胸腺肽α1以及乌司他丁对外源性脑损伤的修复治疗及三维图像重建和脑灌注成像在颅脑损伤动态变化中的价值
2022-05-05杨凯魏书田
杨凯 魏书田


[摘要]目的分析合用胸腺肽α1以及烏司他丁对颅脑损伤患者恢复的效果和CT三维成像以及脑灌注成像在颅脑损伤动态变化中的临床价值研究。方法观察分析晋中市第一人民医院2018年7月至2020年1月收治的251例颅脑损伤患者,采用随机数字表法分为观察组及常规组,常规组接受神经外科常规治疗,观察组接受常规治疗+胸腺肽α1+乌司他丁治疗,并且检测两组在经过三维图像重建和脑灌注成像检测颅脑损伤的结果,以及检测两组经治疗后的颈动脉平均血流量(Qmean)、特性阻抗(Zc)和动态阻力(DR)的脑血流参数指标、炎症因子以及抗炎因子相关指标,如肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素-4(IL-4)、IL-6、IL-10、IL-12、IL-13等。结果经复查后发现脑灌注成像的检测结果更贴合复查结果,观察组Qmean、Zc和DR水平均优于常规组;观察组促炎因子IL-6、TNF-a水平低于常规组,而IL-12则高于常规组;观察组的抗炎因子IL-4、IL-10和IL-13水平高于常规组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论与三维图像重建技术相比,脑灌注成像在颅脑损伤动态变化中的检测结果更可靠、准确。此外,合用胸腺肽α1和乌司他丁是治疗急性脑损伤的可靠方法,对减少脑损伤和恢复脑血流有积极作用。
[关键词]外源性脑损伤;三维图像重建;脑灌注成像;炎症因子
[中图分类号]R651.15 [文献标识码]A [文章编号]2095-0616(2022)01-0016-04
An analysis of the efficacy of thymosin α1 and ulinastatin for repair treatment of exogenous brain injury and a study of the clinical value of 3 D image reconstruction and cerebral perfusion imaging for dynamic changes of craniocerebral injury
YANG Kai WEI Shutian
Department of Neurosurgery,the First People's Hospital of Jinzhong,Shanxi,Jinzhong 030600,China
[Abstract]Objective To analyze the effect of thymosin a1 combined with ulinastatin on the recovery of the patients from craniocerebral injury and to study the clinical value of CT three-dimensional imaging and cerebral perfusion imaging for dynamic changes of craniocerebral injury. Methods A total of 251 patients with craniocerebral injury admitted to and treated in the First People's Hospital of Jinzhong from July 2018 to January 2020 were observed and analyzed. They were divided into the observation group and the conventional group through random