金刚石层倒角参数对PDC切削齿性能的影响规律
2024-01-01张素慧王传留李耿


摘要 聚晶金刚石复合片(polycrystalline diamond compact,PDC)切削齿的综合性能受金刚石层倒角参数的影响较大,特别是其抗冲击性能,但影响规律不明。为探究金刚石层倒角参数对PDC切削齿性能的影响规律,优化PDC切削齿结构并提高PDC钻头的钻进效率,采用目前应用较广的平面型和微弧型PDC切削齿,分别制作0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 mm 4种倒角尺寸和15°、30°、45°3种倒角角度的PDC,得出不同金刚石层倒角参数的PDC切削齿受热后的耐磨性和抗冲击韧性,并对其钻进效率和破损形式进行分析。结果表明:倒角尺寸对PDC耐磨性和抗冲击韧性的影响存在的临界值约为0.3 mm,当倒角尺寸≤0.3 mm时,PDC的磨耗比大、抗冲击韧性低、破损形式多为崩刃;反之倒角尺寸>0.3 mm时,PDC的磨耗比降低、抗冲击韧性提升近1倍,累计吸收功可达1000 J以上,且破损形式多为脱层。倒角角度对PDC耐磨性和抗冲击韧性的影响基本为线性关系,即倒角角度越小,磨耗比越大,抗冲击韧性越低。
关键词 PDC切削齿;金刚石层倒角参数;综合性能;破损形式
中图分类号 TE21;TG74;TQ164 文献标志码 A
文章编号 1006-852X(2024)04-0470-06
DOI码 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2023.0209
收稿日期 2023-09-26 修回日期 2024-01-03
