烧结工艺对CuSnZn合金粉末性能的影响
2024-01-01曹新民鲍丽李振程传卫陈鹏潘建军于奇于新泉



摘要 提高金刚石工具的性能并控制其生产成本已成为工程应用领域的重点研究方向。本研究中,通过雾化法制备不同Zn质量分数(10.00%~30.00%)的CuSnZn合金粉末,在610~655℃不同的热压烧结温度和21 MPa的烧结压力下制备烧结节块,并对烧结节块的理论密度、洛氏硬度、抗弯强度、显微形貌进行分析。结果表明:随着Zn含量升高,CuSnZn合金粉末熔化温度逐渐降低,当Zn质量分数为30.00%时,熔化温度降低到848℃;当Zn质量分数为20.00%时,烧结节块致密度降低至97.6%;烧结节块的抗弯强度先升高后降低,当Zn质量分数为20.00%时,达到最大值542 MPa;烧结节块中的黄铜由α相逐渐转变为α+β相和α+β+β´相,其洛氏硬度显著提升;节块的断裂方式由沿晶断裂逐渐过渡到穿晶断裂。
关键词 CuSnZn合金粉末;致密度;沿晶断裂
中图分类号 TG74 文献标志码 A
文章编号 1006-852X(2024)04-0449-07
DOI码 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2023.0173
收稿日期 2022-10-23 修回日期 2023-09-02
金刚石工具在石材加工中占有重要地位,其性能直接影响石材的加工质量、加工成本[1-4]。近年来,随着石材价格和人工成本不断提高,不仅要求金刚石工具锋利度好、自锐性高,还要求其使用寿命较长,金刚石刀齿较薄,以减小切割阻力,并提高切割效率及石材利用率[5-7]。若要提高生产效率,降低生产成本,则需提高切机功率、切割速率,进而要求金刚石节块锋利度、强度较高,以降低切割过程中断齿的风险。
为改善金刚石工具的锋利度,在不调整金刚石浓度和粒度的前提下,目前常用的方法是提高节块中的Sn含量,以改善节块的脆性,进而提高其锋利度。随着Sn含量升高,烧结节块的硬脆性提升,但降低了节块的强度;同时,CuSn合金的线膨胀系数较大,在烧结冷却过程中合金与金刚石的间隙变大,对金刚石的把持力降低[8-10]。
