2D-3D配准中的初始位姿估计方法
2022-11-01刘传耙宋轶民马信龙
孙 涛,郭 可,刘传耙,张 弢,宋轶民, 3,马信龙
2D-3D配准中的初始位姿估计方法
孙 涛1,郭 可1,刘传耙1,张 弢2,宋轶民1, 3,马信龙2
(1.天津大学机构理论与装备设计教育部重点实验室,天津 300354;2. 天津市天津医院,天津 300211;3. 天津仁爱学院机械工程系,天津 301636)
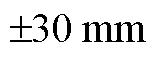
手术导航;2D-3D配准;初始位姿估计;正交双平面投影
在骨科手术中,通常采用成像较快的荧光透视图像为医生提供术中手术器械与病患部位的相对位置信息[1-2],但术中二维图像难以准确反映病患部位的空间位置和解剖信息,因此需要与术前三维CT数据结合,即通过2D-3D图像配准建立2D像素平面与3D模型空间的统一,实现术中、术前图像在空间位置与解剖纹理上的对应关系,从而引导手术的进行,这是病灶精准定位和施术成功的关键[3].
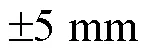
综上,本文提出一种新的初始位姿估计方法,通过正交融合投影原理,构建空间与平面参数间的映射关系,结合区域生长算法完成对多研究对象的5个三维空间参数的有效估计,以增大2D-3D配准的初始变换范围、降低配准时间、提高配准的精度和鲁棒性,并进行实验验证.
1 初始位姿估计方法
1.1 参数映射关系
大部分2D-3D医学图像配准是将三维CT数据通过数字重建影像技术生成DRR(digitally reconstructed radiograph)图像,比较DRR图像与术中平面图像的相似性,再不断改变投影环境下三维物体的空间参数,使得在某个空间参数下投影生成的DRR图像与平面图像的相似性达到最大[17],此时的空间参数就是相同相机坐标投影环境下生成平面图像的三维物体的位姿.因为三维物体的空间位姿的改变会引起DRR图像的改变,所以可建立空间与平面参数间的映射关系.
首先通过模拟术中C臂成像设备的成像过程,构建相应的投影环境来生成DRR图像,其中正交融合投影过程的示意如图1所示.所构建的投影坐标系原点为三维影像中心点,其坐标轴与经CT扫描后所成图像自带的坐标轴平行.
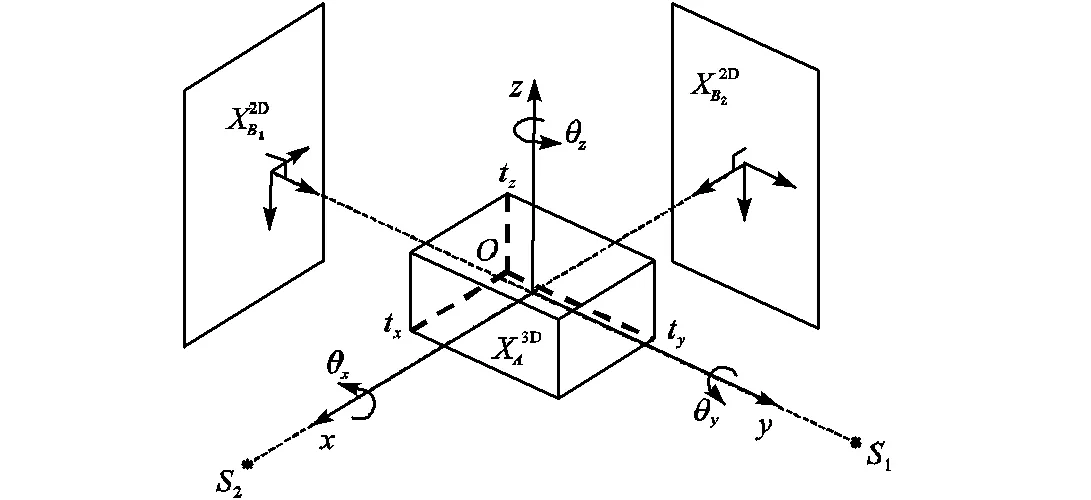
图1 正交融合投影示意
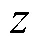
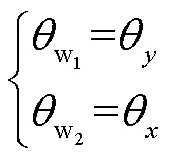
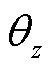
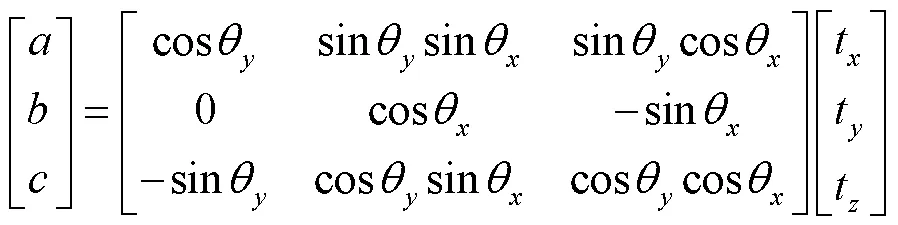
式(2)计算可得

其中
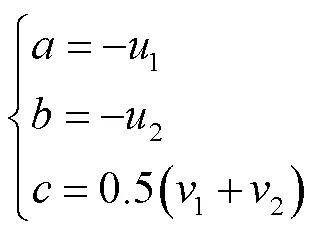
根据上述推导过程,可得空间与平面参数间的映射关系,但平面的参数信息包含在DRR图像灰度信息之中,不能直接提取,因此需要在后续利用对应目标图像与正交双平面模板间的配准来获取平面参数信息.
