The structural characteristics of dietary fibers from Tremella fuciformis and their hypolipidemic effects in mice
2023-01-21ShanshanZhangXinleXuXuCaoTingtingLiu
Shanshan Zhang,Xinle Xu,Xu Cao,Tingting Liu,*
a School of Food Science and Engineering,Jilin Agricultural University,Changchun 130118,China
b Scientific Research Base of Edible Mushroom Processing Technology Integration,Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs,Changchun 130118,China
c Engineering Research Center of Grain Deep-processing and High-effeciency Utilization of Jilin Province,Changchun 130118,China
d Key Laboratory of Technological Innovations for Grain Deep-processing and High-effeciency Utilization of By-products of Jilin Province,Changchun 130118,China
Keywords:Tremella fuciformis Dietary fiber Structural characterization Hypolipidemic effects
ABSTRACT In this study,Tremella fuciformis residues as raw material,dietary fibers from tremella were prepared by multiple enzymes.The structure of dietary fibers from tremella was studied by Fourier transform infrared(FTIR),X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM).We analyzed their lipidlowering properties in vitro (water holding,oil holding swelling cholesterol and sodium cholate binding capacitises) and the hypolipidemic effects in mice.The results showed that tremella dietary fibers presented the infrared absorption spectrum characteristics of polysaccharides and the characteristic diffraction peaks of cellulose type I.SEM results indicated that the surface of insoluble dietary fiber (IDF) was porous,while the soluble dietary fiber (SDF) was relatively compact and spongy.IDF exhibited significantly higher water holding,oil holding,and swelling binding capacities than the corresponding SDF.However,SDF exhibited significantly higher viscosity than IDF.The results showed tremella dietary fibers were significant in swelling,water holding and oil holding,cholesterol and bile acids.In vivo experiment results in mice indicated that SDF has the best effect on hyperlipidemia mice than IDF and total dietary fiber (TDF).SDF showed that the total cholesterol (TC),triglyceride (TG) and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) contents dropped by 28.33%,18.65%,and 48.97%,respectively,while high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) content increased by 43.80% .Compared with the high-fat control (HCM) group,the arteriosclerosis index (AI)and liver index (LI) of the SDF group mice showed significant differences,indicating that SDF has a good auxiliary effect of lowering blood lipids.The administration of tremella fibers improved the lipid metabolism disorderly situation of hyperlipidemia mice.These results provide a reference for further research and rational development of T.fuciformis.
1.Introduction
In recent years,with the improvement of people’s living standards,obesity,diabetes,coronary heart disease and cardiovascular diseases have become the major diseases to endanger people’s health and lives.Epidemiological evidence confirmed that insufficient dietary fiber intake was closely related to increasing risk of these diseases [1].Dietary fiber is a kind of edible non-starch polysaccharides,which cannot be digested and absorbed in the human small intestine.However,it can be partially or completely fermented in the large intestine [2].Relevant studies have shown that dietary fiber has higher water holding capacity,swelling power and other properties.It could reduce blood cholesterol,regulate blood glucose,control weight,improve constipation and prevent cancer [3].Dietary fiber has been widely studied and applied because of its unique physiological and health functions,which is a hot topic in the field of functional food research.However,the physiological functions of dietary fiber are closely related to its structure and composition.According to the different solubility of dietary fiber,it can be divided into soluble dietary fiber (SDF) and insoluble dietary fiber (IDF) [4].SDF plays a role in regulating blood sugar and lowering cholesterol due to its high viscosity and water-holding capacity [4];IDF plays a role in improving constipation,lowering cholesterol,preventing obesity and reduce blood pressure due to its high swelling,oil holding and adsorption properties [5].Wu et al.[6]have reported that the surfaces of the IDF of bamboo shoot were loose and porous with a complicated spatial network structure,so they have strong physical and chemical properties.Some other studies have shown that the gelforming capacity of SDF,such as pectin orβ-glucan,was related to its ability to bind cholesterol and bile acids in the gut and accelerates their extraction [7,8].Wang et al.[9]had found that the changes of physicochemical and functional properties of rice bran dietary fiber after cellulase modification were attributed to a more porous surface structure,reduced crystallinity,and changed chemical composition.Overall,these studies have indicated that chemical composition and structure of dietary fiber leads to different functional and physicochemical properties.
Tremellafuciformis,known as white fungus,belongs to the fungus family.It is recognized as one of the rare edible mushroom for medicine and food,and is mainly distributed in East Asian Countries,such as China [10].T.fuciformisis rich in carbohydrates,colloidal substances,and amino acids that are beneficial to the human body.Relevant studies have shown thatT.fuciformishas the functions of delaying aging [11],anti-oxidation [12],improving human immunity [13],and lowering blood lipid [14].So researches on the active ingredients ofT.fuciformishave become a hot spot in domestic and foreign researchers in recent years.Much tremella residue will be produced after extracting a variety of active ingredients fromT.fuciformis,and the main residue is tremella dietary fiber.As one of the main ingredients in tremella,dietary fiber content is 30% of the dry weight.It is abundant in hemicellulose and cellulose,and it can be used as an ideal dietary fiber raw material.At present,there are many studies on the effect of dietary fiber on reducing blood lipids in mice.Hovever,there are few studies on the structure of tremella dietary fiber and hypolipidemic effects in mice.