聚晶金刚石复合片(polycrystalline diamond com-pact,PDC)切削齿是PDC钻头最主要的切削单元,其作用是碎岩和破煤等,它的性能很大程度上决定了钻头的钻进效果和使用寿命[1]。PDC切削齿的性能除了受配方和合成工艺等方面的影响,还与金刚石层倒角参数密切相关。
DETOURNAY等[2]提出PDC钻头的切削刃很大程度上决定了钻头的钻进性能。莫铭忠等[3]分析了PDC切削刃的形态对锚杆钻头钻进效率和抗冲击韧性的影响,得出在PDC外侧设计局部较大倒角,可减少钻头崩齿。AKBARI等[4-5]通过有限元分析发现,PDC切削齿的攻击性随着倒角尺寸的减小而提高。SHAO等[6]考虑到倒角效应对凿岩的相互作用,预测了PDC切削齿剪切岩石时的切削力和切削效率,并通过立车试验验证了理论模型。文献[7-9]表明:单齿切削力的主要影响因素之一是齿刃部接触弧长,通常PDC切削齿刃部存在倒角。近年来现场反馈证明,在PDC刀具上添加倒角对复杂和坚硬的地层非常有效。
尽管已有较多的PDC单齿切削的相关研究,但多着重于PDC切削齿的空间位置参数(如斜镶角等),关于金刚石层倒角参数对其性能影响的研究较少。且在中硬地层中钻进时,PDC切削齿所受的反作用力多集中在边缘[10]。因此,探究金刚石层倒角参数对PDC切削齿性能的影响规律,可为优化PDC切削齿结构并提高PDC钻头的钻进效率提供参考。
1试验材料与方法
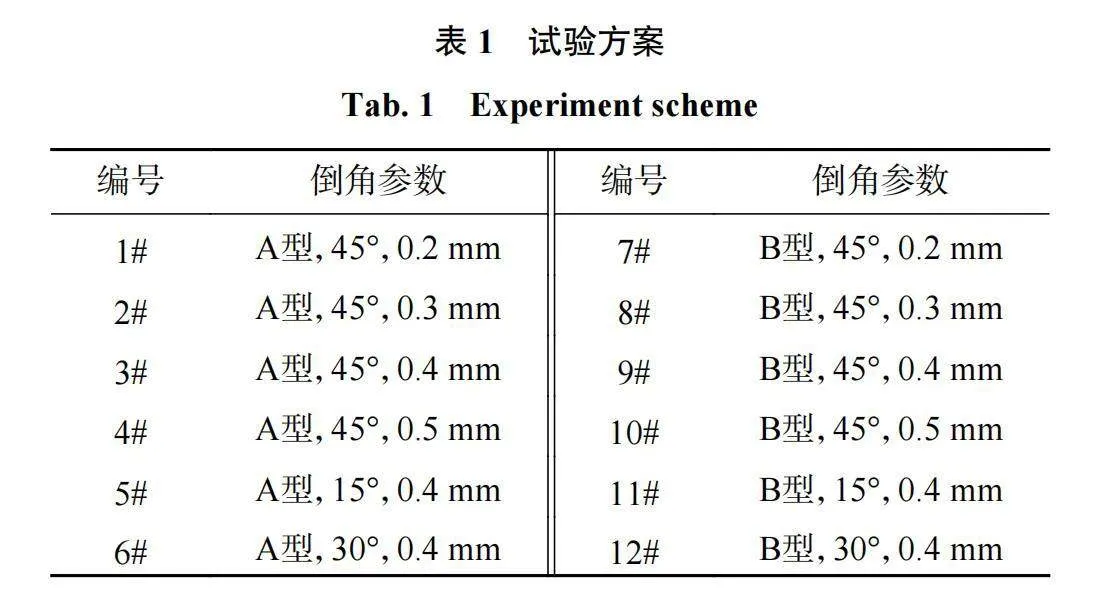