1.2 初始位姿估计原理与方法

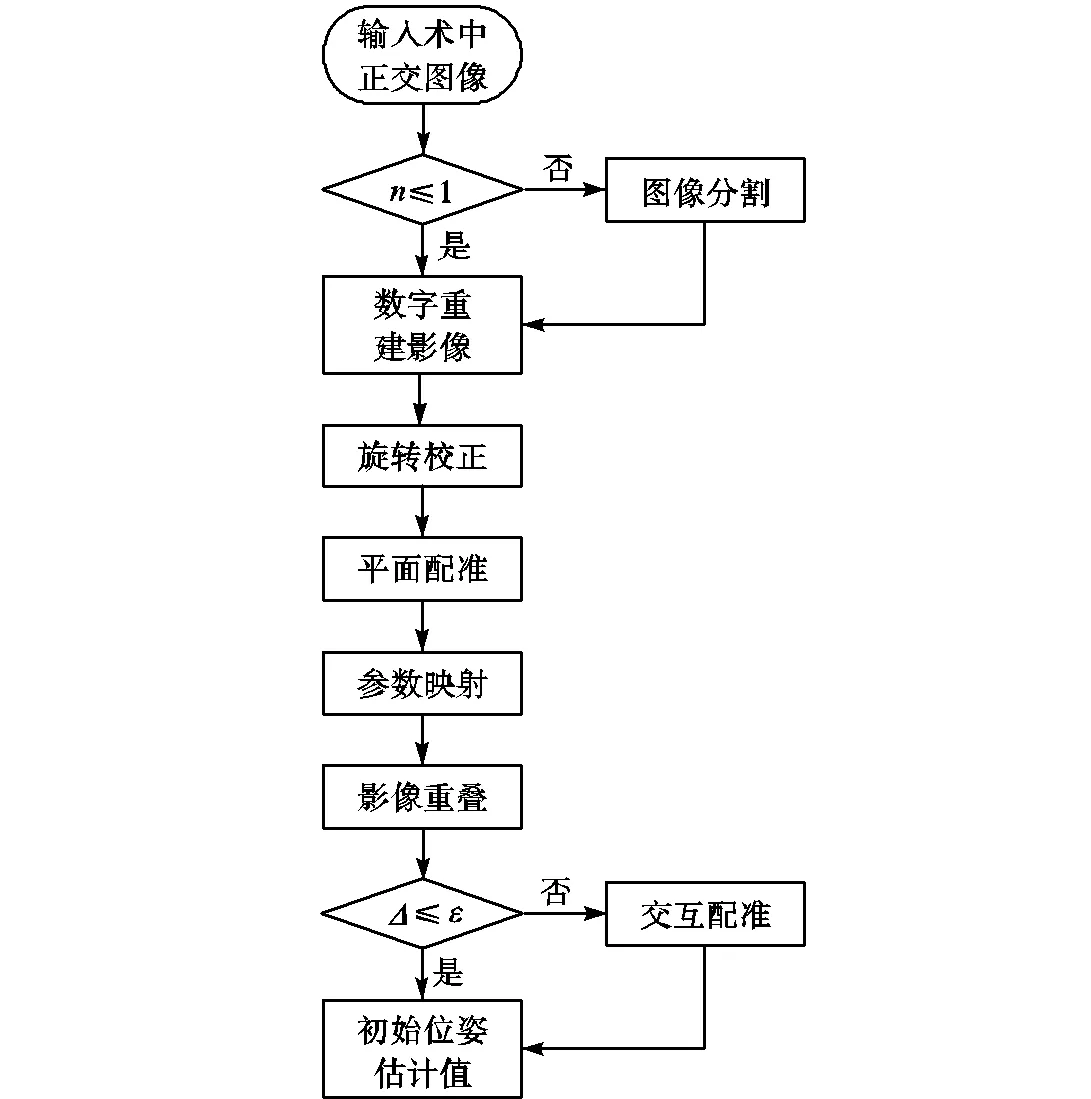
图2 初始位姿估计原理
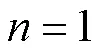
然后,根据需要配准的目标投影生成正交双平面模板,将目标图像和模板的灰度信息进行平面配准,计算得到正侧位平面配准参数.本文采用归一化互相关[20]作为相似性测度来计算初始位姿估计以及后续2D-3D配准过程的平面图像相似性.其中,归一化互相关系数的计算过程可以表示为
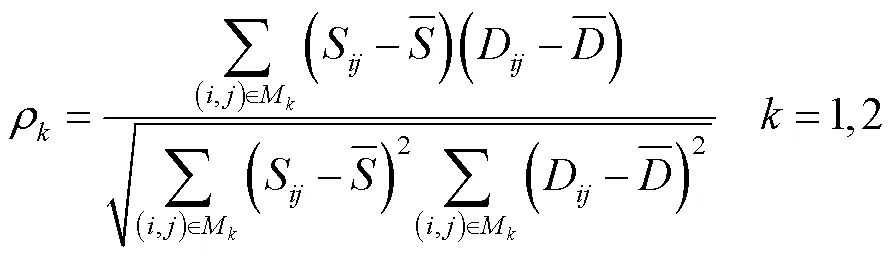

2 实 验
2.1 实验数据与测试环境
本文使用公开的颅骨数据[19]和天津医院提供的完整股骨、包含上下两骨块(近端骨和远端骨)的骨折股骨的CT数据来验证上文提出的初始位姿估计方法.为了方便获得任意位姿下的平面影像,本实验采用DRR影像模拟术中荧光图像进行配准.因为荧光图像成像时,成像设备发出的X射线透过病患部位后强度会减少,不同的组织结构造成的X射线衰减程度有差异,这种差异在荧光图像上显示为各组织结构明暗的不同.