In recent years,healthy diet has become a part of people’s lives.Dietary fiber,as the seventh most important nutrient in food,is playing an increasingly important role in the health care food.Tremella,as a high-quality functional edible mushroom,is also a potential dietary fiber food raw materials.This study mainly used the multiple enzymatic method to prepare tremella dietary fiber,namely SDF,IDF and total dietary fiber (TDF),analyzed their physicochemical and structural properties,and investigated their water holding capacity,swelling power,cholesterol and sodium cholate bindingin vitro.In addition,using the hyperlipidemia mouse experimental models to evaluate its potential blood lipidlowering effects,it is intended to provide a theoretical basis for the development of lipid-lowering functional health foods.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Tremellawas purchased from WalMart Co.,Ltd.(Changchun,China).Tremella residue was obtained after producing tremella polysaccharides [15].α-Amylase (Activity: ≥ 2 000 U/g),protease(Activity: 4 000 U/g) and cellulase (Activity: 40 U/mg) were ordered from Beijing Solarbio Science&Technology Co.,Ltd..All other chemicals were of analytical grade.
2.2 Preparation of dietary fiber samples
The preparation of dietary fiber samples,were carried out based on the method described with minor modification [16].In brief,the remaining residue after the extraction of polysaccharides fromT.fuciformis,which was dried,crushed and sifted to make tremella residue powder.20 g powder was processed in 800 mL deionized water.First,The solution was hydrolyzed by 1 mLα-amylase for 35 min at 75 °C,and then cooled to 60 °C.Then 2 mL protease was added for 30 min.1 mL starch glucoside enzyme was added in the solution at 60 °C for 30 min,and finally the pH value of solution was adjusted to 5.0,and the solution was hydrolyzed by 0.8 g cellulase for 3 h at 50 °C.After inactivation of enzymes,the supernatant was condensed,alcohol precipitated and freeze-dried to achieve SDF,while the sediment was washed and freeze-dried to obtain IDF.TDF was the sum of SDF and IDF.
2.3 Structural properties
2.3.1 Fourier transform infrared (FTIR)
2 mg of SDF,IDF,and TDF dry samples mix uniformly with 200 mg of KBr powder in a mortar.And each sample was pressed tablets under a pressure of 10 MPa.It was choosed to scan the infrared spectrum at 4 000-400 cm-1.
2.3.2 X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD)
The crystal structureof SDF,IDF,and TDF were measured by X-ray diffractometer (MiniFlex600 desktop X-ray diffractometer,Nippon Science Corporation,Japan).Diffraction conditions: Cu target,tube current 5 mA,tube voltage 20 kV,scanning area (2θ) 3°-90°,scanning speed 10°/min,scanning step width 0.01°,continuous scanning mode,height limit IHS 10 mm,receiving slit RS 0.3 mm,divergence slit DS 1.25°,anti-divergence slit SS 1.25°.
2.3.3 Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
The surface and microstructure of dietary fiber samples were measured by SEM (Phenom Pro electron microscope,Netherlands Feina Scientific Instruments Co.,Ltd.).The dietary fiber sample is microscopically 1 000 and 5 000 times respectively by scanning electron microscope,the conditions:accelerating voltage 5 kV,beam intensity standard beam current,probe mode backscatter.
2.4 Functional properties
2.4.1 Rheological property
The rheological properties of the dietary fiber solutions were determined using a rheometer (DHR-1: TA.USA).A parallel plate rotor (diameter 40.0 mm) with a gap of 1 mm was installed on the rheometer.Viscosity (η) was carried out at different shear rates (0.01-1 000 s-1).Let stand was performed allowing 2 min before testing.All measurements were taken at (25.0 ± 0.1) °C and in triplicate,and all experiments were carried out at least in triplicate.The modulus of elasticity (G’) and the modulus of viscosity (G’’) were measured as a function of frequency (0.1-50.0 Hz,strain=1%).
2.4.2 Water holding capacity (WHC)
WHC was determined according to Wang et al.[17]method with minor modification.Firstly,0.50 g (m1) of dietary fiber dried to a constant weight was accurately weighed in a 50 mL beaker,into which 10 mL distilled water was added.The samples were thoroughly stirred to disperse evenly.After sealing,the samples were left overnight at room temperature.Then samples were centrifuged at 4 800 r/min for 15 min.The residue was drained on the quantitative filter paper and quickly weighed (m2).WHC is calculated according to formula:

2.4.3 Oil holding capacity (OHC)
According to Rana et al.[18]method with minor modification.0.5 g of dietary fiber samples into a 50 mL centrifuge tube,add 4 g of soybean oil,seal it in a 37 °C water bath for 4 h,centrifuge at 3 800 r/min for 20 min,absorb the excess oil,and weigh the residue.m1is the weight of the residue (g);m0is the weight of the sample (g).Calculation formula of oil holding capacity is as follows:

2.4.4 Swelling capacity (SC)
According to Sangeethapriya et al.[19]method with minor modification.Weigh 0.2 g of the sample and place them in a 10 mL graduated test tube.Measure the volume of each dry sample.Add 8 mL of distilled water and stir it evenly with a glass rod.Let it stand at room temperature for 12 h.Record the volume of the sample after swelling after absorbing water.V2is the sample volume (mL) after expansion;V1is the dry sample volume (mL);mis the dry sample weight (g).Force calculation formula is as follows:

2.4.5 Cholesterol adsorption capacity (CAC)
According to the method of Benitez et al.[20]method with slightly modified.Take the egg yolk and beat it evenly,add 9 times the volume of distilled water,and use an ultrasonic breaker to beat into a uniform emulsion.The ultrasonic whipping condition of the egg liquid is 5 s ultrasonic time,8 s interval time,and working 40 times,The ultrasonic power is 400 W.Take 30 mL of diluted egg yolk solution in a small beaker,and use 1 mol/L HCl solution to adjust the pH value of the solution to 2 (simulating the environment of the stomach),and 0.1 mol/L NaOH to adjust the pH value of the solution to 7 (simulating the environment of the small intestine).Add 1.000 g of different dietary fiber samples,oscillate the reaction in a 37 °C water bath for 2 h,centrifuge at 4 000 r/min for 20 min,absorb 1.00 mL of supernatant at a wavelength of 550 nm,and determine the absorbance value by the orthophthalaldehyde method.Cholesterol adsorption capacity calculation formula is as follows:

Wheremis the mass of the constant weight sample (g);n1is the cholesterol concentration of the egg yolk emulsion before adsorption(mg/mL);n2is the cholesterol concentration in the supernatant after centrifugation (mg/mL);Vis volume (mL).