number table method,with the conventional group receiving conventional neurosurgical treatment,while the observation group receiving conventional treatment + thymosinzα1 + ulinastatin. The results of the detection of craniocerebral injury by 3 D image reconstruction and cerebral perfusion imaging were checked,and the two groups' cerebral blood flow parameters,including mean blood flow (Qmean)of carotid artery,characteristic impedance (Zc)and dynamic resistance (DR),inflammatory factors and related indicators of anti-inflammatory factors,such as tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α),interleukin-4 (IL-4),IL-6,IL-10,IL-12,IL-13,etc. Results After reexamination,it was found that the detection results of cerebral perfusion imaging were more consistent with the reexamination results,and the Qmean,Zc and DR levels of the observation group were all better than those of the conventional group;the levels of proinflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-αin the observation group were lower than those in the conventional group,while the level of IL-12 was higher than that in the conventional group;the levels of anti-inflammatory factors IL-4,IL-10 and IL-13 in the observation group were higher than those in the conventional group,and the differences in results were all statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion Compared with 3 D image reconstruction technology,cerebral perfusion imaging produces more reliable and sounder detection result for dynamic changes of craniocerebral injury. In addition,the combination of thymosin al and ulinastatin is a reliable method of treating acute brain injury,which is helpful for reducing brain injury and restoring cerebral blood flow. [Key words] Exogenous brain injury;3 D image reconstruction;Cerebral perfusion imaging;Inflammatory factor