为解决高Sn含量节块在高温烧结中Sn易流失的难题,广泛使用CuSn10和CuSn15等预合金粉末,但CuSn合金粉末存在强度偏低、对金刚石把持力弱等问题。为了改善上述问题,在CuSn10合金粉末的基础上添加了不同比例的Zn元素。水雾化工艺制备的CuS-nZn合金粉末氧含量偏高,传统工艺中采用氨分解气还原粉末以降低氧含量,但ZnO不能被氢气还原;采用气雾化工艺制备的CuSnZn合金粉末熔化温度低、流动性好、硬度高[11]。
本研究中,分析了烧结工艺对CuSnZn合金粉末力学性能和微观组织的影响,以期实现CuSnZn合金粉末在金刚石工具中的良好应用。
1试验
1.1CuSnZn预合金粉末制备
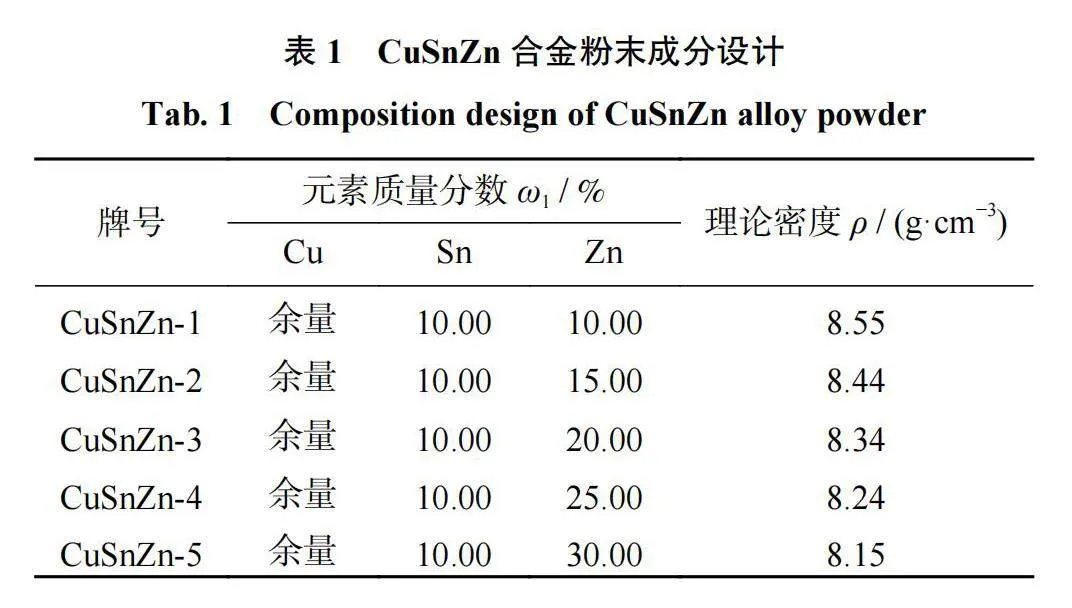
试验选用的原材料为99.95%的铜板、99.95%的锌锭、99.99%的锡锭,采用气雾化工艺制备CuSnZn合金粉末,其中Zn元素的质量分数分别为10.00%、15.00%、20.00%、25.00%、30.00%。5种预合金粉末的成分设计见表1。
1.2试验设备
混料设备为TM三维涡流混料机,热压烧结设备为SJJ-HXP真空热压烧结机,力学性能检测设备为MTS万能力学试验机,熔化温度检测设备为STA-449差热分析仪,硬度检测设备为HR-150A洛氏硬度计,微观组织观察设备为Pro-XL台式扫描电镜。
2结果与讨论
2.1CuSnZn合金熔化温度
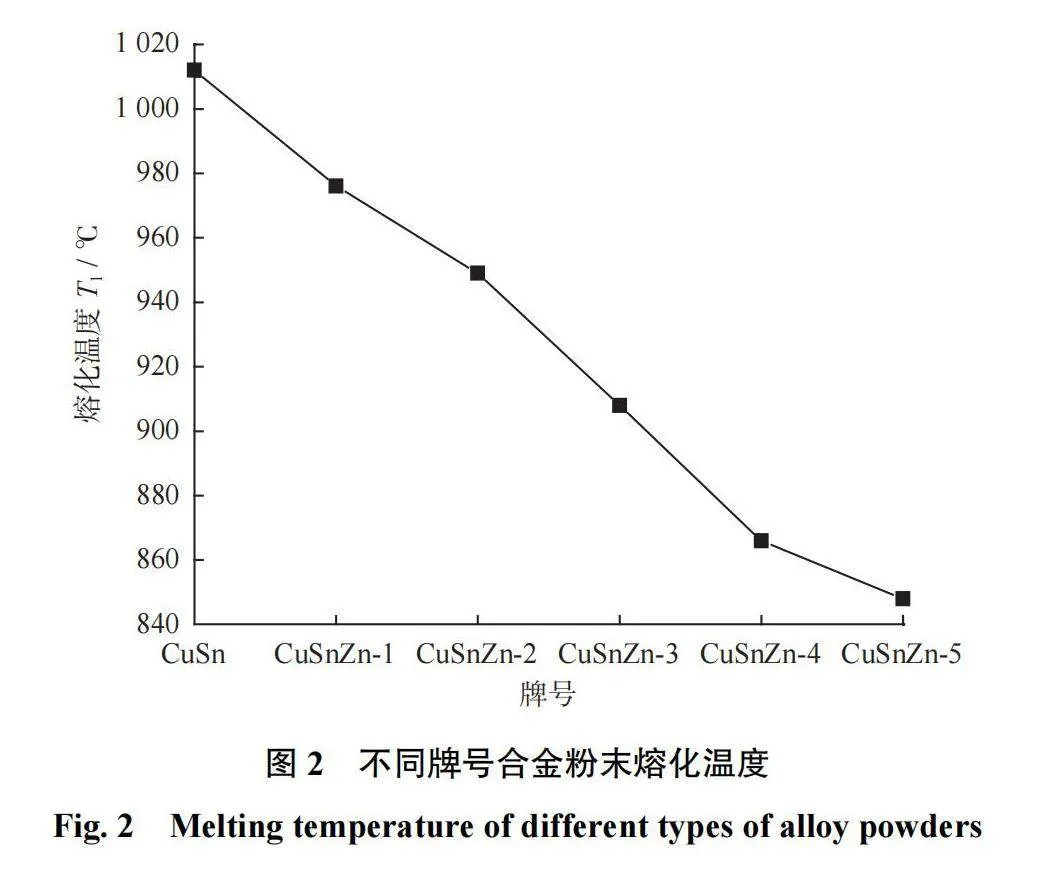
图1所示为CuSnZn三元合金相图。图2所示为不同牌号合金粉末熔化温度曲线。由图2可知:随着Zn含量的升高,CuSnZn合金粉末熔化温度的降低速度先增大后减小,当Zn质量分数为25.00%时,熔化温度降低到866℃;当Zn质量分数为30.00%时,熔化温度降低到848℃。根据Cu-Sn二元相图,CuSn10合金的液相线温度为1012℃,添加30.00%的Zn后合金粉末的液相线温度降低了164℃,熔化温度的降低有利于合金粉末在热压烧结过程中形成液相,改善节块烧结致密度,降低烧结温度和能耗。