PDC直径为(13.44±0.05)mm、高度为(8.0±0.1)mm、金刚石层厚度为1.7 mm,金刚石层与硬质合金基底的结合面为波浪形。PDC表面形状有A型平面型和B型微弧型2种。PDC切削齿外形及金刚石层倒角参数如图1所示。倒角参数取值根据目前常用的矿用PDC切削齿的倒角角度和倒角尺寸进行微调,同时考虑到加工方便,将其分2组进行试验,考察金刚石层 倒角参数对PDC切削齿性能的影响规律。第1组倒角角度均为45°,倒角尺寸h分别取0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 mm;第2组倒角尺寸均为0.4 mm,倒角角度α分别取15°、30°、45°。
为模拟PDC切削齿的焊接过程,试验前先将PDC切削齿加热到750℃并保温15 min,再测试其磨耗比、磨损面积、磨削时间和抗冲击韧性等性能。具体试验方案见表1。
磨耗比按照JB/T 3235-2013《聚晶金刚石磨耗比测定方法》等来测试[11-12],对磨砂轮外径为100 mm、厚度为16 mm,孔径为20 mm,坑深为3.6 mm。
利用车削试验模拟PDC切削齿与岩石相互作用。车削的岩石尺寸为ϕ800 mm×1000 mm,车削转速为100 r/min,单次进深为1 mm,总计车削深度为5 mm。车削后通过工具显微镜测出PDC的磨损面积。
磨削时间即磨削相同直径尺寸砂轮所用的时间,采用直径控制法测试。采用2片砂轮测试磨削时间,用PDC将砂轮直径从100 mm磨到70 mm后记录磨削的总时间。
PDC的抗冲击韧性采用落锤式冲击试验机测试,并通过分级能量测试PDC切削齿的累计吸收功。单次冲击能量分别为10、20、30、40、50 J,每个能量级别冲击10次,若PDC切削齿完好则进行下一个能量级别的冲击,直至PDC切削齿出现破损。
2试验结果与讨论
2.1不同倒角参数PDC切削齿的磨削情况
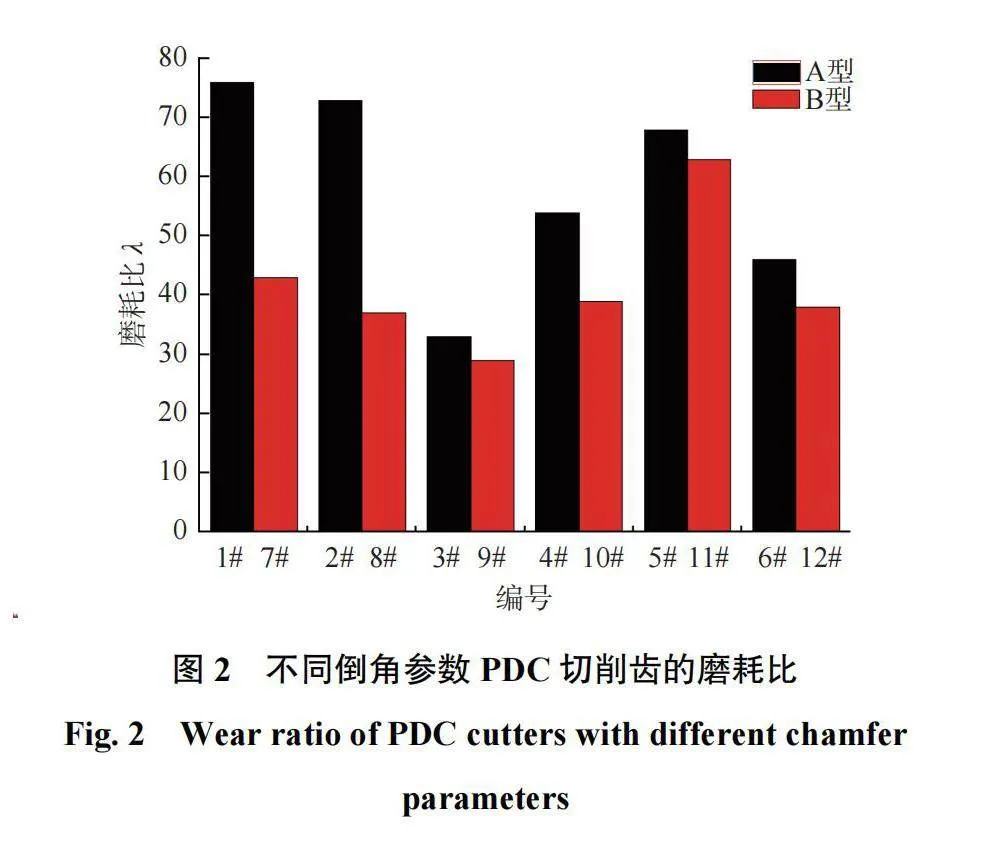
