Comparison of the effects of three kinds of hand exercises on improving limb function in patients after transradial cardiac catheterization
2023-05-14XinyueZhangZhipengBaoLanWeiZairanZhangYanliHuDandanXuWeiSunDongmeiXu
Xinyue Zhang,Zhipeng Bao,Lan Wei,Zairan Zhang,Yanli Hu,Dandan Xu,Wei Sun,Dongmei Xu
Department of Cardiology,The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University,Nanjing,China
Keywords: Coronary artery disease Dynamometer Exercise Edema Pain Percutaneous coronary intervention
ABSTRACT Objectives: This study aimed to compare effects of different hand exercises on improving limb function in patients after transradial cardiac catheterization.Methods:This single-center,randomized clinical trial was conducted from August 20,2020,to July 20,2021,at an academic medical center.A total of 102 participants were selected from a Class A tertiary hospital in Nanjing,China and randomized into three groups: finger exercise group (n=34),acupoint massage group (n=34),and handgrip exercise group (n=34).Symptoms of edema and pain were defined as primary outcomes,while skin temperature and degree of bleeding as secondary outcomes,which were monitored and measured 1,2,and 4 h,after the intervention.Results:Among the 99 participants who completed the process,the palm edema was gradually relieved in the handgrip exercise group at 2 h(H=6.710,P=0.035)and 4 h(H=10.060,P <0.001)following the intervention.The edema of fingers in the handgrip exercise group was obviously relieved at 2 h (H=9.353,P <0.01) and 4 h (H=10.699,P <0.001) following the intervention compared with the other two groups.In addition,the pain score at 4 h (H=7.048,P=0.029) was clearly decreased in the handgrip exercise group.However,there was no significant difference in the punctured limb’s skin temperature (H=0.922,P=0.631) and the degree of bleeding (H=0.123,P=0.940) among the three groups.Conclusions:We found that handgrip exercise is more effective in reducing the edema of the limbs than finger exercise and acupoint massage.
What is known?
·Nurses have a substantial role in promoting the rehabilitation and improving the comfortable postoperative experience for patients receiving transradial cardiac catheterization.
·Effective functional exercises which might improve patients’comfort experience need to be validated.
What is new?
·Handgrip exercise was found more effective in reducing the edema of the limbs than finger exercise and acupoint massage.
1.Introduction
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a surgical intervention for relieving the narrowing or occlusion of the coronary artery.The transradial approach (TRA) is the recommended technique by the European Society of Cardiology guidelines for PCI in acute coronary syndrome[1,2].Also,the TR band(Anscare Medical,Jiangsu,China)is a compression device that assists in radial artery hemostasis after TRA [3].With increasing experience of coronary angiography,TRA complication rate is decreasing;yet,new complications and risks are being described,such as artery occlusion,radial artery spasm,radial artery pseudoaneurysm,arteriovenous fistula,nerve damage,complex regional pain syndrome with different incidence[4].The incidence of radial artery occlusion and radial artery spasm varies widely from 1% to 30% [4] and may occur within 24 h after surgery.Especially,edema and pain are the most common symptoms,which can seriously affect the patient’s comfort and may induce radial artery spasms [5,6].Bleeding complications,which may be occurred in 16% of indicated patients,may reduce the postoperative safety of patients and affect their prognosis of patients [7].These uncomfortable experiences,such as swelling and pain,can be relieved by non-medical means,which fully reflects the attention to patients’ subjective experience and improves the quality of hospitalization.
The complications and management after transradial cardiac catheterization have attracted the attention of cardiovascular scholars and societies[4].From the perspective of clinical nursing,to improve the common uncomfortable experiences,many methods have been tried to relieve the discomfort in the limbs,including the elevation of the operated limb,acupoint massage[8,9],and finger exercise [10].For example,the elevation of the operated limb can promote better venous return and reduce swelling.However,due to the use of a pressor,this method is not effective enough and can be used as an auxiliary hand movement.Acupoint massage is a traditional Chinese medicine treatment that can increase the secretion of endorphins in the body’s pain relief system,activate thick fibers,block the impulse of pain fibers,and weaken the body’s sensitivity to pain[11].However,since acupoint massage involves many acupoints,the steps of finger exercise may be complicated,and the patient’s compliance with body movements is poor.The major limitation of finger exercise involves delicate movements of several small joints and a combination of movements,causing patients to forget the content and sequence of activities easily.