2.4.6 Sodium cholate binding capacity (SCBC)
According to the method of Wang et al.[21]whith slightly modified.50 mg of different dietary fiber samples SDF,IDF and TDF into a 50 mL erlenmeyer flask,add 3 mL of 10 mg/mL pepsin solution prepared with 0.1 mol/L phosphate buffer of pH 6.3,0.01 mol/L of HCl solution 1 mL,digested with shaking in a constant temperature water bath at 37 °C for 1 h to simulate the gastric environment;adjust the pH value to 6.3 with 0.1 mol/L NaOH solution,and then add 4 mL of 10 mg/mL to 0.1 mol/L of pH 6.3.The trypsin solution prepared in phosphate buffer was digested with shaking in a constant temperature water bath at 37 °C for 1 h to simulate the intestinal environment for digestion.Add 4 mL of 0.3 mmol/L sodium glycocholate and 0.3 mmol/L sodium taurocholate to each sample,shake in a 37 °C water bath for 1 h,pour it into a centrifuge tube,centrifuge at 3 800 r/min for 20 min,and take supernatant 2.5 mL,add 7.5 mL volume fraction of 60% sulfuric acid,use colorimetric method,measure the absorbance value at 387 nm wavelength,the calculation formula for the binding ratio of sodium glycocholate and sodium taurocholate are as follows:
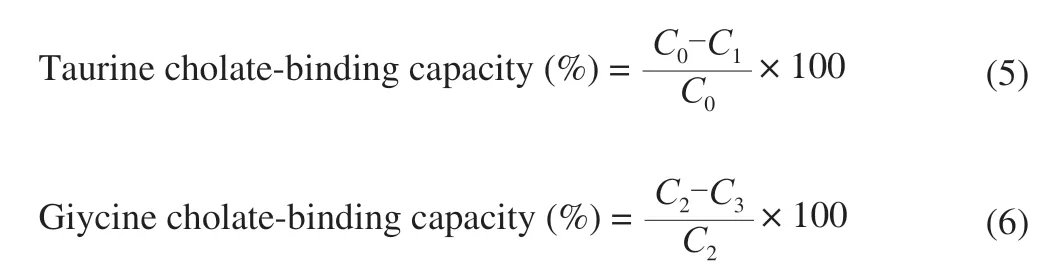
WhereC0andC1are the amount of sodium taurocholate added and remaining adsorption (μmol);C2andC3are the amount of sodium glycocholate added and remaining adsorption (μmol).
2.5 Animal experiments design
For this test,forty healthy male Balb-c mice ((20 ± 2) g) were selected.Animals provided by (Beijing Weitonglihua Laboratory Animal Technology company).Animals were fed individually in cages in a controlled room with the room temperature of 21-23 °C,and humidity of (50 ± 5)% .Mice access food and water freely.After one week of adaptive feeding,they were randomly divided into 2 groups according to their body weight.8 mice were given basic feed as a normal control,and the remaining 32 were given high-fat feed as a high control model.Weigh the mice once a week.The high control model was given high-fat feed for 4 weeks.The 32 hyperlipidemia mice with significantly increased serum total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) contents.
All the successfully modeled mice were grouped and the experiment started.32 rats were divided into 4 groups,blank control(NC) group,high-fat control (HCM) group,SDF,IDF and TDF.The NC group was fed with basic feed,and the other groups were all fed high-fat feed.The sample group was prepared to the corresponding concentration.The intragastric volume was 15 mL/kg.Both the NC group and the HCM group were intragastrically administered with the same volume of normal saline.In our previous study,when the gavage amount of tremella dietary fiber exceeds 1.5 g/kg,it will have a negative impact on mice.This may be due to the high swelling property of tremella dietary fiber and the gas production effect of dietary fiber after fermentation.All 5 groups were fed for 28 days,and the weight was recorded once a week.The dosage is as follows Table 1.
