热爆反应在金刚石表面快速形成TiC涂层
2024-01-01史冬丽马尧李涛







摘要 分别采用Ti/碳黑/diamond和Ti/碳黑/PTFE/diamond粉体为原料,通过热爆反应在金刚石颗粒表面形成以TiC为主的涂层,研究原料中金刚石含量及添加PTFE对金刚石表面TiC涂层的影响。结果表明:2种体系的原料热爆反应后基体的组成为TiC。Ti/碳黑/diamond体系中,当原料中金刚石质量分数为10%~30%时,反应后的金刚石表面均实现良好的TiC涂层涂覆。在Ti/碳黑/PTFE/diamond体系中,当原料中添加质量分数为3%的PTFE并减少原料中碳黑的质量分数时,可明显促进金刚石表面的TiC涂覆;且当原料中金刚石质量分数为80%~90%时,仍可使金刚石颗粒表面实现良好的TiC涂覆。
关键词 Ti-TiC涂层;金刚石;热爆反应;PTFE
中图分类号 TQ164 文献标志码 A
文章编号 1006-852X(2024)04-0463-07
DOI码 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2023.0170
收稿日期 2023-08-25 修回日期 2023-10-24
金刚石具有极高的硬度以及非常好的耐磨性等,在磨削、钻探等加工领域有大量的应用[1-2]。但金刚石晶体主要为共价键结合,其具有较高的惰性,使金刚石与基体或结合剂材料(如金属、树脂或陶瓷等)之间具有较高的界面能,因此金刚石与基体或结合剂间的浸润性很差,表现为彼此间的结合或黏结性较差,使用过程中的金刚石颗粒易脱落或破裂。
在金刚石颗粒表面进行涂覆可有效克服金刚石与基体间难结合的问题[3]。近些年来,化学气相沉积[4]、物理气相沉积[5]、真空微蒸发镀膜[6]、高温熔盐热处理[7]等金刚石表面镀覆技术已广泛应用,但这些镀覆技术也有一些工艺上的缺点,如工艺较复杂或镀覆设备昂贵等。所以,采用一种简单并高效的镀覆工艺应用于金刚石颗粒表面的涂覆是必要的。
热爆反应制备金属间化合物是一种重要的涂覆工艺手段[8-9]。相比常见的镀覆技术,热爆反应技术工艺简单,反应时间极短(通常为几秒钟),使用设备为常见的马弗炉或管式炉,对设备要求较低。最近几年,有一些用热爆反应技术在金刚石颗粒表面实现涂覆的相关报道[10-12]。