外源性脑损伤多指因为炎症、中毒、外伤等外源性物质引起的脑损伤。胸腺肽α1是由28个氨基酸组成的小分子肽[1],是一种具有增强细胞免疫、抗肿瘤和抗炎作用的多向性药物[2]。乌司他丁具有抗炎、抗氧化应激等多重作用,已经被证实对脑损伤患者具有神经细胞功能保护作用[3-5]。本研究通过观察胸腺肽α1和乌司他丁对颅脑损伤手术患者脑保护及炎症反应的影响情况,了解胸腺肽α1和乌司他丁在颅脑损伤手术患者预后中的应用价值以及探讨螺旋CT重建技术及脑灌注成像诊断急性颅脑外伤。现报道如下。
1 資料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取晋中市第一人民医院(我院)2018年7月至2020年1月收治的脑损伤患者251例为观察对象。本研究经医院医学伦理委员会批准,且所有研究对象均知情自愿参与。纳入标准:经本院神经外科诊断为外源性颅脑损伤者。排除标准:具有高血压病史和血管畸形以及各种慢性病患者;已使用影响颅内血流动力学药物的患者。男178例,女73例,年龄19~90岁,平均(61.8±14.2)岁。所有患者均有相应的临床诊断,均采用PGP9.5和GFAP检测。采用随机数字表法将患者分为常规组和观察组,其中常规组125例,男87例,女38例,年龄21~90岁,平均(62.1±13.8)岁,其中硬膜下血肿21例、蛛网膜下腔出血24例、脑内血肿15例、硬膜外血肿24例、脑挫裂伤28例、弥漫性轴索损伤13例,平均病程(3.1±2.5)个月;观察组126例,男91例,女35例,年龄19~88岁,平均(6例±14.5)岁,其中硬膜下血肿22例、蛛网膜下腔出血28例、脑内血肿14例、硬膜外血肿26例、脑挫裂伤26例、弥漫性轴索损伤10例,平均病程(3.5±2.3)个月。两组一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
1.2 方法
患者入院后3~6 h内同时进行头颅CT三维图像重建及脑灌注成像。常规组给予常规抗感染、脱水、营养支持等对症治疗。观察组在常规组基础上,分别于术中和术后在生理盐水中加入胸腺肽α1针剂(海南中和药业有限公司,国药准字H20051916)1.6 mg肌内注射,每日2次,连续3 d后改为每日一次,连续4 d,乌司他丁针剂(广东天普生化医药股份有限公司,国药准字H19990132)200 000 U溶于生理盐水100 ml中,静脉滴注,每日3次,连续使用3 d后改为100 000 U,每日3次,连续4 d。
1.3 观察指标
观察经三维图像重建和脑灌注成像检测后的检测结果,以及颈动脉Qmean、Zc和DR在内的脑血流参数[3-4]。此外还需检测炎症因子包括IL-6、TNF-α和IL-12的表达水平,以及IL-4、IL-10和IL-13等抗炎因子水平。
1.4 统计学处理
2 结果
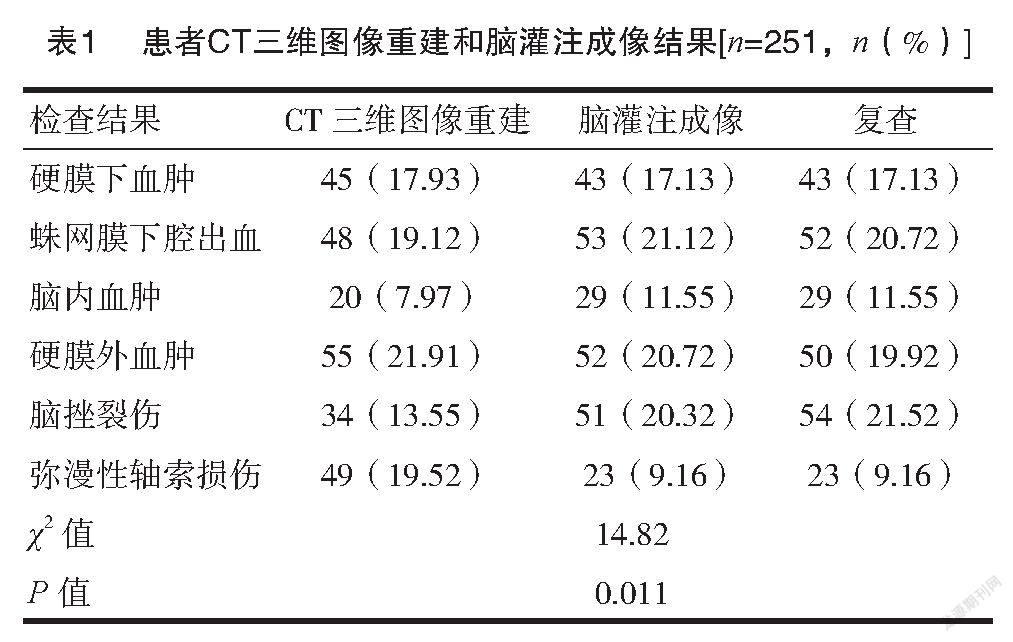
2.1 CT三维图像重建和脑灌注成像检查结果
251例患者均进行CT三维图像重建和脑灌注成像检查,见表1。结果显示,依据复查结果,后者检查的结果更为接近,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
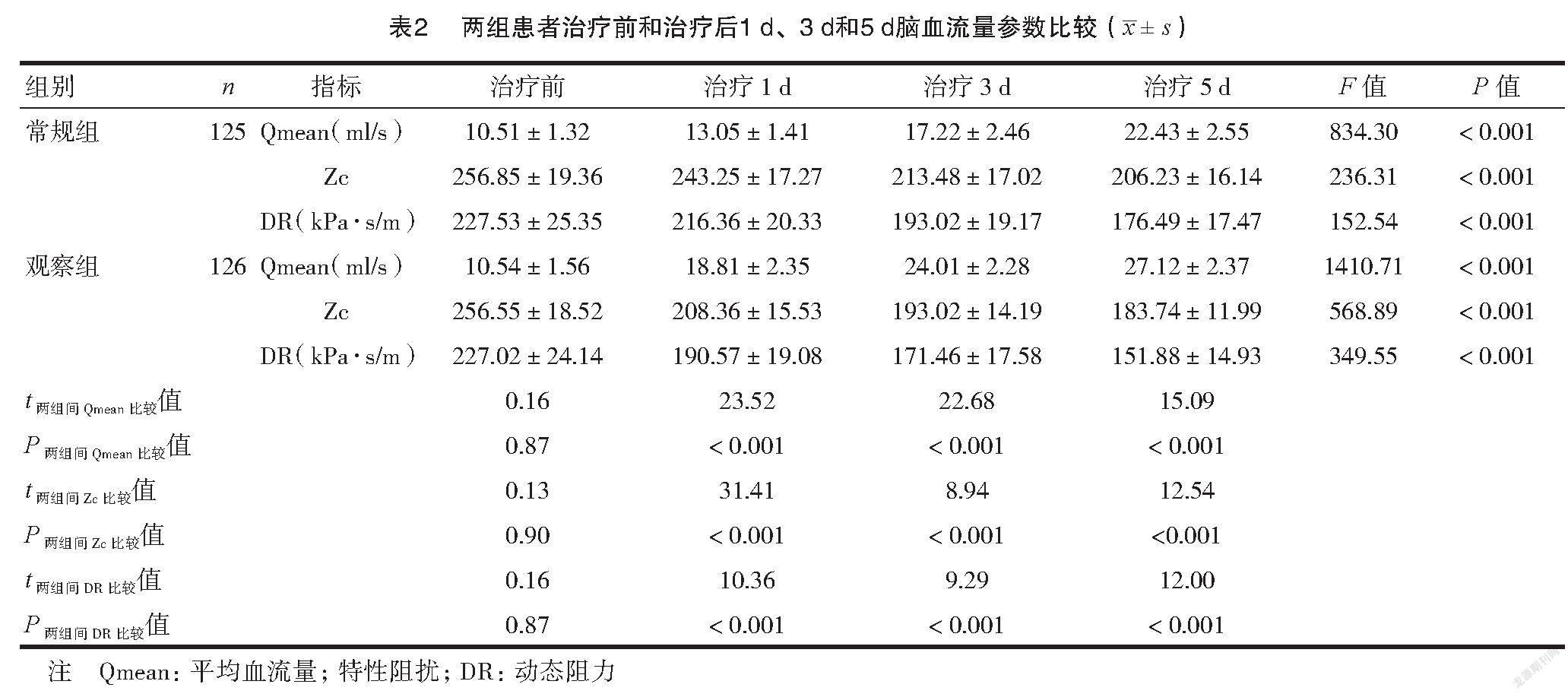
2.2 两组患者治疗前和治疗后脑血流量参数比较
两组患者治疗后颈动脉Qmean、Zc、DR指标观察组均优于常规组,同一时间点Qmean水平显著升高,Zc、DRP水平均低于常规组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表2。
