Factors influencing the quality of sexual life in the older adults: A scoping review
2023-05-14FengpeiZhangZhenYangXuehuaLiAipingWang
Fengpei Zhang,Zhen Yang,Xuehua Li,Aiping Wang
Public Business Department, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Keywords: Aged Influencing factor Sexual life Scope review
ABSTRACT Objective:Older people are often considered asexual,but sex is still important for older adults.So,this review aimed to analyze relevant studies on the sexual life of older adults to clarify factors,and provide a basis for their quality of sexual life.Method: A scoping review was performed according to Arksey and O’Malley’s framwork,aiming to identify eligible research studies in PubMed,Web of Science,CINAHL,and PsycINFO,Cochrane Library,and Scopus databases.Peer-reviewed articles published in Chinese or English language from January 2012 to April 2022 were retrieved.All of identified studies were screened,extracted,and analyzed independently by two researchers.Result:A total of 7,374 studies were retrieved,and 13 eligible studies were finally included.The factors affect the sexual quality of life in older adults that included physiological,sociocultural,and health factors and being affected by marital relationships and a lack of relevant knowledge.Conclusion:The factors that affect the quality of old people’s sex life interact and influence each other.Medical and health professionals can assist with the improvement of sexual health.
What is known?
·Fewer studies on the sexual lives of older adults have been conducted due to the sensitivity and specificity of the topics.
·Older adults are thought to be asexual due to social bias and people’s perceptions of their sexual lives.
What is new?
·This study used the method of scope review to synthesize the influencing factors of the sexual quality of life in older adults,and comprehensively analyzed the influence of the sexual quality of life in older adults.
·Physiological factors,health factors,social culture,marital status,economic status,education level,lack of relevant knowledge,and other factors influence the quality of sexual life.
·Factors influencing older adults’ sexual quality of life interact and influence each other.
1.Introduction
Sex is a core aspect of human life,including sexuality,gender identity and roles,sexual orientation,libido,pleasure,intimacy,and reproduction [1].According to reports,42% of women and 60% of men aged 65-74 still have active sex [2].Older adults continue to enjoy active sexuality at ages 70 and 80,with one-third having sex at least twice a month [3].
But some studies show that[4,5]the continuation of sexual life plays an important role in the life of older people.Physiologically,the sexual life of older adults helps promote blood circulation and the toughness and elasticity of skin,muscles,and joints.Sexual life can also expand arteries and prevent hypertension.Therefore,normal sexual life contributes to physical health [6].From the psychological aspect,sexual life is the inevitable result of the development of love as the sexual life of older adults will increase the love of elderly couples,increase the vitality of life,and enrich the content of life.A study showed that sexual life could influence older adults’subjective well-being and is positively associated with subjective well-being[7].Prolactin release in the brain after orgasm is associated with reducing stress and anxiety,and satisfactory sexual activity has proven to be a reliable way to reduce stress and relieve anxiety,helping people achieve good mental health [8].From the social perspective,older adults’ marital relationship or partnership represents a desire for sexual and emotional intimacy.A harmonious sexual life contributes to the harmony and stability of the older adults’ marital relationship and the harmony of the family relationship.The satisfied sexual life of older adults provides emotional and social support for the marital relationship,providing a basis for positive aging.
However,most studies on sex have excluded the older age population[9].The reasonable sexual needs of older adults cannot be expressed,and long-term repressive demand is beyond their tolerance;they will seek an unreasonable sexual satisfaction approach.The HIV infection rate among older adults is rising owing to a lack of knowledge about HIV and a lack of awareness about risk prevention.It has become one of the social problems that cannot be ignored.Prevalence and incident infections in people 50 and older are increasing faster than in the population.In the USA,between 2015 and 2019,the overall prevalence of people with HIV infection increased by 8%,and incident infections decreased by 4% [10].
In contrast,in people aged 50 years and older,prevalence increased by 40% and incidence by 15%.The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS(UNAIDS) estimates that the number of people aged 50 years or older with HIV infection globally increased from 5.4 million in 2015 to 8.1 million in 2020[10].It is a systematic project worth paying attention to exploring the impact on the sexual quality of life of older adults,guiding older adults to obtain the correct sexual satisfaction,and establishing the corresponding risk prevention awareness.