而DRR影像成像原理是模拟这种透视过程,故模拟生成的荧光影像与术中荧光影像具有一致性,这样不仅减少了患者和医生受到的辐射,也可以将图像生成的真实位姿作为配准结果的评估标准,具有可重复性.同时在实际应用中,本文的数据处理算法对于术中荧光影像与DRR图像的数据差异具有鲁棒性.
本实验使用Visual Studio 2017作为软件平台,结合图像开发工具包ITK(insight segmentation and registration toolkit)编程实现初始位姿估计与2D-3D配准过程,电脑配置为Intel®Xeon®Gold 5120 CPU @2.20GHz处理器,内存为64GB.
2.2 评估方法
以投影生成仿术中平片时三维物体的空间位姿作为“金标准”,用生成的匹配模板进行初始位姿估计,统计估计值与实际真值的误差和不需要人工校正的比例.因为在2D-3D图像配准中使用双平面方法的配准精度要优于单平面[22],且目前多采用Powell优化方法[23]进行配准,所以本文用估计的参数值作为起始搜索位姿,采用双平面Powell法进行2D-3D配准(以下简称结合法),将得到的结果与不使用初始位姿估计的双平面Powell法(以下简称单一法)进行配准的结果进行统计,比较最终配准结果与实际真值的误差.