Previous research indicated that handgrip exercise with a dynamometer as a medium could guide patients to perform functional exercise and promote blood circulation in the upper limbs[12].Furthermore,a previous study reported that handgrip dynamometers could promote blood circulation and increase the blood flow of the radial artery and cephalic vein[13].In the Hand Grip test After Transradial(HANGAR)study,the hand dynamometer applied in patients who underwent transradial PCI promoted the recovery of hand strength[14].In addition,another study demonstrated that low-intensity,short-duration handgrip exercise produces significant elevations in blood pressure [13,15].Furthermore,such isometric handgrip exercise can mobilize the muscles of hand exercise,which has been found to be beneficial for reducing resting arterial pressure in hypertensive individuals[16].Moreover,regular handgrip exercise can improve cardiovascular stress in patients diagnosed with coronary artery disease(CAD)[17].Together,these observations collectively suggest that handgrip exercise helps to promote blood circulation in local limbs.However,whether this handgrip exercise can benefit CAD patients with postoperative limb edema and comfort remains unclear.In particular,there is no comparative analysis with the existing exercise programs such as acupoint massage and finger exercise.Hence,this study aimed to explore the effectiveness of this method and determine which is more conducive to alleviating patients’ discomfort while ensuring its safety.
2.Method
2.1.Study design
This single-center,randomized clinical trial was conducted from August 20,2020,to July 20,2021,at an academic medical center.The computer-generated random allocation number was used to divide participants into three groups,i.e.,finger exercise group,acupoint massage group,and handgrip exercise group.The randomization list was uncovered in the sequence until the patients were confirmed to be enrolled.Patient enrollment was made by an external controller who was blind to the study design.
2.2.Setting and participants
Patients were included from a Class A tertiary hospital in Nanjing according to the following criteria: 1) patients older than 18 years of age diagnosed with CAD who underwent transradial cardiac catheterization;2) positive Allen’s test and the TR band applied after sheath procedure via the radial artery;3) patients willing to perform limb exercise.Exclusion criteria were: 1) diagnosis with coagulation dysfunction;2) the operative limb had a skin infection;3) repetitive radial artery procedure,which might impair blood vessels and its restoration.During the trial,if postoperative bleeding at the puncture site required the replacement of the TR band or deterioration of patients’ condition was observed,that patient was excluded from the study.The sample size was calculated using the following formula [18]:α was set to be 0.05,and β was 0.1.Considering the expected attrition rate of around 20%,the required sample size was 102 participants.
2.3.Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University(approve number:2021-SRFA-329).All participants provided written informed consent.
2.4.Intervention procedure
Coagulation functions in the three groups were all normal before operation.All enrolled patients received dual antiplatelet therapy.The hemostatic device consisting of 1 compactly folded gauze and a TR band was used to compress the wound after the operation[3].The gauze positioned above the arterial puncture site was secured by the TR band,which is a spiral pressure device that relaxes and tightens by rotating.It usually rotates 3 turns after surgery to prevent hemorrhage.A half circle of pressure was sequentially released from the TR band while the pressure of the TR band was decompressed 1 h after the operation.The following three types of hand exercises were started after patients returned to the ward and were in stable condition(usually half an hour after surgery);the treatment lasted 6 h.Each group of exercises was performed every 20 min.These three kinds of hand exercises were carried out by 5 trained ward nurses;the exercise was examined by the project leader.
2.4.1.Finger exercise group
Patients received finger exercises one day before the operation and were required to follow certain steps recorded in an educational video.Active hand movement methods were summarized as six-step finger exercises,including “grip,touch,count,press,stretch,and play”with the surgical side elevated at 30°(Fig.1)[19].“Grip”: involved stretching out the five fingers,turning palms up,and then making a fist;“Touch”:involved the thumb touching the index finger,middle finger,ring finger,and little finger,respectively;“Count”: involved stretching the five fingers,bending the thumb,index finger,middle finger,ring finger,and little finger for many times;“Press”: involved stretching the five fingers,pressing the index finger,middle finger,ring finger and little finger with the thumb in turn;“Extend”: involved putting five fingers together,turning palm up,and then stretching out five vigorously;“Play”:involved using the thumb to hold down the fingertips of the index finger,middle finger,ring finger,and little finger respectively,and then popping the index finger,middle finger,ring finger,and little finger.Each step was performed alternately 10-15 times.