热爆反应通常需要对粉体进行压片处理使其成为压坯,然后加热压坯使其发生反应。此外,热爆反应产生的温度较高,容易实现坯体烧结。由于烧结的块体比较坚硬,通常需把块体砸碎并研磨,才能分离出金刚石颗粒。这样增加了热爆反应工艺的烦琐程度,同时有可能破坏金刚石表面的镀层。如果原料不需要压片,那么在粉末状态下发生热爆反应,生成的产物粉末化,从而比较容易筛分出金刚石。另外,金刚石具有良好的导热性,会吸收热爆反应的热量,这就要求原料中金刚石的质量分数较低(一般lt;40%),才能发生热爆反应,从而实现产物中金刚石的良好镀覆。
因此,基于前人的研究工作[10-12],优化热爆反应工艺,以实现金刚石表面的TiC镀覆。方法是直接对含金刚石的原料混合粉末进行加热,使其发生热爆反应。拟采用Ti/碳黑混合粉末为原料,且添加聚四氟乙烯(polytetrafluoroethylene,PTFE)为辅料,同时添加不同含量的大颗粒金刚石,通过热爆反应在金刚石表面生成TiC涂层。
1实验原料及过程
实验原料为碳黑粉(纯度gt;99.0%,平均颗粒粒径为30 nm),Ti粉(纯度gt;99.0%,平均粒径为53 μm),金刚石颗粒(HD级别,纯度gt;99.0%,平均粒径为500μm),PTFE(纯度gt;99.0%,平均颗粒粒径为3 μm)。
实验过程为:
(1)Ti与碳黑的摩尔比为1∶1,称量后球磨2.0 h,使之混合均匀。
(2)将混合后的粉料与质量分数分别为10%、20%、30%和40%的金刚石手工混合0.5 h,以使金刚石与粉料混合均匀。
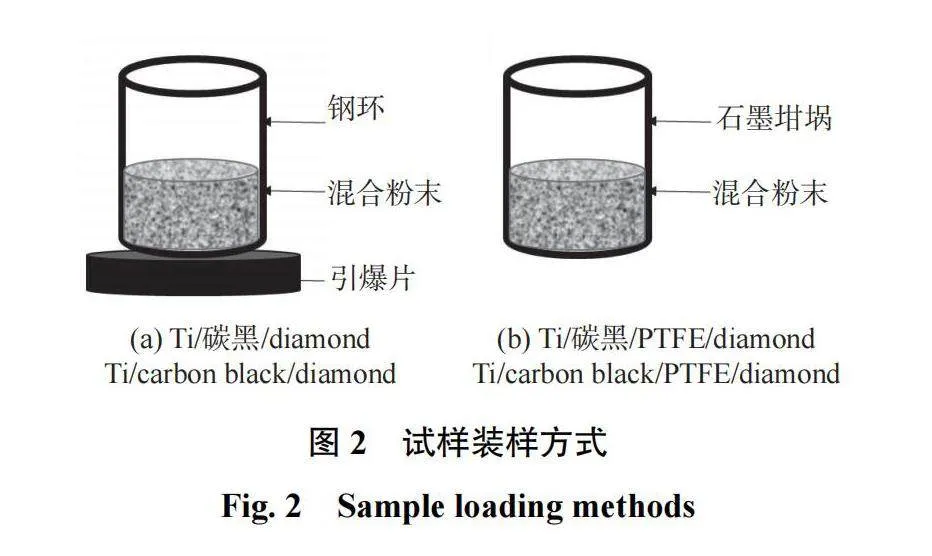
(3)Ti/碳黑/diamond试样的装样方法如图2a所示。由于Ti和碳黑无法直接发生热爆反应,因而利用化学炉法预热可诱发热爆反应,即将能够发生热爆反应的摩尔比为1∶3的Ti-Al压坯作为引爆片放到图2a的钢环下方,从而诱导热爆反应发生。
(4)在Ti/碳黑/diamond原料中添加质量分数为3%的PTFE,试样的装样方法如图2b所示,即把原料粉末放入石墨坩埚中,后将石墨坩埚放入管式炉(SK3-5-12-6型)中加热以诱发热爆反应。其加热方法如下:通入高纯Ar(纯度为99.99%,流量为100 mL/min)以排除管内空气并对试样进行保护,设定升温速率为20℃/min,从室温加热到800℃,再保温1 min,后自然冷却至室温。