2.2CuSnZn合金粉烧结性能
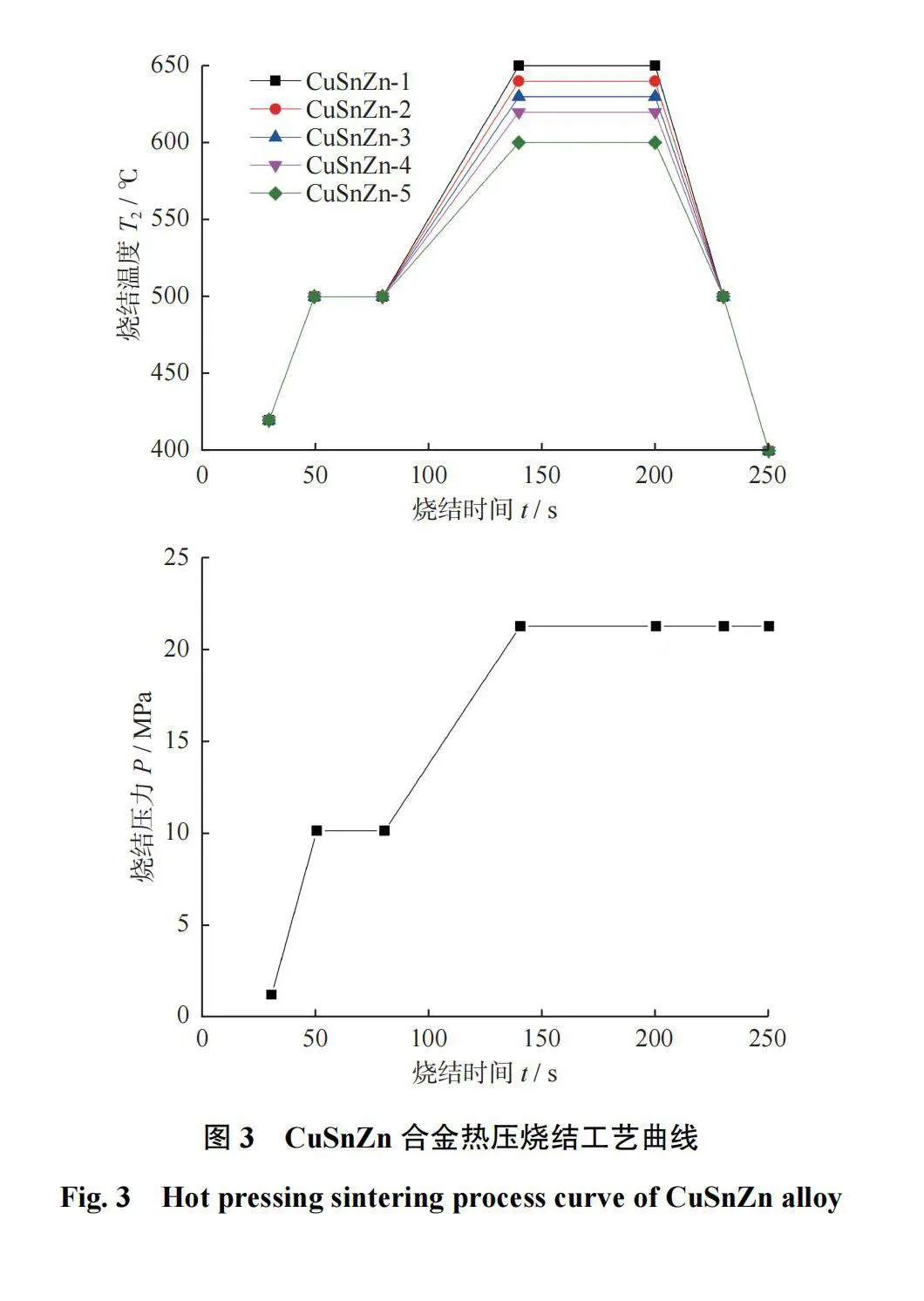
参考合金粉末熔化温度,设计5种CuSnZn合金粉末的热压烧结工艺,烧结时间均为250 s,保温50 s,烧结压力均为21 MPa,节块尺寸为40 mm×30 mm×12mm,牌号为CuSnZn-1、CuSnZn-2、CuSnZn-3、CuSnZn-4、CuSnZn-5的合金粉末的烧结最高温度分别为610、615、630、645、655℃,温度均为红外测温。烧结工艺曲线见图3。
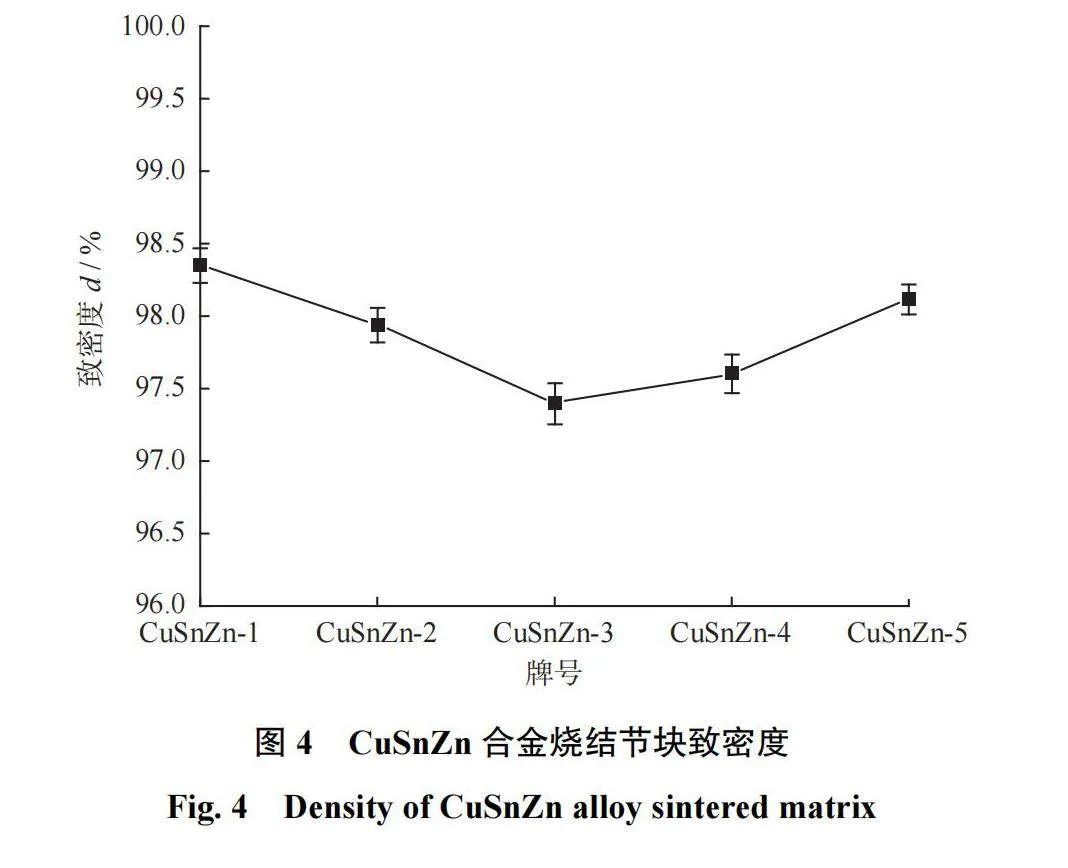
采用阿基米德排水法测试节块致密度,不同牌号合金粉末烧结节块致密度见图4。由图4可知:随着合金粉末中Zn含量升高,节块致密度先降低后升高,当Zn质量分数为10.00%时,节块致密度最高,为98.3%;当Zn质量分数为20.00%时,节块致密度最低,为97.6%。节块致密度最高点和最低点仅相差0.7%,说明CuSnZn合金粉末在低温下实现了致密烧结,能够满足金刚石工具的使用要求。
不同Zn含量的烧结节块洛氏硬度如图5所示。由图5可知:随着Zn含量升高,烧结节块洛氏硬度显著提升,当Zn质量分数为20.00%时,烧结体硬度为100 HRB;当Zn质量分数为30.00%时,烧结体硬度达到最大值105 HRB。根据Cu-Zn二元相图可知,当黄铜中Zn质量分数<30.00%时,都是α相,α黄铜塑性好,硬度低;当Zn质量分数为30.00%~33.00%时,会出现少量β相,(α+β)黄铜在室温下含有硬而脆的β´相。因此,当试验设计的CuSnZn-5合金粉末中Zn质量分数为30.00%时,含有部分β相和β´相,能够提高烧结节块的硬度。