RBF-PU 方法求解二维非局部扩散问题和近场动力学问题*
2022-07-11张尚元聂玉峰李义强
张尚元, 聂玉峰, 李义强
(西北工业大学 数学与统计学院,西安 710129)
引 言
经典的扩散现象和弹性力学问题是通过偏微分方程(partial differential equation,PDE)来刻画的,由于模型在建立之初就默认解具有一定的连续性,因此这类经典模型不适用于解具有奇异性的情形.为此,研究者们提出了非局部扩散模型[1-2]和近场动力学 (peridynamics,PD)模型[3-5],这两类非局部模型方程都是以有限作用范围的积分形式呈现,并且不涉及未知量的空间导数,物体的内力采取非接触的相互作用,这些特点使得它们在表征材料的损伤以及不连续现象时具有明显的优势,已经被广泛应用于含裂纹的热扩散问题[1,6]和固体损伤破坏[7]领域中.
为推动这类有限作用范围的非局部模型在工程实际问题中的应用,国内外许多专家尝试了不同数值方法来求解这类方程.2005 年,Silling 等通过将积分直接近似为有限和,提出了基于求积的无网格配置点法[8].Chen 等在2011 年使用连续有限元和不连续有限元方法求解了一维非局部扩散问题和近场动力学问题,指出在解不连续的情形下,使用不连续有限元可以获得更高的精度[9].针对非局部方程计算量大的问题,Wang 和Tian 等基于刚度矩阵的Toeplitz 结构,给出了一维非局部扩散方程的快速配置点法[10-11],并在后续工作中推广到了二维问题[12-13].2013 年,Tian 和Du 通过将非局部算子看成差分算子的加权平均,提出了基于求积的有限差分方法,用于一维非局部扩散问题的求解[14].2016 年,Lehoucq 等使用径向基函数Galerkin 方法求解了二维非局部扩散问题[15].2017 年,Zhao 等使用局部径向基函数伪谱方法求解了二维非局部扩散问题[16],并在之后推广到了近场动力学问题[17].2018 年,Pasetto 等将再生核方法应用到二维近场动力学问题的数值求解当中[18].2019 年,Du 和Yin 给出了非局部扩散问题的一种协调间断Galerkin 方法[19].2020 年,Zhang 和Nie 将POD 降阶方法用于非稳态非局部扩散问题,加速了非局部离散系统的求解过程[20].2021 年,Liang 等发展了近场动力学问题的边界元方法[21].同年,Lu 和Nie 发展了具有再生性的局部化径向基函数方法来求解非局部扩散问题,解决了再生核增强径向基函数方法在求解非局部扩散方程时不收敛的问题[22].
由于这两类模型方程的非局部特性,经典的数值方法均面临着算法复杂、难以实现和计算量大的问题.对于基于网格的方法,包括分片多项式函数近似的配置点法[10],以及连续/不连续有限元方法[9],由于非局部相互作用范围是一个有限范围的球形邻域,因此这些方法在方程离散时,需要处理网格和球形区域的求交问题,否则将会降低数值精度.对于基于方程弱形式的方法(包括有限元方法[9]、无网格Galerkin 方法[15]等),由于模型方程积分的特性,这就导致方程的弱形式会额外嵌套一层积分,从而在刚度矩阵的形成过程中会出现累次重积分的计算,给问题的求解带来了较大的计算负担.然而,基于径向基函数的无网格方法[23-24]能够避免处理上述提及的区域求交的问题.同时,基于方程强形式的配置点法,可以避免额外一层积分的计算,从而可以节省刚度矩阵生成时的计算量.基于上述分析,无网格配置点法更适合于这两类非局部模型的数值求解.值得注意的是,全局RBF 方法虽然避免了网格生成,但是在计算RBF 插值时,由于插值矩阵规模较大,会出现计算量大、插值矩阵条件数过大的问题,而局部化的RBF 则会降低插值矩阵的条件数,故选择局部化的径向基函数插值更为合理.因此,本文考虑了一种局部化的径向基函数方法-单位分解径向基函数方法来求解这类方程:一方面它不同于文献[15]中基于方程弱形式的无网格Galerkin 方法,是基于方程强形式的无网格配置点法,节省了额外一层的积分计算;另一方面,本文方法不同于有限元方法[9],基函数无网格依赖,免去了区域求交问题.故本文方法在求解非局部问题时具备实施简便、计算量小的优势.
针对二维非局部扩散问题和近场动力学问题,本文采用单位分解径向基函数方法来数值求解.首先概述了RBF 插值和RBF-PU 插值方法;然后给出了RBF-PU 方法应用于非局部扩散问题和近场动力学问题求解时离散系统形成的基本过程;最后用数值实验验证了RBF-PU 方法在求解这两类非局部问题时的有效性.
1 径向基函数插值
1.1 全局径向基函数插值