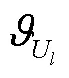
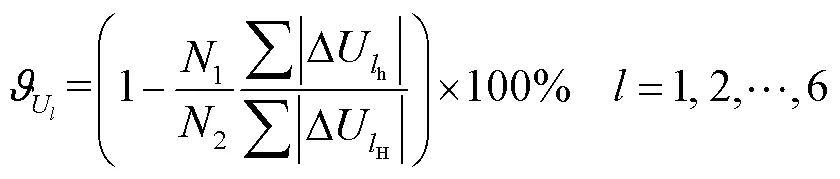
2.3 实验结果与分析
表1 初始位姿估计结果

Tab.1 Results of initial pose estimation
颅骨实验中,单一法与结合法都有较好的配准结果,因此统计每次迭代后所有平移参数和所有旋转参数配准误差绝对数的平均值(以下分别简称为平移配准误差和旋转配准误差)并进行绘制,如图3所示;在完整股骨、骨折股骨近端骨和远端骨的实验中,有10%的实验配准结果严重偏离“金标准”,且全来自于单一法,因此本文仅对剩余实验结果进行统计,绘制每次迭代后的平移配准误差和旋转配准误差图,如图4~图6所示.由于大部分实验经过6次迭代后,配准结果趋于相对稳定,因此只统计各实验前6次迭代过程中的配准误差.

图3 颅骨实验中每次迭代的配准误差
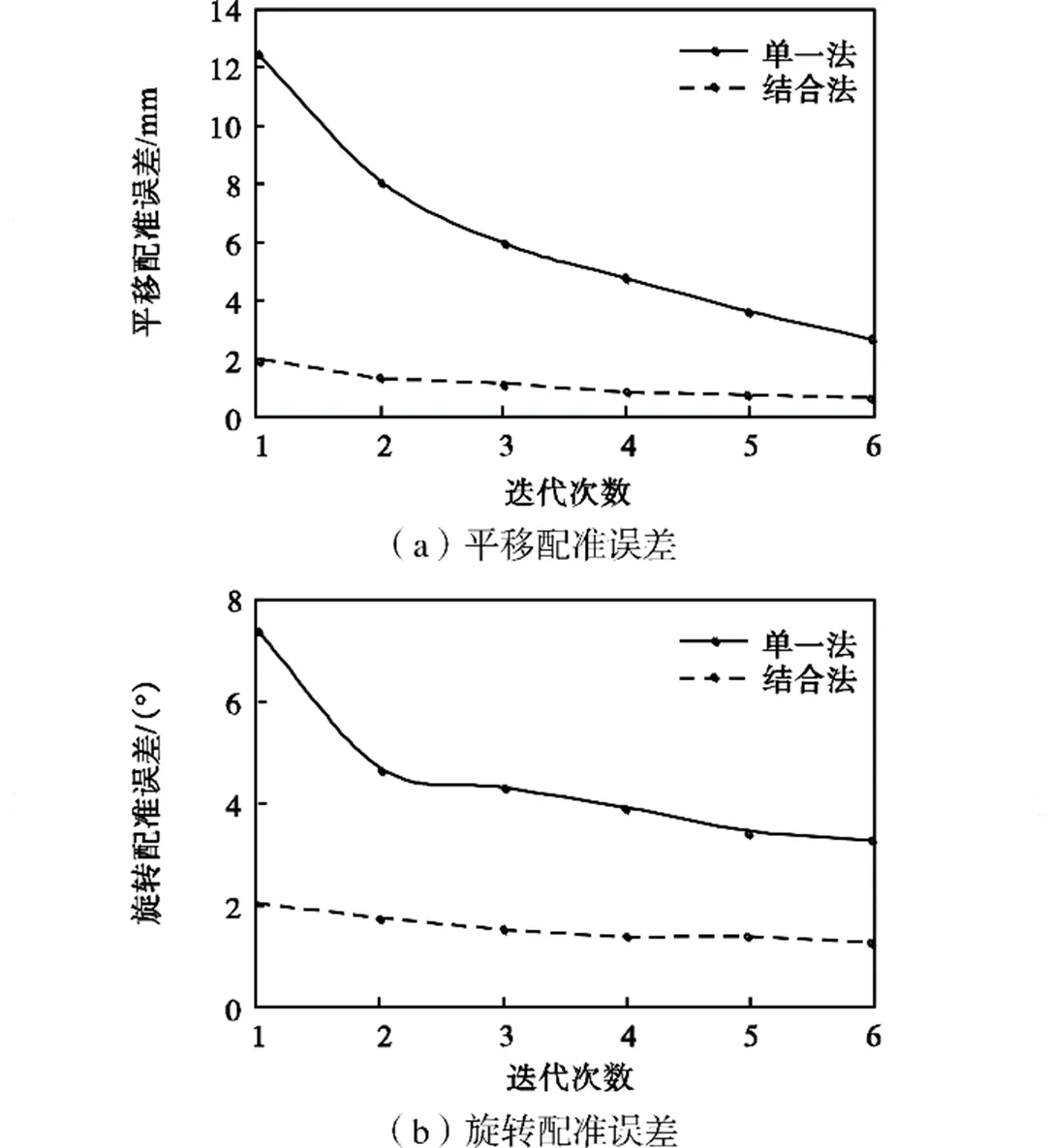
图4 股骨实验中每次迭代的配准误差
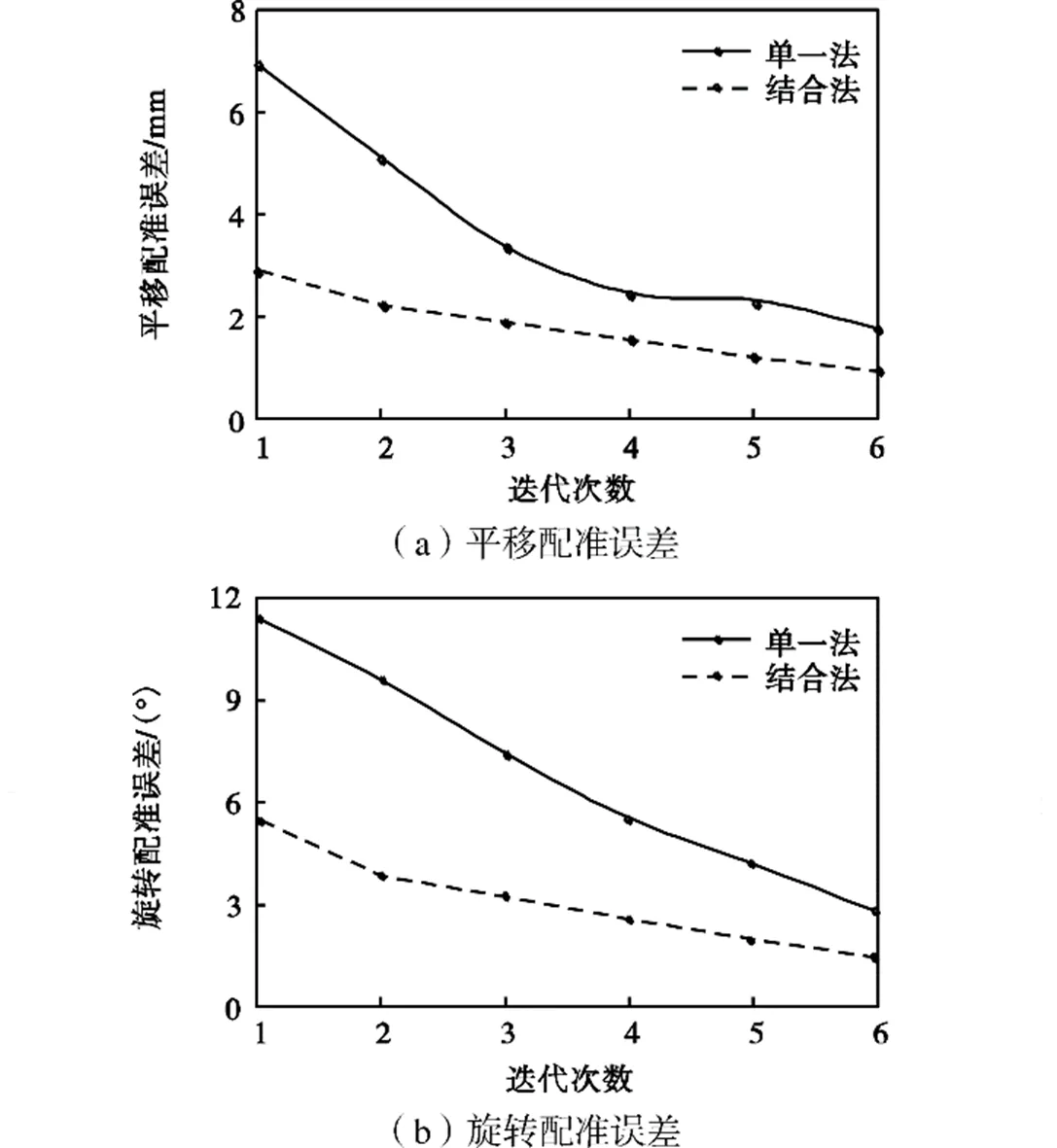
图5 近端骨实验中每次迭代的配准误差