(5)热爆反应后,将反应后的混合物通过F100筛网(筛网网孔尺寸为150 mm)把金刚石颗粒与结合剂粉末分离出来。
金刚石颗粒的光学照片用数码显微镜(徐州乐越安全科技有限公司,Z01-5型)拍摄。热爆样品中结合剂与金刚石颗粒的物相用转靶X射线多晶衍射仪(日本理学公司,Rigaku UltimaⅣ型)分析,分析时扫描速度为10°/min,扫描范围(2θ)为20°~70°或20°~60°。用德国蔡司公司的ZEISS SUPRA 55型扫描电子显微镜(结合能谱仪)观察金刚石颗粒表面的显微形貌,观察时用导电胶黏附金刚石颗粒并将其放置于试样台上。
2实验结果及讨论
2.1Ti/碳黑/diamond体系的热爆反应
图3为不同金刚石质量分数下热爆反应后得到的试样中分离出的金刚石颗粒外观。金刚石原料呈现出淡黄色、半透明的外观。如图3所示:当原料中金刚石的质量分数<40%时,反应后得到黑色金刚石,这表明颗粒表面被很好地镀覆;当原料中金刚石的质量分数为40%时,少量金刚石呈现出其原始的淡黄色,显然这些金刚石的镀覆效果较差。
图4为热爆反应试样中分离出来的结合剂和金刚石颗粒的X射线衍射(XRD)图谱。从图4可见:各热爆试样中结合剂部分的反应产物的主相均为TiC,金刚石颗粒表面涂层的主相为TiC和Ti。此外,还出现了石墨的衍射峰,这表明金刚石表面石墨化;且随着原料中金刚石的含量增加,相应的石墨峰逐渐下降。
文献[13]报道:Ti和C体系发生燃烧反应所产生的绝热温度可达2937℃,而金刚石在Ar保护下的石墨化转变温度通常为1400℃。因此,在高的反应温度和极短的反应时间下,金刚石表面会发生轻微的石墨化。
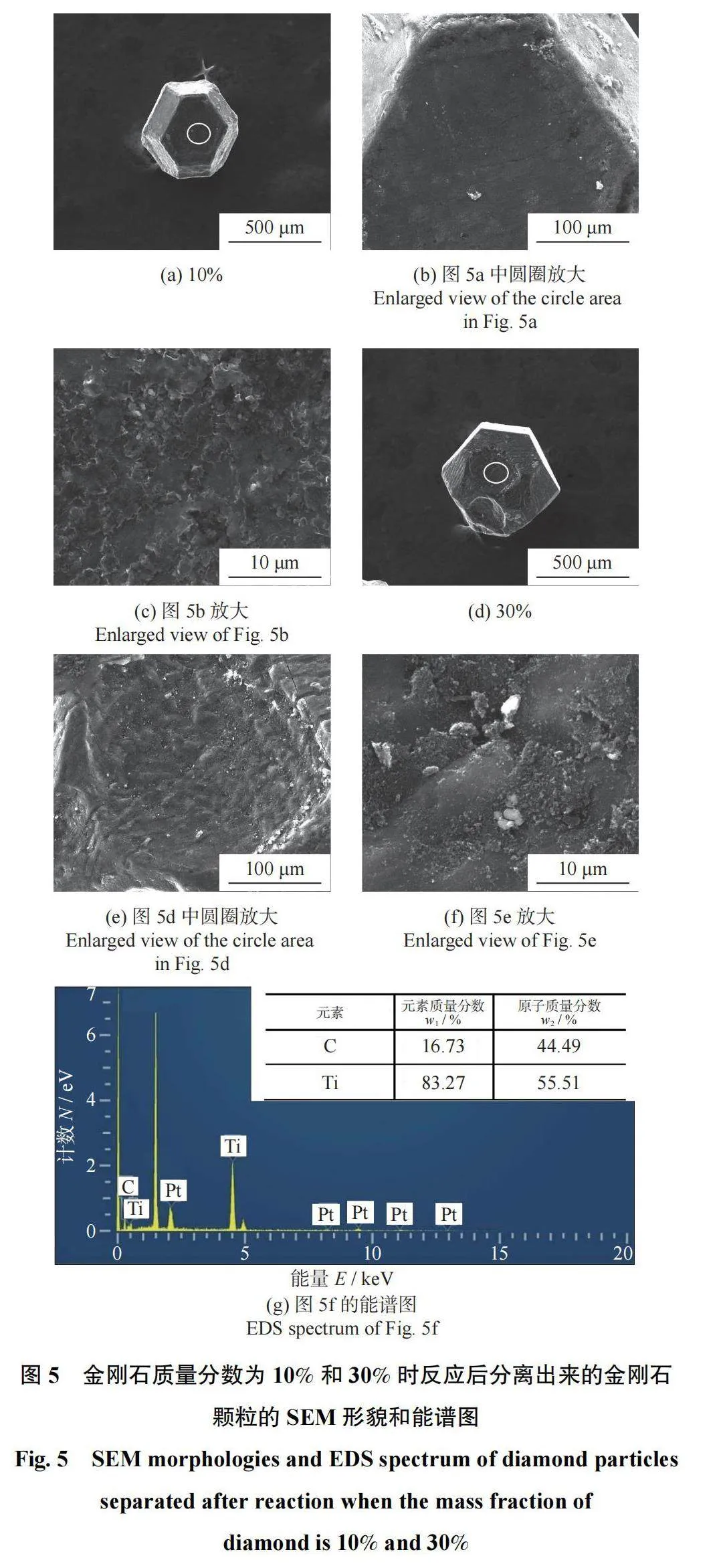
图5为金刚石质量分数为10%和30%时热爆试样中分离出来的金刚石颗粒的SEM形貌和能谱图。对比图5a(金刚石质量分数为10%)和图5d(金刚石质量分数为30%)中的圆圈区域放大图(图5b和图5e)可以发现,金刚石表面的涂层与金刚石结合良好。比较图5c和图5f可知:随着金刚石含量增加,涂层中的晶粒粒度尺寸有所下降。且图5g的能谱结果表明:金刚石表面涂层中只有Ti和C元素存在,而存在的Pt元素是检测时导电胶中的外来元素。