1.2 单位分解径向基函数插值


图1 无网格点和PU 覆盖示意图Fig. 1 A set of regular meshless points and a set of circular PU patches
定义指标集I(x)={l:x∈Ωl},则式(6)中的求和索引可以用k∈I(x)简化.用Wendland 函数φ (r)来构造函数φj(x):

2 非局部问题的RBF-PU 方法
2.1 圆盘上的数值积分
在PD 的数值计算中,会大量涉及到圆盘上的数值积分.为了降低计算复杂度,通常的做法是将圆盘的积分转化为矩形上的积分(如图2),矩形上的数值积分直接由一维积分的张量积来获得.对于二维问题,利用极坐标变换:

图2 极坐标变换Fig. 2 Polar transformation

有了这些基本工具,下面给出RBF-PU 方法形成离散系统的过程.
2.2 非局部扩散方程的RBF-PU 方法
二维非局部扩散方程为

2.3 近场动力学方程的RBF-PU 方法
考虑向量形式的二维近场动力学运动方程:


3 数 值 实 验

3.1 非局部扩散方程
算例1 取问题(16)的精确解为

核函数为

对区域采用两种离散方式:一种是在每个方向上均匀离散为N份,均匀离散下离散点的示意图和生成的矩阵结构如图3 所示;另一种采用相同数量的Halton点进行离散,离散点的分布和形成的刚度矩阵的结构如图4 所示.分别对两种离散形式沿每个方向分别取10~60 个离散点(以1 0为增量),进行数值计算,均匀离散的数值结果如表1 所示.从矩阵条件数看,RBF-PU 方法的条件数在离散点数量为60×60时为1010~1011量级,而全局RBF 方法参见文献[22]表7 中的结果为1014~1015量级,由此可见,RBF-PU 方法在一定程度上降低了刚度矩阵的条件数.从求解时间上看,RBF-PU 方法在离散点数量为60×60时的计算时间约为25 min,对同等规模的问题,全局RBF 方法约耗时10 h 4 min(参见文献[22]表6 中的结果),基于分片线性基函数的配置点法约耗时14 h 21 min(参见文献[13]表1 中的结果),可以看出RBF-PU 方法求解时间更短,效率更高.在表1 最后一行60×60离散下的误差反而比50×50离散下的误差大,原因有两点:一是影响RBF-PU 方法精度的参数包括点的分布,PU 块内点的数量,由于PU 块的大小没有随着离散点的增加而改变,因此导致插值矩阵进一步恶化,导致误差增大.二是由于方程本身的核函数奇异,影响数值积分的精度,由于数值积分点数量固定,在离散点数目较小的时候,数值离散的误差占主导地位,但随着离散点数目增加,数值积分的误差开始占据主导地位,最终导致误差增大,这样的现象在文献[16]表2、3 中也可以观察到.图5 给出了在50×50的情况下数值结果和误差的分布图.Halton点离散下的数值结果如表2 所示.图6 给出了50×50的情况下的数值结果和误差的分布图.数值实验结果表明,RBF-PU 方法在两种离散方式下在求解非局部扩散方程时都是有效的.

