电子束熔化成形与锻造Ti6Al4V合金的腐蚀行为对比研究
2023-04-29邓浩周吕俊张海成罗恒军谢静向伟邱文彬陈龙庆
邓浩 周吕俊 张海成 罗恒军 谢静 向伟 邱文彬 陈龙庆
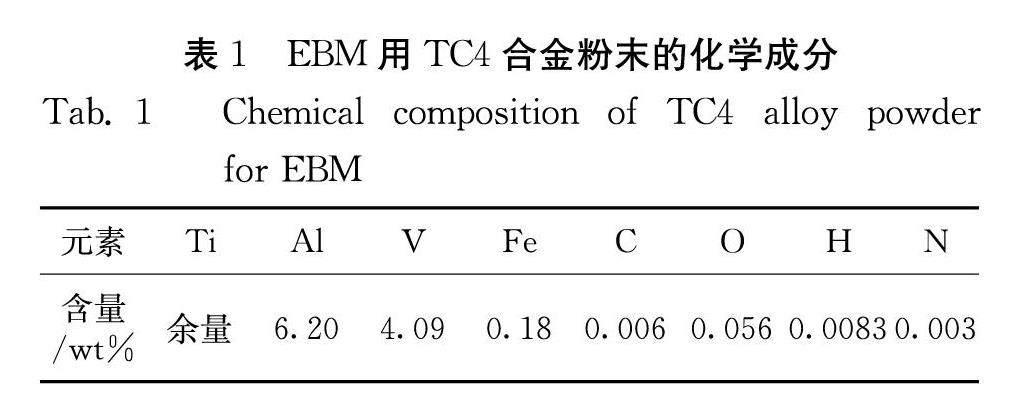
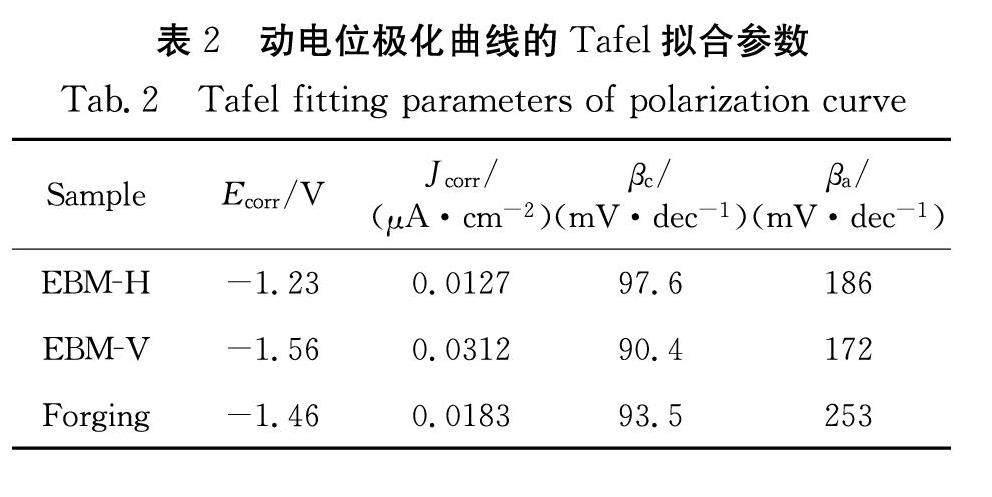
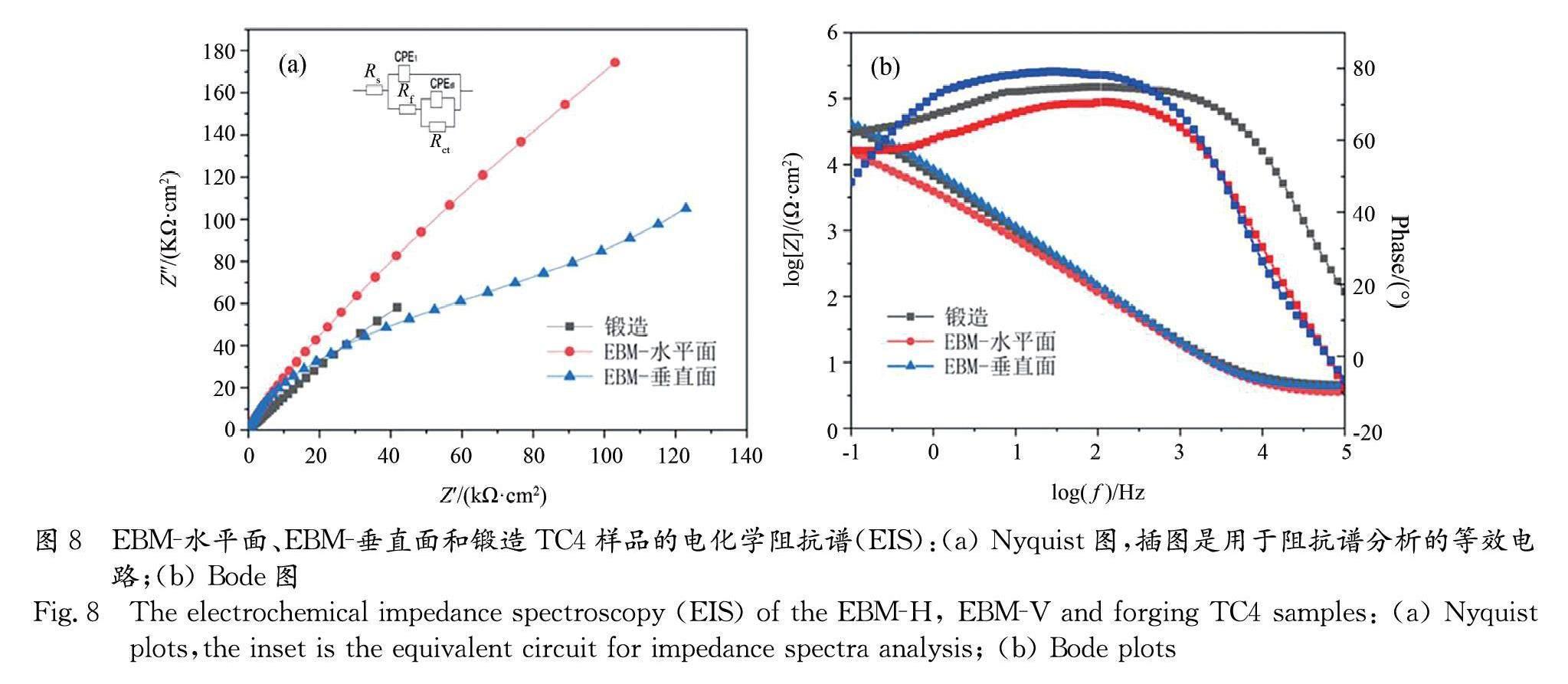
本工作采用电化学工作站研究了电子束熔化技术(EBM)成形TC4样品和传统锻造TC4在3.5 wt% NaCl溶液中的电化学腐蚀行为.结果表明EBM成形TC4样品的非平衡微观结构使其与传统锻造的TC4相比,表现出不同的耐腐蚀性.EBM成形TC4样品与锻件TC4相比,EBM成形样品不同平面存在耐蚀性差异,而且EBM水平面大于锻件,EBM垂直面小于锻件.EBM成形TC4样品垂直面出现的腐蚀性能的各向异性主要是β柱状晶导致的.在腐蚀的过程中,点蚀优先发生在α晶界,因为晶界能量较高,形成多孔的钝化层.本项工作有助于丰富增材制造制备TC4合金在航空钛合金领域的腐蚀性能研究.
TC4钛合金; 电子熔化技术; 增材制造技术; 化学腐蚀
TG142A2023.034002
收稿日期: 2022-10-21
基金项目: 四川省科技厅重点研发计划(2022YFG0102, 2021YFH0174)
作者简介: 邓浩(1993-), 重庆南川人, 博士, 主要研究方向为材料成形.E-mail: denghaoscu@126.com
通讯作者: chenlongqing@scu.edu.cn
Comparison study of corrosion behavior between electron beam melting formed and forged Ti6Al4V alloys
DENG Hao1, ZHOU Lü-Jun 2, ZHANG Hai-Cheng 1,3, LUO Heng-Jun 1,XIE Jing 1, XIANG Wei 1, QIU Wen-Bin2, CHEN Long-Qing 2
(1. Wanhang Die Forging Co., Ltd., China National Erzhong Group Co., Ltd., Deyang 618013, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Radiation Physics and Technology, Ministry of Education, Institute of Nuclear Science and Technology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, China;
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China)
In this work, the electrochemical dissolution behavior of electron beam melting (EBM)-formed TC4 samples and conventionally forged TC4 in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution was investigated by using an electrochemical