总之,Ti/碳黑/diamond体系发生热爆反应可在金刚石表面形成TiC涂层,但绝热温度会导致金刚石表面石墨化。同时,能够被镀覆的金刚石量较少,且需要进行引爆处理,才能发生热爆反应。因此,有必要继续优化及改进其热爆反应工艺。
2.2Ti/碳黑/PTFE/diamond体系的热爆反应
PTFE是一种重要的用于燃烧反应的反应促进剂。在Si-C等低热量体系中,通过引入PTFE可以诱发燃烧合成[14-16]。已有研究表明:Ti和PTFE在较低的温度下就会发生剧烈的化学反应,一般起爆温度为550℃[17]。因此,在Ti和碳黑的混合原料中引入少量的PTFE,通过Ti和PTFE反应释放出的大量的热,来诱发Ti和C之间的热爆反应,最后合成出TiC材料。即释放的大量的热促进了TiC在金刚石颗粒表面形成,而无须化学炉法引爆。
图6为不同金刚石质量分数下试样中分离出来的 金刚石颗粒的外观。由图6可知:当原料中金刚石的质量分数≤60%时,金刚石颗粒表面得到了良好的镀覆处理;当金刚石质量分数达到80%时,一些金刚石颗粒表面出现漏镀现象。显然,添加PTFE可显著促进金刚石表面的镀覆。
图7为热爆反应后,试样中金刚石颗粒的XRD图谱。从图7可见:金刚石表面涂层的组成为TiC和Ti,且很难观察到石墨的衍射峰,这表明在该反应体系下抑制了金刚石表面的石墨化。
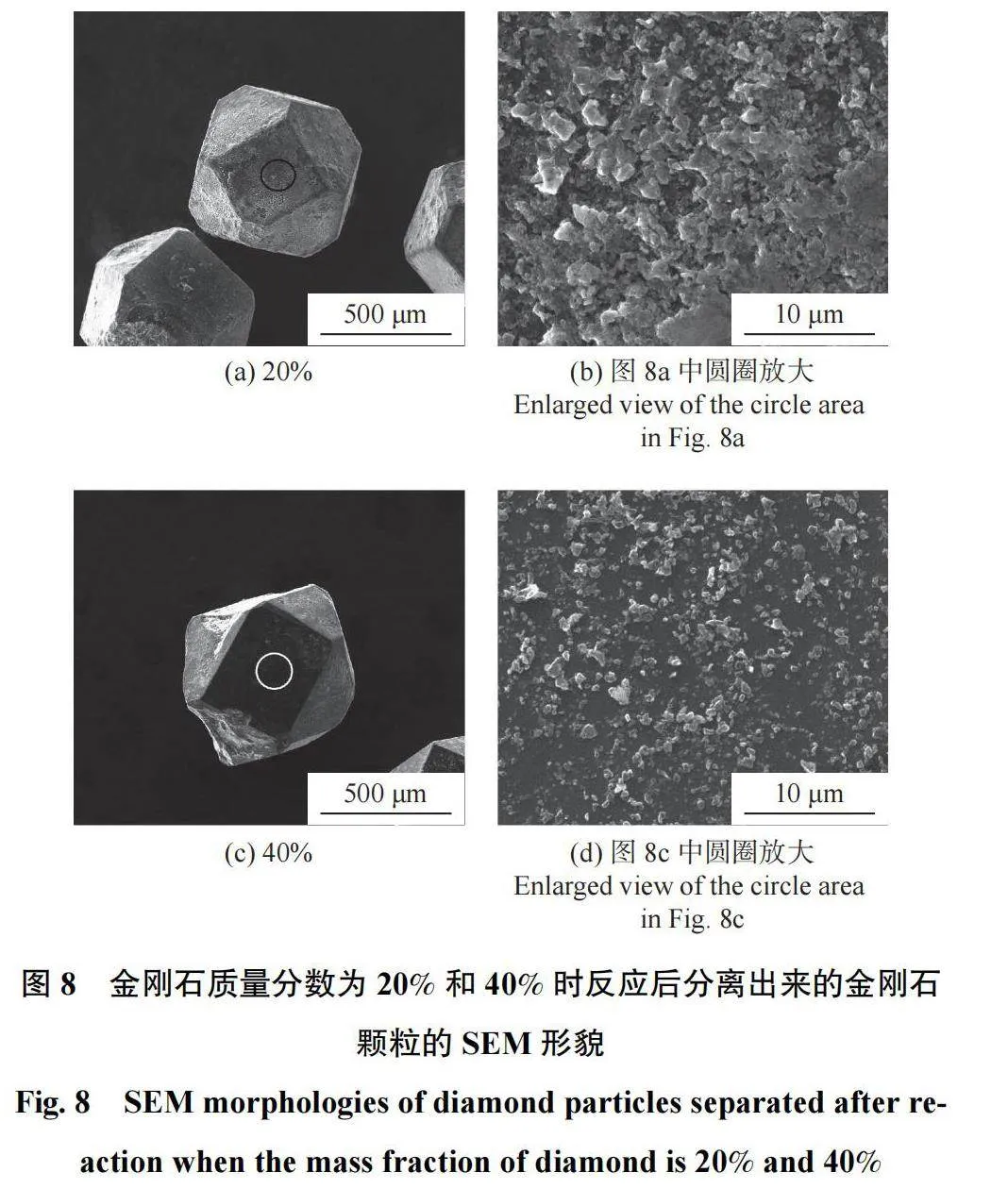
图8为金刚石质量分数为20%和40%时反应后分离出来的金刚石颗粒的SEM形貌。对图8a和图8c中的圆圈区域分别放大得到图8b和图8d,可以观察到金刚石表面的涂层与金刚石表面结合良好;且随着金刚石含量增加,涂层中的晶粒尺寸有所下降,涂层未完全覆盖金刚石颗粒表面。
由文献[18]可知,Ti/碳黑/PTFE/diamond体系发生如下反应:
其中:(C 2 F 4)n为PTFE分子式,T ad为反应的绝热温度,为反应焓变。
当温度达到500℃时,Ti和PTFE开始发生反应,生成TiF 3和C。研究表明,式(2)的激活能为364 kJ/mol[19],且式(2)的热爆临界反应温度为1527℃[13]。因此,添加微量的PTFE,利用其和Ti反应释放的大量能量,就足以诱发Ti和C的反应,从而引发式(2)的自发反应。