试验设计的合金粉末中含有元素Sn,按照特殊的黄铜中加入元素的“锌当量系数”来推算,元素Sn的“锌当量系数”为2,黄铜中加入质量分数为10.00%的Sn,相当于黄铜中减少20%的α相组织,增加相应的α+β相组织,使得烧结节块硬度进一步提高。
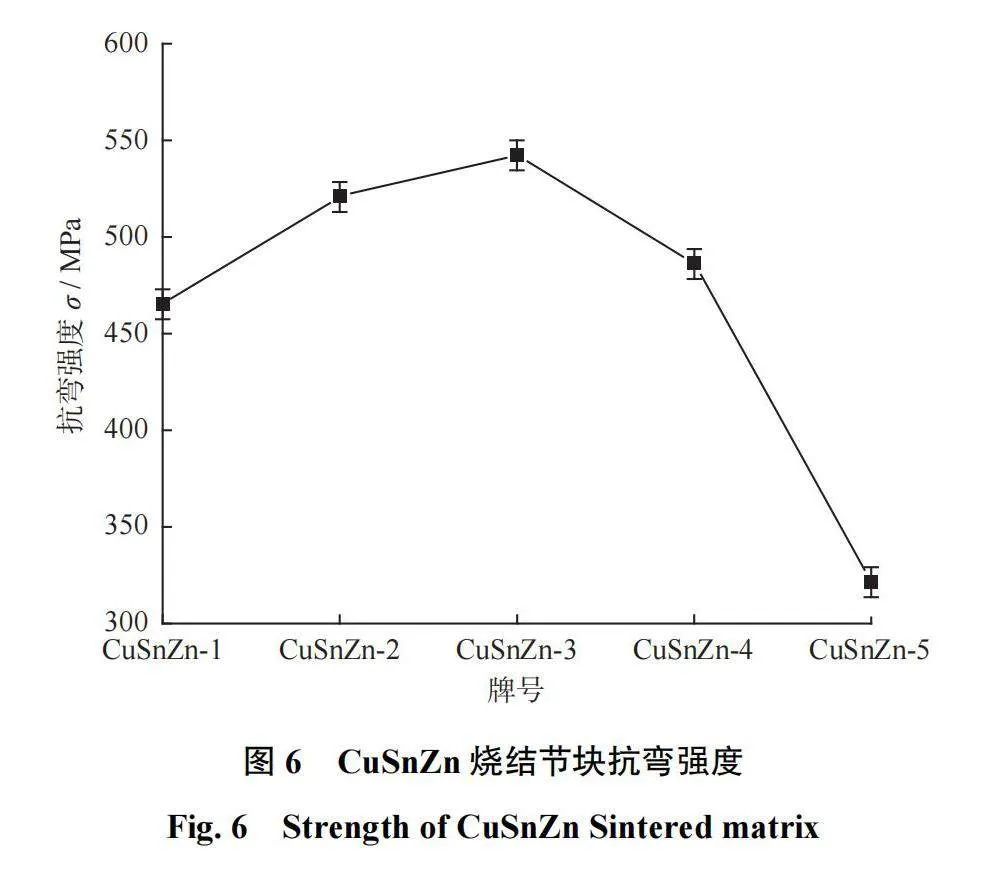
CuSnZn烧结节块抗弯强度如图6所示。由图6可知:随着Zn含量升高,烧结节块的抗弯强度先升高后降低,当Zn质量分数由10.00%增高至20.00%时,抗弯强度由465 MPa升至最高,为542 MPa,升高了14%;当Zn质量分数为30.00%时,烧结节块的抗弯强度仅为322 MPa,较最高时下降了41%。
2.3CuSnZn合金粉烧结节块微观组织
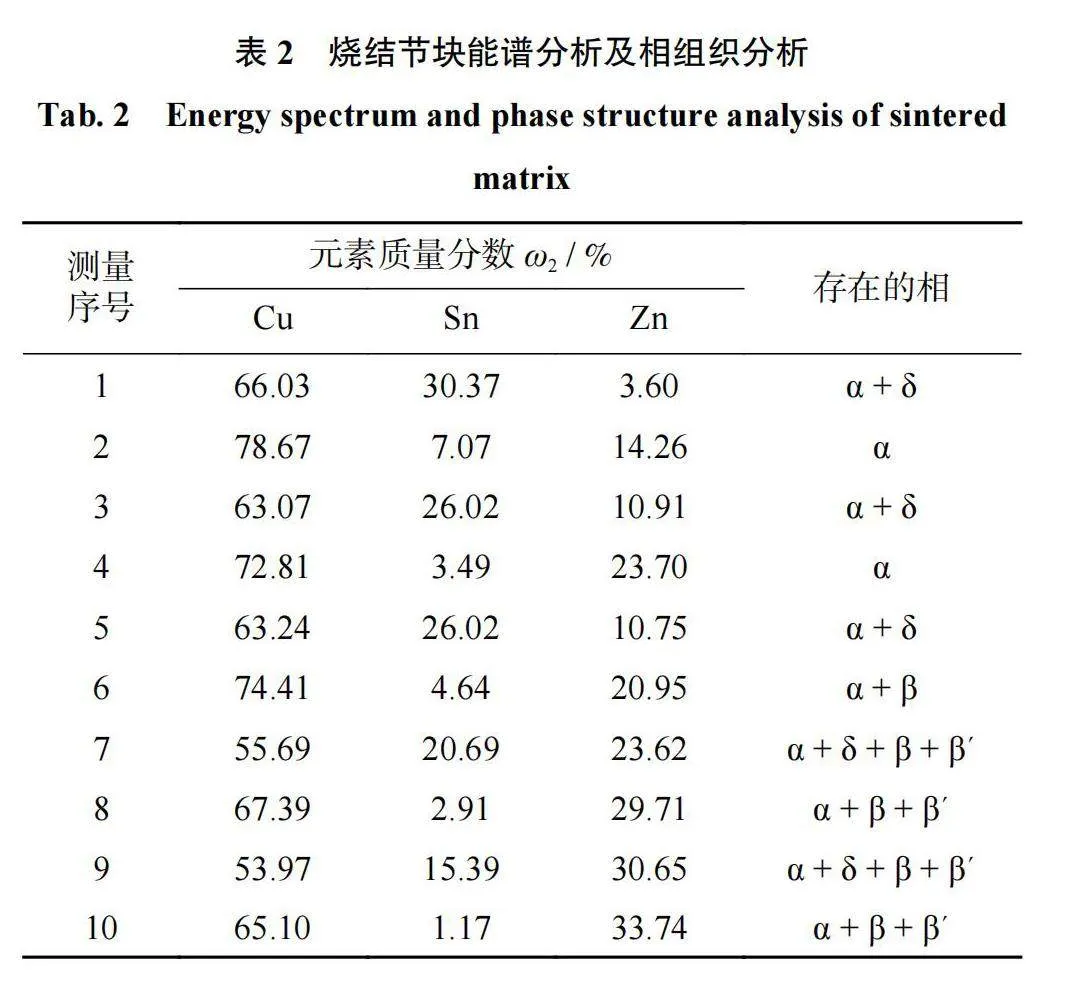
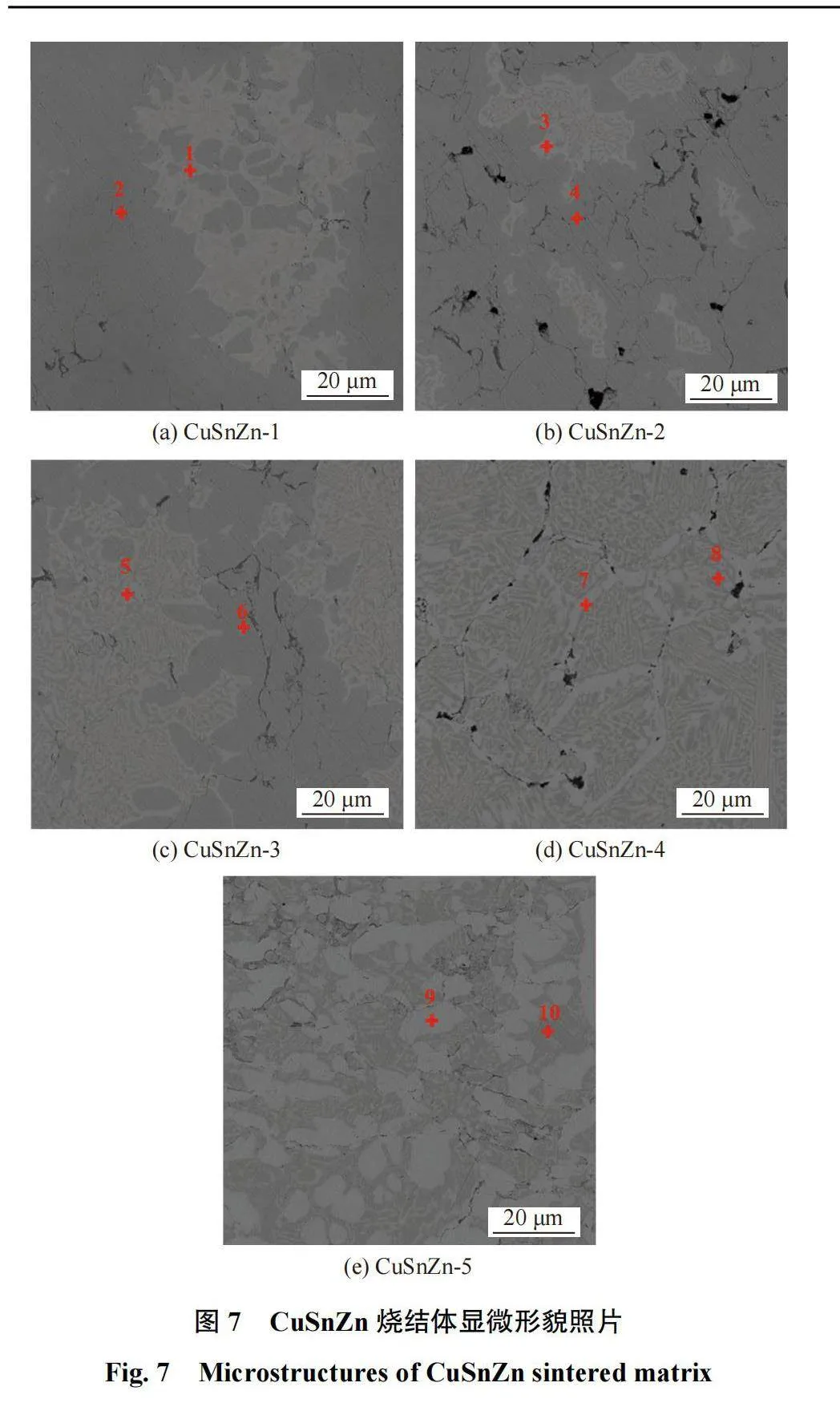
CuZnSn合金粉烧结节块显微组织如图7所示。图7中均可观察到浅灰色和深灰色2种相组织,其中图7a、图7b、图7c中的浅灰色相组织分布不均匀,且团聚在一起;随着Zn含量升高,图7d、图7e中的浅灰色相组织逐渐增多,与深灰色组织交互均匀分布。
选取浅灰色和深灰色组织进行EDS分析,结果如表2所示。由表2可知:Zn质量分数为10.00%时合金中浅灰色相为α+δ(Cu,Sn)相,深灰色相为α(Cu,Zn)相固溶体;当Zn质量分数为20.00%时,烧结节块中逐渐出现黄铜的β相;随着Zn含量的进一步升高,烧结节块中的β相逐渐增加,并出现一定量的β´相,β´相具有一定的硬脆性,表现为烧结节块硬度升高、韧性降低。
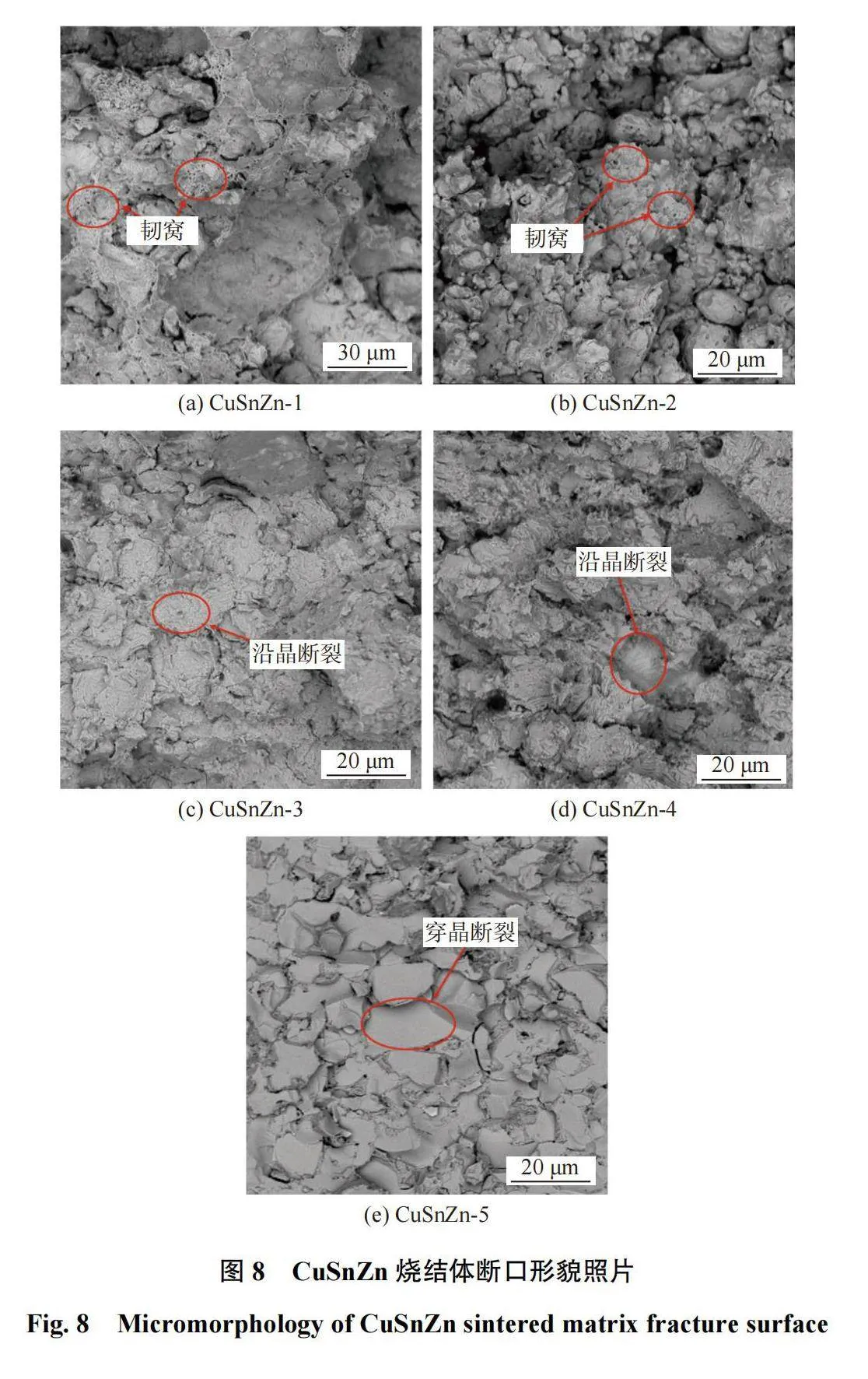
2.4CuSnZn合金粉烧结节块断口形貌