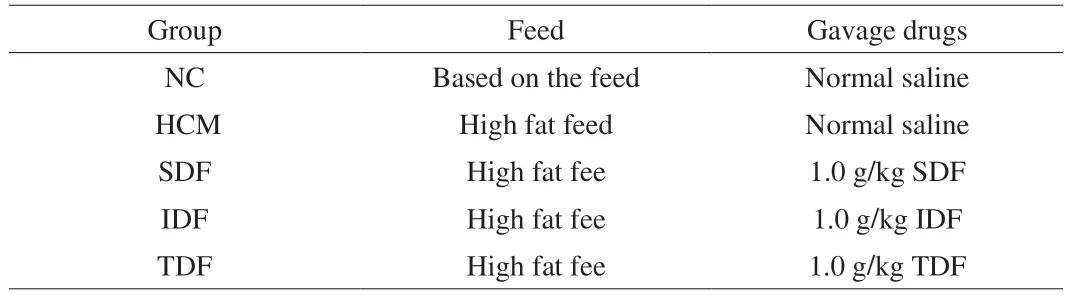
Table 1 Treatment groups of hyperlipidemic mice.
2.6 Serum analysis
One day before the end of the experiment,each group was fasted for 16 h without water.Under ether anesthesia,3 mL of rat blood was taken from the abdominal aorta and centrifuged at 4 000 r/min for 30 min at 4 °C.Serum is aliquoted into EP tubes and stored in a refrigerator at -20 °C for analysis [22].
The contents of TG,TC,high density lipoprotein cholesterol(HDL-C),and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in serum were determined according to the method described on the kit.According to the following formula,we can calculate arteriosclerosis index arteriosclerosis index (AI) and liver index (LI).
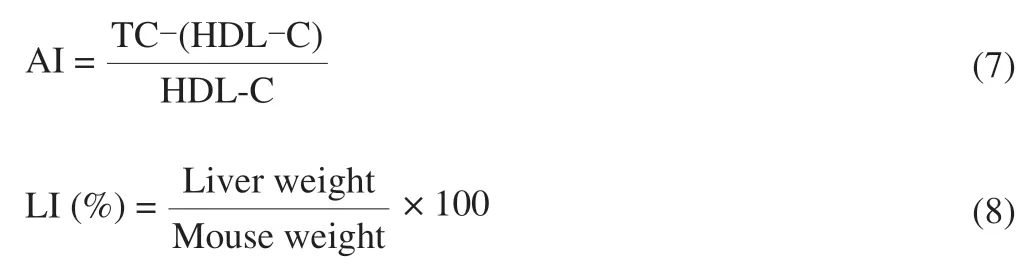
2.7 Statistical analyses
All results are expressed as mean ± SD.Pvalues less than 0.05 were considered to indicate a significant difference between treatments.Data were analyzed using Origin 8.0 and SPSS 11.5 software.
3.Results and discussion
3.1 Preparation of dietary fibers
IDF and SDF were extracted fromT.fuciformisresidues powder by multiple enzymes,and the extraction yields were 60.21% and 5.65%,respectively.The yield of total dietary fibers was 65.86%,and the ratio of SDF/IDF was 1:12.042.According to the recent study,enzyme hydrolysis,especially cellulose,could significantly increase the SDF yield by hydrolyzing insoluble fibers into soluble yield [23].
3.2 FTIR
Fourier infrared spectroscopy can reflect some functional groups of the sample.Fig.1 shows the FTIR chart of dietary fibers from tremella residue.It can be seen from the figure that the absorption peaks of IDF and TDF are similar,which may be due to the relatively high content (91.2%) of IDF in TDF.The three kinds of dietary fibers present a large and smooth absorption peak at about 3 410 cm-1,which is caused by the stretching vibration of the -OH in the dietary cellulose,indicating that there may be more hydroxyl groups and bound water molecules;the three dietary fibers similar absorption peaks appear at 2 922,1 636,and 1 038 cm-1,which represented the vibrations of C-H,C=O,and C-O-C respectively [24,25].In addition,the absorption peaks in the range of 1 200-1 450 cm-1are due to C-H The variable angle vibration was caused by the characteristic absorption peak of polysaccharides;Two absorption peaks at 1 436 cm-1and 1 636 cm-1were advantages,showed that hemicellulose contents were higher.The peak intensities of SDF at 1 255 cm-1and 1 636 cm−1were relatively stronger,indicating that the lignin contents in the SDF were rich,and its structure were orderly.The absorption peak at 1 038 cm-1is caused by the stretching vibration of C-O-H and the C-O-C of the aromatic ring [26].In summary,the IDF,SDF and TDF from tremella residues all show the infrared absorption spectrum characteristics of polysaccharides.
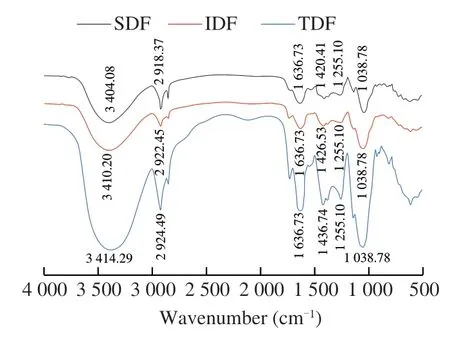
Fig.1 Infrared spectra of dietary fibers from T.fuciformis.
