji J,Yang H.Using Probiotics as Supplementation for Helicobacter pylori antibiotic therapy[J].Int J Mol Sci,2020,21(3):1136.DOI:10.3390/ijms21031136.
[73]Barnes RJ,Uff JS,Dent JC,et al.Long-term follow up of patients with gastritis associated with Helicobacter pylori infection[J].Br J Gen Pract,199 41(348):286-288.
[74]Glynn JR.Helicobacter pylori and the heart[J].Lancet,1994,344(8916):146.DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92754-5.
[75]Sutter MC.Lessons for atherosclerosis research from tuberculosis and peptic ulcer[J].CMAJ.1995,152(5):667-670.
[76]Niemel S,Karttunen T,Korhonen T,et al.Could Helicobacter pylori infection increase the risk of coronary heart disease by modifying serum lipid concentrations[J].Heart,1996,75(6):573-575.DOI:10.1136/hrt.75.6.573.
[77]Birnie DH,Holme ER,McKay IC,et al.Association between antibodies to heat shock protein 65 and coronary atherosclerosis.Possible mechanism of action of Helicobacter pylori and other bacterial infections in increasing cardiovascular risk[J].Eur Heart J,1998,19(3):387-394.DOI:10.1053/euhj.1997.0618.
[78]Kountouras J,Papaefthymiou A,Polyzos SA,et al.Impact of Helicobacter pylori-related metabolic syndrome parameters on arterial hypertension[J].Microorganisms,2022,9(11):2351.DOI:10.3390/microorganisms9112351.
[79]Xiong X,Chen J,He M,et al.Helicobacter pylori infection and the prevalence of hypertension in Chinese adults:the Dongfeng-Tongji cohort[J].J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich),2020,22(8):1389-1395.DOI:10.1111/jch.13928.
[80]González A,Casado J,Gündüz MG,et al. 4-dihydropyridine as a promising scaffold for novel antimicrobials against Helicobacter pylori[J].Front Microbiol,2022,13:874709.DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2022.874709.
[81]Gajewski A,Gawrysiak M,Krupa A,et al.Accumulation of deleterious effects in gastric epithelial cells and vascular endothelial cells in vitro in the milieu of Helicobacter pylori components,7-ketocholesterol and acetylsalicylic acid[J].Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(11):6355.DOI:10.3390/ijms23116355.
[82]Li B,Xia Y,Hu B.Infection and atherosclerosis:TLR-dependent pathways[J].Cell Mol Life Sci,2020,77(14):2751-2769.DOI:10.1007/s00018-020-03453-7.
[83]Gonciarz W,Lechowicz ,Urbaniak M,et al.Searching for serum biomarkers linking coronary heart disease and Helicobacter pylori infection using infrared spectroscopy and artificial neural networks[J].Sci Rep,2022,12(1):18284.DOI:10.1038/s41598-022-23191-z.
[84]Kim SB,Kim N,Park J,et al.Preventive effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on the coronary heart diseases depending on age and sex with a median follow-up of 51 months[J].Helicobacter,2023,28(4):e12969.DOI:10.1111/hel.12969.
[85]Chen Y,Yang C,You N,et al.Relationship between Helicobacter pylori and glycated hemoglobin:a cohort study[J].Front Cell Infect Microbiol,2023,13:1196338.DOI:10.3389/fcimb.2023.1196338.
[86]Goldenring JR,Mills JC.Cellular plasticity,reprogramming,and regeneration:metaplasia in the stomach and beyond[J].Gastroenterology,2022,162(2):415-430.DOI:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.036.
[87]Azami M,Baradaran HR,Dehghanbanadaki H,et al.Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with the risk of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance:an updated systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Diabetol Metab Syndr,202 13(1):145.DOI:10.1186/s13098-021-00765-x.
[88]Esmaeili Dooki MR,Alijanpour Aghamaleki M,Noushiravani N,et al.Helicobacter pylori infection and type 1 diabetes mellitus in children[J].J Diabetes Metab Disord,2020,19(1):243-247.DOI:10.1007/s40200-020-00497-1.
[89]Gamil NM,Abd El Fattah MA,Ahmed MAE,et al.Lansoprazole enhances the antidiabetic effect of dapagliflozin in fortified diet-fed streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats[J].J Biochem Mol Toxicol,2020,34(4):e22451.DOI:10.1002/jbt.22451.
[90]Zhang J,Hai X,Wang S,et al.Helicobacter pylori infection increase the risk of subclinical hyperthyroidism in middle-aged and elderly women independent of dietary factors:Results from the Tianjin chronic low-grade systemic inflammation and health cohort study in China[J].Front Nutr,2023,10:1002359.DOI:10.3389/fnut.2023.1002359.
[91]Silva IN,Maral LV,Queiroz DMM.Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with thyroid dysfunction in children with congenital hypothyroidism[J].Front Pediatr,2022,10:875232.DOI:10.3389/fped.2022.875232.
[92]Wenzek C,Boelen A,Westendorf AM,et al.The interplay of thyroid hormones and the immune system-where we stand and why we need to know about it[J].Eur J Endocrinol,2022,186(5):R65-R77.DOI:10.1530/EJE-21-1171.
[93]Yamaguchi H,Osaki T,Kai M,et al.Immune response against a cross-reactive epitope on the heat shock protein 60 homologue of Helicobacter pylori[J].Infect Immun,2000,68(6):3448-3454.DOI:10.1128/IAI.68.6.3448-3454.2000.
(收稿日期:2023-05-29)