图3 均匀离散无网格点的分布和非局部扩散方程矩阵结构:(a) 无网格点分布和单位分解划分; (b) 矩阵结构Fig. 3 The distribution of points and the matrix structure of nonlocal diffusion under uniform discretization: (a) the distribution of meshless points and PU patches;(b) the matrix structure
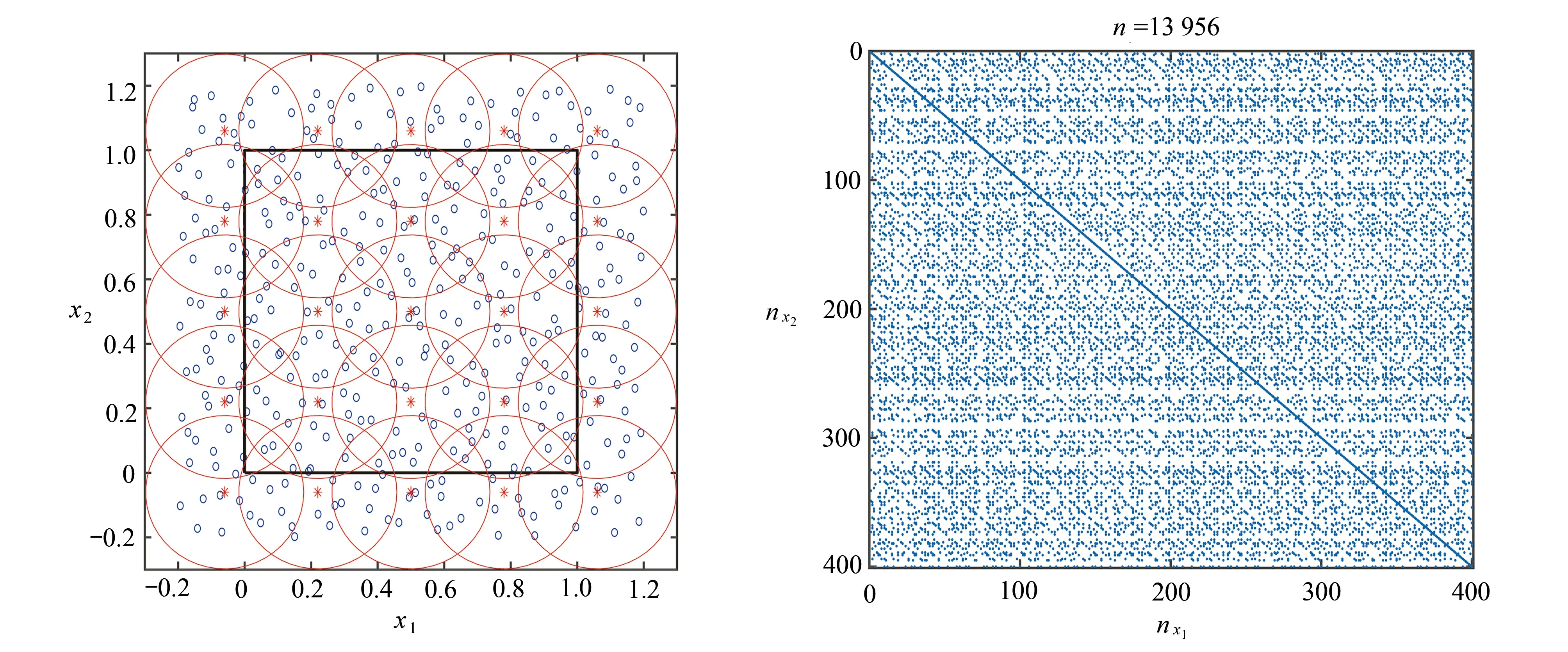
图4 Halton 离散下点的分布和非局部扩散方程矩阵结构:(a) Halton 点的分布和单位分解划分;(b) 矩阵结构Fig. 4 The distribution of points and the matrix structure of nonlocal diffusion under Halton discretization: (a) the distribution of Halton points and circular PU patches; (b) the matrix structure

图5 均匀离散下非局部扩散方程数值解和误差分布:(a) 数值解; (b) 误差分布Fig. 5 The numerical solution and the error distribution for the nonlocal diffusion equation under uniform discretization: (a) the numerical solution;(b) the error distribution

图6 Halton 离散下非局部扩散方程的数值结果和误差分布图:(a) 数值解; (b) 误差分布Fig. 6 The numerical solution and the error distribution for the nonlocal diffusion equation under Halton discretization: (a) the numerical solution;(b) the error distribution