3.3 XRD
Dietary fiber is mainly composed of crystalline and amorphous regions.The amorphous area is mainly manifested in amorphous cellulose,hemicellulose and lignin.It can be seen from Fig.2 that the three kinds of dietary fibers of tremella are similar in shape,showing obvious crystal diffraction peaks at the scanning angle 2θof 19.28°,20.35° and 23.12°.The IDF and TDF were all at the scanning angle 2θof 17.15°.Two sub-diffraction peaks also appeared,showing the characteristic diffraction peaks of cellulose I,which indicated that the crystal type of the dietary fiber from tremella residues belonged to cellulose I [27].There was basically no change in the peak positions of the three dietary fibers,indicating that the crystalline area of the dietary fiber was basically unaffected,but the intensity of diffraction was somewhat different.It may be that the enzymatic treatment has little effect on the crystalline area of the dietary fibers of different components.
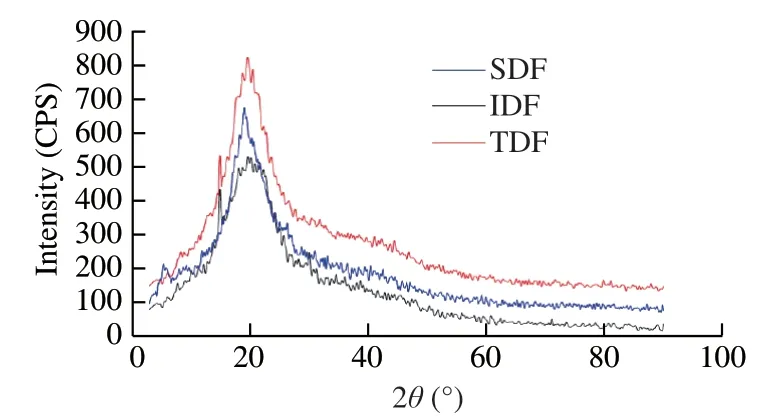
Fig.2 XRD diagrams of dietary fibers from T.fuciformis.
3.4 SEM
It could be seen from Fig.3 that the surface of SDF was relatively compact and smooth,showing a spongy network structure;the surface of IDF was relatively rough,with more ravines and voids,and the honeycomb-type network structure was tightly protruding with many obvious cracks and voids;TDF had both a dense structure and a rough structure,which was relatively loose.In addition,the edges were also loose and uneven,and there were faults in the microstructure.It might be due to the hydrolysis of the tremella residues after being treated with multiple enzymes,so that the water molecules can further penetrate into the tremella residues,while the enzyme continue to undergo hydrolysis,so that the dietary fiber of the tremella residues presented a loose and porous surface structure.The loose structure of IDF increased its water holding capacity and swell capacity,and also had a certain impact on its adsorption capacity [2].
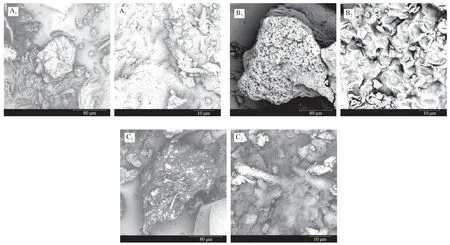
Fig.3 SEM of dietary fibers from T.fuciformis (1 000×,5 000×).(A) SDF;(B) IDF;(C) TDF.
3.5 Rheological property of SDF
Viscosity is a necessary physicochemical property of SDF,which is recognized as relation to physiological activity,such as regulate blood glucose and cholesterol content,extended gastric emptying time and slower transport time in the small intestine [28].Viscosity of dietary fiber solution showed in Fig.4.The different concentrations of SDF solution showed typical non-Newtonian behavior and an obvious shear-thinning area.With the shear rate increased,the viscosity decreased.However,the 50 mg/mL solution was the highest in all solutions.For example,the viscosity at a shear rate of 1 s-1was 4.043,8.471,29.348 Pa·s for 15,35,and 50 mg/mL,respectively.When the shear rate is lower,the structure and chemical composition of SDF could be the main factors to affect the viscosity of SPF solutions.According to the result that increasing intestinal viscosity could effectively decrease cholesterol concentration and play a role in reducing blood lipid [29].
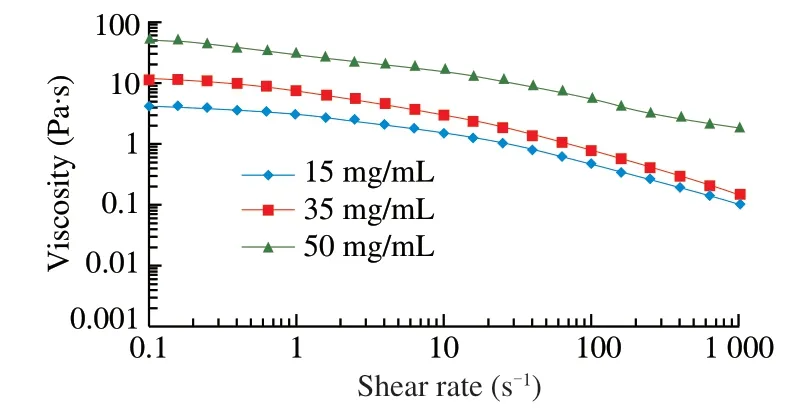
Fig.4 Viscosity of soluble dietary fiber (concentration of SDF solution,15,35 and 50 mg/mL).