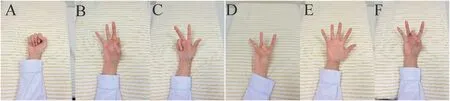
Fig.1.The six-step finger exercise.(A) Grip;(B) Touch;(C) Count;(D) Press;(E) Stretch;(F) Play.
2.4.2.Acupoint massage group
In this group,based on raising the surgical hand by 30°,each finger and the palms were massaged by a caregiver for 1 min.Then,each acupoint(Hegu,Houxi,Waiguan,and Shousanli)was pressed 10 times (Fig.2).The targeted acupoints were marked by the investigator,and caregivers were taught to do the massage following the above methods.
2.4.3.Handgrip exercise group
The operated hand’s maximum voluntary contraction (MVC)was measured twice before surgery.The mean of two readings was calculated according to visual feedback obtained using the dynamometer.Postoperative patients squeezed the dynamometer with the maximum endurance of the surgical side limb at 10%-15%MVC,which was concluded from the preliminary experiment in consideration of the safety of the puncture sites(Fig.3).The slope pillow supported the forearm of the operative hand at 30°.Participants were thereafter instructed to squeeze and loosen the dynamometer 30 times at 10%-15% MVC in 1 min.The procedure was repeated twice for each training session with a 5-min rest to avoid the extreme pressor responses elicited by fatiguing isometric efforts.
2.5.Measures
The circumference of the palm and middle finger generally evaluated the degree of distal limb edema.The middle fingers were used as indicators to assess phalanx swelling[20,21].The outcomes included a symptom of edema and pain score as primary outcomes,with the degree of bleeding and skin temperature as secondary outcomes.Because the patient had finger edema that even spread to the entire palm,the degree of edema was evaluated by measuring the circumference of the finger and palm.Considering that the pressure hemostasis time of the TR band compressor was generally 4-6 h after the time was exceeded,the pressure was completely relieved.Therefore,the edema and skin temperature symptoms were monitored and measured at 1,2,and 4 h after the intervention and the pain score was assessed 4 h after the intervention.In addition,compression at the puncture site was removed 24 h after the operation,at which time the degree of bleeding was clearly observed.
2.5.1.Symptom of edema
The following steps were used to measure the circumference of the palm: first,palms were placed together,starting from the midpoint of the second knuckle of the thumb,and the length of one circle of the palm was measured;second,excluding the thumb,one circle was made around the palm inside and outside the horizontal lines;finally,the average of the two measurement results was used as the circumference of the hand.Similarly,middle finger circumference was assessed by two measurements of the middle proximal phalanges.
2.5.2.Pain score
Patient’s pain was assessed by the visual analogue scale (VAS)[22],where 0 indicated no pain and 10 indicated the most pain.According to the degree of pain,the patient chooses a number to represent the degree of pain.The higher the score,the more severe the pain.