不同倒角参数PDC切削齿的磨耗比如图2所示。由图2可知:当倒角角度相同,倒角尺寸≤0.3 mm时,磨耗比较大(1#、2#、7#、8#);当倒角尺寸gt;0.3 mm时,磨耗比相对较小(3#、4#、9#、10#)。A型比B型PDC切削齿表现得更明显。当倒角尺寸相同,倒角角度为15°时,磨耗比最大(5#、11#);倒角角度为30°时,磨耗比次之(6#、12#);倒角角度为45°时,磨耗比相对较小(3#、9#)。由此说明倒角尺寸相同时,倒角角度越小,磨耗比越大,二者呈负相关。当倒角角度和倒角尺寸相同时,A型PDC切削齿磨耗比均大于B型对应的值,其耐磨性更好。
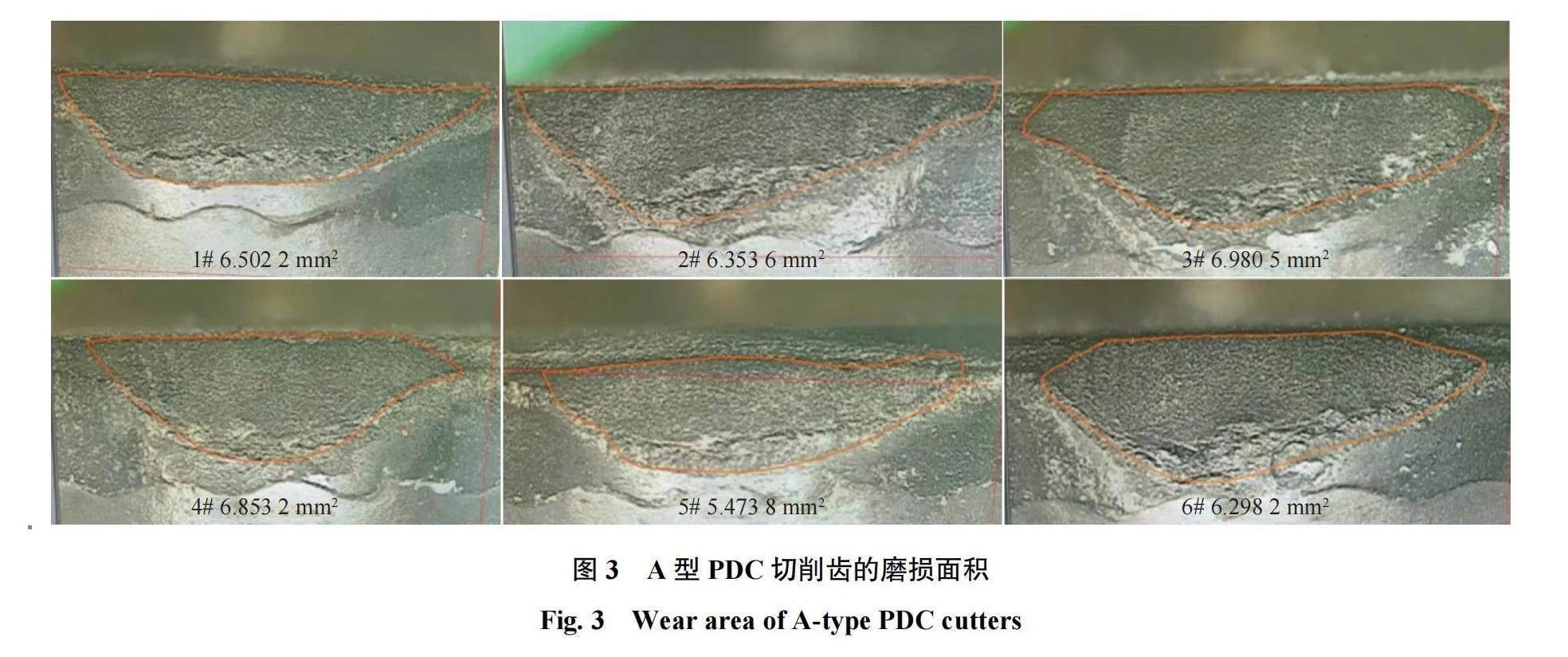
选择磨耗比较大的A型PDC切削齿进行车削试验,其磨损面积如图3所示。由图3可知:当倒角角度相同、倒角尺寸不同时(1#~4#),倒角尺寸≤0.3 mm的磨损面积较小(1#、2#),倒角尺寸gt;0.3 mm的磨损面积略大(3#、4#)。这与磨耗比的变化规律大致相同,即磨损面积小的磨耗比较大,磨损面积大的磨耗比较小。当倒角尺寸相同、倒角角度不同时(5#、6#、3#),倒角角度为15°的磨损面积最小(5#),倒角角度为30°的磨损面积次之(6#),倒角角度为45°的磨损面积相对较大(3#)。这与磨耗比的变化规律完全一致,即倒角尺寸相同时,倒角角度越小,磨损面积越小,磨耗比越大。
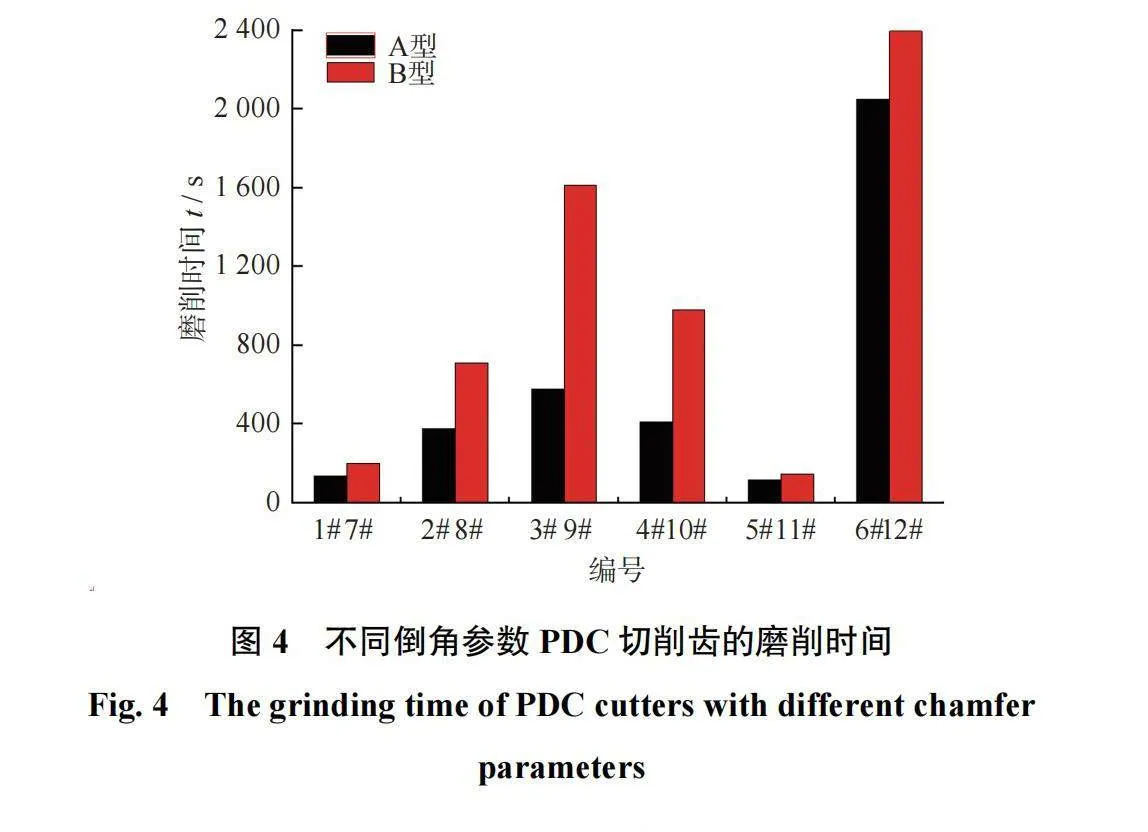