Researchers showed that the factors affecting the sexual quality of life in older adults lack systematic induction and arrangement.In China,the sexual life of older adults has not received much attention from too many people,and lack of related studies.Therefore,this study used a five-step systematic review of the relevant literature on factors affecting the sexual quality of life in older adults was conducted,aimed to analyze the influencing factors affecting the sexual quality of life in older adults to provide a foundation for improving the quality of sexual life of older adults.
2.Methods
2.1.Review design
The scope of the review report framework proposed by Arksey and O’Malley[11] is as follows: 1) establish the research problem;2) identify relevant studies;3) screen the literature;4) data extraction and data charts;5) organize and summarize;6) report the results.This study report follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews(PRISMA-ScR).
2.2.Establish the research problem
Relevant studies in the past ten years on the sexual lives of nonhospitalized older adults over 60 years were reviewed to identify the factors that influence the quality of the sexual lives of older adults.
2.3.Identify relevant studies
Develop retrieval strategies,use themes and free words as retrieval fields,and use advanced retrieval methods.The search terms are formulated using the PCO principles,P (Population),C(Concept),and O (Outcome).As retrieval words in English,“older adults”or“old people”or“aged,”“sexual”or“sexuality,”“quality of sexual life” or “sexual satisfaction,” and “sexual quality influence factor”were used.From January 2012 to April 2022,PubMed,Web of Science,CINAHL,PsycINFO,Cochrane Library,and Scopus were searched.Furthermore,manual retrieval ofSexual and Relationship Therapy,Journal of Aging and Health,International Journal of Nursing Studies,andSexual Science in Chinawere used for the present studies.The retrieval time is from database establishment to April 31,2022.Appendix A presents the retrieval strategy.
Studies that met the following criteria were included: 1) the participants in the study were over 60 years old,healthy,or with chronic disease;2) the research topic is the factors that influence the quality of sexual life in older adults;3) the types of literature included qualitative study,quantitative study,mixed study,literature review,systematic review,or meta-analysis;4) the language used is either Chinese or English.The exclusion criteria were included: 1) the participants were lesbians,gays,bisexuals,transgenders (LGBT),and queer older adults;2) the literature is an abstract and conference papers;3) full text unavailable;4) duplicate publications.
2.4.Study selection and data charts
Two researchers independently screened all literature.In the event of a disagreement,a third researcher was consulted to determine whether or not to include the information.The literature data extraction form is designed before data extraction,and the literature data is extracted based on the content of this form.The content includes the following information: literature author,publication country,publication time,research type,and influencing factors.
3.Results
3.1.Literature search results
In this research,a total of 8,895 articles were retrieved,where 493 themes were repeated,8,355 articles had reading titles and abstracts,47 articles remained,read the full text excluding 41 articles,seven articles were included through references,and 13 articles were included(Fig.1).
3.2.Basic characteristics of the literature
This study included 13 articles,including 8 English and 5 Chinese articles.Two were cross-sectional studies,nine were reviews,one was a systematic evaluation,and one was a book.Table 1 presents the details of the study.
3.3.Influencing factors
Thematic analysis was used in this study to read the literature repeatedly,extract the information from the literature,code the information,form the theme,summarize the theme,and finally,14 eligible studies,with five themes chosen from the literature: 1)physiological factors;2) sociocultural factors;3) health factors;4)marital relationship;and 5) lack of relevant knowledge(Table 1).

Table 1 (continued)
3.3.1.Physiological factors
Age and senescence lead to the decline of hormone levels,which affect the changes in sexual organs and sexual functions of older adults,thus affecting sexual desire and sexual experience.Eleven of the included literature mentioned the influence of physiological factors on the sexual life of older adults,as reported by researchers[12,13].There is less mucus secretion,weak ejaculation,and less semen secretion before ejaculation when men’s sexual desire declines and erections require more stimulation and last less time.The refractory period lasts for a long time.Increased sexual arousal,decreased vaginal lubrication,vaginal mucosa thinning,and painful sexual intercourse require more time in women,as does less frequency and intensity of orgasm.Table 2 presents all the details.