表1 均匀离散非局部扩散方程数值结果(δ=0.2)Table 1 Numerical results of the nonlocal diffusion equation under uniform discretization (δ=0.2)
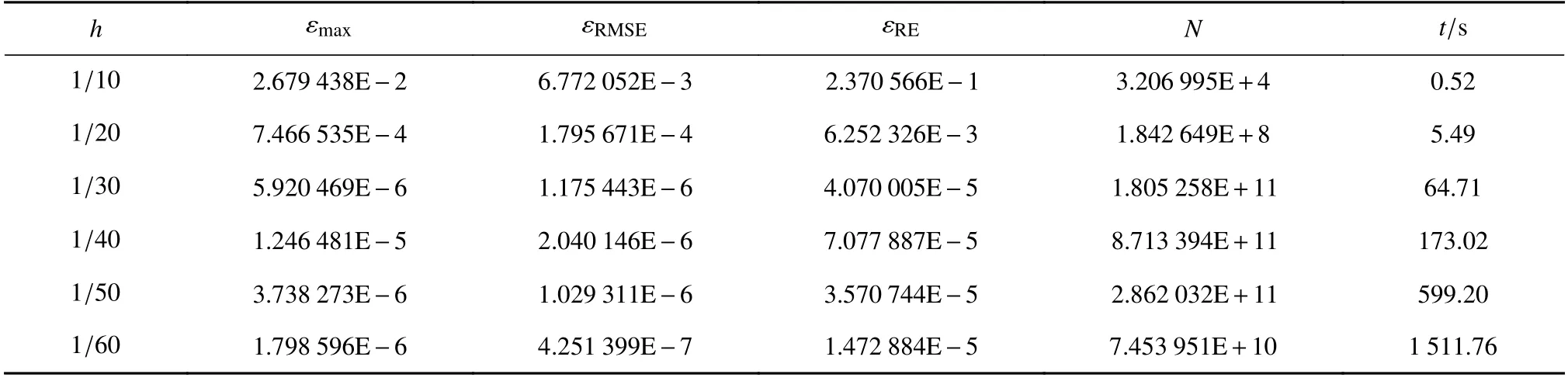
表2 离散非局部扩散方程的数值结果(δ=0.2)Table 2 Numerical results of the nonlocal diffusion equation under Halton discretization (δ=0.2)
3.2 近场动力学方程
算例2 取二维近场动力学问题(20)的精确解为
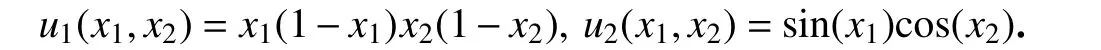
核函数为

在均匀离散的情况下对该问题进行了数值实验,图7 给出了均匀离散下点的分布和最终形成的矩阵结构,计算给出了两个方向的位移场在不同数目的离散点下位移的数值结果,位移场在x和y方向的数值结果分别如表3 和表4 所示.表中数据显示,RBF-PU 方法在求解近场动力学方程的时间比相同离散的非局部扩散方程更低,原因在于在此算例中采取的单位分解划分更小,导致局部插值矩阵的规模更小,节省了刚度矩阵生成的时间.与此同时,在50×50的离散点下位移和误差的分布如图8 和9 所示.计算结果表明,RBF-PU 方法在求解向量形式的近场动力学方程时也是有效的.