不同倒角参数PDC切削齿的磨削时间如图4所示。由图4可知:当倒角角度相同、倒角尺寸不同时,倒角尺寸≤0.3 mm的磨削时间较短(1#、2#、7#、8#);倒角尺寸gt;0.3 mm的磨削时间相对较长(3#、4#、9#、10#)。这与磨耗比的变化规律有一定的关联,即磨耗比较大的磨削时间短。当倒角尺寸相同、倒角角度不同时,倒角角度为15°的磨削时间极短(5#、11#),倒角角度为30°和45°的磨削时间较长。另外B型微弧型的磨削时间均长于A型平面型的磨削时间。实验结果表明倒角尺寸与耐磨性之间存在约为0.3 mm的临界值。当倒角尺寸≤0.3 mm时,PDC切削齿磨耗比大、磨损面积小、磨削时间短;当超过临界值时,磨耗比降低、磨损面积增大,磨削时间延长。倒角角度与耐磨性之间为线性关系,即倒角角度越小磨耗比越大。PDC切削齿表面形状对耐磨性的影响与倒角角度相似,A型平面型(相当于较小的倒角角度)磨耗比更大,B型微弧型(相当于较大的倒角角度)降低了其耐磨性和攻击性,增加了切削时间。
2.2不同倒角参数PDC切削齿的抗冲击韧性
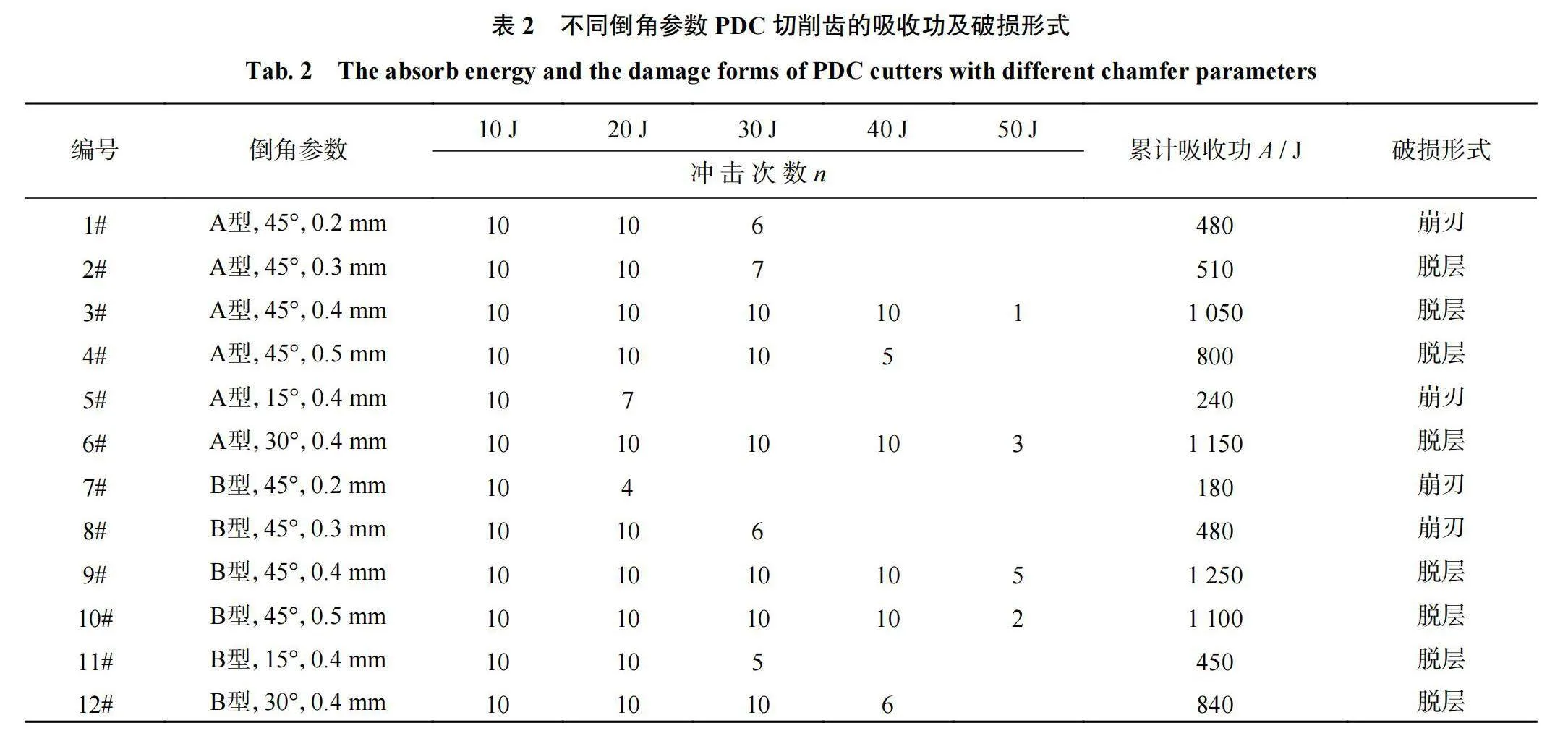
不同倒角参数PDC切削齿的吸收功和破损形式见表2,累计吸收功为所有能量级别吸收功的总和。
从表2可以得出:当倒角角度相同、倒角尺寸不同,且倒角尺寸≤0.3 mm时(1#、2#、7#、8#),PDC切削齿破损的能量级别在30 J以下,累计吸收功较小,约500 J,破损形式以崩刃为主;倒角尺寸≥0.4 mm时(3#、4#、9#、10#),PDC切削齿的破损能量级别都在40 J以上,大部分可达到50 J,累计吸收功基本在1000 J以上,个别表现出不足1000 J。但总体吸收功较大,与倒角尺寸≤0.3 mm时的吸收功相比较,提升了近1倍。由于其破损的能量级别较高,破损形式均为脱层。