2.5.3.Skin temperature
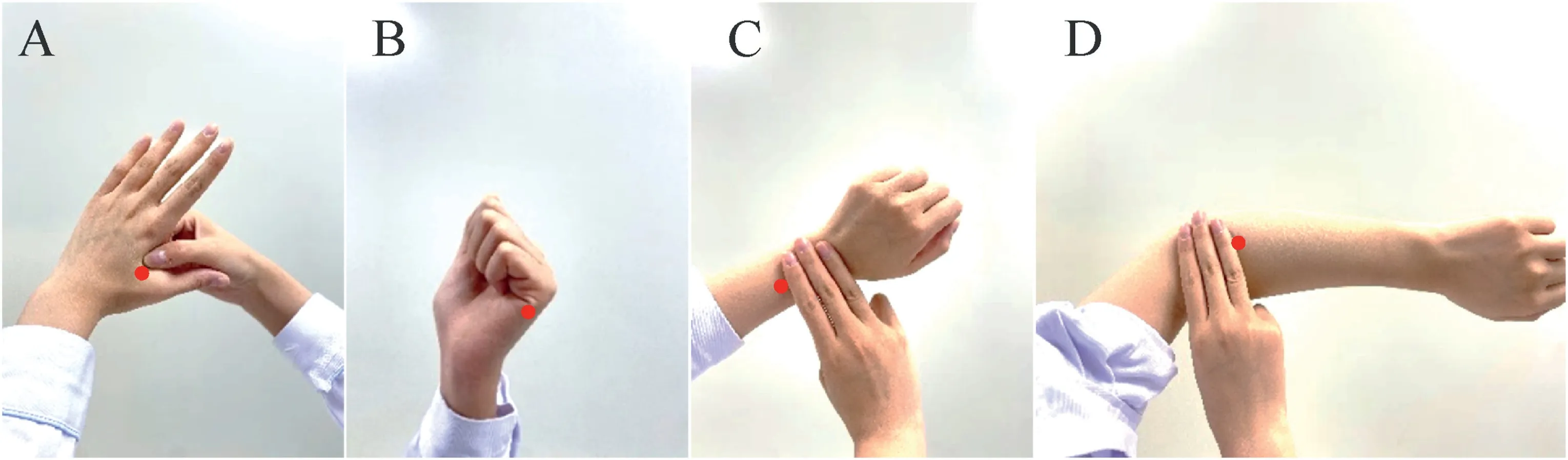
Fig.2.The four acupoints on the hand.(A) Hegu;(B) Houxi;(C) Waiguan;(D) Shousanli.
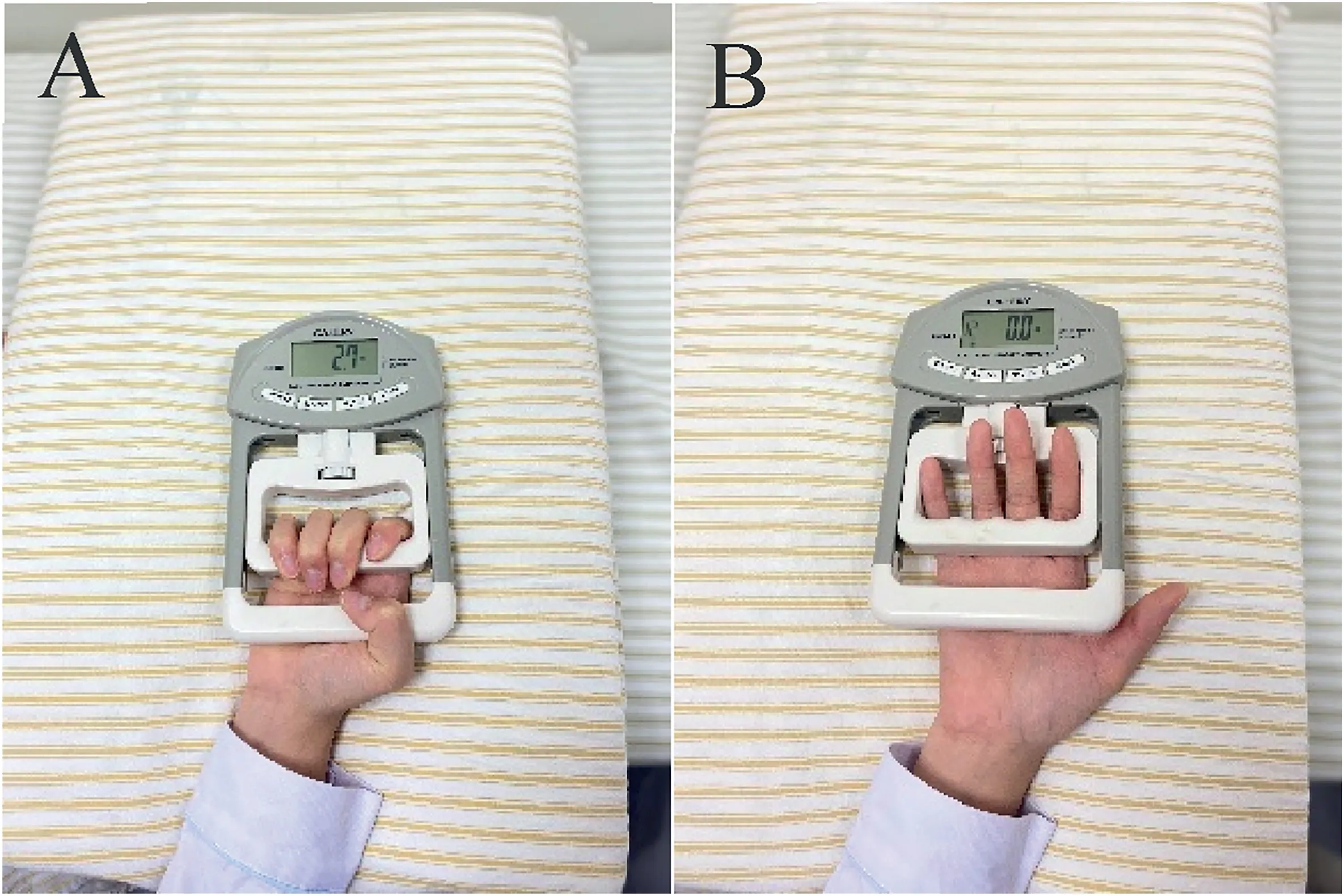
Fig.3.The hand-held dynamometer.(A) Squeeze;(B) Loosen.
The skin temperature was measured with the forehead thermometer;the average temperature of the middle finger,the thenar,and the back of the hand were measured.All trials were performed in the soundproof room with the temperature maintained at 24± 2°C.
2.5.4.Degree of bleeding
The degree of bleeding was assessed after 24 h and divided according to Christenson’s judgments [23]: 1) no bleeding at the puncture site;2)mild bleeding:the diameter of the puncture site <2 cm,or the diameter of the hematoma in the forearm was <2 cm;3) obvious bleeding:the diameter of the puncture site was >2 cm,or the diameter of the hematoma in the forearm was >2 cm,even requiring another pressure dressing.
2.6.Data collection
Researchers uniformly trained data collectors on how to measure palm circumference,skin temperature and pain score.Nurses explained to patients that a score of 0 indicated no pain,1 indicated slight pain,and 10 indicated severe pain to help them quantify the degree of pain.The data recording was conducted under the unified supervision of the researchers.
2.7.Data analysis
SPSS 24.0 statistical software was used for data analysis.Continuous variables were described as either mean (standard deviation) or median (interquartile range),whereas categorical variables were given as numbers (percentages).One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for data conforming to a normal distribution,and a non-parametric test was used otherwise.The Scheff′e test was used to compare any two groups.The chi-square test was used for categorical data.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1.The participants’ demographic and clinical health characteristics