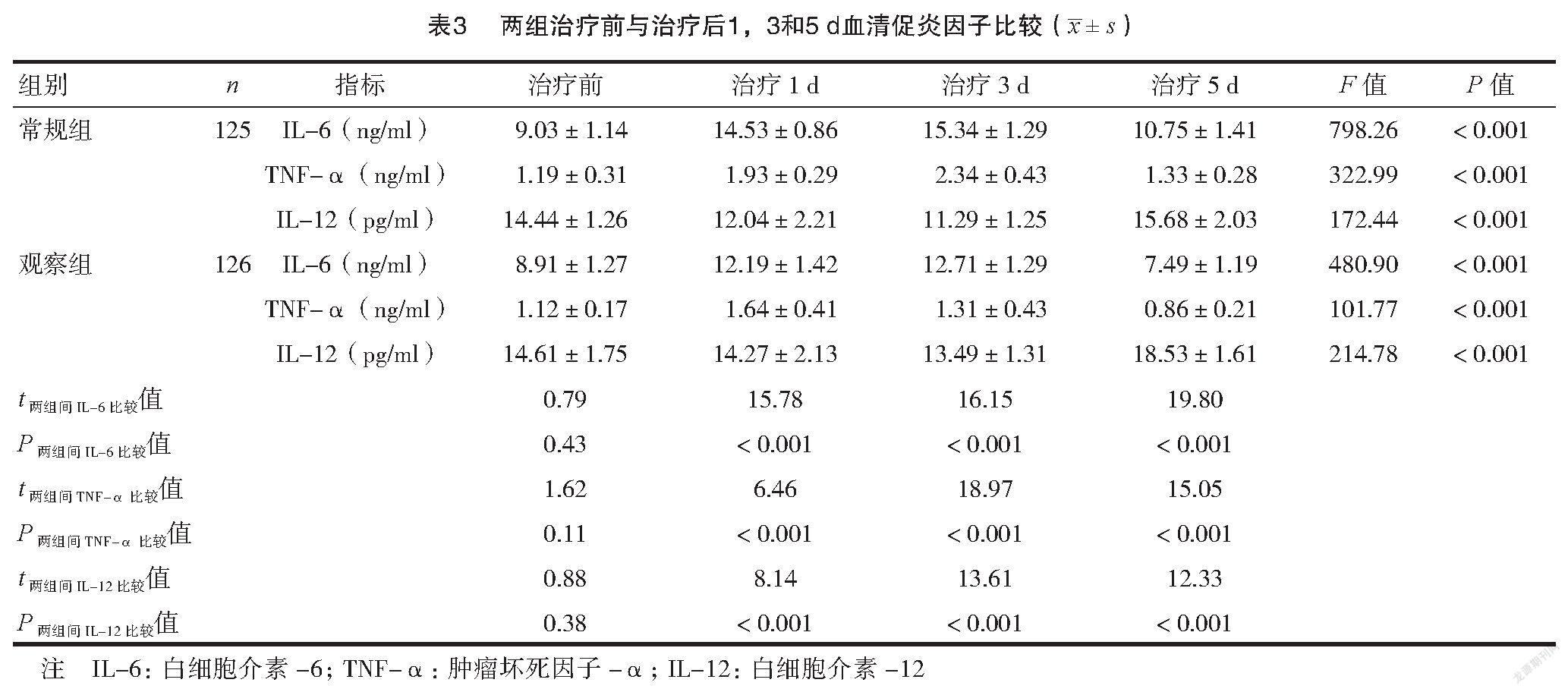
2.3 两组患者治疗前和治疗后血清促炎因子水平的比较
治疗1、3和5 d后,两组患者IL-6和TNF-α先升高后降低,IL-12先降低后升高,检测同一时间点IL-6、TNF-α水平观察组显著低于常规组,IL-12观察组高于常规组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表3。
2.4 两组患者治疗前和治疗后血清抗炎因子比较
治疗1、3、5 d后,两组患者的血清抗炎因子IL-4、IL-10和IL-13含量均呈先上升后下降趋势,同时间点水平检测发现观察组抗炎因子含量高于常规组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表4。
3 讨论
众所周知,脑损伤的危害是极其严重的,不仅会出现意识障碍、头痛、恶心、呕吐等症状,还会导致脑部血流量异常,机体整体炎症应激异常等[6-8]。为了更好地保护大脑,改善脑血流和神经功能相关指标是其关键[9-11]。本研究结果表明,Qmean、Zc、DR指标观察组均优于常规组。炎症反应与机体疾病状态密切相关。结果表明两组患者IL-6和TNF-α先升高后降低,IL-12先降低后升高,检测同一时间点IL-6、TNF-α水平,观察组显著低于常规组,IL-12观察组显著高于常规组;而观察组的IL-4、IL-10和IL-13含量明显高于常规组。胸腺素α1是临床常用的一种免疫兴奋剂,可靶向脑损伤后机体免疫抑制状态,作为一种正常的机体物质,对脑组织无负刺激作用[12-13]。乌司他丁是近年来临床应用较多的药物,对多种疾病患者的多系统器官保护作用已得到证实[14-15],胸腺肽α1和乌司他丁可通过不同机制抑制急性创伤后脑组织内环境的快速恶化。
综上所述,脑灌注成像检测结果更可靠、准确。此外,胸腺肽α1和乌司他丁是治疗急性脑损伤的可靠方法,对减少脑损伤和恢复脑血流有积极作用,这是治疗脑损伤患者的理想方法,值得在今后临床实践中推广应用。
[参考文献]
[1] Yasir N Jassam,Saef Izzy,Michael Whalen,et al. Neuroimmunology of traumatic brain injury:Time for a paradigm shift[J]. Neuron,2017,95(6):1246-1265.
[2] Asimina Dominari,Donald Hathaway lii,Krunal Pandav,et al. Thymosin alpha 1:A comprehensive review of the literature[J]. World J Virol,2020,9(5):67-78.
[3]赵天补,田昌俊.乌司他丁通过SIRT1、PGC-1a调节氧化应激对失血性休克大鼠脑损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国现代应用药学,2021,38 (6):692-696.
[4] Ting Liu,Xing-Zhi Liao,Mai-Tao Zhou. Ulinastatin alleviates traumatic brain injury by reducing endothelin-1[J]. Transl Neurosci,2021,12(1):1-8.
[5] Tao Cui,Gangyi Zhu. Ulinastatin attenuates brain edema after traumatic brain injury in rats[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys,2015,71 (2):595-600.