当倒角尺寸相同倒角角度不同时,倒角角度为15°的PDC切削齿破损能量级别在30 J以下(5#、11#),累计吸收功较小,均<500 J;倒角角度为30°和45°时,PDC切削齿破损的能量级别都在50 J(6#、3#、12#、9#),累计吸收功较大,基本>1000 J或接近该值,破损形式均为脱层。另外,通过计算A型平面型和B型微弧型的累计吸收功的平均值发现,B型微弧型平均吸收功较大。结果表明倒角尺寸与冲击韧性之间存在的临界值同样约为0.3 mm。当倒角尺寸≤0.3 mm时,吸收功较小,破损形式表现为崩刃;当倒角尺寸>0.3 mm时,吸收功较大,破损形式表现为脱层。倒角角度与冲 击韧性之间基本接近线性关系,即倒角角度越小,吸收功越小,冲击韧性越低。
3结论
通过对PDC切削齿金刚石层倒角参数的分析,得出倒角参数对PDC切削齿磨耗比、磨损面积、磨削时间和吸收功影响较大。
(1)倒角尺寸对PDC切削齿的耐磨性和抗冲击韧性的影响存在的临界值约为0.3 mm。当倒角尺寸≤0.3 mm时,PDC切削齿磨耗比大、磨削时间短,抗冲击韧性低,破损形式多为崩刃;反之倒角尺寸>0.3 mm时,PDC切削齿磨耗比降低、磨削时间增加,抗冲击韧性提升近1倍,累计吸收功可达1000 J以上,破损形式多为脱层。
(2)倒角角度对耐磨性和抗冲击韧性的影响基本呈线性关系,即倒角角度越小,磨耗比越大,抗冲击韧性越低;反之倒角角度越大,磨耗比越小,抗冲击韧性越高。
(3)PDC切削齿表面形状对耐磨性和抗冲击韧性的影响与倒角角度相似,A型平面型磨耗比大、磨削时间短;B型微弧型磨耗比小,但冲击韧性高。
参考文献:
[1]张富晓,黄志强,周已.PDC钻头切削齿失效分析[J].石油矿场机械,2015,44(9):44-49.