From August 2020 to July 2021,a total of 102 CAD patients were randomized into the finger exercise group (34 patients),acupoint massage group (34 patients) and handgrip exercise group (34 patients).Finally,treatment was completed by 32 patients in the finger exercise group,34 in the acupoint group and 33 in the handgrip exercise (3 patients withdrew from the treatment halfway because of a violation of the protocol).There were no significant differences in age,sex,history of the disease,diseased vessels,palm circumference,finger circumference,and pain perception between the 3 groups (allP>0.05) (Table 1).
3.2.The symptom of edema and pain
Among the three groups,there was no reduction in the middle finger and palm circumference at 1 h (H=3.569,P=0.168;H=1.862,P=0.394).However,the edema of patients’ middle fingers in the handgrip exercise group was gradually relieved at 2 h(H=9.353,P<0.001) and 4 h (H=10.699,P<0.001) after the intervention compared with the other two groups.Similarly,the edema of patients’ palm in the handgrip exercise group was gradually eased at 2 h (H=6.710,P=0.035) and 4 h (H=10.060,P<0.01) following the intervention compared with the other two groups.More precisely,the difference in circumference of patients’middle finger and hand in handgrip exercise was significantly greater compared to the acupoint massage group and finger exercise group.Also,there was no difference between the acupoint massage group and the finger exercise group according to the Scheff′e test.Meanwhile,the pain score at 4 h(H=7.048,P=0.029)was decreased in the handgrip exercise and was lower than that in the acupoint massage group and finger exercise group,while there was no difference in the acupoint massage group and finger exercise group(Table 2).