Fig.5 showed the dynamic viscoelastic behaviors of SDF.BothG’ andG’’ were showed in Fig.5.G’ andG’’ increased with the rise of fluency,which were dependent in frequency.At low frequency,G’
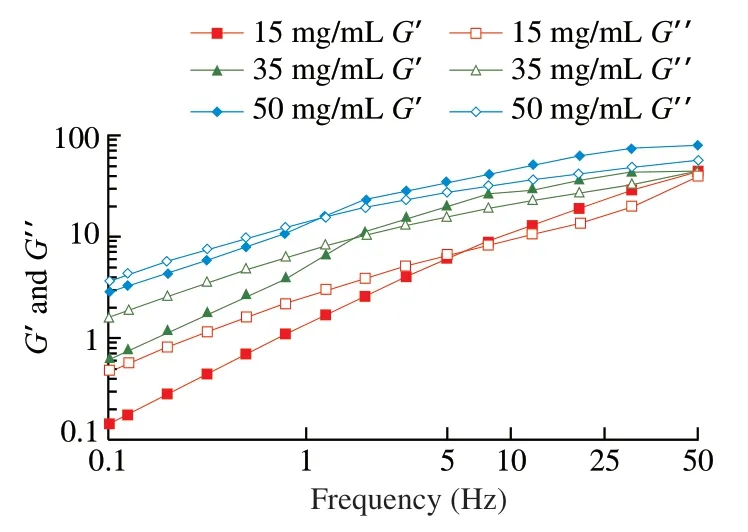
Fig.5 Dynamic viscoelastic behaviour of soluble dietary fiber (concentration of SDF solution,15,35 and 50 mg/mL).
3.6 WHC,OHC and SC
The WHC,OHC and SC of dietary fiber affected the physiological activity of dietary fiber.The Table 2 showed that the IDF showed higher WHC ((15.22 ± 0.13) g/g) and SC ((16.88 ± 0.29) mL/g),which might be related to the honeycomb network structure of IDF extracted by enzymatic method.These results were consistent with those of previous studies suggesting that the IDF of citrus peels had stronger WHC,OHC,and SC than SDF [31].However,SDF also showed better in WHC and SC because of its high viscosity.During the enzymatic treatment,part of the glycosidic bonds are hydrolyzed,and the fiber molecules dissolve more soluble small molecules.During this process,the surface structure of the dietary fiber particles changes significantly,and this structure exposes more hydrophilicity.The group has a larger specific surface area,and other substances or solvents can form more capillaries,which may lead to a larger adsorption capacity,so it has a good WHC and SC [32].
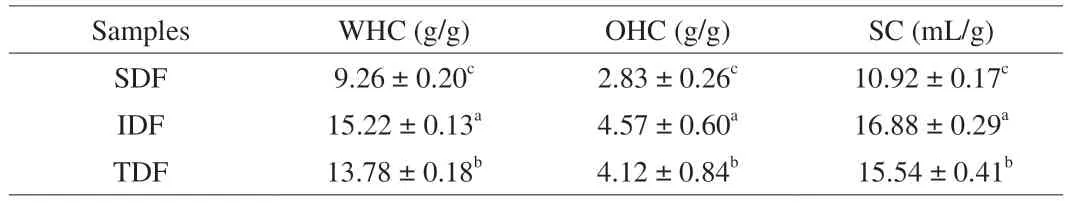
Table 2 WHC,OHC and SC of fiber samples.
OHC can reduce serum cholesterol levels by absorb fat or oil in the human digestion system [33].The OHC of IDF was(4.57 ± 0.60) g/g,which was higher than that of SDF ((2.83 ± 0.26) g/g)and TDF ((4.12 ± 0.84) g/g).It might be due to the higher content of lignin in IDF prepared from tremella residue,which contribute to excrete oil/fat from the body [25].Moreover,the surface features,overall charge density,and hydrophobic nature,might also contribute to the oil/fat binding capacity of dietary fibers [34].Interestingly,the oil/fat holding capacity of TDF was similar to that of IDF.
3.7 Cholesterol adsorption capacity evaluation
As shown in Table 3,the experiment simulates the gastrointestinal environment in the human body,respectively revealing the adsorption effect of IDF,SDF and TDF on cholesterol under the conditions of simulating human stomach and small intestine.Under the same pH value,the cholesterol adsorption capacity of IDF,SDF and TDF showed significant difference,which was statistically significant (P<0.05).When pH=2,the adsorption capacity of SDF was the best,and the adsorption capacity was (8.89 ± 0.47) mg/g;when pH=7,the highest was (37.05 ± 0.36) mg/g.It was consistent with the conclusion that there were more spongy structures and high viscosity of SDF,which was more conducive to the adsorption of dietary fiber to cholesterol.
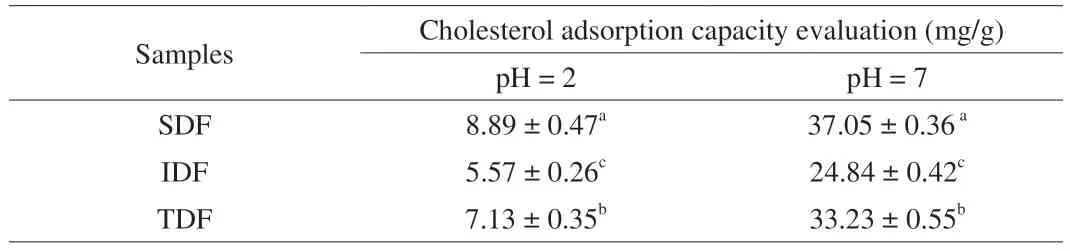
Table 3 In vitro adsorption capacities to cholesterol of fiber samples.