CuZnSn合金粉烧结节块断口形貌如图8所示。图8a、图8b中节块断面粗糙,均可从中观察到明显的韧窝,断口表面有颗粒的剥离,剥离面光滑平整,判定为相组织的晶界剥离断裂。从图8c、图8d中观察到大量解理断裂面,以及少量光滑凹陷的沿晶断裂,烧结节块的硬脆相组织分布均匀,硬脆相与韧性固溶体相夹杂引起断裂呈台阶状分布,且相界面的硬脆组织均匀分布导致部分沿晶断裂。图8e中断口平整,各相表现为脆性的穿晶断裂,烧结体的韧性消失,整体表现为硬脆性,裂纹沿着硬脆组织穿过相界面和晶粒,形成光滑平整的断裂面。由图8可知,随着Zn含量的升高,烧结节块的晶粒逐渐长大。由于烧结节块的强度与晶粒尺寸密切相关,晶粒尺寸越大,单位体积中的晶粒数目就越少,每个晶粒上承受的压力越大,其强度越低。因此,当Zn质量分数>25.00%时,烧结节块的强度逐渐降低。
3结论
(1)随着Zn含量升高,CuSnZn合金粉末熔化温度的降低速度先增加后减小,当Zn质量分数为30.00%时,熔化温度降低到848℃,较CuSn10的熔化温度降低了164℃。
(2)随着Zn含量升高,烧结节块中黄铜由α相逐渐转变为α+β相和α+β+β´相,节块的洛氏硬度显著提升;烧结节块的抗弯强度先升高后降低,当Zn质量分数为20.00%时,达到最大值542 MPa。
(3)当Zn质量分数为10.00%、15.00%时,在烧结节块断口观察到明显的韧窝,断口表面有颗粒的剥离,剥离面光滑平整,为相组织的晶界剥离断裂;当Zn质量分数为20.00%、25.00%时,在烧结节块断口观察到大量解理断裂面,以及少量光滑凹陷的沿晶断裂,其中部分为沿晶断裂、部分为穿晶断裂;当Zn质量分数为30.00%时,烧结节块断口平整光滑,裂纹沿着硬脆组织穿过相界面和晶粒,为穿晶断裂。
参考文献:
[1]中国石材协会.金刚石锯片在国内石材领域中的应用及市场前景[J].石材,2012(12):25-28.China Stone Material Association.Application and market prospect of diamond saw blade in domestic stone material field[J].Stone,2012(12):25-28.