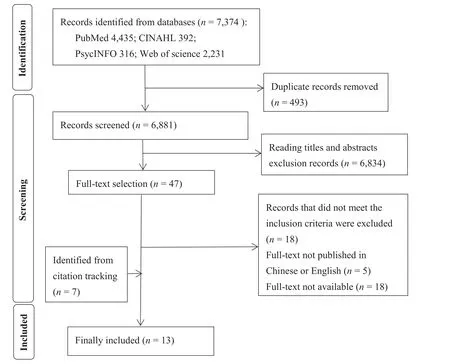
Fig.1.Flowchart of the study selection process.
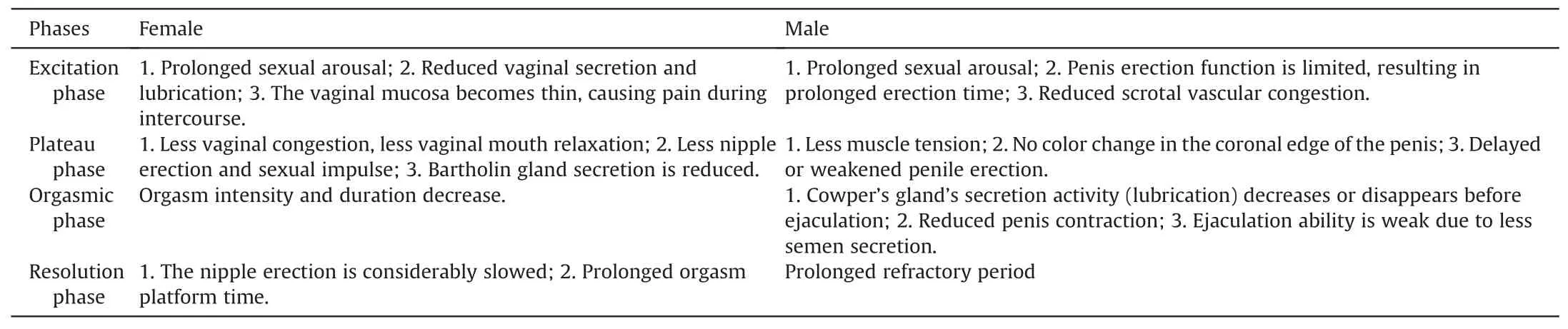
Table 2 Sexual physiological changes among older adults.
3.3.2.Social-cultural factors
3.3.2.1.Social biases.Sociocultural factors play an essential role in the sexual lives of older adults,“Age discrimination,” “stigmatization,” and “stereotypes” exist in people’s understanding.Older people are considered asexual;they are forbidden to live with sex and are not sexually desirable and incompetent [7].Thus,sex is a privilege reserved for young people.Some even regard older people’s sexual behavior as abnormal,stupid,or embarrassing,labeling them asexual.These stereotypes cause older people to suppress their sexual needs and even stop having sexual relationships [14].Some find older people’s sexual lives amusing,while others associate sex with physical attractiveness and beauty.This disgusting stereotype makes older adults feel ashamed or guilty about sexual desire,afraid of being labeled “inappropriate,” or “weird,”“obscene,”or“dirty old people,”and thus suppressing their sexual needs [15].
3.3.2.2.Economic status and education level.Researchers believe that education affects the sexual life of older adults,and older people with higher education levels have better acceptance and tolerance towards sex [16].They mentioned the influence of economic status on the sexual desire of older adults in their studies[16,17].When the economic situation was superior,the sexual desire of older adults would be enhanced.In older people,libido declines because of financial constraints.
3.3.2.3.Cognitive attitude of older adults towards sex.Some older people believe sex becomes less important as they age because sex is only essential to young people[9].They believe that sexual ability deteriorates with age,and old age restricts their sexual life.As their sexual function declines,older men increasingly“cannot,” “should not,” or “do not need” psychological expression and doubt their sexual ability [18].Women are traditionally defined as mothers who lose their ability to reproduce after menopause and believe they have no reason to engage in sexual activity.As a result,they decide to forego having a sexual life [9].