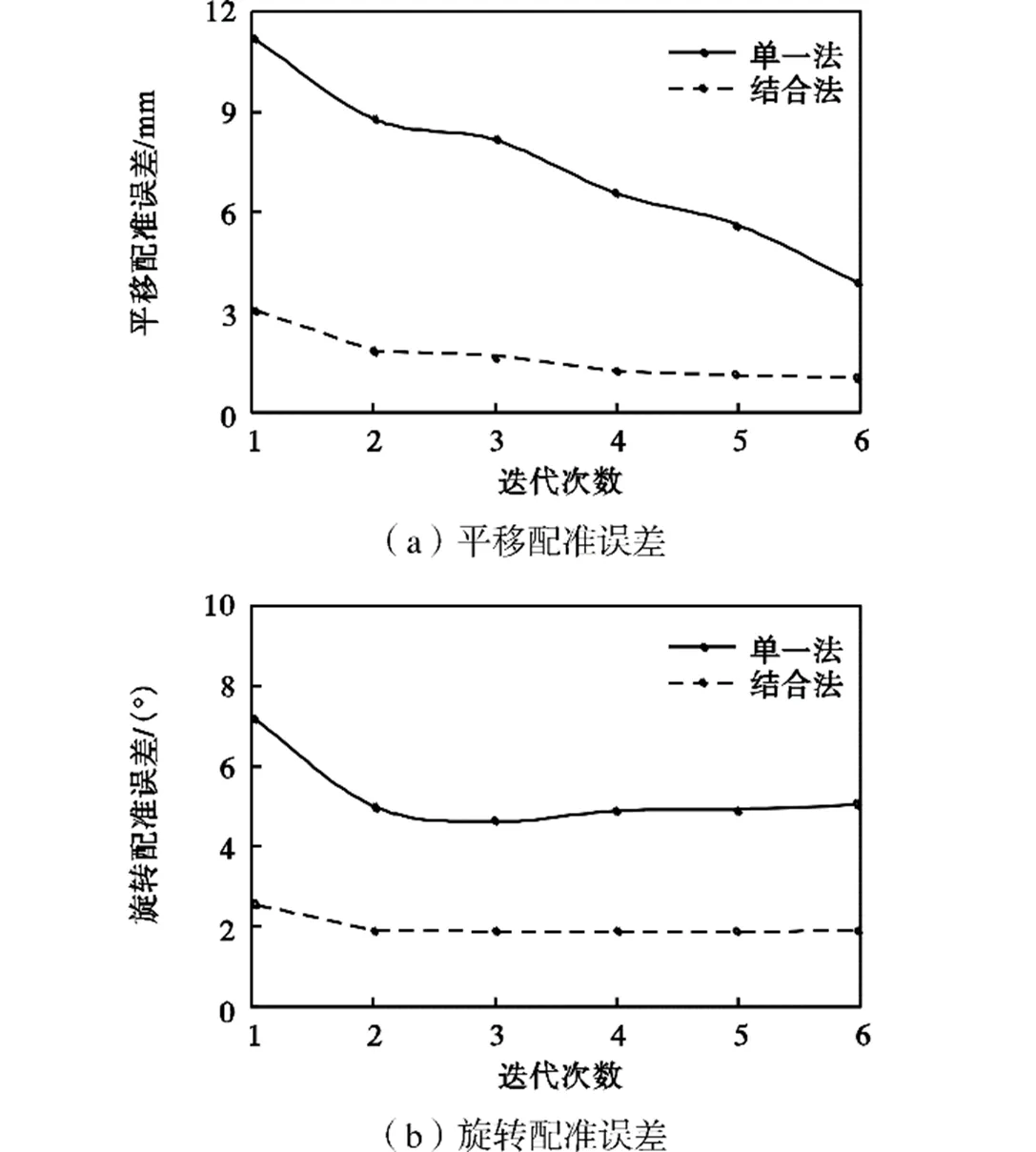
图6 远端骨实验中每次迭代后的配准误差
各研究对象配准统计结果表明,使用单一法进行2D-3D配准时,平均迭代次数为7.5次,平均配准时间为8089s;而基于结合法的2D-3D配准平均迭代次数为3次,平均配准时间(包括初始位姿估计时间)为4330s.与单一法相比,结合法在平均迭代次数上降低60%,平均配准时间上缩短46.5%,并且具有精度高、鲁棒性好的优点,最终2D-3D配准结果中各参数的配准误差的平均值±标准差统计结果如表2 所示.