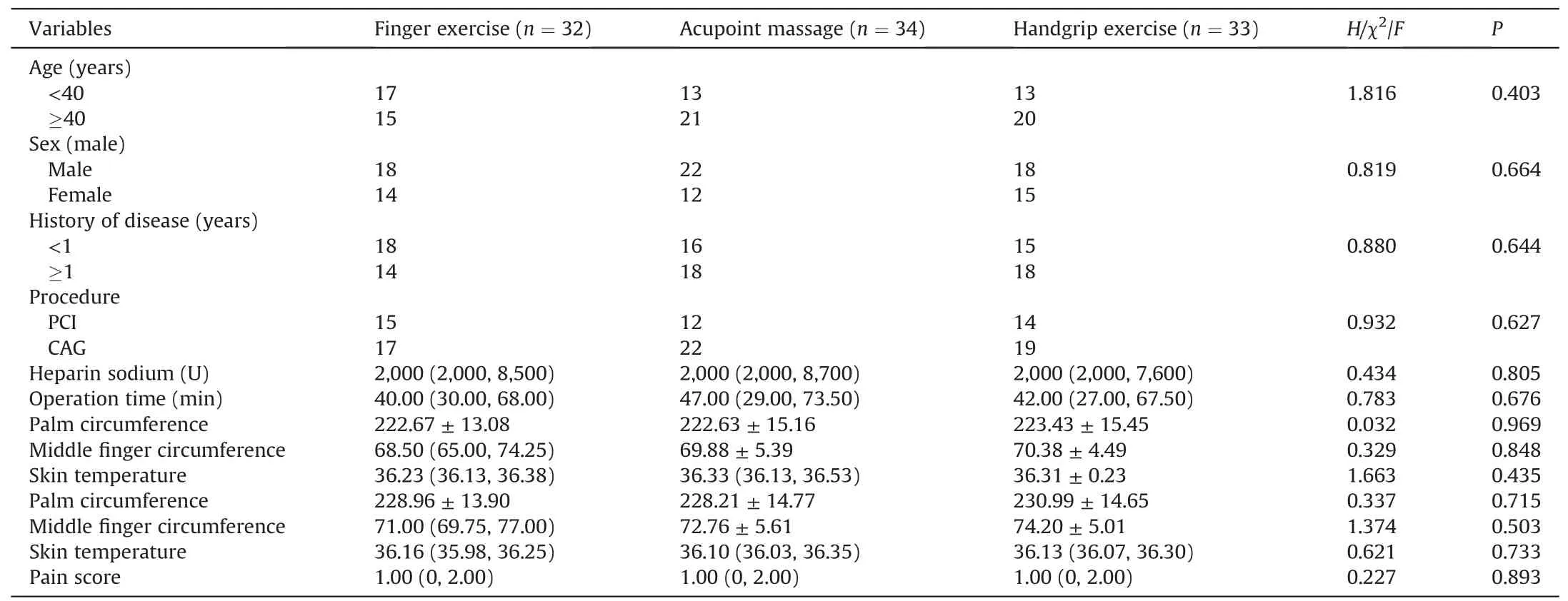
Table 1 Characteristics of patients at baseline.