3.3.3.Health factors
3.3.3.1.Physical health status.Good health is associated with continued sexual life;however,illness accompanies older adults after old age.Abhishek Ramesh et al.showed that some diseases could harm the sexual function of the older adults,and these diseases affect the sexual needs and confidence of older adults in the process of sexual life [10].Researchers also stated that one of the most common reasons for older people discontinuing sex is physical illness [11].Sometimes a decrease in sexual life is caused by unfounded health anxiety(for example,following a heart attack or stroke)[24].Sexual encounters become exhausting or painful(e.g.,respiratory disease or arthritis).Diseases that impair the sexual organs’ responsiveness (e.g.,diabetes or peripheral vascular disease).A disease reduces one’s self-esteem or attractiveness(such as mastectomy or colostomy),including libido (e.g.,depression,liver failure,and Parkinson’s disease) [19].
The treatment of diseases is accompanied by applying drugs,such as antidepressants,antipsychotics,benzodiazepines,antihypertensive drugs,thiazide diuretics,statins,and anticonvulsants that can interfere with sexual function.Drugs such as levodopa,lamotrigine,and trazodone have excessively irritating functions[10].
3.3.3.2.Mental health.Researchers analyzed National Social Life,Health,and Aging Project (NSHAP) data and reported that anxiety scores correlated with sexual difficulty in both men and women[19].Increased anxiety is associated with a lack of sexual interest in women and men with orgasmic disorder and a lack of sexual pleasure in women [25].Depressive symptoms are related to the orgasmic disorder and erectile in men.Researchers showed that anxiety affects the sexual function of the older adults,especially the sexual arousal ability of women,which may be related to excessive vigilance and concern [26].According to the literature,older women with psychiatric symptoms and poor psychological status had lower libido.Simultaneously,depression can also cause sexual function problems.Yu et al.found that anxious older adults had significantly lower sexual life quality than non-anxious older adults.Lack of or reduced sexual life quality would also increase the risk of psychological problems in middle-aged and older adults,with mutual influence between the two [27].
Researchers mentioned that the burden of caring is a common experience of older adults.Caring for sick partners puts pressure on older adults,especially when the partner is physically weak or suffers from dementia [12].Family caregivers can experience fatigue,guilt or resentment,financial stress,and other worries that affect their sexual life in intimate relationships [28].Therefore,there is a positive correlation between mental health and sexual function in later life.
3.3.4.Marital relationship
Stable sexual partners influence the sexual quality of life in older adults.The feasibility of a partner’s sexual life is linked to the quality of both couples’ sexual lives,and many women do not engage in sexual activity when they are not with a partner.Garrett pointed out in her study that the biggest obstacle to sexual behavior is the lack of a partner.The loss or absence of a partner significantly impacts one’s sexual life.Furthermore,a satisfying sexual life is often the result of many years of intimate feelings,unified communication,and good relationships [19].
3.3.5.Lack of relevant knowledge
3.3.5.1.Lack of sexual health-related knowledge.One of the primary causes of sexual dysfunction in older adults is a lack of sexual knowledge and sexual ignorance.The perception of sexual problems as a“normal”part of aging prevents older people from seeking treatment for sexual problems.They do not address sexual problems because they lack relevant information about sexual health,claiming that sexual dysfunction is health-irrelevant[20].
3.3.5.2.Lack of guidance on sexual life in the state of disease.
After major health events(such as a heart attack or concerns about negative health consequences for themselves or their partners),older people mistakenly believe they should not have sex[12].Even older people will stop having sex because of their partner’s illness[20].
3.3.5.3.Lack of relevant knowledge among medical professionals.
Many older people believe that healthcare providers do not provide adequate information about sexual problems or have sufficient knowledge to resolve sexual issues[20].Ramesh et al.[13] argued that health professionals lack knowledge about the sexuality of older adults.Negative attitudes and a lack of sufficient expertise were widespread.It is also challenging for many health professionals when discussing sexual issues with older people,who need more evidence of supportive sexual life and provide realistic and encouraging sexual advice [19].