[2]李子石,程凯.金刚石锯片技术发展现状和走势分析[J].石材,2014(6):27-30.LI Zishi,CHENG Kai.Diamond saw blade technology development status and trend analysis[J].Stone,2014(6):27-30.
[3]甘树才,杨春明,徐吉静,等.油页岩灰渣制备人造大理石及其性能[J].吉林大学学报,2011,41(3):879-884.GAN Shucai,YANG Chunming,XU Jijing,et al.Preparation of artificial marble from oil shale ash and its properties[J].Journal of Jilin University,2011,41(3):879-884.
[4]栾芝芸,孙建国.新型金刚石节块圆片锯的切割性能试验[J].工具技术,2000,34(7):7-8.LUAN Zhiyun,SUN Jianguo.Cutting performance test of anew diamond nodular block circular saw[J].Tool Engineering,2000,34(7):7-8.
[5]舒士韬.关于提高大理石出材率和利用率的若干问题[J].广东建材,1999(2):13-19.SHU Shitao.Some issues on improving marble yield and utilization rate[J].Guangdong Building Materials,1999(2):13-19.
[6]王博,冯振昌,肖博.影响金刚石锯片基体物理性能的关键因素分析[J].施工技术,2016,45(12):796-797.WANG Bo,FENG Zhenchang,XIAO Bo.Key factors of the physical properties of the diamond Saw blades[J].Construction Technology,2016,45(12):796-797.
[7]储志强,郭学益,刘东华.切割石材用金刚石制品胎体粉末配方的设计依据和优化原则[J].金属材料与冶金工程,2016(6):3-8.CHU Zhiqiang,GUO Xueyi,LIU Donghua.Design basis and optimization principles for the formulation of diamond product casing powder for cutting stone[J].Metal Materials and Metallurgy Engineering,2016(6):3-8.
[8]于奇,马佳,钟素娟,等.铜锡预合金粉热压性能研究[J].粉末冶金工业,2019,29(1):13-17.YU Qi,MA Jia,ZHONG Sujuan,et al.Study on hot pressing properties of Cu-Sn pre-alloyed powder[J].Powder Metallurgy Industry,2019,29(1):13-17.
[9]蒙光海,雷晓旭,卢安军,等.CuSn15和Fe对无压烧结金刚石工具胎体性能的影响[J].粉末冶金技术,2015,33(2):105-110.MENG Guanghai,LEI Xiaoxu,LU Anjun,et al.Effects of CuSn15 and Fe on the properties of pressureless sintered diamond tools matrix[J].Powder Metallurgy Technology,2015,33(2):105-110.