workstation. The results show that the non-equilibrium microstructure of the EBM formed TC4 samples makes them exhibit different corrosion resistance compared to the conventionally forged TC4. The corrosion resistance of the EBM formed TC4 samples differs in different planes compared to the forged TC4, with the EBM horizontal plane being larger than the forged one, but the EBM vertical plane being smaller than the forged one. The anisotropy of the corrosion properties appearing in the vertical plane of the EBM formed TC4 samples is mainly caused by the β-columnar grain. In the process of corrosion, pitting preferentially occurs at α grain boundaries because of the higher grain boundary energy and the formation of porous passivation layers. This work is helpful to enrich the study of corrosion energy of TC4 alloy prepared by additive manufacturing in the field of aerospace titanium alloys.
TC4 titanium alloy; Electron melting technology (EBM); Additive manufacturing technology (AM); Chemical corrosion
1 引 言
钛(Ti)及其钛合金具有优异的综合性能,如低密度、高比强度、耐腐蚀、无磁、无毒等,因此被广泛应用在生物医学、海洋和航空航天等领域[1-4].TC4(Ti-6Al-4V)是典型的α+β双相结构的钛合金,强度和塑性匹配极佳,是应用最广泛的通用钛合金之一[5, 6].近几年,由于航空工业的不断发展,部件轻量化设计的要求也越来越高,因而采用钛合金替代传统碳钢的趋势越发显著.另一方面,随着设计理念的不断升级,新型部件逐渐向集成化、拓扑性发展[7],由原来的多个部件焊接或栓接转变为整体制造成形,由原来的规则、实心构型转变为复杂、镂空构型.这对传统制造工艺提出了极大的挑战:材料利用率将更低,加工周期将更长,成品率将更低.而且最为关键的是,大部分优化设计结构无法采用传统工艺进行制造.这些都极大地限制了航空工业的发展.增材制造技术[8, 9](Additive Manufacturing,AM)是新发展起来的有别于传统工艺的颠覆性制造技术,基于离散-堆积的原理,能够直接近净成形无限复杂的结构部件.并且经过多年的不断发展和进步,该技术已经能够生产出近乎完全致密、力学性能媲美锻造工艺的构件.因此,AM技术被认为是传统制造工艺的极好补充.在众多AM