[6] Babru B Samal,Cameron K Waites,Camila Almeida- Suhett,et al. Acute response of the hippocampal transcriptome following mild traumatic brain injury after controlled cortical impact in the rat[J]. J Mol Neurosci,2015,57(2):282-303.
[7]卞益同,陈苗苗,李华,等.基于结构磁共振探讨创伤性脑损伤后内嗅皮层改变与认知功能的关系[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2021,42(6):875-879.
[8] Teodor T Postolache,Abhishek Wadhawan,Adem Can,et al. Inflammation in traumatic brain injury[J]. J Alzheimers Dis,2020,74(1):1-28.
[9] Michael A Vella,Marie L Crandall,Mayur B Patel. Acute management of traumatic brain injury[J]. Surg Clin North Am,2017,97(5):1015-1030.
[10] Chao Chai,Rui Guo,Chao Zuo,et al. Decreased susceptibility of major veins in mild traumatic brain injury is correlated with post-concussive symptoms:A quantitative susceptibility mapping study[J]. Neuroimage Clin,2017,15:625-632.
[11] Marieke Begemann,Mikela Leon,Harm Jan van der Horn,et al. Drugs with anti-inflammatory effects to improve outcome of traumatic brain injry[J]. Sci Rep,2020,10:16179.
[12]向常清,賀海波,张家俊,等.胸腺肽α1和乌司他丁对急性颅脑损伤患者的免疫调理作用[J].中国现代医学杂志,2016,26(3):50-54.
[13] Ge Wang,Fen He,Yunlong Xu,et al. Immunopotentiator thymosin alpha-1 promotes neurogenesis and cognition in the developing mouse via a systemic Th1 bias[J]. Neurosci Bull,2017,33(6):675-684.
[14] Lei Cui,Wei Cao,Yanmin Xia,et al. Ulinastatin alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by activating the Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway[J]. Ann Transl Med,2020,8(18):1136.
[15] Zhi Liang,Xue Xu,Xiang Qi,et al. Efficacy and safety of ulinastatin on cognitive dysfunction after general anesthesia in elderly patients[J]. Medicine,2021,100 (13):e24814.