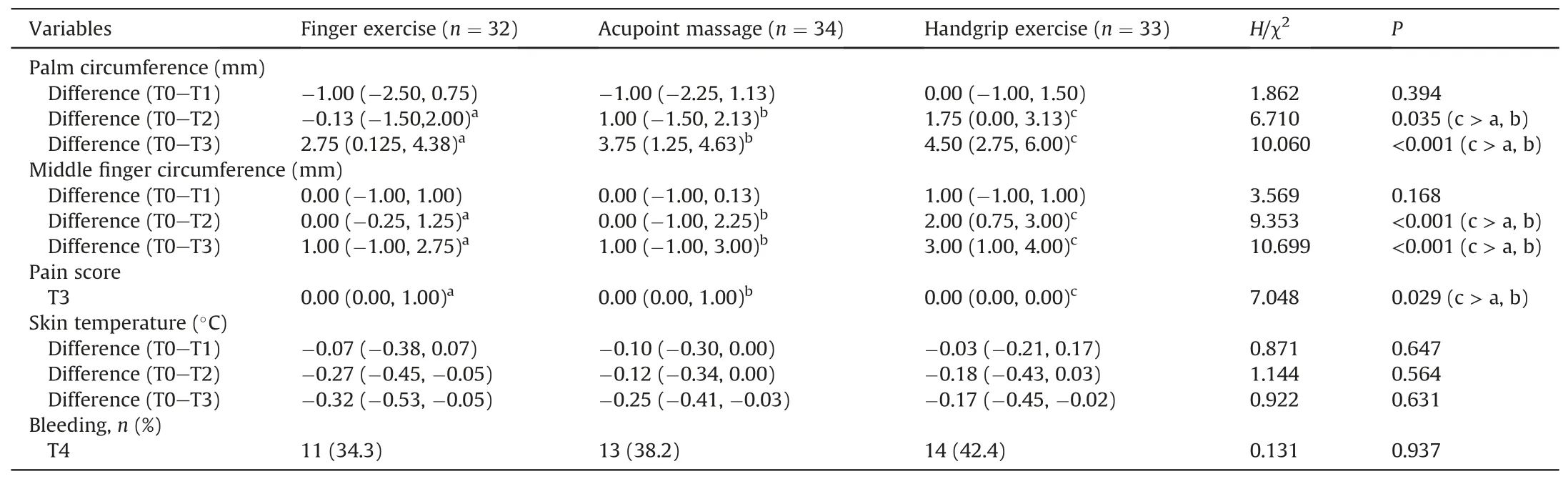
Table 2 Comparison of pre-and post-intervention outcomes between participants with different methods
3.3.The skin temperature and bleeding
In terms of safety,the skin temperature of hands was gradually recovered in all three groups,which identically shown no significant difference (H=0.871,P=0.647;H=1.144,P=0.564;H=0.922,P=0.631).Besides,bleeding from the puncture site after surgery was seen in all patients,and there was no significant difference in the degree of bleeding among the three groups(H=0.123,P=0.940) (Table 2).
4.Discussion
In this trial,we investigated the effect of common hand exercises on the comfort of surgical side limbs.Considering the safety of those three training methods on surgical limbs by comparing the degree of bleeding at the puncture site,there was no significant difference in the three groups.More importantly,we found that handgrip exercise was more effective in reducing the edema of the limbs than finger exercise and acupoint massage.The hand-held dynamometer exercise significantly reduced the palm circumference and middle finger circumference starting from the 2 h postintervention;during this period,the gap in middle finger circumference before and after an intervention gradually widened from 2.00 mm to 3.00 mm.As expected,the edema of the middle finger and even other fingers in the handgrip exercise group was obviously relieved compared with other groups.Also,the palm circumference decreased by 1.75 mm,even 4.5 mm from the 2 h.The degree of improvement in edema in the handgrip exercise group was better compared to other groups,while the differences between the other two groups were not significant.This may be due to the peripheral blood circulation starting from the fingers and gradually extending to the palm.More interestingly,our study continued to trace the changes up to 6 h after surgery and found that the degree of edema of the limbs of the three groups of patients gradually stabilized,which may be due to the gradual relaxation of the patients’ wound pressure in the sixth hour,allowing the targeted limb to return to normal blood flow.