[2]ZHANG Fuxiao,HUANG Zhiqiang,ZHOU Yi.Failure analysis of PDC bit cutter[J].Oil Field Equipment,2015,44(9):44-49.DETOURNAY E,DEFOURNY P.A phenomenological model for the drilling action of drag bits[J].International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciencesamp;Geomechanics Abstracts,1992,29(1):13-23.
[3]莫铭忠,莫一君,刘振辉.锚杆钻头PDC倒角对钻进效率的影响[J].超硬材料工程,2017,29(2):35-38.MO Mingzhong,MO Yijun,LIU Zhenhui.Influence of PDC chamferof anchor bits on its drilling efficiency[J].Superhard Material Engineering,2017,29(2):35-38.
[4]AKBARI B,MISKA SZ,YU M,et al.The effects of size,chamfer geometry,and back rake angle on frictional response of PDC cutters[M]//[s.n.].Paper presented at the 48th U.S.rock mechanics/geomechanics symposium.Minneapolis,Minnesota:[s.n.],2014.
[5]ROSTAMSOWLAT I,AKBARI B,EVANS B.Analysis of rock cutting process with ablunt PDC cutter under different wear flat inclination angles[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2018,171:771-783.
[6]SHAO FY,LIU W,GAO DL.Effects of the chamfer and materials on performance of PDC cutters[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2021,105(108887):1-10.
[7]黄鹏.PDC钻头切削齿在砾岩层中磨损规律研究[D].荆州:长江大学,2021.HUANG Peng.Research on the wear law of PDC bit cutting teeth in conglomerate layer[D].Jingzhou:Yangtze University,2021.
[8]谭凯文.PDC钻头破岩机理实验研究[D].北京:中国石油大学,2017.TAN Kaiwen.Study on the rock fragmentation mechanism of PDC bit[D].Beijing:China University of Petroleum,2017.
[9]李劲,尹卓,刘忠,等.PDC齿破岩力预测模型研究[J].石油机械,2021,49(8):23-29.
[10] LI Jin,YIN Zhuo,LIU Zhong,et al.Research on rock breaking force prediction model of PDC cutter[J].China Petroleum Machinery,2021,49(8):23-29.
[10]张绍和,谢晓红,王佳亮.复合片斜镶角对钻头钻进性能的影响[J].西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2012,34(1):171-175.ZHANG Shaohe,XIE Xiaohong,WANG Jialiang.Research of bit’s performance affected by the cutting angle of PDC[J].Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Scienceamp;Technology Edition),2012,34(1):171-175.
[11]全国磨料磨具标准化技术委员会.聚晶金刚石磨耗比测定方法:JB/T3235−2013[S].北京:机械工业出版社,2014.National Abrasives Standardization Technical Committee.Testing method for abrasion ratio of polycrystalline diamond:JB/T 3235−2013
[12][S].Beijing:China Machine Press,2014.煤炭行业煤矿专用设备标准化技术委员会.金刚石复合片不取心钻头:MT/T 786−2011[S].北京:煤炭工业出版社,2011.Technical Committee for Standardization of Special Equipment for Coal Mines,Coal Industry.Polycrystalline diamond compact non-core bit:MT/T 786−2011[S].Beijing:Coal Industry Press,2011.