同时,在上述的热爆反应中,PTFE与Ti反应会产生一定量的C,这相当于增加了原料中C的含量。且PTFE分解出来的C活性要比金刚石颗粒表面的C原子的活性更高[14-15],会更容易与Ti反应。这就导致能够沉积到金刚石表面的Ti的量大为减少,进而使原料中金刚石含量较高,其表面的涂覆效果较差。因此,如果把原料中碳黑的含量适当降低,就有可能促进高含量金刚石的有效镀覆。
基于原来的原料配比,图9为原料配比中碳黑质量分数降低10个百分点的情况下,得到的金刚石质量分数为80%和90%时的热爆合成样品中筛分的金刚石晶粒的典型外观。由图9可知:降低原料中碳黑的含量,以PTFE为化学促进剂,可以实现高含量金刚石的良好镀覆。
综合起来,采用Ti/碳黑/diamond和Ti/碳黑/PTFE/diamond粉体为原料,经过热爆反应后,在金刚石颗粒表面形成TiC涂层。且优化后者的制备工艺,使原料中金刚石的质量分数达到90%,仍可在其表面实现良好镀覆。与此形成对比的是,文献[10-12]中的热爆反应在金刚石表面镀覆,在原料金刚石镀覆效果较好的情况下,原料中金刚石的质量分数最高达40%。
因此,本研究可以节约大量的结合剂粉末,同时得到的粉体容易分离出金刚石。另外,借鉴本研究工作,还可以类比拓展到其他碳化物材料(如SiC等)在金刚石颗粒表面的镀覆,从而促进热爆反应在金刚石镀覆上的实际应用。
3结论
通过热爆反应在金刚石颗粒表面形成了TiC涂层,得出如下结论:
(1)以Ti/碳黑/diamond为原料,采用化学炉法可以诱发热爆反应,生成的样品中结合剂的主相为TiC;且当原料中的金刚石质量分数为30%或更低时,在金刚石颗粒表面涂覆TiC的效果良好。
(2)使用PTFE为促进剂可以直接诱导Ti/碳黑/PTEE/diamond的热爆反应,从而在金刚石表面生成TiC。当原料中的金刚石质量分数≤60%时,在金刚石颗粒表面涂覆TiC的效果良好。同时,适当降低原料中碳黑的含量,可以促进金刚石颗粒在质量分数为90%或更高时获得更好的TiC表面涂层。
参考文献:
[1]TONSHOFF HK,DENKENA B,APMANN HH.Diamond tools for wire sawing metal components[J].Key Engineering Materials,2003,250:33-40.