The results also indicated that pH value was a certain effect on the adsorption of cholesterol.The adsorption capacity of IDF,SDF and TDF at pH=7 (simulating small intestine environment)was significantly better than that of pH=2 (simulating stomach environment).Ability,it could be inferred that the absorption ability of dietary fiber to cholesterol mainly works in the small intestine,and SDF had the strongest absorption ability to cholesterol in the small intestine.
3.8 Sodium cholate binding capacity
Dietary fiber can absorb bile acid in the small intestine and promote the excretion of bile acid can promote the elimination of bile acid in the small intestine,achieve cholesterol degradation and reduce blood lipids in the body [35].Table 4 showed the adsorption capacity of SDF,IDF and TDF on sodium cholate (sodium taurocholate,sodium glycocholate).The binding capacities of SDF to sodium cholate were significantly higher than IDF and TDF.This may be because the SDF presented a gel-like structure in the solution,which acted like an exchange resin to adsorb and bind bile acids.Bile acids and their salts could be combined in the small intestine and excreted with the type [36].Therefore,more cholesterol needed to be converted into bile acids to compensate for the excreted part,so that the cholesterol content in the body was reduced and the blood lipid level was reduced [37].While IDF could absorb more oil and sodium nitrite,SDF generally showed more promising capacities for binding cholesterol and bile acids.In the sodium cholate experiment,TDF always showed a similar trend as IDF,which could be explained by the high content (91.2%) of IDF in the TDF sample.

Table 4 In vitro adsorption capacities to sodium cholate binding capacity of fiber samples.
3.9 Effect of dietary fiber on blood lipid level of mice
It could be seen from the Fig.6 that the serum TC and TG levels of mice in the normal group were before and after modeling.There was no obvious difference;however,the serum TC and TG content of the model group mice before modeling showed extremely significant differences (P<0.01) compared with the model group.In addition,after 4 weeks of modeling,the serum TC and TG contents of the HCM group mice fed high-fat diet were significantly higher than those of the NC group mice fed normal diet.The contents of TC and TG indicates that the model is successful.
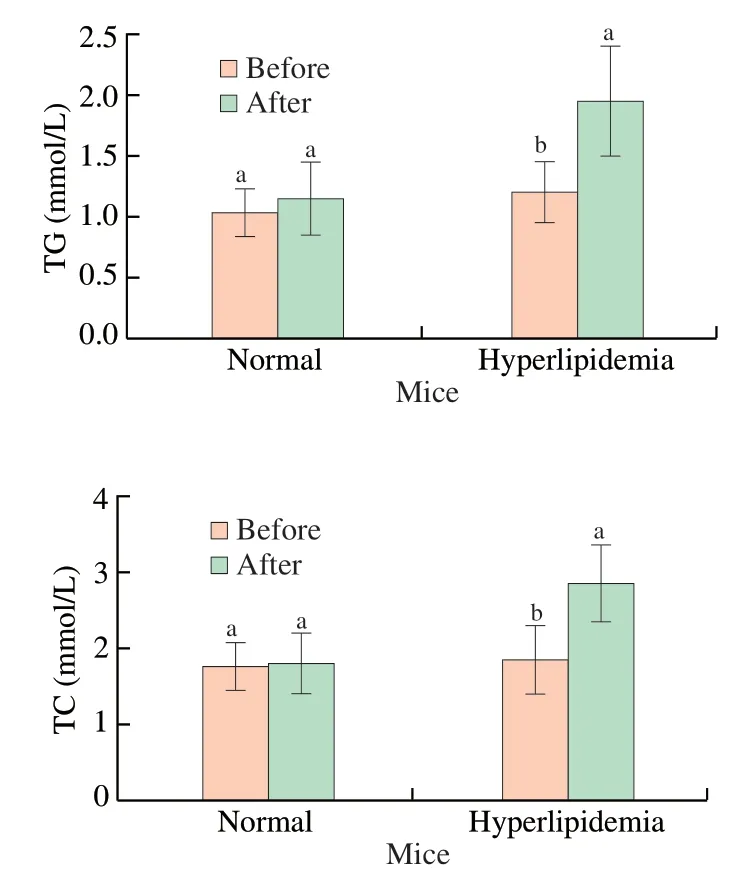
Fig.6 Increase of TC and TG contents of the hyperlipidemia mice induced by high-fat diet.
High levels of TC,TG or LDL-C are risk factors for coronary heart disease and other diseases [38].However,HDL-C helps to remove excess cholesterol out of the body,thereby lowering blood lipid levels [39].As shown in Table 5,compared with HCM group,the dietary fiber group can significantly reduce the serum TC and TG content of hyperlipidemia mice (P<0.05).And SDF exhibited more significant effects on lipid levels in mice than IDF and TDF,SDF decreased by 28.33% .This is partly because high-viscosit of SDF cholesterol adsorption effect,which reduces lipid levels,and partly due to SDF’s unique dense spongy structure,which increases the contact area with cholesterol and bile acids and promotes the absorption of bile acids.