表2 2D-3D参数配准误差

Tab.2 2D/3D parameter registration errors

图7 各实验的参数配准误差精度提升率
3 结 论
本文提出了一种正交双平面模板匹配初始位姿估计方法,该方法利用正交融合投影原理构建了正交投影下三维空间参数与平面图像坐标参数间的映射关系,将已知位姿投影下的DRR图像作为匹配模板与待配准的图像进行比较,通过平面坐标参数的变化来对空间参数值进行估计,并且基于区域生长算法实现多个研究对象的配准.为了验证本文提出的初始位姿估计方法的有效性,采用了颅骨、完整股骨、骨折股骨的近端骨和远端骨作为研究对象,各目标通过20组实验进行初始位姿估计与后续2D-3D配准实验对比.得到全文结论如下.

(2) 在2D-3D配准实验中,相较于单一法,结合法在整体配准时间上平均缩短46.5%,在各实验中单个平移参数精度最高提升46.5%,单个旋转参数精度最高提升91.1%,同时实验结果也兼具了良好的鲁 棒性.
(3) 通过各组实验,验证了在较大的初始位姿偏差下,本文提出的初始位姿估计方法对不同研究对象都具有很好的适应性,这也将有助于为骨科手术中的多模影像导航系统提供最佳或接近最佳的搜索参数选择.
[1] Russakoff D B,Rohlfing T,Mori K,et al. Fast generation of digitally reconstructed radiographs using attenuation fields with application to 2D-3D image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging,2005,24(11):1441-1454.
[2] Khamene A,Bloch P,Wein W,et al. Automatic registration of portal images and volumetric CT for patient positioning in radiation therapy[J]. Medical Image Analysis,2006,10(1):96-112.
[3] Markelj P,Tomazevic D,Likar B,et al. A review of 3D/2D registration methods for image-guided interventions[J]. Medical Image Analysis,2012,16(3):642-661.
[4] Frederik M,Vandermeulen D,Paul S,et al. Comparative evaluation of multiresolution optimization strategies for multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information[J]. Medical Image Analysis,1999,3(4):373-386.
[5] Kaiser M,John M,Heimann T,et al. 2D/3D registration of TEE probe from two non-orthogonal c-arm directions[C]//International Conference on Medical Imaging Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Boston,USA,2014:283-290.
[6] Muhit A,Pickering M R,Ward T,et al. A comparison of the 3D kinematic measurements obtained by single-plane 2D-3D image registration and RSA[C]//32nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Buenos Aires,Argentina,2010:6288-6291.
[7] Miao S,Wang Z J,Liao R. A convolutional neural network approach for 2D/3D medical image registration[J]. Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials-Rapid Communications,2015,4(3):636-648.
[8] Pickering M R,Muhit A,Scarvell J M,et al. A new multi-modal similarity measure for fast gradient-based 2D-3D image registration[C]//Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology-Society. Minneapolis,USA,2009:5821-5824.
[9] Akter M,Lambert A J,Pickering M R,et al. Robust initialisation for single-plane 3D CT to 2D fluoroscopy image registration[J]. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering:Imaging & Visualization,2015,3(3):147-171.
[10] Livyatan H,Yaniv Z,Joskowicz L. Gradient-based 2D/3D rigid registration of fluoroscopic X-ray to CT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging,2003,22(11):1395-1406.
[11] Van der Bom M J,Bartels L W,Gounis M J,et al. Robust initialization of 2D-3D image registration using the projection-slice theorem and phase correlation[J]. Medical Physics,2010,37(4):1884-1892.
[12] Andreas V S,Tom C,Graeme P. Increasing the automation of a 2D-3D registration system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging,2013,32(2):387-399.
[13] Akter M,Lambert A J,Pickering M R,et al. Improved robustness of 3D CT to 2D fluoroscopy image registration using log polar transforms[C]//International Conference on Electrical. Rajshahi,Bangladesh,2016:1-5.
[14] Miao S,Wang Z J,Liao R. A CNN regression approach for real-time 2D/3D registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging,2016,35(5):1352-1363.
[15] Piat S,Miao S,Liao R,et al. Dilated Fully Convolutional Network for Multi-Agent 2D/3D Medical Image Registration:US,2019050999A1[P]. 2019-02-14.
[16] Litjens G,Kooi T,Bejnordi B E,et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis[J]. Medical Image Analysis,2017,7(5):60-88.