[2]TONSHOFF HK,DENKENA B,APMANN HH,et al.Diamond tools in stone and civil engineering industry:Cutting principles,wear and applications[J].Key Engineering Materials,2003(250):103-109.
[3]朱振东,刘豪,张甜,等.金刚石表面镀覆技术与应用的研究进展[J].超硬材料工程,2021(3):28-32.ZHU Zhendong,LIU Hao,ZHANG Tian,et al.Research progress of plating technology on the diamond surface and its application[J].Superhard Material Engineering,2021(3):28-32.
[4]黄本生,李慧,江仲英,等.金刚石CVD金属化及其应用[J].真空科学与技术学报,2011,31(6):754-759.HUANG Bensheng,LI Hui,JIANG Zhongying,et al.Diamond metallization by chemical vapor deposition and its applications[J].Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology,2011,31(6):754-759.
[5]HU G,YANG J,LIU Y.Deposition of tungsten-titanium carbides on surface of diamond by reactive PVD[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,1999,9(4):838-841.
[6]MIYAKE S,SHINDO T,MIYAKE M.Regression analysis of the effect of bias voltage on nano-and macrotribological properties of diamond-like carbon films deposited by afiltered cathodic vacuum arc ion-plating method[J].Journal of Nanomaterials,2014(1/2):1-13.
[7]DAOUSH WM,PARK HS,HONG SH.Fabrication of TiN/cBN and TiC/diamond coated particles by titanium deposition process[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2014,24(11):3562-3570.
[8]JIAO XY,CAI XP,NIU G,et al.Rapid reactive synthesis of TiAl 3intermetallics by thermal explosion and its oxidation resistance at high temperature[J].Progress in Natural Science:Materials International,2019,29(4):447-452.
[9]LIU Y,SUN Z,CAI X,et al.Fabrication of porous FeAl-based intermetallics via thermal explosion[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2018,28(6):1141-1148.
[10]LIANG B,DAI Z,ZHANG Q,et al.Coating of diamond by thermal explosion reaction[J].Diamond and Related Materials,2021,119:108572.
[11]ZHAO H,YIN X,WANG Y.Coating diamond surfaces in aTi/Si/carbon black/diamond system via thermal explosion[J].Diamond and Related Materials,2022,127:109195.
[12]LI Q,ZHANG Q,LIANG B,et al.Coating on the surface of diamond particles by thermal explosion reaction method[J].Journal of Superhard Materials,2022,44(3):191-197.
[13]殷声.燃烧合成[M].北京:冶金工业出版社,1999.YIN Sheng.Combustion synthesis[M].Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press,1999.
[14]YANG K,YANG Y,LIN ZM,et al.Mechanical-activation-assisted combustion synthesis of SiC powders with polytetrafluoroethylene as promoter[J].Materials Research Bulletin,2007,42(9):1625-1632.
[15]ZURNACHYAN AR,KHARATYAN SL,KHACHATRYAN HL,et al.Self-propagating high temperature synthesis of SiC–Cu and SiC–Al cermets:Role of chemical activation[J].International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials,2011,29(2):250-255.
[16]BAGHDASARYAN AM,HOBOSYAN MA,KHACHATRYAN HL,et al.The role of chemical activation on the combustion and phase formation laws in the Ni–Al-promoter system[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,188:210-215.
[17]LEE I,REED RR,BRADY VL,et al.Energy release in the reaction of metal powders with fluorine containing polymers[J].Therm Anal Calorim,1997,49(3):1699-1705.