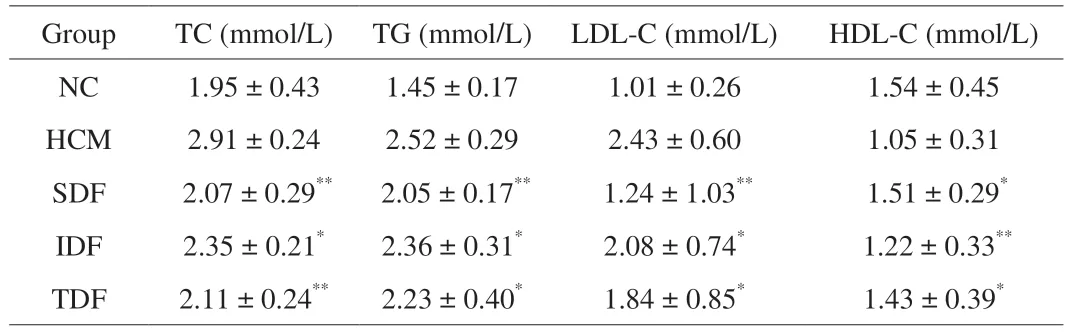
Table 5 Effect of dietary fiber on blood lipid level of mice.
In addition,the TC and TG value of the mice in the dietary fiber group did not show a significant difference compared with the TC and TG value of the normal group of mice (P<0.05),indicated that the hyperlipidemia model mice after the dietary fiber intervention,The blood lipid level has been reduced to a relatively healthy level.
The LDL-C data in Table 5 showed the LDL-C value of the three dietary fiber groups was significantly different from the LDL-C value of the HCM group mice serum (P<0.05),in which SDF decreased by 48.97% and TDF decreased by 24.28%,IDF dropped by 14.40% .It indicated that three dietary fibers could effectively reduce the LDL-C concentration in the serum of hyperlipidemia mice,of which SDF had the most obvious effect.Interesting,compared with the HCM group and NC of mice,TDF group and the SDF group was significantly different in HDL-C levels (P<0.05),in which the effect of SDF was more obvious,increased by 43.80% .This indicated that SDF had a higher effect on raising HDL-C levels in hyperlipidemia mice.Although the WHC,OHC and SC of IDF are higher than the SDF,but SDF possesses high viscosity and special porous spongy structure to endow them with higher cholesterol absorption ability,encourages the transformation of cholesterol to bile acid in liver juice causes the liver to absorb higher LDL and reduces serum lipid levels.The results are consistent with the research of Theuwissen et al.[40].
According to Table 6,AI was closely related to atherosclerosis.Compared with the NC group,the AI of the HCM group was significantly higher,which was 1.77 due to the high-fat diet.The AI of the three groups of dietary fiber was significantly different from HCM group.It suggested that tremella dietary fiber,especially SDF,could reduce total plasma levels,thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.Long-term intake of high-fat diet can cause organ lesions in the tested mice,which is reflected by the LI.Compared with the HCM group,the LI of the three groups of dietary fiber groups all decreased to different degrees.

Table 6 Effect of dietary fiber on blood lipid level of mice.
4.Discussion
As we all known,much tremella residue would be produced after the extraction of numerous active substances from tremella.And tremella dietary fiber was the main residue.In this paper,SDF,IDF,and TDF was prepared by multiple enzyme.The structural characterizations of the three dietary fibers showed that all three fiber samples retained most of the active groups,showed the characteristics of the infrared absorption spectrum of polysaccharides,exhibited the characteristic diffraction peaks of cellulose type I.IDF exhibited significantly higher WHC,OHC and SC than the corresponding SDF.However,SDF exhibited significantly higher viscosity than IDF.Moreover,we found that all fiber samples presented significant binding capacities of cholesterol and bile acids,eventually promoted the elimination of bile acid,thereby lowering blood lipids,which might be partly mechanism for their hypolipidemic effect.Among them,SDF was the most significant,generally showed more promising capacities to bind cholesterol and bile acids.However,in vivoexperiments have shown that SDF,IDF and TDF have a certain effect on reducing TC,TG,LDL-C contents,AI,LI and increasing HDL-C content.Among them,SDF has the best effect on hyperlipidemia mice.The TC,TG and LDL-C contents dropped by 28.33%,18.65%,and 48.97%,respectively,while HDL-C content increased by 43.80% .Compared with the HCM group,the AI and LI of the SDF group mice showed significant differences,indicating that SDF has a good auxiliary effect of lowering blood lipids.This article mainly explored the blood lipid-lowering effects of tremella dietary fiber,namely SDF,IDF and TDF,in order to improve the comprehensive utilization of high added value of tremella,and provide a theory for the development and application of tremella dietary fiber in food and health care products.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgement
The study was financially supported by the Key Projects of the National Research and Development Program of China(2018YFD0400204).
杂志排行
食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- Colloidal nanoparticles prepared from zein and casein:interactions,characterizations and emerging food applications
- Biological factors controlling starch digestibility in human digestive system
- Preparation methods,biological activities,and potential applications of marine algae oligosaccharides: a review
- Development of hyaluronic acid-based edible film for alleviating dry mouth
- Mushroom β-glucan and polyphenol formulations as natural immunity boosters and balancers: nature of the application
- Preparation of multicore millimeter-sized spherical alginate capsules to specifically and sustainedly release fish oil