The dynamometer application could significantly relieve the edema of limbs in CAD patients within 2-4 h after surgery,which aligns with the concept of rapid functional recovery of postoperative trauma.Straining compression on the puncture site to accelerate hemostasis is common for CAD patients after transradial access.Regularly releasing the pressure of the puncture site,coordinated with physical activities,can help to better relieve the edema of the limbs.Studies have shown that two main factors,muscle and respiratory pumps,are recognized as the peripheral venous return to the heart [24].Hand exercises,such as grasping empty fists and gripping hand muscle developer,can increase venous return without the influence of systemic circulation[25].As a way of the venous return,simply performing finger movements or acupoint massage may not have a significant intervention effect due to the small degree of muscle contraction.Instead,handgrip exercise is conducted to utilize the promoting effect of the muscle pump on peripheral venous flow velocity.Also,using a dynamometer for resistance training and handgrip exercise can help stretch the forearm muscles,contract the flexor muscles of the hand,and effectively promote the return of blood and lymph.Masashi et al.[26]reported increasing isometric exercise intensity shifting the threshold of the muscle metaboreflex to higher blood flow levels.Additionally,grasping the dynamometer at a frequency of 25 times/min is favorable for improving hemodynamics to the greatest extent[12].In their study,Comerota et al.[27]explored the mechanism of physical exercise on peripheral blood flow and found that this type of exercise can help to increase fibrinolytic activity and reduce plasminogen activator-1,thereby increasing tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-RA) and enhancing plasmin dissolution,which increases blood flow velocity and promotes blood circulation.Unlike other resistance training,such as gripping a bouncy ball,the hand-held dynamometer exercise can restore gripping strength by avoiding excessive or insufficient grip strength,thus affecting the handgrip exercise [28].Regarding operability,a gripping dynamometer gives patients a sense of grasping an object to improve their compliance,distracting patients’ attention and relieving pain perception.
According to the statistical results,there was no difference in skin temperature at each time point in the three groups,possibly due to the following reasons: first,there was no significant difference in skin temperature before the operation,and the external room temperature was relatively constant,so it had little effect on local skin temperature;second,the local skin temperature is also related to the human core temperature,and the body temperature of the patients in each group was normal.Therefore,the local palm temperature fluctuation range was small,and the difference was not statistically significant.As for the degree of bleeding,the coagulation function of the three groups was normal,and there was no significant difference in the amount of heparin used during the operation,which had a little different effect on the degree of bleeding at the puncture site.In addition,the grip strength of the handgrip exercise group was also in the safe range,so the safety of the three functional exercise methods was relatively consistent.Yet,more in-depth and accurate reasons need to be further explored.
5.Limitations
The present study has some limitations.First,the circumference of the palm and middle finger significantly recovered 4 h after the intervention;yet,further long-term observation is needed.This also makes it difficult to judge when the swollen limbs can return to their original circumference.Second,we set the gripping strength of the intervention group at 10%-15% MVC according to the preliminary experiment but did not further explore how much MVC is suitable for CAD patients after the transradial approach.Therefore,more intensive studies are needed to investigate the effect of handgrip exercise on the postoperative function of limbs and what range of MVC is the most conducive to limb recovery.
6.Conclusion
Employing the electronic dynamometer to perform handgrip exercise can effectively promote blood circulation and relieve limb edema for CAD patients after transradial access.In the handgrip exercise group,the edema of the finger has been eased,and the circumference of the hand has decreased after the intervention compared to the other two groups.Furthermore,our results showed that this approach positively affected the patient’s pain perception,which was relieved from the 4 h after intervention and could also guarantee the security of the handgrip exercise.
Funding
This study has been supported and funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.72204120) and Young Scholars Fostering Funding of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (PY2021047).
Data availability statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Xinyue Zhang:Conceptualization,Software,Investigation,Resources,Data curation,Writing-original draft,Funding acquisition.Zhipeng Bao:Software,Validation,Formal analysis,Visualization.Lan Wei:Validation,Investigation.Zairan Zhang:Investigation.Yanli Hu:Investigation.Dandan Xu:Investigation.Wei Sun:Conceptualization,Methodology,Visualization,Writing-review &editing.Dongmei Xu:Conceptualization,Methodology,Supervision,Resources,Project administration.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate all the beneficial comments given by our instructor and members of research group.
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2023.03.011.
杂志排行
International Journal of Nursing Sciences的其它文章
- A feasibility study on home-based kyphosis-specific exercises on reducing thoracic hyperkyphosis in older adults
- Development and validation of dynamic nomogram of frailty risk for older patients hospitalized with heart failure
- Validation of the Portuguese version of the social isolation scale with a sample of community-dwelling older adults
- Effects of pre-operative education tailored to information-seeking styles on pre-operative anxiety and depression among patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: A randomized controlled trial
- Factors influencing the quality of sexual life in the older adults: A scoping review
- The trajectories of physical growth in 4 months postnatal corrected age among preterm infants discharged from neonatal intensive care units and associated factors: A prospective study