[18]鱼银虎,汪涛,张洪敏,等.PTFE促发TiC陶瓷粉体低温固相合成研究[18][J].无机材料学报,2015,30(3):272-276.YU Yinhu,WANG Tao,ZHANG Hongmin,et al.Low temperature combustion synthesis of TiC powder induced by PTFE[J].Journal of Inorganic Materials,2015,30(3):272-276.
[19]DUNMEAD SD,READEY DW,SEMLER CE,et al.Kinetics of combustion synthesis in the Ti-C and Ti-C-Ni systems[J].Journal of American Ceram Society,1989,72(12):2318-2324.
作者简介
史冬丽,女,1974年生,高级工程师。主要研究方向:超硬材料及制品。
E-mail:shidongli@zzpolis.com
(编辑:周万里)
Rapid formation of TiC coating on diamond surface through thermal explosion reaction
SHI Dongli,MA Yao,LI Tao
(Zhengzhou Bolisen New Material Technology Co.,Ltd.,Zhengzhou 450001,China)
Abstract Objectives:Coating treatment on the surface of diamond particles is an important technique to effectively overcome the problem of difficult bonding between diamond and substrate,and the thermal explosion reaction is acom-mon surface coating technique for diamond particles.However,this technology has disadvantages such as difficulty in separating diamonds from the product and alow proportion of diamonds,which increases its complexity and production costs,greatly limiting the promotion and application of this technology.This article aims to introduce polytetrafluoro-ethylene(PTFE)into thermal explosion reaction technology to form acoating mainly composed of TiC on the surface of diamond particles.It is expected to optimize the coating preparation process and promote the popularization and applica-tion of thermal explosion reaction technology in the field of diamond plating,so as to improve the wear resistance and service life of the diamond tools.Methods:Using two raw material systems,Ti/carbon black/diamond and Ti/carbon black/PTFE/diamond powders,the thermal explosion reaction of Ti/carbon black/diamond is induced by the chemical furnace method,and the intense chemical reaction between PTFE and titanium at low temperature ensures that the Ti/carbon black/PTFE/diamond system directly undergoes athermal explosion reaction.At the same time,the TiC coat-ing can be generated on the surface of diamond particles by adjusting the ratio of raw materials and triggering the thermal explosion reaction under high temperature conditions.The macroscopic morphology of diamond particles be-fore and after coating is observed and compared by optical microscope to roughly infer the plating condition,and the phase compositions of the coating were analyzed by X-ray diffraction.Then the scanning electron microscope and the energy dispersive spectroscopy are used to observe the surface morphology of diamond particles,determine the element-al compositions,and infer the surface reaction state.Results:The thermal explosion reaction of both raw material sys-tems can form aTiC coating on the surface of diamond.The main phase of the binder reaction product is TiC,and the main phases of the coating on the surface of diamond particles are TiC and Ti.But for the Ti/carbon black/diamond sys-tem,the chemical furnace method is needed to induce athermal explosion reaction.When the diamond mass fraction in the raw material is 30%or lower,the TiC coating on the surface of the diamond particles is good.When asmall amount of PTFE is introduced into the Ti/carbon black/diamond system,the reaction between Ti and PTFE releases alarge amount of heat,which induces the thermal explosion reaction between Ti and carbon black and synthesizes TiC,and fi-nally forms aTiC coating on the surface of diamond particles.In addition,the system does not need the chemical fur-nace method to detonate.When the diamond mass fraction in the raw material is less than or equal to 60%,the diamond particle surface coated with TiC coating is good.At the same time,appropriately reducing the content of carbon black in the raw materials can enable diamond to obtain agood TiC coating on its surface even when the mass fraction of dia-mond is 90%or higher.Conclusions:TiC coatings are prepared on the surface of diamond particles using thermal ex-plosion reaction technology,and the important effects of raw material compositions and PTFE additives on the forma-tion of diamond particles'surface coating are revealed.Adding an appropriate amount of PTFE can directly induce the thermal explosion reaction,which greatly promotes the increase of the proportion of diamond in the raw material,and effectively improves the formation quality of the coating.This can greatly save binder powder,thereby reducing produc-tion costs,while obtaining loose powder products that are easy to separate from diamonds.In addition,drawing on the work of this study,other carbide materials(such as SiC)can be analogously extended for coating on the surface of dia-mond particles,thereby promoting the promotion and the application of thermal explosion reactions in diamond coating.
Key words Ti-TiC coating;diamond;thermal explosion;PTFE