图7 均匀离散下无网格点的分布和近场动力学方程矩阵结构:(a) 无网格点分布和单位分解划分; (b) 矩阵结构Fig. 7 The distribution of points and the matrix structure for the peridynamic equation under uniform distribution: (a) the distribution of meshless points and circular PU patches; (b) the matrix structure
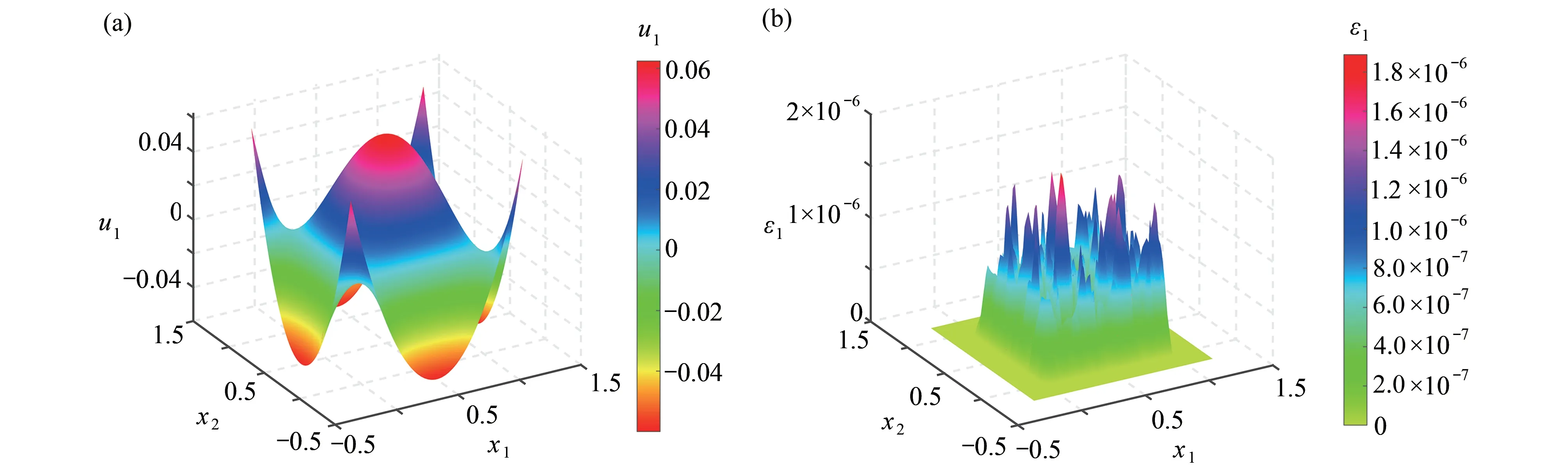
图8 近场动力学方程x方向数值解和误差分布:(a) 数值解; (b) 误差分布Fig. 8 The numerical solution and the error distribution of the peridynamic equation in the x direction: (a) the numerical solution; (b) the error distribution
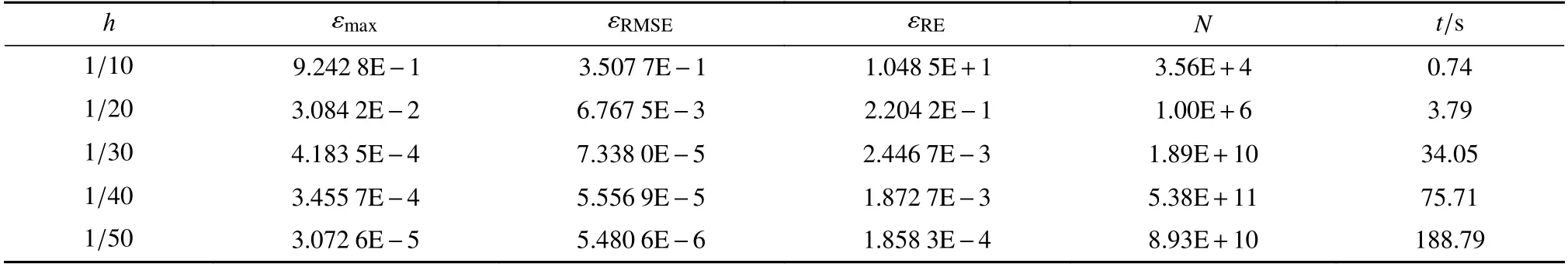
表3 模型的x 方向位移的数值解u 1(δ=0.2)Table 3 Numerical results of displacement in the x direction for the peridynamic model u 1 (δ=0.2)

表4 模型的y方向位移数值解u 2 (δ=0.2)Table 4 Numerical results of displacement in the y direction for the peridynamic model u 2 (δ=0.2)