[17] 王 雷. 影像导航手术中2D/3D图像配准[D]. 长春:中国科学院,2015.
Wang Lei. 2D/3D Image Registration in Image-Guided Surgery[D]. Changchun:Chinese Academy of Sciences,2015(in Chinese).
[18] 孙 涛,闫 巍,孙振辉,等. 外固定支架模型重建软件开发与安装参数识别研究[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版),2020,53(6):593-600.
Sun Tao,Yan Wei,Sun Zhenhui,et al. Software development and pose acquisition of the Taylor spatial frame[J]. Journal of Tianjin University(Science and Technology),2020,53(6):593-600(in Chinese).
[19] Akter M,Lambert A J,Pickering M R,et al. A 2D-3D image registration algorithm using log-polar transforms for knee kinematic analysis[C]//International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Fremantle,Australia,2012:1-5.
[20] Wu J,Kim M,Peters J,et al. Evaluation of similarity measures for use in the intensity-based rigid 2D-3D registration for patient positioning in radiotherapy[J]. Medical Physics,2009,36(12):5391-5403.
[21] Zhu Z,Li G. An automatic 2D-3D image matching method for reproducing spatial knee joint positions using single or dual fluoroscopic images[J]. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering,2012,15(11):1245-1256.
[22] Zhu Z,Massimini D F,Wang G,et al. The accuracy and repeatability of an automatic 2D-3D fluoroscopic image-model registration technique for determining shoulder joint kinematics[J]. Medical Engineering & Physics,2012,34(9):1303-1309.
[23] Ding H Y,Bian Z F. A sub-pixel registration approach based on powell algorithm[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica,2009,38(12):3322-3327.
Initial Pose Estimation Method in 2D/3D Registration
Sun Tao1,Guo Ke1,Liu Chuanba1,Zhang Tao2,Song Yimin1, 3,Ma Xinlong2
(1. Key Laboratory of Mechanism Theory and Equipment Design of Ministry of Education,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300354,China;2. Tianjin Hospital,Tianjin 300211,China;3. Department of Mechanical Engineering,Tianjin Renai College,Tianjin 301636,China)
In this paper,we propose a new initial pose estimation approach based on parameter mapping and image segmentation,focusing on the problems of small initial parameter transformation range and single registration object in the 2D/3D medical image registration process. This approach expands the range of initial motion deviation of 3D object spatial parameters and solves the issues regarding few estimable parameters and multibone image registration difficulty of the surgical navigation system during the registration process. First,the region growth algorithm is used to segment the multibone image and extract the target of interest to complete the target-data acquisition to be registered. Second,a projection imaging model is constructed based on the principle of orthogonal fusion projection to decompose the spatial rigid body transformation parameters into the positive lateral plane and establish the mapping relationship between spatial and plane parameters. Then,the orthogonal biplane template generated using the projection is matched with the corresponding target image,and the registration parameters of the obtained positive and lateral plane are converted into spatial parameters,to achieve the effective estimation of the initial pose of the 3D object. The method was verified based on computed tomography data of the skull,intact femur,and fractured femur. Then,the method was compared with the traditional 2D/3D image registration method. The experimental results showed that the proposed method could make the initial transformation range of the five spatial parameters reach ±30mm or ±20°,and different research objects within this range show a good initial pose estimation effect. Compared with the traditional image registration method,the overall registration time of the 2D/3D iterative optimization based on the above method is 46.5% shorter on average,the registration accuracy of a single translation parameter is up to 69.2%,and the registration accuracy of a single rotation parameter is up to 91.1%. Simultaneously,the final registration results have adequate robustness.
surgical navigation;2D/3D registration;initial pose estimation;orthogonal biplane projection
the National Key Research and Development Program of China(No.2018YFB1307800),the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.51775367),Tianjin Science and Technology Plan Project(No.18PTLCSY00080,No.20201193,No.18YFSDZC00010).
10.11784/tdxbz202010007
TP391
A
0493-2137(2022)02-0143-08
2020-10-07;
2021-02-25.
孙 涛(1983— ),男,博士,教授,stao@tju.edu.cn.Email:m_bigm@tju.edu.cn
宋轶民,ymsong@tju.edu.cn.
国家重点研发计划资助项目(2018YFB1307800);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51775367);天津市科技计划资助项目(18PTLCSY00080,20201193,18YFSDZC00010).
(责任编辑:王晓燕)