4.Discussion
4.1.Multiple factors simultaneously affect the sexual quality of life of older adults
Physical aging in older adults causes changes in physical appearance,including sexual organs and functions.Thus,older adults are no longer regarded as attractive or sexually capable and are considered asexual and no longer in need of sex.Sexual life is thought to be associated with youth,and the sexual lives of older adults are regarded as a “should not.” These prejudices prevent older people from adequately expressing their sexual needs,leading to incorrect perceptions of older adults when influenced by social bias.They feel they no longer need sexual life when they are old,and sexual life is “old and not respected.” Even if they encounter problems in sexual stamina or issues that seriously impact the quality of their sexual life,they are ashamed to seek help.These factors tend to cause older adults to suppress or discontinue having sex,even if they have sexual needs.Sexual needs and sexual perception in later life are determined by both sexual knowledge and attitudes toward sex,and the two have a significant positive relationship [29].A lack of sexual knowledge affects the healthy and reasonable sexual life of older adults.If older adults experience long-term illness,the disease tends to affect the quality of their sexual lives.The disease and its related treatment bring many challenges to intimacy and sexual life.Sexual ability is affected by illness and psychological factors (anxiety,depression).Older people and their partners are often unaware of the impact of disease on sexual life or are restricted in their ability to obtain information.Many older adults abstain from sexual activity because they lack knowledge about it.The lack or reduced quality of sexual life can affect the mental health of older adults.Studies showed that a lack of or reduced quality of sexual life had a causal relationship with negative psychological problems[20,30].Dopamine secretion in the nervous system is increased by healthy and appropriate sexual behaviors,promoting negative emotional resolution[31-33].Emotionally related sexual function can be harmed by negative psychological issues [27].Sexual disharmony may affect the intimate relationship between couples or partners and the quality of sexual life in older adults.Furthermore,this disharmony will place psychological pressure on older adults,which is not good for their health.It is not a single factor that influences the sexual life quality of older adults but rather the cumulative effect of many factors.Thus,improving the quality of life of older adults should be addressed in various ways.
4.2.The role of medical and health professionals in improving the sexual quality of life of older adults
Sex and intimacy are essential for an older adult’s health;some still desire sex.Health professionals should discuss these issues with older adults,keep an open mind,have an open conversation,provide“one-on-one”discussions,and provide guidance or advice.Health professionals should increase the availability of sexual information and education so that older people know that a reasonable sexual life is healthy,can reduce stress,prevent some diseases,and promote harmony in intimate relationships,as well as publicizing knowledge related to the sexual lives of older adults,providing sexual life strategies and intervention measures in the case of disease.In addition,older adults should be encouraged to seek professional help to obtain correct guidance to prevent them from ignoring their sexual needs and prevent sexually transmitted diseases among older adults to some extent.
5.Limitations
There are some limitations of this study.Because of cultural differences and language limitations,there are few studies on the quality of sexual life in the older adults,so there is no comprehensive search of non-English databases.Due to less literature retrieval,there may be an incomplete summary of influencing factors.This study only described the included literature,and the quality of the literature was not evaluated.Furthermore,there is limited literature on similar topics,so that the follow-up research topic can be expanded.
6.Conclusion
Sexual problems in older adults are medically necessary and socially significant.The quality of sexual life in the older adults are affected by physiological factors,social-cultural factors,health factors and other factors,and these factors were found to influence each other.Treating older adults’sexual lives correctly and guiding them to a healthy sexual life is critical in promoting the healthy aging of older adults.
Funding
Nothing to declare.
Data availability statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
CRedit authorship contribution statement
Fengpei Zhang: Conceptualization,Methodology,Validation,Formal analysis,Investigation,Data curation,Writing -original draft,Writing -review &editing,Project administration.Zhen Yang:Conceptualization,Methodology,Validation,Formal analysis,Investigation,Resources,Data curation,Writing-review&editing,Resources.Xuehua Li: Methodology,Validation,Formal analysis,Investigation,Resources,Writing-review&editing.Aiping Wang:Conceptualization,Methodology,Validation,Writing -review &editing,Supervision,Project administration.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Appendices.Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2023.03.006.
杂志排行
International Journal of Nursing Sciences的其它文章
- A feasibility study on home-based kyphosis-specific exercises on reducing thoracic hyperkyphosis in older adults
- Development and validation of dynamic nomogram of frailty risk for older patients hospitalized with heart failure
- Validation of the Portuguese version of the social isolation scale with a sample of community-dwelling older adults
- Effects of pre-operative education tailored to information-seeking styles on pre-operative anxiety and depression among patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: A randomized controlled trial
- Comparison of the effects of three kinds of hand exercises on improving limb function in patients after transradial cardiac catheterization
- The trajectories of physical growth in 4 months postnatal corrected age among preterm infants discharged from neonatal intensive care units and associated factors: A prospective study