图9 近场动力学方程y方向数值解和误差分布:(a) 数值解; (b) 误差分布Fig. 9 The numerical solution and the error distribution of the peridynamic equation in the y direction: (a) the numerical solution; (b) the error distribution
4 结 论
本文发展了求解二维非局部扩散和近场动力学问题的RBF-PU 方法,该方法无网格依赖性、精度高、易于编程实现.通过数值算例验证了该方法对此类非局部方程求解的有效性.基于本文的工作,可以考虑将此类方法用于更加复杂的非线性、高维近场动力学模型的数值计算当中.
参考文献( References ) :
[1]B OBARU F, MONCHAI D. The peridynamic formulation for transient heat conduction[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2010, 53(19/20): 4047-4059.
[2]D U Q, GUNZBURGER M, LEHOUCQ R B, et al. Analysis and approximation of nonlocal diffusion problems with volume constraints[J].SIAM Review, 2012, 54(4): 667-696.
[3]S ILLING S A. Reformulation of elasticity theory for discontinuities and long-range forces[J].Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2000, 48(1): 175-209.
[4]S ILLING S A, EPTON M, WECKER O, et al. Peridynamic states and constitutive modeling[J].Journal of Elasticity, 2007, 88(2): 151-184.
[5]黄 丹, 章青, 乔丕忠, 等. 近场动力学方法及其应用[J]. 力学进展, 2010, 40(4): 61-70. (HUANG Dan, ZHANG Qin,QIAO Pizhong, et al. A review on peridynamics(PD) method and its application[J].Advances in Mechanics,2010, 40(4): 61-70.(in Chinese))
[6]G U X, ZHANG Q, MADENCI E. Refined bond-based peridynamics for thermal diffusion[J].Engineering Computations, 2019, 36(8): 2557-2587.
[7]李 天一, 章青, 夏晓舟, 等. 考虑混凝土材料非均质特性的近场动力学模型[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2018, 39(8): 913-924. ( LI Tianyi, ZHANG Qing, XIA Xiaozhou, et al. A peridynamic model for heterogeneous concrete materials[J].Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2018, 39(8): 913-924.(in Chinese))
[8]S ILLING S A, ASKARI E. A meshfree method based on the peridynamic model of solid mechanics[J].Computers and Structures, 2005, 83(17/18): 1526-1535.
[9]C HEN X, GUNZBURGER M. Continuous and discontinuous finite element methods for a peridynamics model of mechanics[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 200(9/12): 1237-1250.
[10]W ANG H, TIAN H. A fast Galerkin method with efficient matrix assembly and storage for a peridynamic model[J].Journal of Computational Physics, 2012, 231(23): 7730-7738.
[11]T IAN H, WANG H, WANG W. An efficient collocation method for a nonlocal diffusion model[J].International Journal of Numerical Analysis and Modeling, 2013, 10(4): 815-825.
[12]W ANG C, WANG H. A fast collocation method for a variable-coefficient nonlocal diffusion model[J].Journal of Computational Physics, 2017, 330: 114-126.
[13]W ANG H, TIAN H. A fast and faithful collocation method with efficient matrix assembly for a two-dimensional nonlocal diffusion model[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 273: 19-36.
[14]T IAN X C, DU Q. Analysis and comparison of different approximations to nonlocal diffusion and linear peridynamic equations[J].SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2013, 51(6): 3458-3482.
[15]L EHOUCQ R B, ROWE S T. A radial basis function Galerkin method for inhomogeneous nonlocal diffusion[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 299: 366-380.
[16]Z HAO W, HON Y C, STOLL M. Localized radial basis functions-based pseudo-spectral method (LRBF-PSM) for nonlocal diffusion problems[J].Computers and Mathematics With Applications, 2017, 75(5): 1685-1704.
[17]Z HAO W, HON Y C. An accurate and efficient numerical method for solving linear peridynamic models[J].Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2019, 74: 113-131.
[18]P ASETTO M, LENG Y, CHEN J, et al. A reproducing kernel enhanced approach for peridynamic solutions[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 340: 1044-1078.
[19]D U Q, YIN X B. A conforming DG method for linear nonlocal models with integrable kernels[J].Journal of Scientific Computing, 2019, 80(3): 1913-1935.
[20]Z HANG S Y, NIE Y F. A POD-based fast algorithm for the nonlocal unsteady problems[J].International Journal of Numerical Analysis and Modeling, 2020, 17(6): 858-871.
[21]L IANG X, WANG L J, XU J F, et al. The boundary element method of peridynamics[R/OL]. 2021(2021-06-16)[2021-10-29].https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.08008.
[22]L U J X, NIE Y F. A collocation method based on localized radial basis functions with reproducibility for nonlocal diffusion models[J].Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2021, 40(8): 271-294.
[23]洪 文强, 徐绩青, 许锡宾, 等. 求解Bratu型方程的径向基函数逼近法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2016, 37(6): 617-625.(HONG Wenqiang, XU Jiqing, XU Xibin, et al. The radial basis function approximation method for solving Bratu-type equations[J].Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2016, 37(6): 617-625.(in Chinese))
[24]李 怡, 吴林键, 舒丹, 等. 基于Gauss全局径向基函数的近岸浅水变形波高数值计算新方法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2014,35(8): 903-912. (LI Yi, WU Linjian, SHU Dan, et al. A new method to calculate the wave height of deformed shallow water based on the gauss global radial basis function[J].Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2014,35(8): 903-912.(in Chinese))
[25]W ENDLAND H.Scattered Data Approximation[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005.
[26]S HEPARD D. A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data[C]//Proceedings of the 1968 23rd ACM National Conference(ACM 68). New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 1968: 517-524.