作者简介
张素慧,女,1988年生,博士研究生、助理研究员。主要研究方向:钻探机具性能测试与分析。
E-mail:zhangsuhui1221@163.com
(编辑:王洁)
Influence of diamond layer chamfer parameters on performance of PDC cutters
ZHANG Suhui1,2,WANG Chuanliu 2,LI Geng 2
(1.China Coal Research Institute,Beijing 100013,China)
(2.Xi'an Research Institute(Group)Co.,Ltd.,China Coal Technologyamp;Engineering Corp.,Xi'an 710077,China)
Abstract Objectives:The precise control of diamond layer chamfer parameters has acomplex influence on the com-prehensive performance of PDC cutters.This control not only helps to expand ideas in PDC cutter design but also im-proves the overall efficiency of drilling tools.To fully analyze the effect of diamond layer chamfer parameters on the performance of PDC cutters,this study examined the correlation between the chamfer size and chamfer angle of the dia-mond layer and the performance of PDC cutters,namely wear resistance,impact toughness,drilling efficiency,and damage forms.It provided ascientific basis for optimizing the structure of PDC cutters to enhance the operational effi-ciency and reliability of PDC bits under complex geological conditions.Methods:The study combined experimental re-search and theoretical analysis.Two types of PDC cutters,planar type and micro-arc type,which are widely used in the market at present,were selected as experimental objects.Samples with different chamfer sizes(0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5 mm)and chamfer angles(15°,30°,45°)were prepared using precision machining techniques.The samples were systematic-ally heat-treated to simulate the actual welding process before testing,and the performance of the PDC cutters was eval-uated by analyzing wear resistance,impact toughness,and drilling efficiency.Additionally,the interaction between the PDC cutter and rock was simulated by turning experiments,and the wear area and the damage forms were observed,measured,and analyzed using amicroscope.Results:The experimental results revealed the influence of diamond cham-fer parameters on the performance of PDC cutters.On the one hand,the chamfer size had acritical value of about 0.3mm.When the chamfer size was less than or equal to this critical value,the wear ratio of PDC cutters was high,the grinding time was short,the energy level of breakage was low,impact toughness was low,and the primary form of dam-age was broken edges,which adversely affected the service life and drilling efficiency of the cutter.When the chamfer size exceeded the critical value,the PDC cutter wear ratio decreased,the grinding time increased,the damage energy level was high,impact toughness nearly doubled,the accumulated absorbed energy reached more than 1000 J,and the predominant damage form was delamination,effectively extending the service life of the cutter.On the other hand,the influence of chamfer angle on the wear resistance and impact toughness of PDC cutters exhibited alinear relationship.As the chamfer angle increased,the wear ratio of PDC cutters gradually decreased,the wear area increased,indicating a decrease in wear resistance,and impact toughness increased correspondingly.In addition,the influence of the PDC cut-ter's shape on wear resistance and impact toughness was similar to that of the chamfer angle,namely,planar cutters had a high wear ratio and short grinding time,while micro-arc cutters had areduced wear ratio but improved impact tough-ness.This provided an important basis for optimizing the chamfer angle and designing the shape structure of PDC cut-ters.By moderately increasing the chamfer angle or adopting acamber design,the comprehensive performance of the cutter could be improved to acertain extent.Conclusions:Through systematic experiments and analysis,the effect of diamond chamfer parameters on the comprehensive performance of PDC cutters is revealed.Especially,the discovery of the critical value of chamfer size provides guidance for the optimal design of PDC cutters.The fine regulation of dia-mond layer chamfer parameters presents anew approach to improving the performance of PDC cutters.In the develop-ment and production of PDC bits,the influence of these parameters should be fully considered.The performance of PDC cutters can be optimized by accurately regulating the chamfer size,chamfer angle,and shape structure,thereby fur-ther enhancing the drilling efficiency and service life of PDC bits.
Key words PDC cutter;diamond layer chamfer parameters;comprehensive performance;damage form