[10]曹彩婷,刘一波,徐良,等.高Sn含量Cu-Sn预合金粉热压烧结行为及性能的研究[J].金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2016,36(2):67-72.CAO Caiting,LIU Yibo,XU Liang,et al.Study of hot pressing sintering behavior and properties of high Sn content Cu-Sn pre-alloyed powders[J].Diamondamp;Abrasives Engineering,2016,36(2):67-72.
[11]刘志环,张绍和.FeNiCo预合金粉末的烧结特性及其在金刚石绳锯中的应用[J].中国有色金属学报,2019,29(6):1257-1267.LIU Zhihuan,ZHANG Shaohe.Sintering properties of FeNiCo pre-alloyed powder and its application in diamond wire saw[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2019,29(6):1257-1267.
作者简介
曹新民,男,1969年生,本科。主要研究方向:制备金刚石工具用混料、冷压、热压及相关成套设备、金刚石工具用合金粉末。
E-mail:zzjxyjs@126.com
通信作者:李振,男,1982年生,硕士。主要研究方向:有色金属材料及粉末。
E-mail:xxcyzx602@163.com
(编辑:李利娟)
Effect of sintering process on properties of CuSnZn alloy powder
CAO Xinmin1,BAO Li 1,LI Zhen 2,CHENG Chuanwei 3,CHEN Peng 4,PAN Jianjun 1,YU Qi1,YU Xinquan 1
(1.Zhengzhou Research Institute of Mechanical Engineering Co.,LTD.,Zhengzhou 450001,China)
(2.Zhengzhou Emerging Industry Technology Research and Promotion Center,Zhengzhou 450001,China)
(3.Zhengzhou Science and Technology Innovation Service Center,Zhengzhou 450001,China)
(4.Henan Xinda Fusion Technology Co.,LTD.,Zhengzhou 450001,China)
Abstract Objectives:Diamond tools are crucial in stone processing,and their performance is directly related to pro-cessing quality and cost.With the rise of stone and labor costs,the performance requirements on diamond tools are also increasing,including sharpness,self sharpening,tool life,and cutting efficiency.To improve efficiency and reduce costs,users often increase the cutting machine power and speed,which further requires diamond tools to have higher sharpness and strength at the risk of breakage.A practical method method is to increase the content of tin(Sn)in the segment to enhance its brittleness without changing the diamond concentration and particle size.However,an increase in Sn content will reduce the strength of the segment and may lead to adecrease in the holding force between CuSn al-loy and diamond.For example,the commonly used CuSn10 and CuSn15 pre alloy powders in industry have low strength and weak holding force on diamond.Therefore,it is necessary to improve the powder properties and pro-cessing technology.Methods:Adding Zn element to CuSn10 alloy powder can improve powder strength and holding force.CuSnZn-x alloy powder(mass fraction of Zn,x=10.00%,15.00%,20.00%,25.00%,30.00%)was prepared by at-omization process.The hot pressing sintering temperatures were 610℃,615℃,630℃,645℃,655℃,and the sinter-ing pressure was 21 MPa.The melting temperature of CuSnZn alloy powder was tested using adifferential thermal ana-lyzer.The density of the sintered segment was tested using Archimedes drainage method.The bending strength of the sintered segment was tested using mechanical performance testing equipment.The Rockwell hardness of the sintered segment was measured using aRockwell hardness tester.The microstructure morphology of the sintered segment and its fracture were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy.Other performances of samples with different Zn contents were analyzed and compared as well,namely theoretical density,Rockwell hardness,and flexural strength,to study the influence of Zn content on sample microstructure.Results:With the increase of Zn content,the rate of decrease in melt-ing temperature of CuSnZn alloy powder first increases and then decreases.When the Zn mass fraction is 30%,the melt-ing temperature decreases to 848℃,which is 164℃lower than that of CuSn10.As the Zn content increases,the brass in the sintered segment gradually transforms from the αphase to the α+β phase and then the α+β+β´phase,resulting in a significant increase in the Rockwell hardness of the segment.The bending strength of the sintered segment first in-creases and then decreases,reaching amaximum value of 542 MPa when the Zn mass fraction is 20.00%.When the mass fraction of Zn is 10.00%and 15.00%,obvious toughness dimples are observed on the fracture surface of the sintered segment,and particle peeling is observed on the fracture surface.The peeling surface is smooth and flat,indic-ating grain boundary peeling fracture of the phase structure.When the mass fraction of Zn is 20.00%and 25.00%,a large number of cleavage fracture surfaces are observed on the fracture surface of the sintered segment,and asmall amount of smooth concave transgranular fracture is observed,which is partially intergranular fracture and partially transgranular fracture.When the mass fraction of Zn is 30.00%,the fracture surface of the sintered segment is flat and smooth,and the crack passes through the phase interface and grain along the hard and brittle structure,which is trans-granular fracture.Conclusions:Adding Zn element can effectively reduce the melting point of alloy powder,and with the increase of Zn content,the hardness of sintered samples increases while the toughness decreases.When the Zn con-tent is 30.00%,the melting temperature of CuSnZn alloy powder reaches its minimum value.When the Zn content ex-ceeds 25.00%,the strength of the sintered samples will gradually decrease.Therefore,in actual production,the appropri-ate amount of Zn addition and sintering process should be selected based on comprehensive consideration of demand.
Key words CuSnZn alloy powder;density;intergranular fracture
